20 Overview of Antimicrobial Drugs and Their Mechanisms
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Chemotherapy
the use of a drug to treat a disease
Paul Ehrlich
research involved staining bacteria in blood samples, speculated about chemical agents with selective toxicity
Alexander Fleming (1928)
discovered the first presence of antimicrobial compound (Penicillium notatum mold on solid media)
Selective toxicity
killing/inhibiting harmful microbes without damaging the host
Antimicrobial drugs
A compound that kills or interferes with the growth of microbes within a host
Antibiotic
a substance produced by a microbe that, in small amounts, inhibits another microbe
Sulfanilamides
First antimicrobial drugs developed by a team of scientists at Bayer, known as 'Sulfa' (Prontosil Red).
Bactericidal
Directly kills microbes
Bacteriostatic
Inhibits bacterial growth
Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis
A mode of action for antibiotics that prevents the formation of the bacterial cell wall.
Inhibition of Protein Synthesis
A mode of action for antibiotics that prevents the production of proteins necessary for bacterial growth.
Targeting of Plasma Membrane
A mode of action for antibiotics that disrupts the integrity of the bacterial cell membrane.
Inhibition of Nucleic Acid Synthesis
A mode of action for antibiotics that interferes with the replication and transcription of bacterial DNA.
Inhibition of Key Metabolite Synthesis
A mode of action for antibiotics that blocks the synthesis of essential metabolites in bacteria.
Penicillin
Originally isolated from Penicillium mold, it prevents peptidoglycan crosslinking in bacterial cell walls.
Natural Penicillins
Penicillins that are derived from natural sources.
Synthetic Penicillins
Penicillins that are chemically manufactured.
structure of various penicillin
common nucleus, B-lactam ring
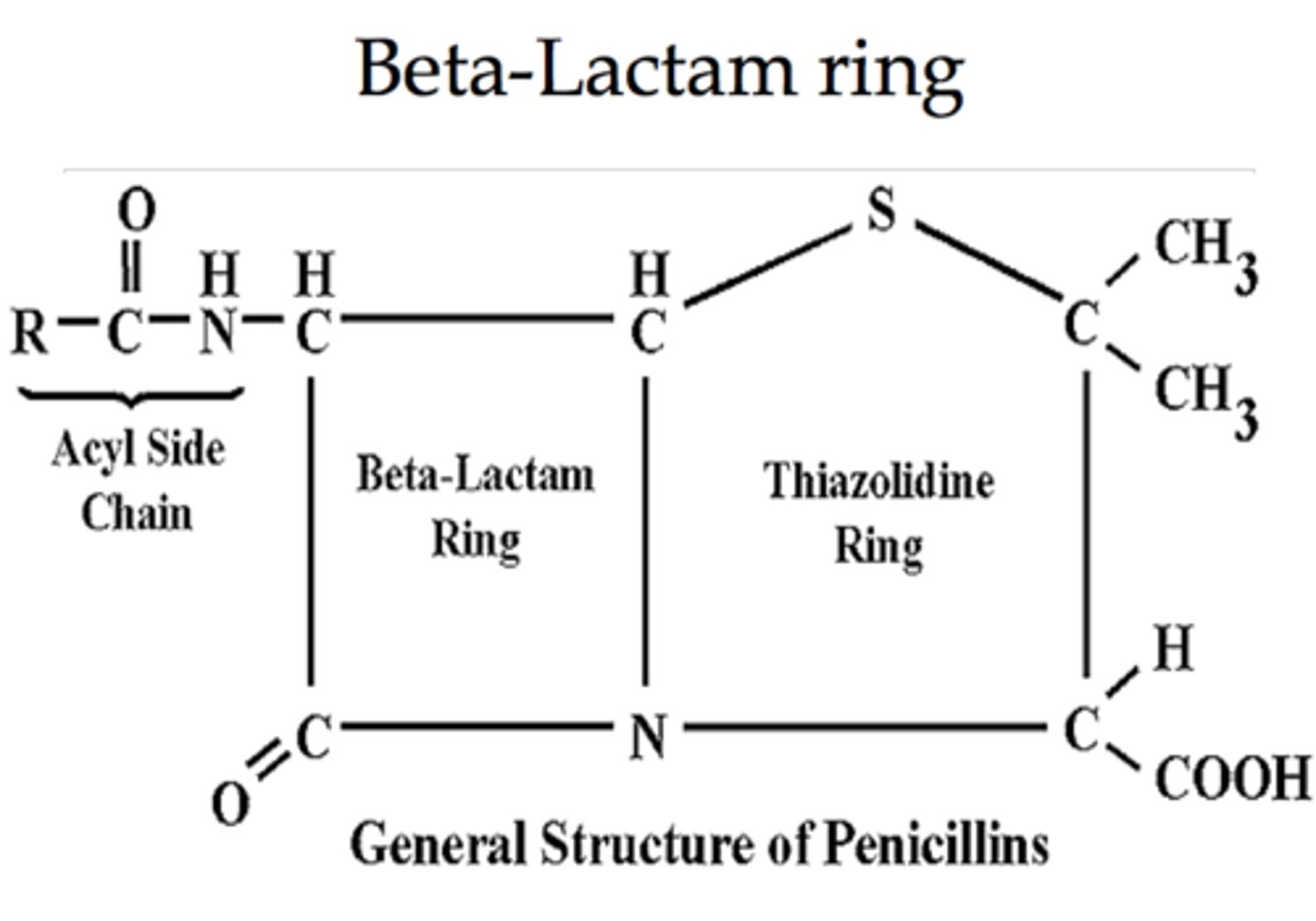
Penicillin G
An injectable form of penicillin effective against Gram-positive bacteria.
