Chapter 1- Micro intro
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Microbiology
the study of microorganisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells)
- it encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, protistology, mycology, immunology, and parasitology
Domains of life
All microbes: Bacteria, Archaea
Some microbes: Eukarya (not humans)
Excludes viruses and prions
Prokaryotes
unicellular, no nucleus, have cell walls
domain bacteria & archaea
Viruses
acellular (domainless)
Eukaryotes
uni- or multicellular, have nucleus, have membrane-bound organelles (domain eukarya)
- ex. fungi, algae, protozoa, helminths
Size of microbes
small -> large
atom, lipids, protein, (microbes begin), polio virus, flu virus, smallpox virus, bacteria, mitochondria (same size as bacteria), RBC, plant/animal cell, pollen/human egg, frog egg
viruses much smaller than bacteria
Spontaneous generation
notion that life arises from non-living matter and many experiments prove that these are wrong
ex. fleas come from dust, maggots come from rotting meat, frogs come from floods (they lay their eggs in any water source), and mice come from grain (when there is a lot of grain, mice make a home there)
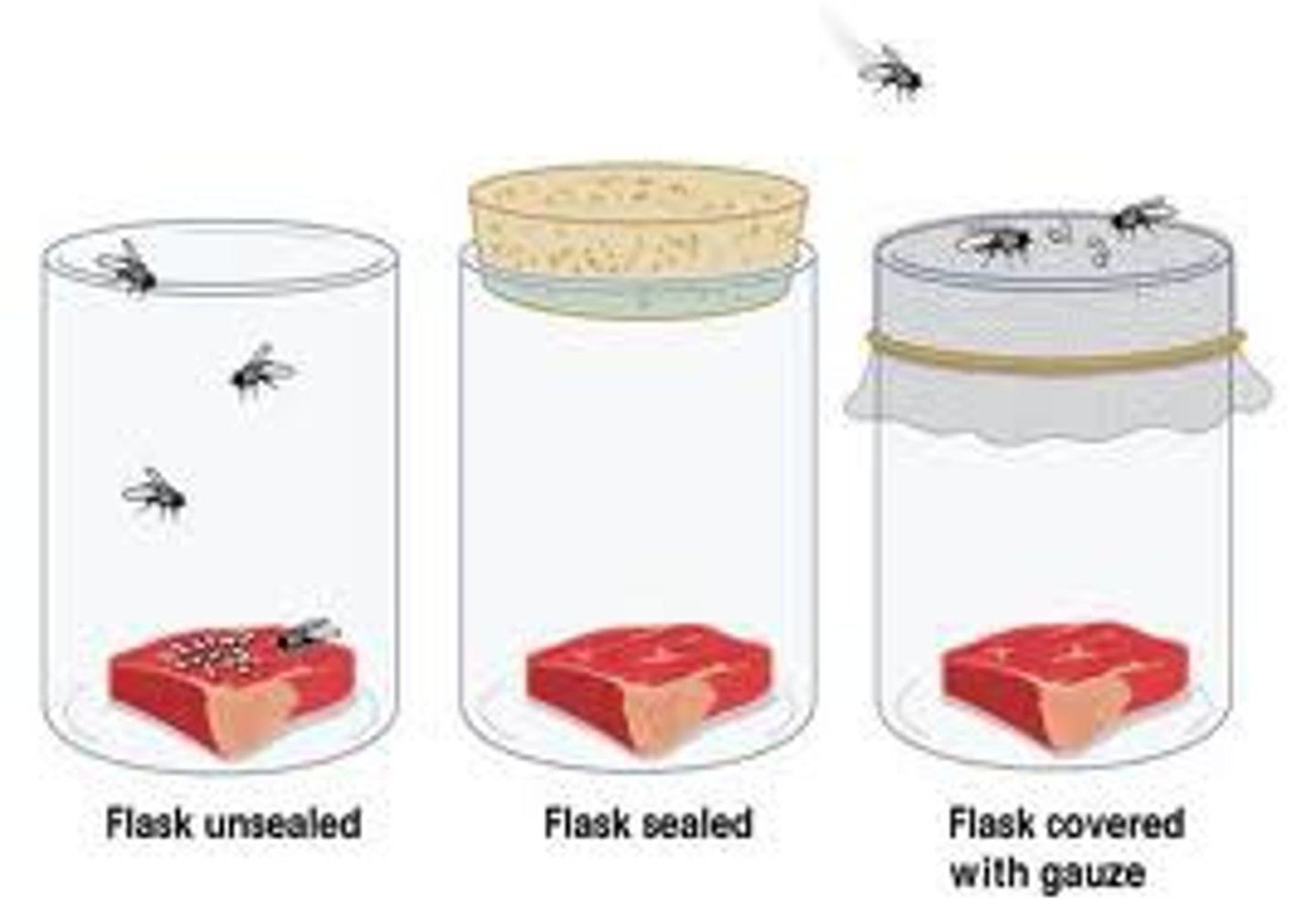
