ALL KINESIOLOGY FLASHCARDS
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
202 Terms
How many bones does an upper limb have, and what are they?
Humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges
30 in total
What are the joints of an upper limb?
Shoulder joint
Elbow joint
Radioulnar joint
Wrist
Carpo-metacarpal joint
Metacarpophalangeal joint
Interphalangeal joint
What is the radioulnar joint?
Where the radius and ulna articulates
A pivot joint allowing pronation and supination
What is the anular ligament?
Holds the radioulnar joint in place
Allows the radius to pivot
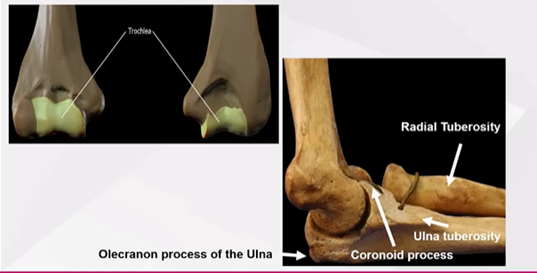
How is the elbow joint structured?
Contains the radial and ulna tuberosity, with the ulna tuberosity flattening to form the coronoid process
The olecranon and trochlear of the humerus allows the ulna to articulate
What are the anterior muscles of the elbow?
Bicep brachii
Brachialis
Brachioradialis
Pronator teres
Pronator quadratus
What are the posterior muscles of the elbow?
Tricep brachii
Anconeus
Supinator
Tricep brachii O + I
O = Infraglenoid tubercle of scapula
I = Olecranon of the ulna
Bicep Brachii short head O + I
O = coracoid process of scapula
I = Radial tuberosity
Bicep brachii long head O + I
O = Supraglenoid tubercle of scapula
I = Radial tuberosity
What is wrist movement primarily caused by?
The radius and proximal carpals, which forms the radiocarpal joint
What type of joint is the thumb?
Saddle joint
Wrist flexors O + I
O = Anteromedially on forearm
I = Anteriorly at the hand
Wrist extensors O + I
O = Posteromedially on forearm
I = Posteriorly at the hand
What is lateral epicondylitis?
Tennis elbow
Overuse injury of the wrist extensors and supination which attach to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus
What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
Overuse injury causing numbness, tingle feeling
Caused by repetitive gripping
Caused by nerve compression by tendons on the medial nerve
What bones articulate at the knee?
Femur
Tibia
Patella
What are the 2 knee joints?
Tibiofemoral joint
Patellofemoral joint
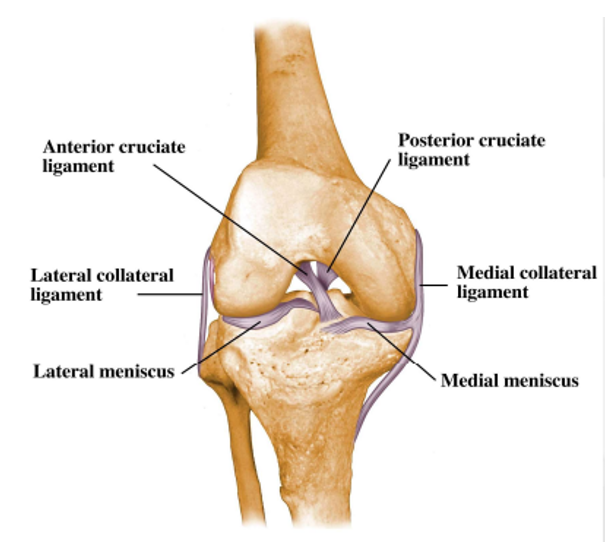
What are the ligaments of the knee
Anterior cruciate ligament
Posterior cruciate ligament
Lateral collateral ligament
Medial collateral ligament
Lateral menisci
Medial menisci
Where is the patella?
Embedded into the quadricep and patella tendon
What are the functions of the patella?
Acts as a lever arm for quadricep (10-30% more torque)
Protects the anterior knee structures
What are the muscles of the quadricep?
Rectus femoris
Vastus medialis
Vastus intermedius
Vastus lateralis
Rectus femoris O + I
O = AIIS
I = Tibial tuberosity
Vastus medialis O + I
O = Medial side of linea aspera
I = Tibial tuberosity
Vastus intermedius O + I
O = Anterolateral femur
I = Tibial tuberosity
Vastus medialis O + I
O = Greater trochanter
I = Tibial tuberosity
What are the muscles of the hamstring?
