AICE Enviornmental Exam Study Guide
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study guide filled with term, case studies and organizations from the syllabus to reveiw before the exam
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1
New cards
what are the 7 continents?
Africa, Antarctica, Asia, Europe, North America, South America and Oceania
2
New cards
what are the 5 oceans?
Atlantic Ocean, Pacific Ocean, Indian Ocean, Arctic Ocean and Southern Ocean
3
New cards
LIC example
Nigeria
* Birth rate; 5.3 per women
* Death reate; 11.4/1000
* Infant mortality; 72.2/1000
* Life expectancy; 54.7 yrs
* 95.1 mil people in poverty
* education; 62.02% as of 2018
* presidential system
* 9.7% unemployment
* Birth rate; 5.3 per women
* Death reate; 11.4/1000
* Infant mortality; 72.2/1000
* Life expectancy; 54.7 yrs
* 95.1 mil people in poverty
* education; 62.02% as of 2018
* presidential system
* 9.7% unemployment
4
New cards
MIC example
Namibia
* Birth rate; 3.34 per woman
* Death rate; 7.7%
* Infant mortality; 30.1/1000
* Life expectnacy; 63.7 yrs
* 43.3% poverty rate
* Education; 92% of adults
* representative democracy
* 21.7% unempolment rate
* Birth rate; 3.34 per woman
* Death rate; 7.7%
* Infant mortality; 30.1/1000
* Life expectnacy; 63.7 yrs
* 43.3% poverty rate
* Education; 92% of adults
* representative democracy
* 21.7% unempolment rate
5
New cards
HIC example
United States
* Birth rate; 1.64 per women
* Death rate; 9.07%
* Infant mortality; 5.4/1000
* Life expectancy; 77.3 yrs
* Poverty rate; 11.6%
* education; 95% high school education
* democracy
* 3.5% unemployment March of 2023
* Birth rate; 1.64 per women
* Death rate; 9.07%
* Infant mortality; 5.4/1000
* Life expectancy; 77.3 yrs
* Poverty rate; 11.6%
* education; 95% high school education
* democracy
* 3.5% unemployment March of 2023
6
New cards
what is the definittion of sustainability?
(from syllabus)
(from syllabus)
the ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
7
New cards
what are the major gases of the atmosphere?
Nitrogen, oxygen coarbon dioxide, argoin water vapor
8
New cards
what is the composition of earth’s atmosphere in order?
troposhere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere
9
New cards
biome
a large area characterized by its vegetation, soil, climate, and wildlife.
five major types of biomes: aquatic, grassland, forest, desert, and tundra
five major types of biomes: aquatic, grassland, forest, desert, and tundra
10
New cards
niche
the role an organism plays in a community
11
New cards
what are examples of biotic interactions?
* competiton (intra \[between difference species\] and inter \[between the ame species\]- specific)
* grazing (eating folliage)
* predation (eating othert animals)
* grazing (eating folliage)
* predation (eating othert animals)
12
New cards
what is the equation for photosynthesis?
(know both word and chemical equations)
(know both word and chemical equations)
* carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
* 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
* 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
13
New cards
how is energy lost in a food chain?
respiration and waste
14
New cards
what is aerobic respiration?
the chemical reactions in cells that break down glucose molecules and release energy, carbon dioxide and water
15
New cards
carbon cycle
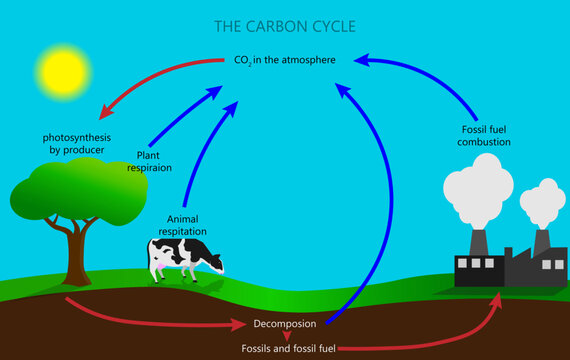
16
New cards
how has the investigation of climate change developed?
* limited amount of historical data made it difficult to compare past CO2 levels
* development of scientific theory and advances in technology currentlyt produce more reliable results
* meauseing past CO2 levels with ancient ice
* development of scientific theory and advances in technology currentlyt produce more reliable results
* meauseing past CO2 levels with ancient ice
17
New cards
how does unreliable data lead to false reporting?
