L14 Metabolism and thermoregulation
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Energy metabolism
All chemical reactions in the body which are involved in energy storage and usage
Catabolism
Anabolism
Catabolism
Breakdown, energy producing
Anabolism
Building, energy storage
ATP
Universal energy carrier
Capture free energy by catabolism of macronutrients
Aerobic (O2)
Anaerobic
Needed for labour/work or storage
Catabolism: glucose oxidation
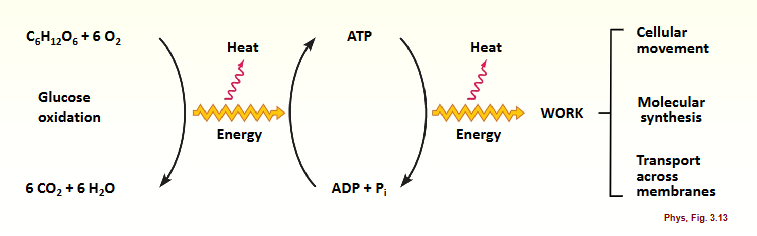
Uptake of carbohydraes - glucos
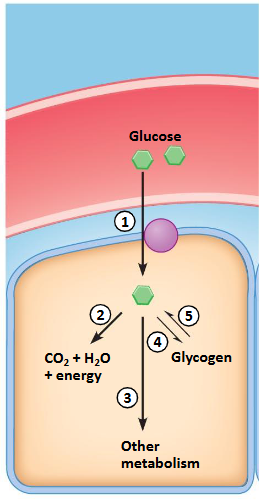
Uptake of glucose: glucose transporters
Used for energy: glycolysis, Krebs, OXPHOS
Metabolized via other routes: glycerol, fatty acids, nucleotides
Storage: glycogen (glycogenesis), (mainly muscle, liver, but also brain)
Glycogen broken down to glucose (glycogenolysis)
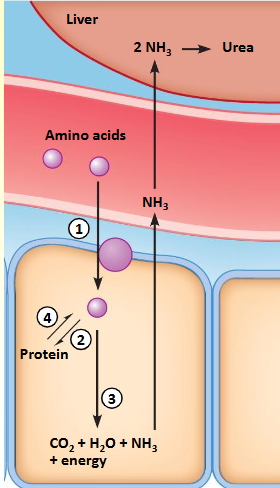
Uptake of proteins - amino acids
Uptake: specialized transporters
Storage: assembled to proteins
Used: deamination NH3 (Krebs, OXPHOS)
Proteins degraded to amino acids (proteolysis) if necessary
Proteins always have a functional role
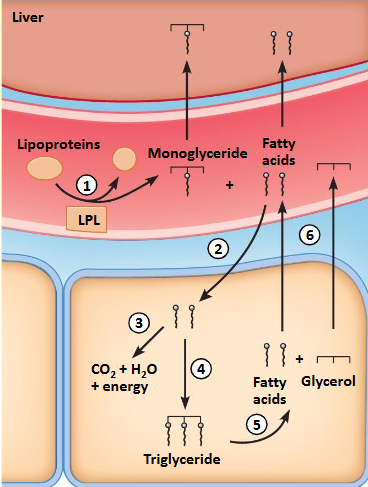
Uptake of fats - triglycerides
Lipoproteins in blood, broken down to free fatty acids and monoglycerol (lipoprotein lipase)
Uptake: diffusion into cell
Used: fatty acids broken down into acetyl CoA (Beta-oxidation) and oxidized Krebs, OXPHOS
Storage: fatty acids and glycerol assembled into triglycerides (lipogenesis)
Triglycerides broken down (lipolysis)
Metabolism of macronutrients
Proteins → amino acids