Bicep femoris
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Bicep femoris O + I
O = Long head - ischial tuberosity, short head - linea aspera
I = Head of fibula
Semitendinosus O + I
O = Ischial tuberosity
I = Anteromedial tibia
Semimembranosus O + I
O = Ischial tuberosity
I = Medial condyle of tibia
What a biarticulating muscle?
A muscle which is involved in multiple joint actions
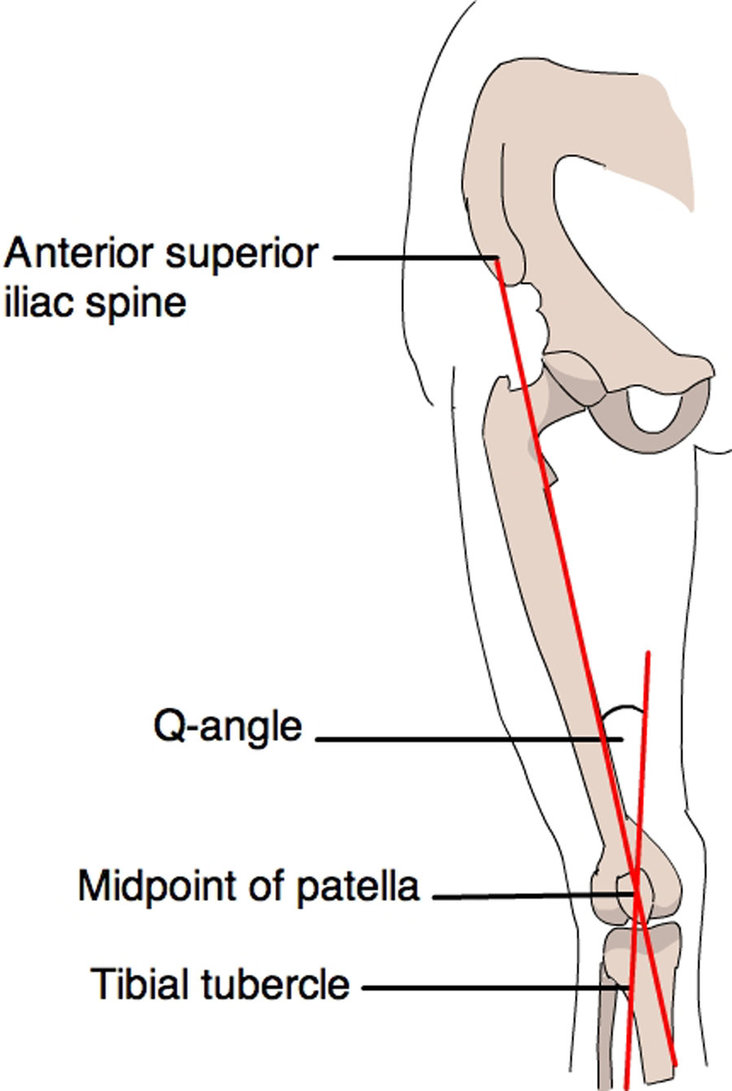
What is the Q angle?
The angle of line of pull of the quadricep
Drawn between the ASIS to patella, and tibial tuberosity to patella
Men = 12-13°, Women = 16-18°
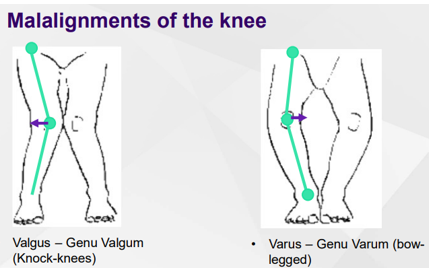
What are the 2 malalignments of the knee?
Valgus = knees come in together
Varus = knees are apart
What is chondromalacia patella?
Pain at the front of knee due to patellofemoral cartilage damage, and mistracking the patella
What are risk factors for chondromalacia patella?
High patella
Valgus (high Q angle)
Pronation
Weak vastus medialis
What factors affect ACL ruptures?
70% are non contact
Caused by cutting and decelerating soon after ground contact
What are the functions of the foot?
Load bearing
Locomotion
Shock absorption
Acts as a 2nd class lever
How many bones are in the foot?
26
What does the longitudinal arch of the foot travel through?
Calcaneus
Talus
Navicular
Cuboid
Tarsals
What does the transverse arch of the foot travel through?
5 Metatarsals
What is pes planus?
Flat footed:
Low arched foot
Good shock absorption
Poor propulsion
What is pes cavus?
