ET&P EKG interpretation and cardiac diagnosis
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
who captured the first actual electrical rhythym? when?
Alenxander Muirhead, 1869
capillary electrometer
electric potentials produced movement 1873
who recorded the first electrogram? when? what did it do?
AD waller, 1887, used capillary electrometer to measure through the chest wall
what did Einthoven do?
•used the capillary electrometer, revised it, improved it and decided it was inadequate
Einthoven created the String Galvanometer (first EKG machien)
very big, 600 pounds
used until vacuum tube amplififer develoepd in 1920s
true or false EKG is by nature 3 dimensional?
true
Einthovens triangle
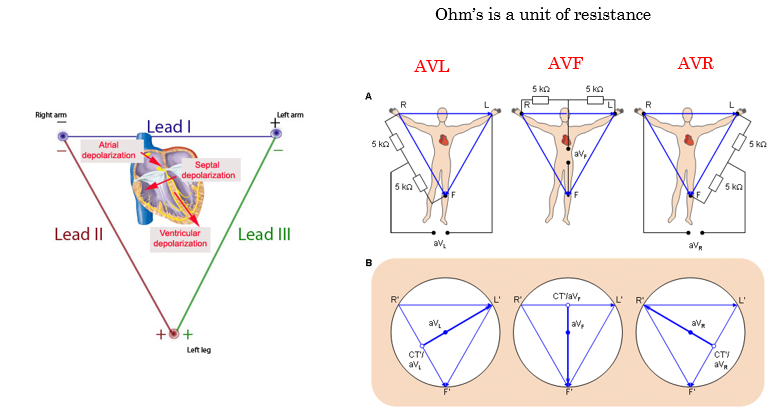
what is Ohm’s?
unit of resistance
general overview inspection; step 1
•Rate
•Rhythm
•Shape of each Wave (and how tall and wide)
•Ventricular Activity
•Atrial Activity
•Atrioventricular relationship
Normal Sinus Rhythm
Cardiac Dysrythmias
describe ventricular activity
•Rate
Irregular can be identified immediately
Bradychardia
Tachycardia
•Shape and Duration
QRS – each one identical?
Narrow QRS less than .10 second = supraventricular origin
Distorted shape greater than .10 second = ectopic focus
(originates outside the ventricle)
describe atrial activity
•P Waves
•Rate, Rhythm and Shape
•PR interval
-below 120ms can mean signal traveling between atria and ventricles too quickly
-begininning of P wave to beginnning of QRS complex
-prenatal contaction=extra P-wave
•Unexpected P waves
•Atrial flutter or fibrillation
•P waves initiated outside the atrium
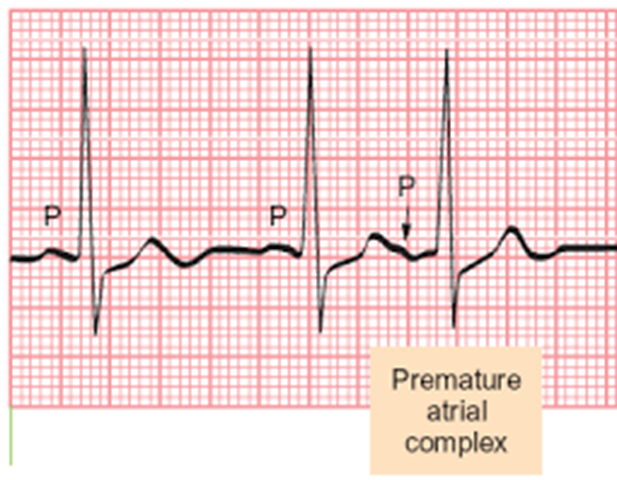
atrioventricular relationship
P wave to QRS ratio 1:1,
—-2:1 or more means not all atial impulses get through
•1) is each P wave followed by a QRS complex?
•2) is each QRS followed by a single P Wave?
•Does a pattern exist?