Glycogen → glucose
Triglycerides → glycerol + fatty acids
glycolysis
pyruvate
acetyl coa
krebs cycle
oxidative phosphorylation
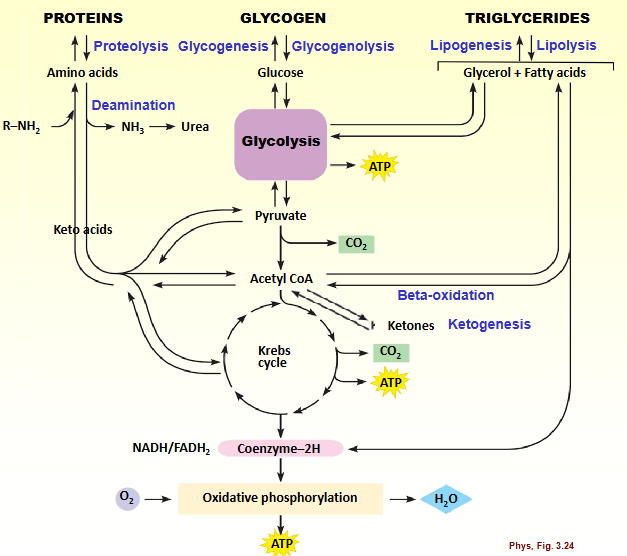
proteolysis
proteins → amino acids
glycogenesis
glucose → glycogen
glycogenolysis
glycogen → glucose
lipogenesis
glycerol + fatty acids → triglycerides
lipolysis
triglycerides → glycerol + fatty acids
Gluconeogenesis
Needs ATP, liver (also kidneys, not muscle)
actie low blood glucose levels
metabolic process of creating glucose (sugar) from non-carbohydrate sources, such as lactate, glycerol, and amino acids
Glucose oxidation - pathway
Glycolysis
Pyruvate → acetyl CoA
Krebs cycle (TCA)
Electron transfer system
Stepwise energy loss (final acceptor is O2)
Oxidative phosphorylation/chemi-osmotic coupling
ATP generated using H+ production (glucose)
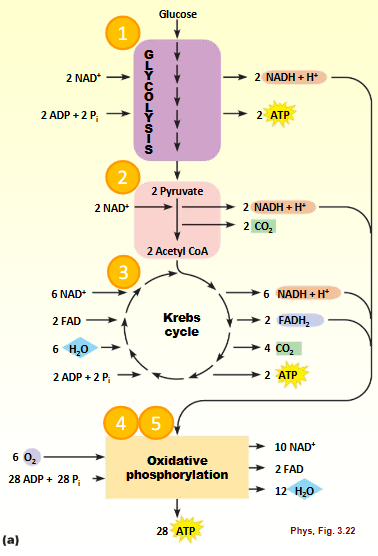
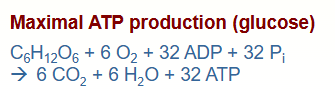
Maximal ATP production (glucose)
32ATP
Anaerobic situations (low oxygen)
No O2 available as an electron acceptor
No activity of Krebs cycle and OXPHOS
Accumulation of pyruvate and NADH → shutdown glycoglysis
Anaerobic glucose oxidation
Pyruvate → lactate : 2ATP + 2NAD+
Inefficient ATP production
Cori cycle
Liver converts lactate into glucose
Efficiency ATP production
Aerobic
Anaerobiv
Aerobic 32.7%
Anaerobic 2%
Why choose anaerobic ATP production
It is much faster than aerobic respiration, useful in situations of sudden, high energy demand (e.g. sprinting)
Energy balance
Energy in = energy out
Energy in
food, alcohol
energy out
basal metabolism (bmr)