Arched foot:
High arched foot
Poor shock absorption
Good propulsion
What is the plantar fascia?
Ligamentous structure connecting the foot to the skins
What is plantar fasciitis?
Overuse of the plantar fascia caused by:
Obesity
Long periods of standing
Tight dorsi-flexors
What is the ankle joint and what does it consist of?
Hinge joint
Consists of tibia, fibula and talus
What is the subtalar joint?
A transverse tarsal joint
Consists of talus, calcaneus, navicular and cuboid
Allow inversion, everison, pronation and supination
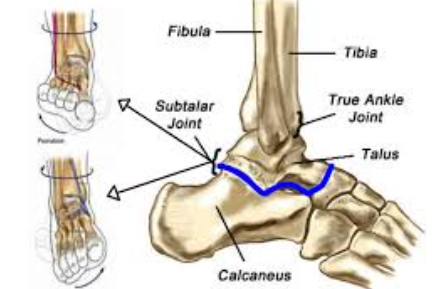
What is a tarsometatarsal joint?
Joint between the metatarsals
What is the metatarsophalangeal joint?
Joint between metatarsals and phalanges
What is the interphalangeal joint?
Joint between the phalanges
What are the superficial posterior muscles of the ankle and their movement?
Gastrocnemius and soleus
Primary plantar flexors
Gastrocnemius O + I
O = posterior of femoral condyles
I = calcaneus
Soleus O + I
O = Posterior of the proximal fibula and tibia
I = calcaneus
What are the deep posterior muscles of the ankle?
Tibialis posterior
FDL + FHL
Tibialis posterior O + I
O = Interosseous membrane
I = navicular cuneiforms of metatarsals 2,3,4,5
What are the anterior muscles of the ankle and their movement?
Tibialis anterior
EDL
EHL
Primary dorsi-flexors
What are the lateral muscles of the ankle and their movement?
Peroneus longus
Peroneus brevis
Peroneus tertius
Primary evertors
What is shin splints?
Either:
Small tears in muscle attached to tibia
Stress fractures of tibia
What are ankle dislocations?
Overstretch of ligaments supporting the ankle
90% are caused by inversion
What is an achillies rupture?
Pain in the heel caused by:
Sudden dorsi-flexion when muscles are contracted
Heavy activation of achilles tendon after long period of inactivity
What is a flat bone?
Thin and curved
Used for protection
What is a long bone?
Diaphysis is longer than width
Contains epiphysis at end
Used as lever arm for movement
What is an irregular bone?
Has an irregular shape and size
What is a sesamoid bone?
Bone embedded within tendon
What is a short bone?
Short and cuboidal shape
Used for weight bearing and stability
What is the axial skeleton?
Bones associated with the skull, spine, ribs and sternum
What is the appendicular skeleton?
Bones associated with shoulder girdle, pelvic girdle and 4 limbs
What is a fibrous joint?
Bones are connected by fibrous tissue
Provides no movement
What is a cartilaginous joint?
Bones are connected by cartilage
Provides slight movement
What is a synovial joint?
Joint contains synovial fluid for lubrication and shock absorption
Allows free movement
What is a hinge joint?
Allows flexion and extension
e.g. knee
What is a ball and socket joint?
Allows all movements
e.g. shoulder
What is a condyloid joint?
Allows flexion and extension, adduction and abduction, and circumduction
e.g. Wrist
What is a pivot joint?
Allows rotation around an axis
e.g. neck
What is a gliding joint?
Allows Sliding of 2 bones over each other
e.g. between tarsals
What is a saddle joint?
Bones have a concave and convex part which saddle on eachother
e.g. thumb
What bones make up the shoulder girdle?
Clavicle
Scapula
Manubrium of the sternum (superior part of the sternum)
What are the 2 joints of the shoulder girdle?
