Physiology Chapter 26 S25
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Gametes are produced by
gonads.
Egg and sperm cells have how many chromosomes?
23 chromosomes.
Interstitial cells produce
androgens.
Which is the name for the male gonad?
prostate gland
ovaries
vas (ductus) deferens
seminal vesicle
testis
testis
Which statement most accurately describes how the sex of a human embryo is determined?
Embryos with the SRY gene become male; embryos without the gene become female.
Embryos with one X chromosome become male; embryos with two X chromosomes become female.
Embryos exposed to estrogen become female; embryos exposed to testosterone become male.
Embryos with a genital tubercle become male; embryos without the tubercle become female.
Embryos with the SRY gene become male; embryos without the gene become female.
The fold of skin that covers the tip of the penis is the
prepuce.
The erectile tissue that immediately surrounds the urethra is the
corpus spongiosum.
In the condition known as cryptorchidism, the
testes fail to descend into the scrotum.
The small paired glands at the base of the penis that produce a lubricating secretion are the
bulbourethral glands.
Sperm production occurs in the
seminiferous tubules.
The structure that carries sperm from the epididymis to the urethra is the
ductus deferens.
The following is a list of structures of the male reproductive tract.
1. vas deferens
2. urethra
3. ejaculatory duct
4. epididymis
Identify the order in which sperm pass through these structures from the testes to the penis.
4, 1, 3, 2
(epididymis
vas deferens
ejaculatory duct
urethra)
Testosterone are produced by the __________in testes.
interstitial cells of Leydig
Memorize this:
MEMORIZED?
The structure that transports the ovum to the uterus is the
Fallopian tube.
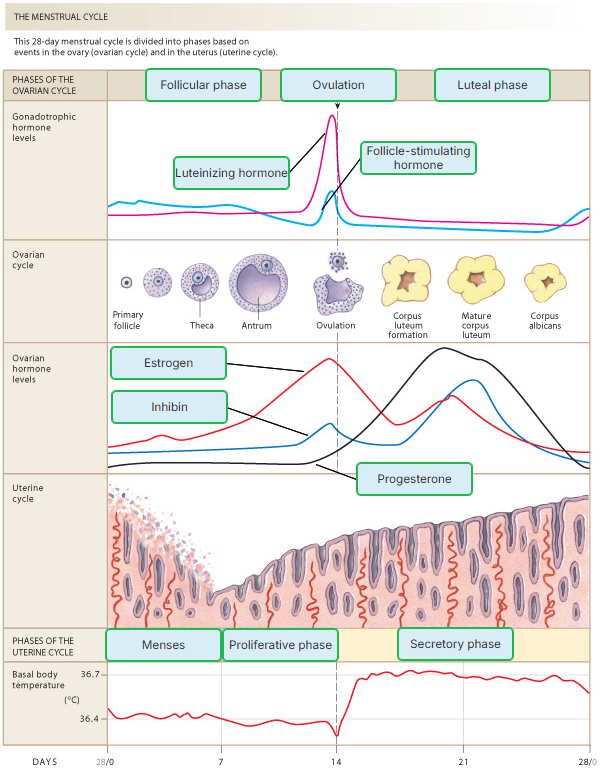
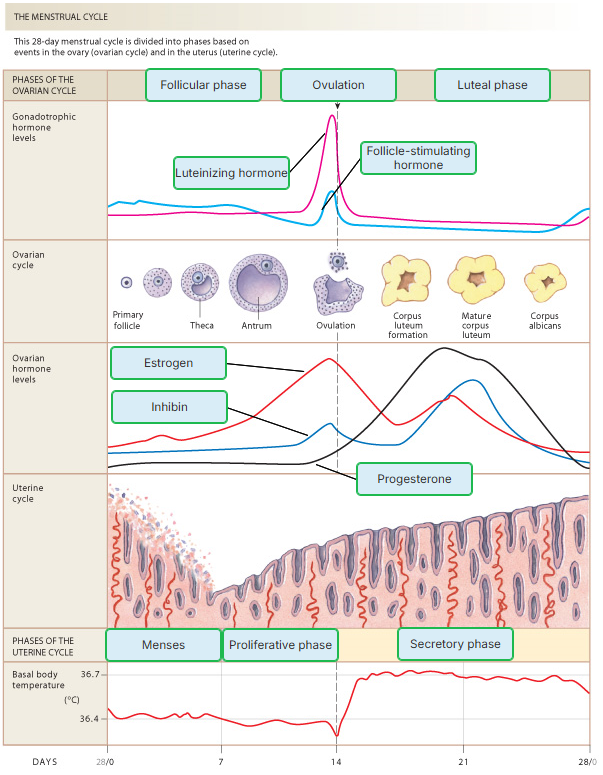
The surge in LH and FSH that occurs during the middle of the ovarian cycle triggers
ovulation.
The dominant hormone secreted by the corpus luteum during the luteal phase is
progesterone.
