Ionic crystals
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are the 4 main types of crystal structures?
Ionic
Metallic
Simple molecular (covalent)
Macromolecular (Giant covalent structures)
Describe the structure of ionic compounds.
Consists of a lattice of positive and negative ions held together by strong electrostatic forces.
Give examples of ionic compounds.
Sodium chloride (NaCl)
Caesium chloride (CSCl)
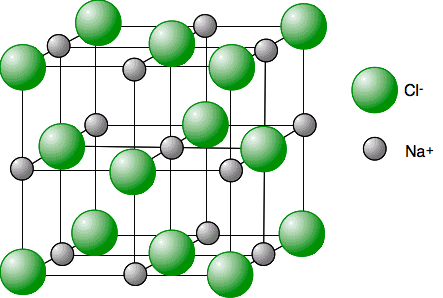
Describe the arrangement of ions in sodium chloride.
Each sodium ion is surrounded by 6 chloride ions.
Each chloride ion is surrounded by 6 sodium ions.
What is the coordination number of each sodium ion in NaCl?
6.
What is the coordination number of each chloride ion in NaCl?
6.
What is the coordination number of sodium chloride?
6:6.
What is the crystalline structure of sodium chloride (NaCl)?
Face-centred cubic.
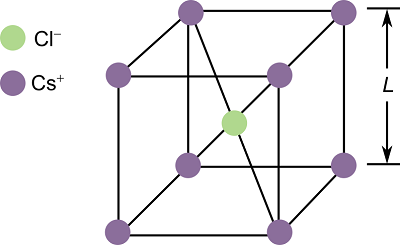
Describe the arrangement of ions in caesium chloride.
Each caesium ion is surrounded by 8 chloride ions.
Each chloride ion is surrounded by 8 caesium ions.
What is the coordination number of each caesium ion in caesium chloride?
8.
What is the coordination number of each chloride ion in caesium chloride?
8.
What is the coordination number of caesium chloride?
8:8.
What is the crystalline structure of caesium chloride (CsCl)?
Body-centred cubic.
Why does caesium chloride (CsCl) have a different structure to sodium chloride (NaCl)?
Caesium ion are larger than sodium ion hence it can be surrounded by greater number of chloride ions.
State the properties of ionic compounds.
High melting and boiling points
Crystalline
Brittle
Conduct electricity only when molten or dissolved in water.
Soluble in polar substances i.e. water.
Why do ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points?
Electrostatic forces holding the ions together are strong and require a lot of energy to break.
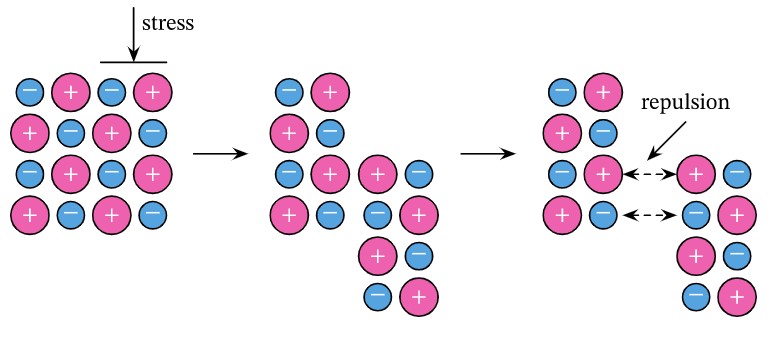
Why are ionic compounds brittle?
When an external force is applied, the lattice arragement of ions are disrupted, causing them to break apart.
Why do ionic compounds conduct electricity only when molten / dissolved in water?
When molten / dissolved in water, ions are free to move and so, can transfer electrical charge.
Why are ionic compounds soluble in water?
Positve ion from the ionic compound is attracted to the negative end of the water molecule (oxygen).
Negative ion is attracted to the positive end of the water molecule (hydrogen).