Acromioclavicular joint
Sternoclavicular joint
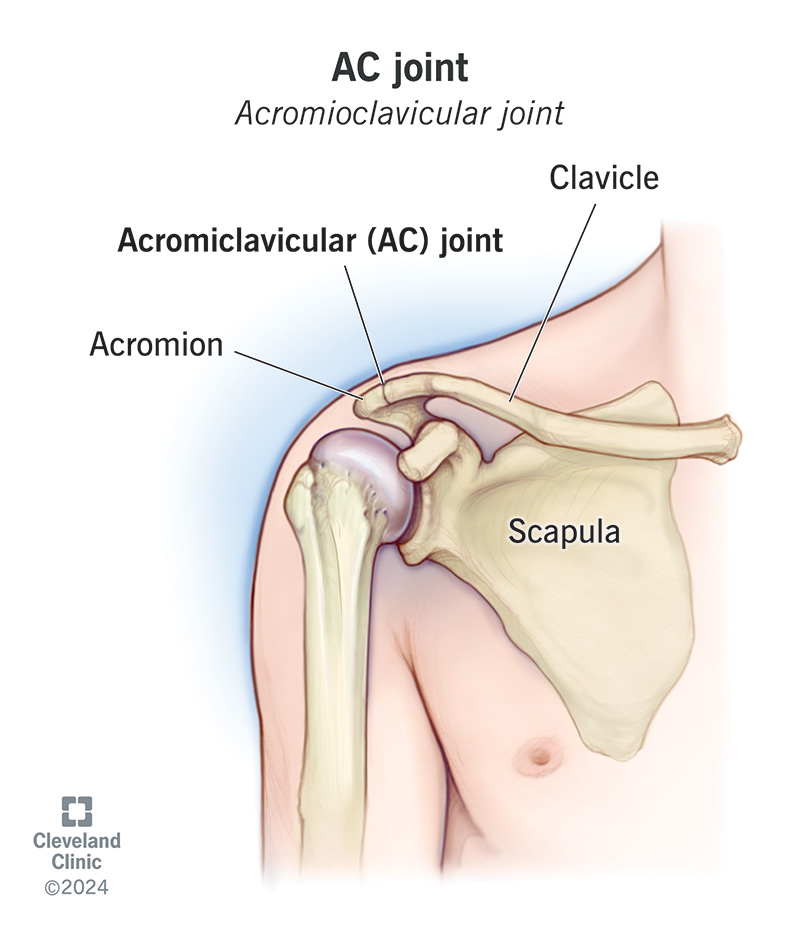
What is the acromioclavicular joint?
Formed by the acromion process of the scapula and the lateral of the clavicle
Is a gliding joint
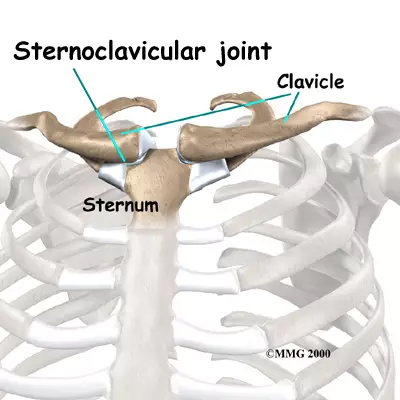
What is the sternoclavicular joint?
Formed by the manubrium of the sternum and medial of the clavicle
Only connection of the axial and appendicular skeletal system
Is a saddle joint
What are the movements available at the shoulder girdle?
Elevation
Depression
Abduction
Adduction
Upwards rotation
Downwards rotation
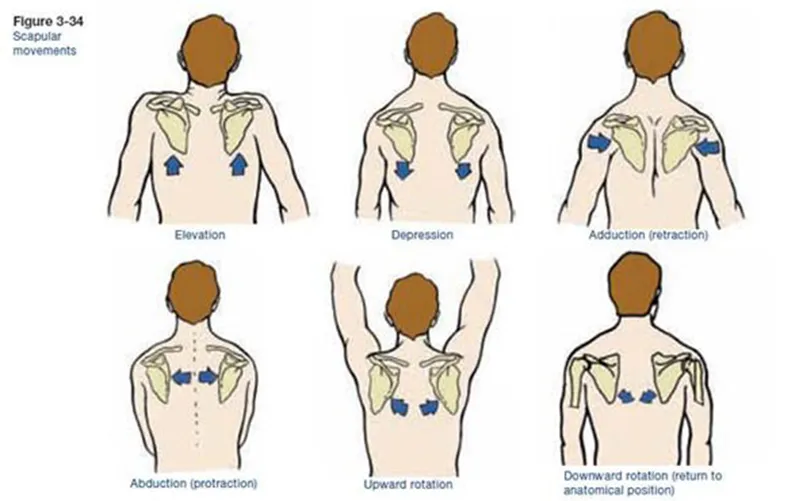
What are the posterior muscles at the shoulder girdle?
Trapezius
Rhomboids
Levator scapulae
What are the anterior muscles at the shoulder girdle?
Pectoralis major
Serratus anterior
What is the nuchal ligament?
Ligament supporting the weight of the head
What are the movements available due to the rhomboids?
Elevation
Adduction
Downwards rotation
Rhomboid O + I
O = C7 to T5
I = Inferior medial part of scapula
What are the movements available due to the levator scapulae?