Menstruation is triggered decreased levels of
progesterone.
Which occurs during days 7-14 of the menstrual cycle?
ovulation
menses
proliferative phase
secretory phase
proliferative phase
Which occurs during days 14-28 of the menstrual cycle?
ovulation
proliferative phase
menses
secretory phase
secretory phase
During ovulation, an oocyte released out of a
dominant follicle.
Which is NOT a part of the ovarian cycle?
luteal phase
ovulation
corpus luteum formation
menses
follicular phase
menses
The first phase of the ovarian cycle is the __________ phase.
follicular
Which of the following is part of the female external genitalia?
Uterus
Labia majora
Ovary
Fallopian tube
Labia majora
What is the third phase of the ovarian cycle called, and what occurs during this time?
Luteal phase; transformation of a ruptured follicle into a corpus luteum
Sperm cannot fertilize an egg until they
undergo capacitation.
The embryo forms from the
inner cell mass of the blastocyst.
The hormone that is the basis for a pregnancy test is
human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
The hormone mainly responsible for milk production is
prolactin.
The hormone mainly responsible for the milk let-down reflex is
oxytocin.
During pregnancy, ________ contributes to the development of the milk-secreting ducts of the breast.
estrogen
Place the events of fertilization and implantation in order.
1. Implantation of the developing embryo.
2. The developing embryo becomes a blastocyst which consists of a hollow ball of cells.
3. Mitosis occurs in the Fallopian tube.
4. The cortical reaction occurs, preventing polyspermy.
5. The egg is fertilized by the sperm.
5, 4, 3, 2, 1
(The egg is fertilized by the sperm.
The cortical reaction occurs, preventing polyspermy.
Mitosis occurs in the Fallopian tube.
The developing embryo becomes a blastocyst which consists of a hollow ball of cells.
Implantation of the developing embryo.)
The role of the corpus luteum is to secrete __________.
progesterone and estrogen
How does a sperm manage to penetrate the corona radiata and the zona pellucida and fertilize an egg?
Through an acrosomal reaction
Which is responsible for the cessation of reproductive cycles in women?
The anterior pituitary no longer produces lutenizing hormone.
The hypothalamus no longer produces gonadotropin releasing hormone.
The ovaries produce more estrogen.
The ovaries no longer produce progesterone.
The ovaries are unable to respond to lutenizing hormone or follicle stimulating hormone.
The ovaries are unable to respond to lutenizing hormone or follicle stimulating hormone.
In the mature reproductive systems of males and females, the __________ produce the gametes, while the __________ function(s) to achieve the union of two gametes.
gonads; genitals
To achieve a typical female developmental pattern, every cell in a human embryo must _____.
have a single active X chromosome and be unexposed to fetal androgens
The time period when we can be said to have a "bipotential gonad" ends _____.
near the end of the second month of gestation, due to the presence or absence of the SRY gene product
Blood flow to the erectile tissue of the penis _____.
is increased by activity in parasympathetic neurons
The testes are outside of the abdominal cavity because _____.
sperm production is impaired at the normal body temperature found in the abdominal cavity
The Sertoli cells of the seminiferous tubules require stimulation from __________ in order to
follicle-stimulating hormone and testosterone; support spermiogenesis
Ovarian steroids exert negative feedback on the hypothalamic-pituitary reproductive axis _____.
with the exception of a brief phase preceding ovulation
In non-pregnant women, the gonadotropins _____.
are protein hormones synthesized in the anterior pituitary gland
Very shortly after ovulation, the ovulated egg _____.
is swept up by the fimbria into the Fallopian tube
After ovulation, follicular cells remaining in the ovary become a __________ ; if fertilization occurs, then __________ maintains this ovarian structure through the first trimester of pregnancy.
corpus luteum; chorionic gonadotropin
Test results showed that a 22-year-old woman with delayed puberty responded normally to injected estradiol and to injected gonadotropins, but she did not respond to injection of gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Her disorder is most likely due to _____.
a defect in the anterior pituitary gland
Both testes and ovaries contain the enzyme __________, which converts testosterone to the female sex hormone __________.
aromatase; estradiol
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
When estrogen levels rise rapidly, feedback changes from negative to positive and secretion of LH increases.
Pituitary gonadotropins inhibit GnRH by a long-loop feedback path.
As androgen levels go up, FSH secretion decreases.
When gonadal steroid levels are low, LH secretion increases.
Pituitary gonadotropins inhibit GnRH by a long-loop feedback path.
The acrosome is what?
A lysosome-like vesicle that contains enzymes essential for fertilization
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
The placenta receives as much as 10% of the total maternal cardiac output.
Cells that will become part of the placenta form finger-like choronic villi that penetrate the endometrium.
The embryo takes 4 or 5 days to move through the Fallopian tube into the uterine cavity.
The extra embryonic membranes include the allantois, which secretes amniotic fluid.
The extra embryonic membranes include the allantois, which secretes amniotic fluid.