Penicillin V
An oral form of penicillin that is effective against Gram-positive bacteria.
Oxacillin
A synthetic penicillin
that resists destruction by penicillinase (a type of β-lactamase), but can still fit into penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), blocking cell wall synthesis and killing bacteria.
Penicillinase
An enzyme produced by some bacteria that inactivates penicillin.
MRSA
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, a type of bacteria resistant to many antibiotics.
Potassium Clavulanate
A non-competitive inhibitor of penicillinase used to overcome bacterial resistance.
Dosage Characteristics of Penicillin G
Refers to the concentration of Penicillin G in blood over time after administration.
D-D transpeptidase
The bacterial enzyme responsible for crosslinking of peptidoglycan chains in the cell wall.
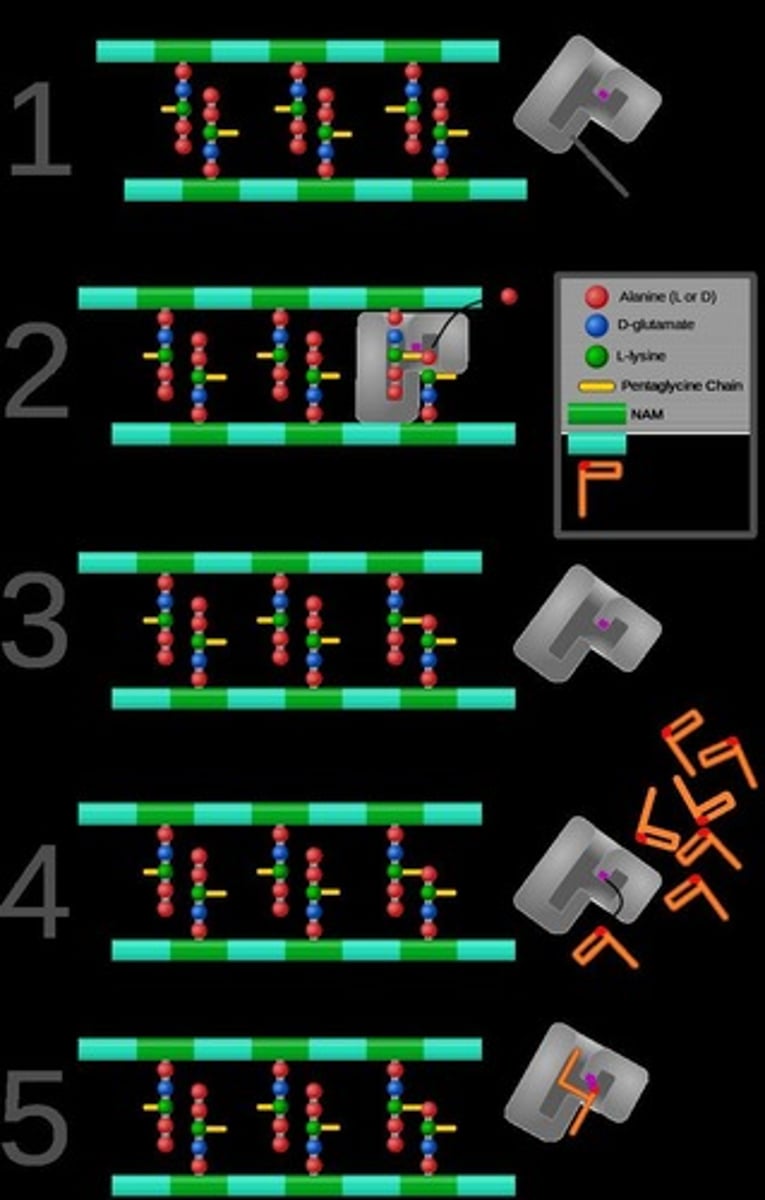
mechanism of penicillin
1. Binds to PBPs→ Penicillin binds to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), which help build the cell wall.