•PR interval – start of P wave to start of QRS
—-Represents the start of atrial depolarization to the start of ventricular depolarization
•PR interval should be consistent, no longer than .2 seconds
slide11
identify normal sinus rhythm
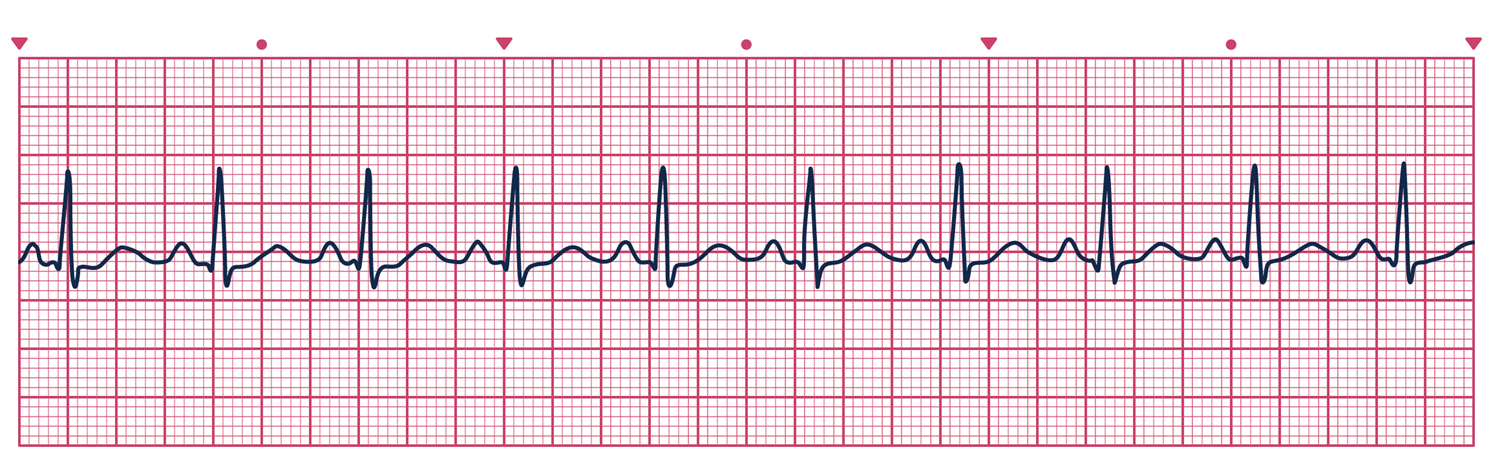
which?
bradycardia
preventricular contractiuons
atrial flutter
atrial fibrilation
complete AV block
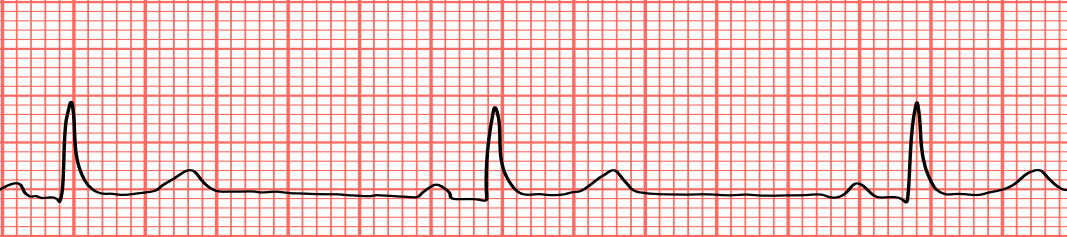
bradycardia
which?
bradycardia
preventricular contractiuons
atrial flutter
atrial fibrilation
complete AV block
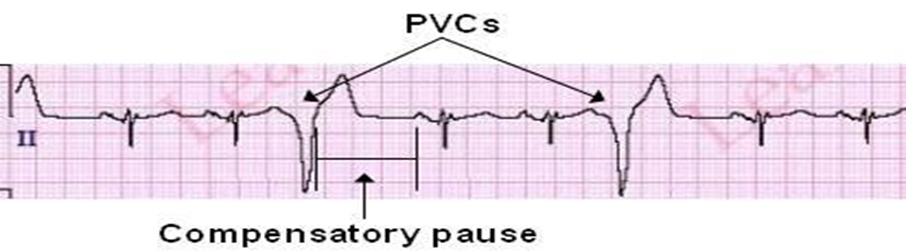
preventricular contractions
which?