Elevation
Adduction
Downwards rotation
Levator scapulae O + I
O = C1 to C4
I = Superior medial part of scapula
What are the movements available due to the trapezius?
Upper fibres = adduction + elevation
Middle fibres = adduction
Lower fibres = adduction, depression and downwards upwards
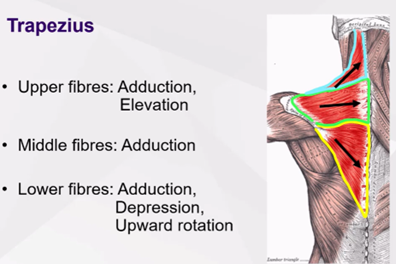
What are the movements available due to the serratus anterior?
Abduction
Upwards rotation
Serratus O + I
O = Upper 9 ribs
I = Medial anterior part of scapula
What are the movements available due to the pectoralis minor?
Abduction
Depression
Downwards rotation
Pectoralis minor O + I
O = Ribs 3,4,5
I = Coracoid process of scapula
What is the most broken bone in the body?
Clavicle
Which part of the clavicle breaks the most?
Middle or lateral third
What is the glenoid fossa?
Cavity on the lateral superior portion of the scapula
Used for humerus articulation
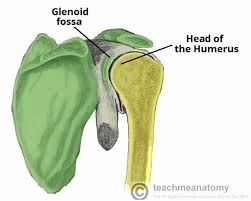
What structures provide stability at the shoulder joint?
Rotator cuffs
Labrum
Glenohumeral ligaments
Fibrous cartilage
What are the 4 rotator cuff muscles?
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Subscapularis
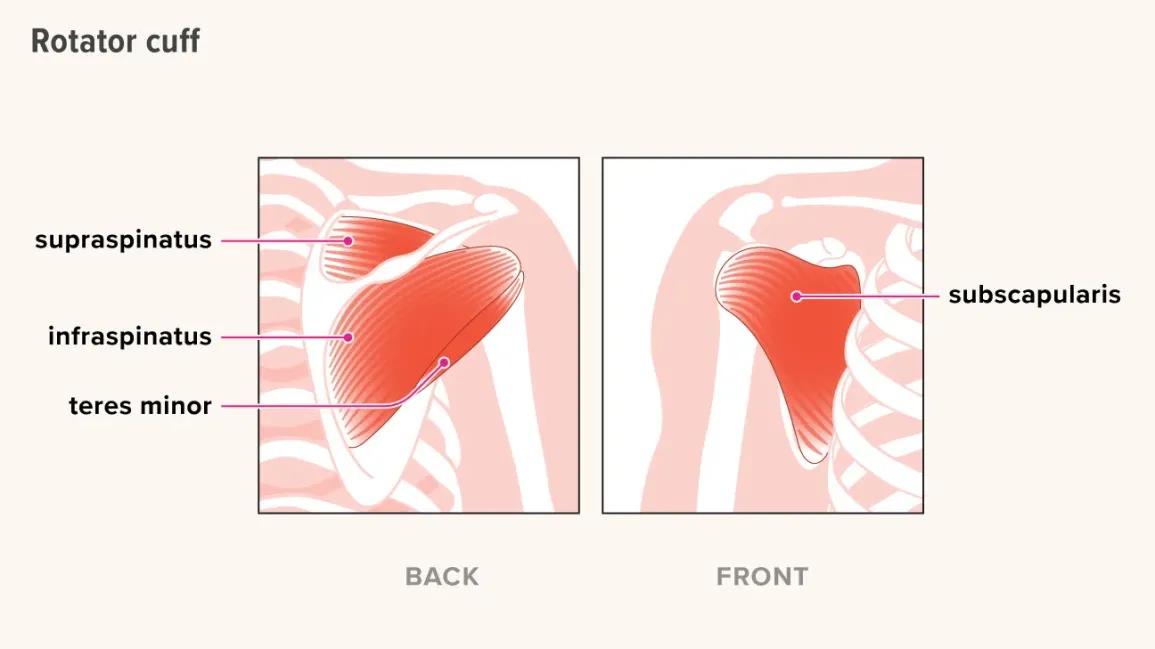
What are the superficial muscles of the glenohumeral joint?
Pectoralis major
Lat dorsi
Teres major
Deltoid
What are the deep muscles of the glenohumeral joint?
All rotator cuff muscles
What movements does the Pectoralis major carry out?
Adduction
Horizontal adduction
Inwards rotation