2. Blocks Peptidoglycan Cross-Linking→ Stops the cross-linking of peptidoglycan, a key cell wall component.
3. Weakens the Cell Wall→ The wall can't handle pressure → becomes unstable.
4. Bacteria Burst (Lysis)→ Water rushes in → the bacteria explode and die.
Evolution of Bacterial Resistance
The process by which bacteria develop the ability to resist the effects of antibiotics.
Augmentin
Combined with broad range synthetic penicillins.
Cephalosporins
Closely resembles penicillin and inhibits cell wall synthesis by the same mechanism.
First-generation Cephalosporins
Narrow spectrum; act against gram-positive bacteria.
Second-generation Cephalosporins
Extended spectrum includes gram-negative bacteria.
Third-generation Cephalosporins
Includes pseudomonads and is administered by injection.
Fourth-generation Cephalosporins
Administered orally.
Bacitracin
Inhibits cell wall synthesis and blocks transport of NAG and NAM building blocks across the cell membrane.
Vancomycin
Narrow spectrum that kills mostly Gram-positive bacteria by stopping their cell walls from being built properly and one of the last lines of defense against MRSA.
Steps of Protein Synthesis Inhibition by Antibiotics
1. Antibiotic attaches to bacterial ribosome→ It sticks to the ribosome, which is the bacteria's protein making machine.
2. Blocks ribosome function→ Prevents the ribosome from reading the bacterial RNA instructions.
3. Stops protein production→ No proteins get made, and bacteria can't grow or fix themselves
4. Bacteria stop growing or die→ Without proteins, bacteria cannot survive or multiply.
Chloramphenicol
Binds to 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of peptide bond; broad spectrum.
Streptomycin
Binds to 30S ribosomal subunit and interferes with proper reading of the mRNA codon; effective against Gram-/+ bacteria and Mycobacteria.
Tetracyclines
Binds to 30S ribosomal subunit and interferes with
docking of tRNA; blocking peptide synthesis, broad spectrum.
Erythromycin
Binds to 50S ribosomal subunit blocking the peptide tunnel; effective against Gram+ bacteria
Linezolid
Completely synthetic drug that binds to 50S ribosomal and prevents binding to 30S subunit; effective against Gram+ bacteria, may help delay bacterial resistance
Daptomycin
Attacks bacterial plasma membrane, changes membrane structure, and stops DNA, RNA, protein synthesis; effective against Gram+ bacteria.
Polymyxin B
Binds and destabilizes both outer and cytoplasmic membrane of Gram- bacteria; used topically.
Rifamycins
Inhibits synthesis of mRNA by binding to bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase; used to treat tuberculosis and leprosy.
Aminoglycosides
Class of antibiotics including Streptomycin that interferes with protein synthesis.
Macrolides
Class of antibiotics including Erythromycin that binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit.
Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis
Antibiotics that prevent the formation of bacterial cell walls.
Gram-positive bacteria
Bacteria that retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining procedure.
Gram-negative bacteria
Bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain and are characterized by a thin peptidoglycan layer.
Ciprofloxin
Chemical synthesized (not isolated from microbe) that inhibits bacterial DNA Gyrase blocking DNA replication.
Quinolones and Fluroquinolones
A class of antibiotics that inhibit bacterial DNA replication.
Anthrax
An infectious disease that ciprofloxin is used to treat.
Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim
Drug synergism (smaller dosage if two are combined), Inhibits synthesis of metabolic intermediates of Thymidine (eventually inhibiting DNA synthesis), often used to treat urinary tract infections (alternative to penicillin)
Drug Synergism
The phenomenon where smaller dosages are effective when two drugs are combined.
PABA (para-aminobenzoic acid)
competes with sulfamethoxazole to inhibit the synthesis of dihydrofolic acid in bacteria
Dihydrofolic acid
A precursor in the synthesis of tetrahydrofolic acid, which is inhibited by trimethoprim.
Tetrahydrofolic acid
A critical metabolite for the synthesis of proteins, DNA, and RNA.
Amphotericin B
An antifungal drug that binds ergosterols and leads to damage of the cell membrane.
Acyclovir
An antiviral drug that resembles the nucleoside deoxyguanosine and blocks DNA synthesis.
Chloroquine
An antiprotozoan drug used to treat and prevent malaria, targeting merozoites. (prevents inactivation of toxic metabolic
byproduct)
Artemisinin
An antiprotozoan drug used to treat and prevent malaria, targeting sporozoites.
Niclosamide
An antihelminthic drug that prevents ATP generation in tapeworms.
Praziquantel
An antihelminthic drug that alters membrane permeability in flatworms and flukes.