bradycardia
preventricular contractiuons
atrial flutter
atrial fibrilation
complete AV block
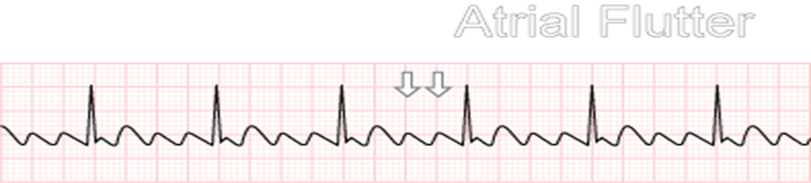
atrial flutter
which?
bradycardia
preventricular contractiuons
atrial flutter
atrial fibrilation
complete AV block
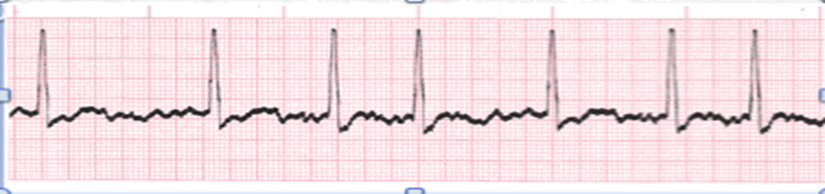
atrial fibrillation
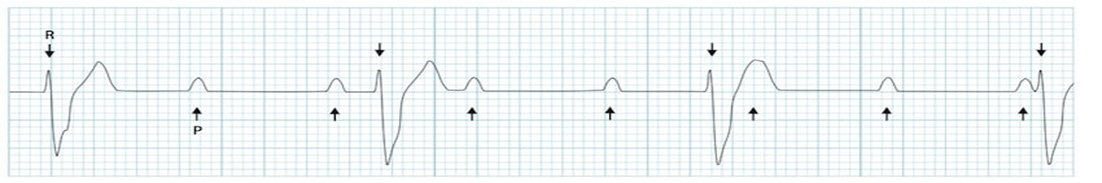
which?
bradycardia
preventricular contractiuons
atrial flutter
atrial fibrilation
complete AV block
comlpete AV block
atrial fib vs artial flutter
Atrial Flutter
Atria beat regularly but much faster than usual and more often than the ventricles
Atrial Conduction is coordinated
Atrial Fibrillation
Atria beat irregularly, more chaotic.