* limited amount of data
* lack of public and media knowledge
* uncertainty in climate models
* lack of public and media knowledge
* uncertainty in climate models
18
New cards
methods of data collection using technology
* geospatial systems
* satellite sensors
* radio tracking
* computer modelling
* crowd sourcing
* satellite sensors
* radio tracking
* computer modelling
* crowd sourcing
19
New cards
dependancy ratio equation
(ages 0-14 + ages 65 and over/ages 15-64) x100
20
New cards
what are impacts of aging populations?
* lower tax revenues
* higher pension spending
* pressure on health care
* pressure to raise retirement age
* higher pension spending
* pressure on health care
* pressure to raise retirement age
21
New cards
gross pimary productivity
The total amount of carbon compounds produced by photosynthesis of plants in an ecosystem in a given period of time.
22
New cards
net primary productivity
the amount of carbon retained in an ecosystem (increase in biomass); it is equal to the difference between the amount of carbon produced through photosynthesis (GPP) and the amount of energy that is used for respiration (R)
23
New cards
what is ecosystem productivity? (from syllabus)
the rate of production of biomass for an ecosystem
24
New cards
what is the energy transfer between trophic levels?
10% of energy from the lower trophic level is transferred to the other
25
New cards
what are benefits of conserving biodiveristy?
* resources of potential medicines
* food, wood, fibres, oils and fuels
* diversity in genes
* ecological services
* cultural and recreational value
(remeber 3-4)
* food, wood, fibres, oils and fuels
* diversity in genes
* ecological services
* cultural and recreational value
(remeber 3-4)
26
New cards
what is CITES?
an international treaty to protect endangered plants and animals from the threats of international trade; effective since 1975
27
New cards
what is the international whaling commision (IWC)?
the global body charged with the conservation of whales and the management of whaling
* implemented an indefinite moratorium/halt on whlaing and the designation of ocean sanctuaries
* implemented an indefinite moratorium/halt on whlaing and the designation of ocean sanctuaries
28
New cards
what is the European Union Common Fisheies Policy (EUCFP)?
a set of rules for sustainably managing European fishing fleets and conserving fish stocks established in 1970
* manages fisheries to stop overfishing
* manages fisheries to stop overfishing
29
New cards
what is the International Tropical Timber Organisation (ITTO)?
an intergovernmental organization promoting the sustainable management and conservation of tropical forests and the expansion and diversification of international trade in tropical timber from sustainably managed and legally harvested forests
* __**basically regulates deforestation**__
* __**basically regulates deforestation**__
30
New cards
what is the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List?
the world's most comprehensive information source on the global conservation status of animal, fungi and plant species.
31
New cards
what are impacts of human activity on biodiversity?
• deforestation leading to fragmentation
• fuel wood and timber collection
• agricultural expansion
• mineral extraction
• hydroelectric and reservoir projects
• climate change
• exploitation of individual species
(remeber 3-4)
• fuel wood and timber collection
• agricultural expansion
• mineral extraction
• hydroelectric and reservoir projects
• climate change
• exploitation of individual species
(remeber 3-4)
32
New cards
what is the Antartic treaty of 1965?
prohibits nuclear testing, military operations, economic exploitation, and territorial claims in Antarctica
33
New cards
what is the world food programme?
an international organization within the United Nations that provides food assistance worldwide
* It is the world's largest humanitarian organization and the leading provider of school meals
* It is the world's largest humanitarian organization and the leading provider of school meals
34
New cards
examples renewable resources
biofuels (biomass including wood, bioethanol and biogas)
geothermal energy
hydroelectric dams
tidal energy
wave energy
solar energy
wind energy
geothermal energy
hydroelectric dams
tidal energy
wave energy
solar energy
wind energy
35
New cards
examples of non-renewable resources
fossil fuel (oil, natural gas, coal)
nuclear energy using uranium as a fuel
nuclear energy using uranium as a fuel
36
New cards
energy securtiy definition (from syllabus)
the reliable availability of energy sources at an affordable price with a consideration of the environmental impacts
37
New cards
what is long term energy security? (from syllabus)
supply of energy that is in line with economic developments and environmental needs
38
New cards
what is short term energy security? (from syllabus)
systems that react promptly to sudden changes in the supply-demand balance
39
New cards
what are the causes for energy insecurity?