thermogenesis
physical activity
positive balance
in>out
energy storage (fat)
negative balance
in<out
energy liberation
Energy balance during the day
energy intake
energy use
energy intake - discontinuous
energy use - continuous with spikes
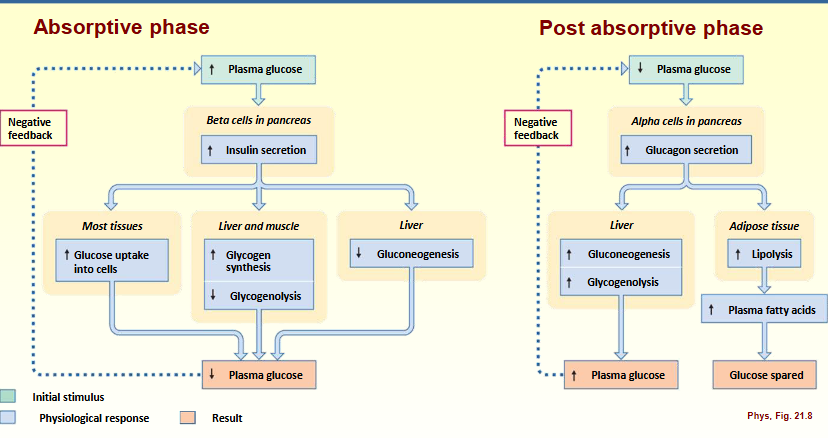
Absorptive phase
3-4 hours after meal
absorption nutrients from digestive tract
energy in > energy out
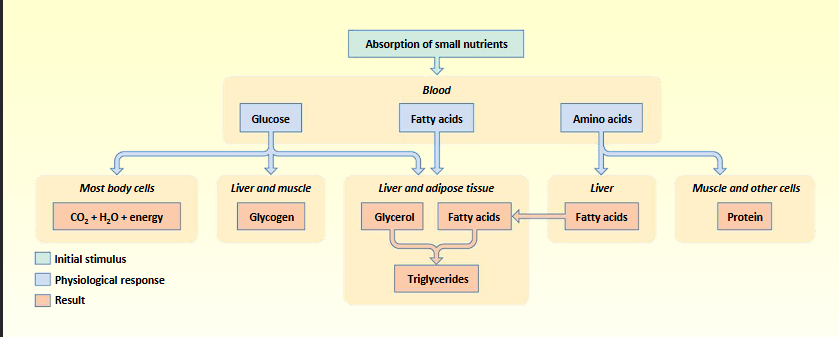
postabsorptive phas
between meals
no absorption of nutrients
energy in < energy out
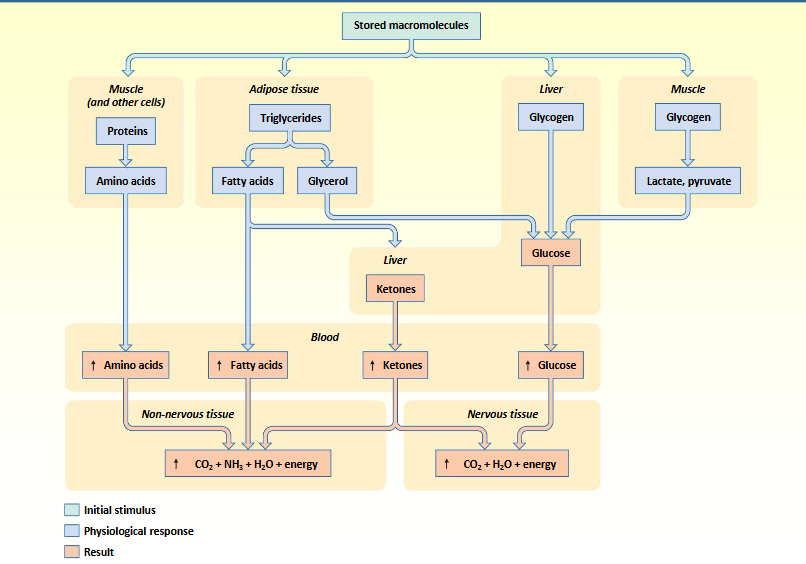
summary of (post) absorptive phase
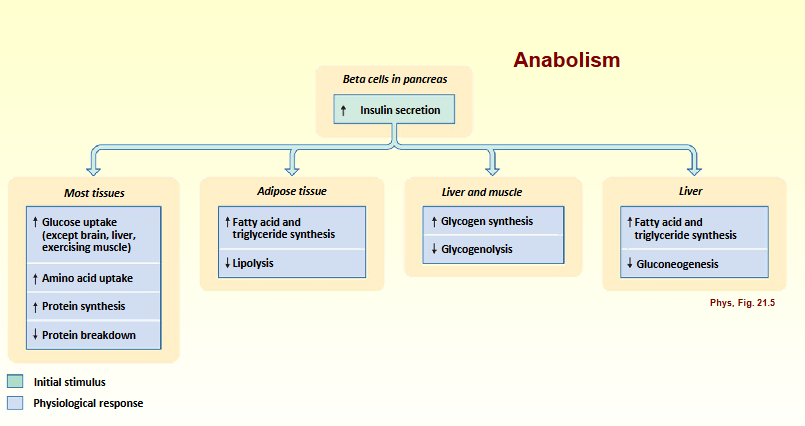
anabolism - positive energy balance
storing nutrients/energy
glycogenesis
lipogenesis
catabolism - negative energy balance
liberation of energy
glycogenolysis
lipolysis
proteolysis
gluconeogenesis
hormonal regulation of energy balance
Anabolism | Metabolism | Catabolism |
Glycogen ← | Glucose | ← Glycogen |
Triglycerides ← | Fatty acids | ← Triglycerides |
Protein ← | Amino acids | ← protein |
Insulin Sex steroids (Growth hormone) (Thyroxine) | (Glucagon) (Epinephrine) (Glucocorticoids) (Growth hormone) |
Insulin
Sole hormone that actively reduces blood glucose levels
Anabolism
Glucagon
Catabolism
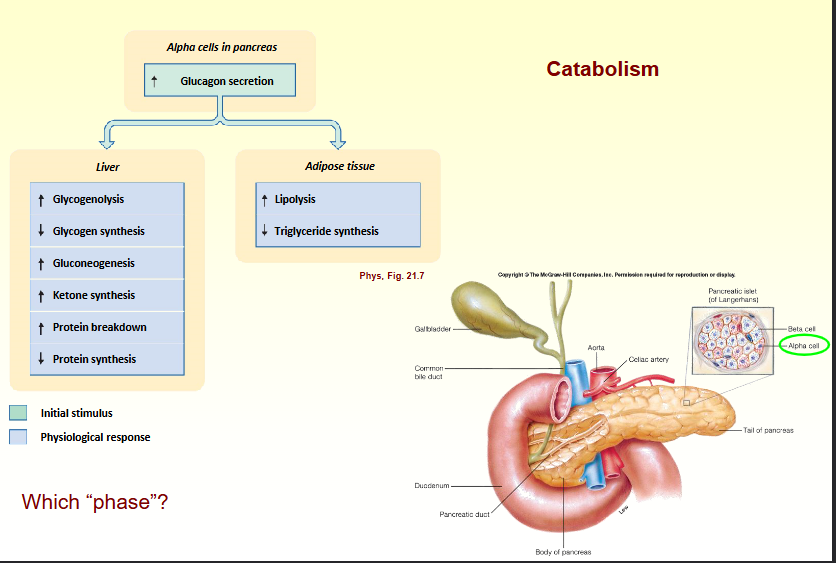
Insulin vs glucagon
Blood glucose mainly regulated via insulin and glucagon
Insulin lowers high blood sugar by helping cells take up glucose, while glucagon raises low blood sugar by signaling the liver to release stored glucose
Temperature balance
Heat production
Thermogenesis