Atrial Conduction is disorganized
FAR MORE COMMON
Atrial ablation treatment technique (catuerizes/burns on either end to prevent electrical activity (around heart), need multiple times
what is the instant recognition of a heart attac?
ST elevation
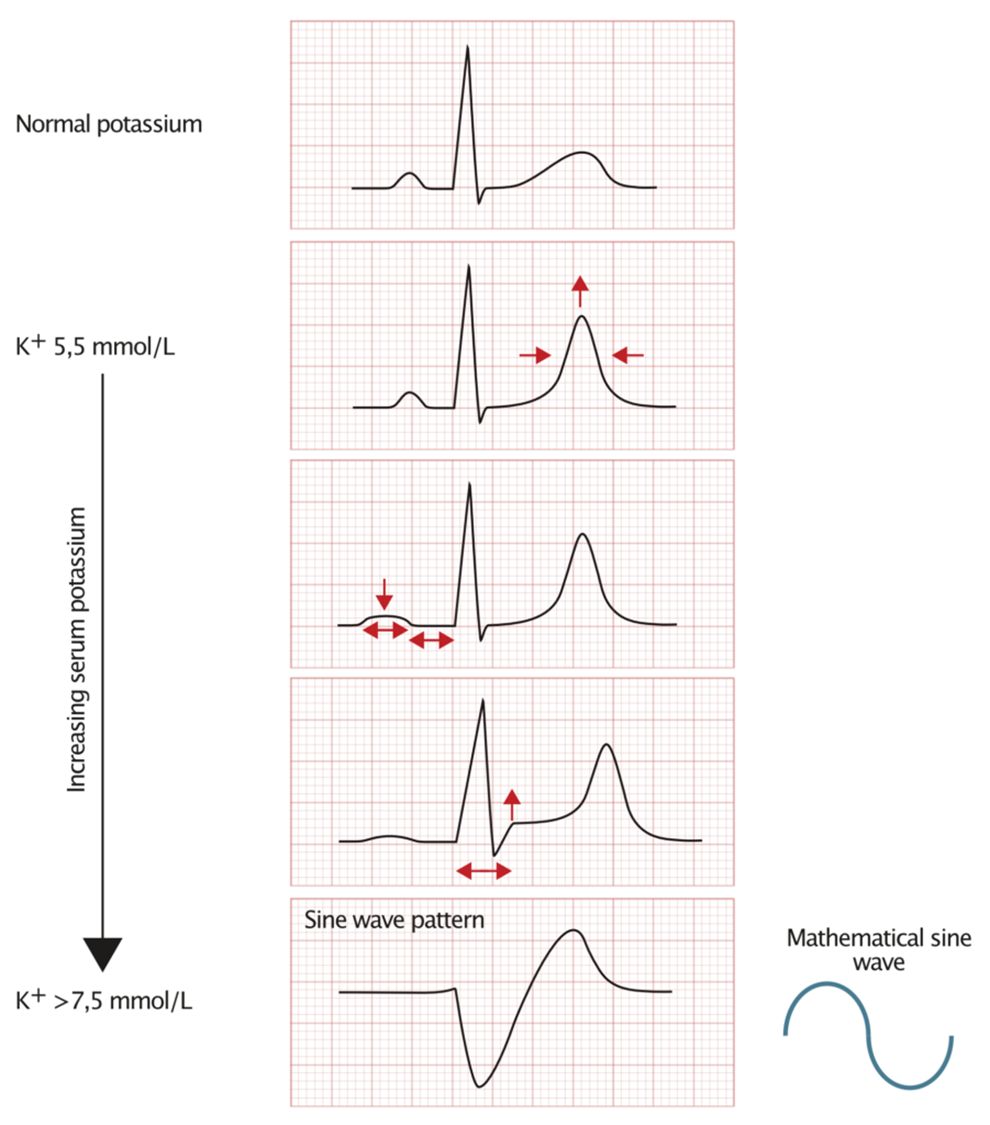
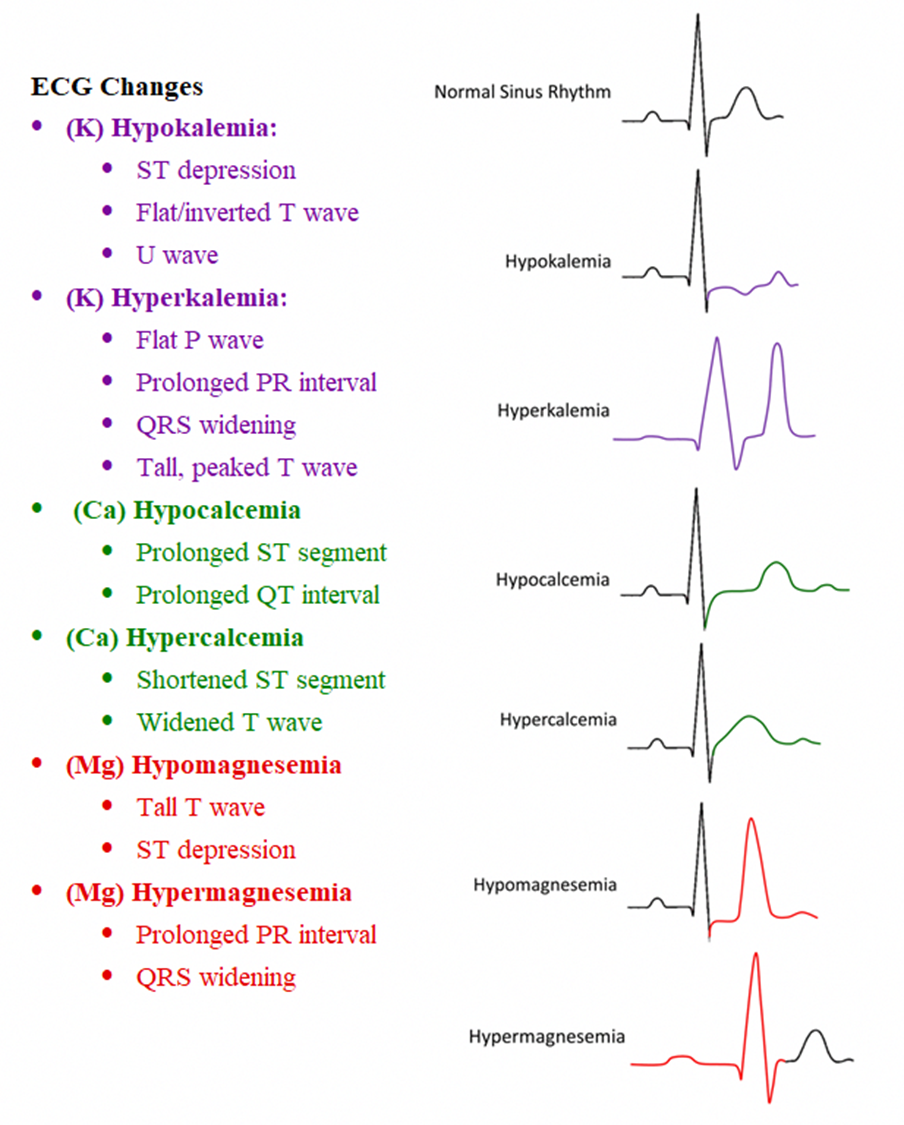
electrolyte changes in EKG
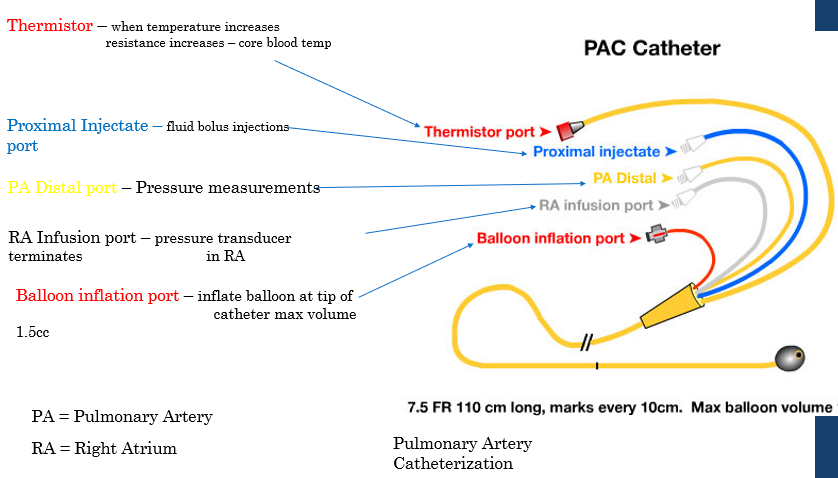
explain heart cath. factors
outpatient procedure
minimally invasive (compared to open heart)
diagnostic as well as theraputic
what is the called the widow maker?
the left anterior descending artery→ if it stops, heart dies
echocardiagram
ultrasound of the heart
can look at the chambers
3d
CAT scan
purely software driven
pixels of calcium solidified are counted to generate3 a score. calcium # found as it appears white and it counted
not as intense as MRI
calcium score
→ 0-100=good
→ 100-200=get checked out
→ 200-300=cath lab
→ 400+=surgery asap
scale goes to 1200
EKG stress test
regular stress test annual vs diagnostic(if something came it, can get checed)
nuclear stress test = radioactive nucleotide→ visible via CAT scan to see what heart looks like
incremntally stressing the heart to monitor the adaptability of the heart muscles effectiveness
angiogram
diagnostic oimaging
ability to make a picture of the inside of vessels and organs
echocardiogram usually better