• fossil fuel depletion • inequality in global energy resources • population growth • differing energy needs of countries in different income groups • climate change • supply disruption – natural disasters, piracy, terrorism (remeber 3-4)
40
New cards
what are strategies form managing energy insecurity?
• increasing energy efficiency • increasing energy production • reducing reliance on fossil fuels • investing in renewable resources and carbon neutral fuels • development of alternative energy technologies • investment in local energy projects • rationing (remeber 3-4)
41
New cards
what are impacts of waste disposal methods?
• contamination of soil leading to leaching and contamination of ground water • build-up and release of the greenhouse gas methane (CH4) with a danger of explosions • visual and noise pollution and unpleasant odour • risk of spread of disease • release of toxic substances • bioaccumulation and biomagnification • plastics and microplastics in oceans (remeber 3-4)
42
New cards
what is the distribution of earth’s water?
• salt water in oceans
• surface fresh water – ice sheets, glaciers, lakes, rivers, swamps, marshes, permafrost
• sub-surface fresh water – soil moisture, ground water, permafrost
• atmospheric water
• surface fresh water – ice sheets, glaciers, lakes, rivers, swamps, marshes, permafrost
• sub-surface fresh water – soil moisture, ground water, permafrost
• atmospheric water
43
New cards
what is water security? (from syllabus)
the ability to access sufficient quantities of clean water to maintain adequate standards of food and manufacturing of goods, adequate sanitation and sustainable health care
44
New cards
what is acid deposition? (from syllabus)
a mix of air pollutants that deposit from the atmosphere as acidic wet deposition (with a pH
45
New cards
what are the impacts of acid deposition on:
• aquatic environments
• vegetation and crops
• stone and brick buildings
• aquatic environments
• vegetation and crops
• stone and brick buildings
• the effects on fish gills (clogging) and fish populations (reduction in egg hatching)
• defoliation and reduced crop yield
• enhanced chemical weathering
• defoliation and reduced crop yield
• enhanced chemical weathering
46
New cards
what is photochemical smog? (from syllabus)
a mixture of air pollutants and particulates, including ground level ozone, that is formed when oxides of nitrogen and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) react in the presence of sunlight
causes: eye and respiratory irritation • decreased crop yields • deterioration of plastics and rubber
causes: eye and respiratory irritation • decreased crop yields • deterioration of plastics and rubber
47
New cards
how does ozone depletion occur?
CFCs move into the stratosphere and break down in the presence of ultraviolet light to release a chlorine atom • rapid reactions between chlorine atoms and ozone breaks down ozone (O3) to oxygen (O2), causing ozone depletion • chlorine atoms remain in the stratosphere and can continue to destroy ozone
48
New cards
how is ozone concentration measured?
using the dobson unit
49
New cards
what is an ozone hole? (from syllabus)
an area where the average concentration of ozone is below 100 Dobson Units
50
New cards
what are greenhouse gases?
gases in the atmosphere that absorb infrared radiation and identify some common greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane)
51
New cards
what are major sources of greenhouse gas emissions from human activities?
• combustion of fossil fuels (carbon dioxide and water vapour)
• rice fields and livestock (methane)
• landfill sites (methane)
• rice fields and livestock (methane)
• landfill sites (methane)
52
New cards
what is the Kyoto Protocol 1992?
implemented the objective of the UNFCCC (United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change) to reduce the onset of global warming by reducing greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere
* it failed
* it failed
53
New cards
What is the Paris agreement of 2016?
sets out a global framework to avoid dangerous climate change by limiting global warming to well below 2°C and pursuing efforts to limit it to 1.5°C
* experts don’t believe it is enough
* experts don’t believe it is enough
54
New cards
what are geo-engineering strategies to conteract climate change?
* solar radiation management (SRM) –
* albedo enhancement (increaseing land/cloud brightness to reduce absorption rates)
* space reflectors
* stratospheric aerosols (aerosols spayed into the atmosphere to promote reflectivity)
* albedo enhancement (increaseing land/cloud brightness to reduce absorption rates)
* space reflectors
* stratospheric aerosols (aerosols spayed into the atmosphere to promote reflectivity)