Metabolism
Muscle contraction
Heat loss
Heat loss (Tb>To) or gain (Tb<To)
Heat exchange
Radiation
Evaporation
Convection
Conduction
Radiation
Sun and animals, mainly infrared
Evaporation
Conversion liquid to gas, heat loss
Convection
Heat exchange to moving gas or liquid
Conduction
Heat exchange between objects that are in contact
Thermoregulation
Strict regulation of the body temperature within the limits
Poikilothermic vs homeothermic animals
Poikilothermic animals
Body temperature is not regulated, but conform to the (outside) environment
Homeothermic animals
Body temperature regulated to be kept constant independent from environment
Thermoregulation: behaviour
Torpor: reduced activity
conserving energy, 7 degrees celcius reduction of body temperature
thermogenesis, movement (flying)
Hibernation
reduced temperature, low → extended sleep, e.g. bear, high → real hibernation (hamster)
thermogenesis, shivering, non-shivering: brown fat
Thermoregulation: adaptations
Thermogenesis
Insulation
Evaporation: sweating
Thermoregulation: adaptations
Thermogenesis
Shivering - increased muscle activity: ATP production 33% efficient, 67% lost as heat
Non-shivering - mitochondrial uncoupling
Thermoregulation: adaptations
Sweating
Ecrine glands, from birth
skin: mainly head, palms, soles
Aocrine glands, from puberty
in hair follicles, e.g. armpits
sympathetic nervous system stimulates sweat production. ACh is the neurotransmitter
Thermoregulation via blood supply through the skin
cold zone, vasoconstriction → shivering
warm zone, vasodilation → sweating