Ivermectin
An antihelminthic drug that causes paralysis in roundworms, some ticks, and mites.
Kirby-Bauer Test
A test used to identify antibiotic susceptibility.
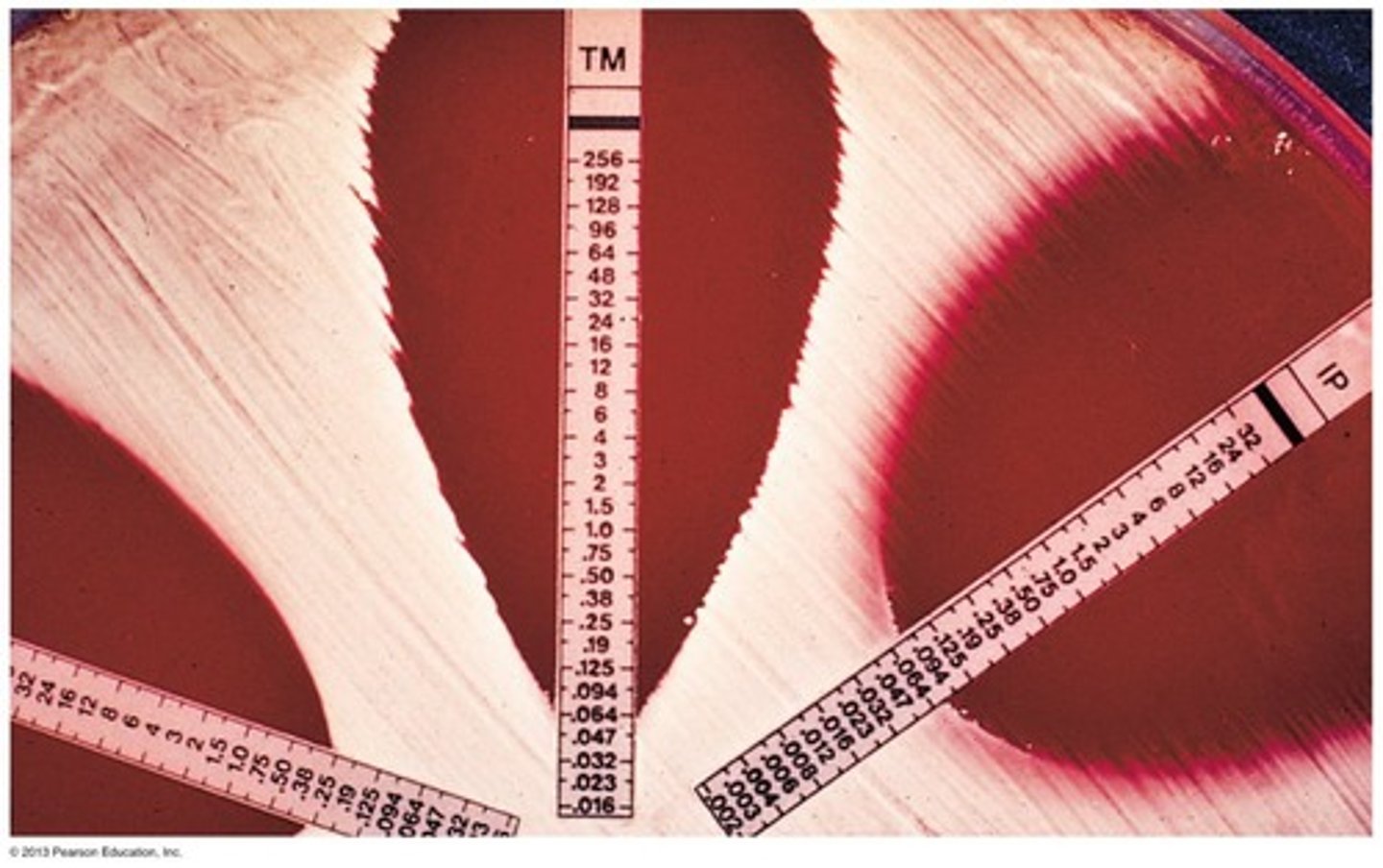
E Test
A test used to determine Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (M.I.C.).
Misuse of Antibiotics
Includes using outdated antibiotics, using them for inappropriate conditions, and failing to complete the prescribed regimen.
Development of Antibiotic Resistance
A problem exacerbated by the misuse of antibiotics and large-scale antibiotic use in agriculture.
Blocking entry
One of the modes of bacterial resistance to antibiotics.
Inactivation by enzymes
A mode of bacterial resistance where enzymes inactivate antibiotics.
Alteration of target molecule
A mode of bacterial resistance where the target of the antibiotic is altered.
Efflux of antibiotic
A mode of bacterial resistance where bacteria pump out the antibiotic.