Francesco Redi's Experiment
refutes spontaneous generation; involves rotting meat with maggots; uses 3 jars
1. open container: formation of maggots in meat after the flies showed up
2. cork-sealed container: no formation of maggots in meat
3. gauze-covered container: no formation of maggots in meat but there were flies and maggots both on top of the gauze (large particles can't get in through gauze)
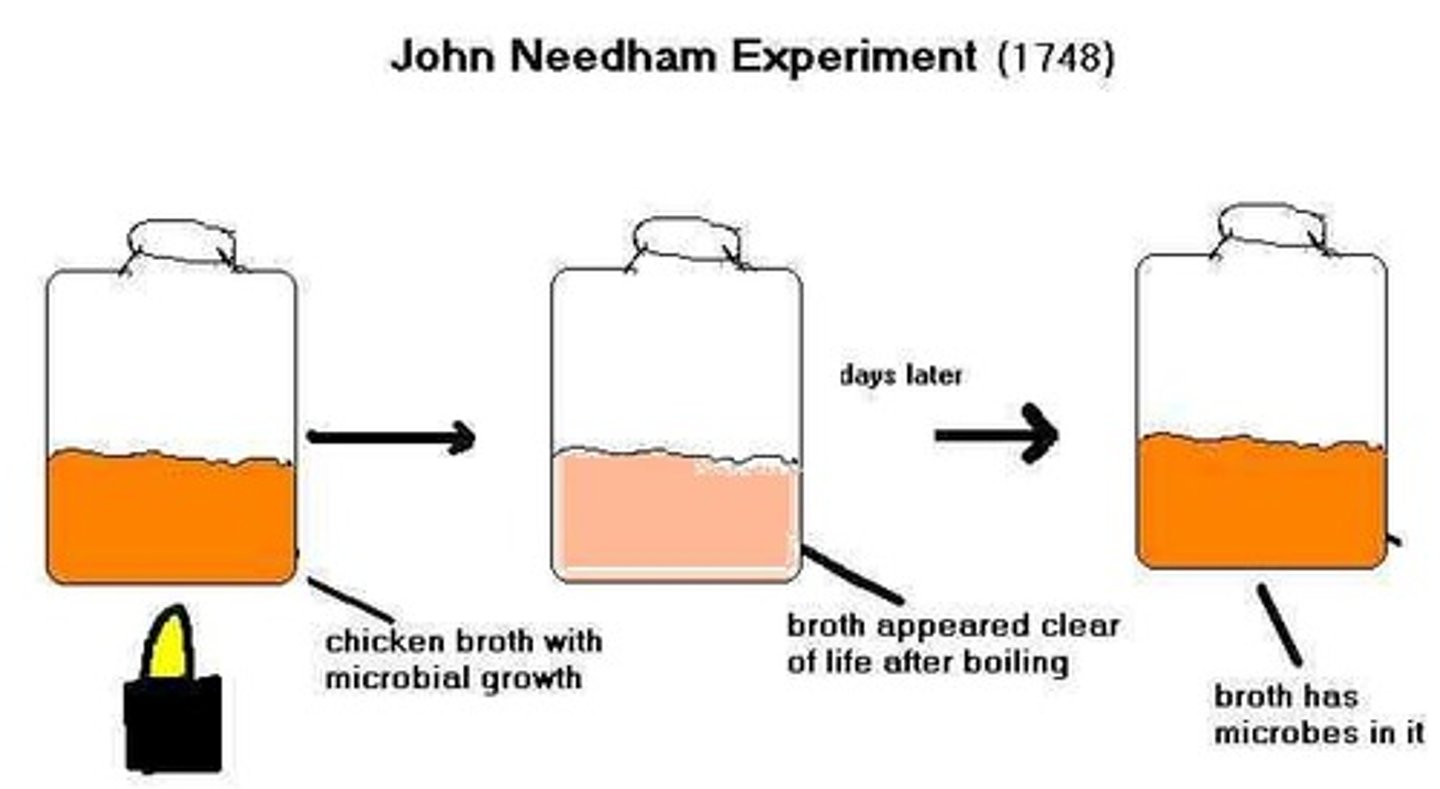
Needham's Experiment
supports spontaneous generation with boiled broth
1. heat broth
2. cool broth and let it sit
3. determine if something is in it based on cloudiness
result: broth was cloudy
Spallanzani's Experiment
refutes spontaneous generation; has control group
boiled sealed and unsealed broth
- when broth was heated and flask was left open, there was growth
- when broth was heated and the flask was sealed, there was no growth; when they left it open again there was growth
- only the one that is open growths, so it probably comes from air
Needham and Spallanzani differences
1. Needham's flask wasn't completely sealed
2. sterility
3. different boiling times (if you don't boil long enough, you don't kill everything, so it can grow back
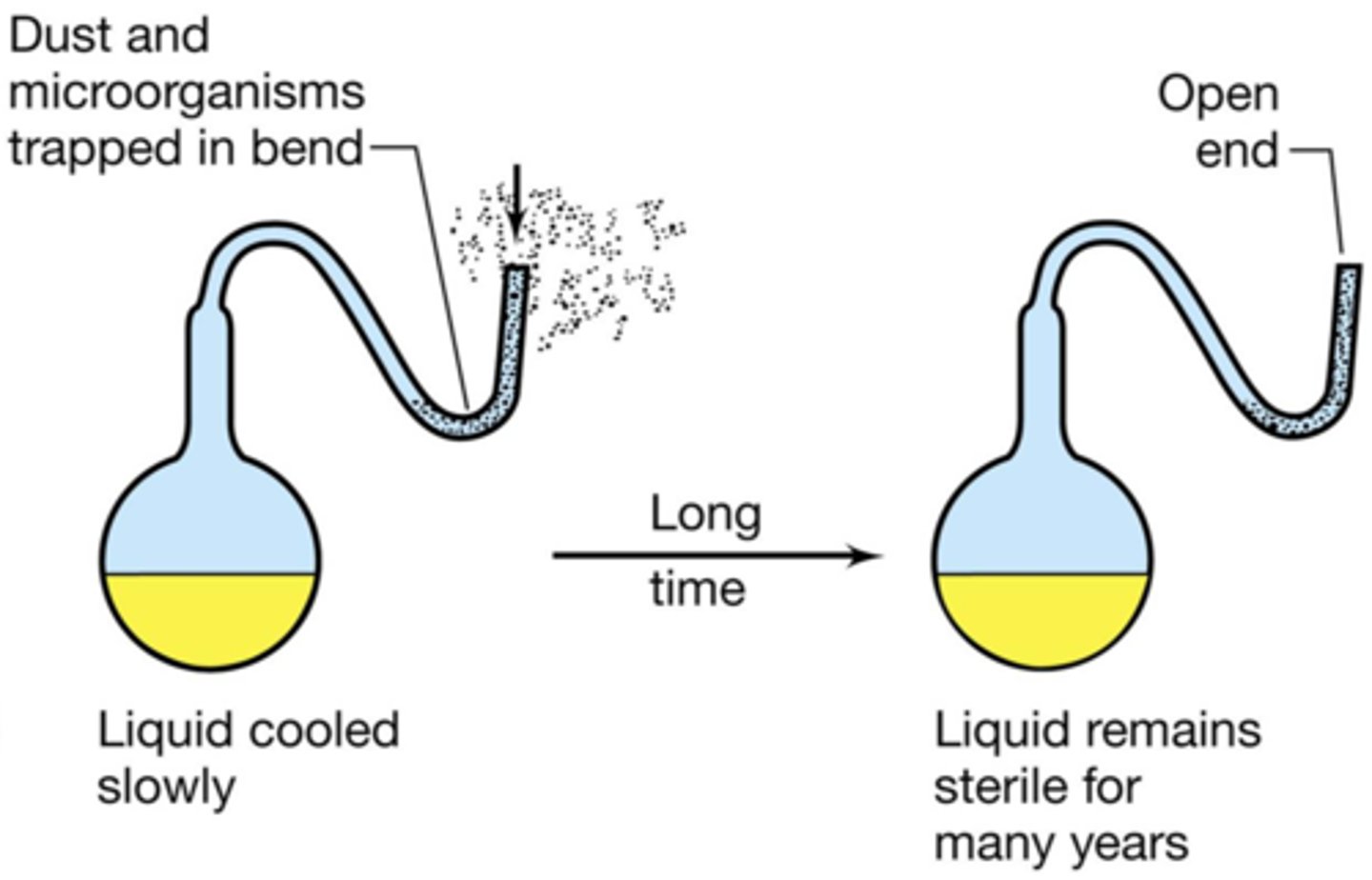
Louis Pasteur's Experiment
definitively disproves spontaneous generation, so we know that there is something in the air that causes growth
- he uses boiling broth which kills microorganisms
- he uses swan-neck flasks so the curve of the flask prevents outside air from entering the flask- no contamination
- when the neck of the flask is broken off, bacteria reach the sterile broth and organism growth occurs
Antony van Leewenhoek
"wee animalcule" is what he called them, meaning tiny animals
- 1st person credited with observing microbes
- he built microscopes
Cell Theory
living things are made of cells
- Robert Hooke: coined the term "cell" when looking at cork
- he also had his own microscope
- he observed the cork (dead cells) and said that they look like jail cells, so he called them cells
Matthais Schleiden
observed cells in plant tissue
Theodor Schwann
observed cells in animal tissues
Cell theory: cells divide to make new cells
1st to observe: Rudolf Virchow, Robert Remark
Walter Flemming discovered mitosis
- bacteria replicate differently (not mitosis)
Hippocrates
Father of medicine; disease has natural cause
Thucydides
- advocated for evidence-based analysis of cause and effect
- plague survivors don't get sick again (suggested immunity)
Marcus Terentius Varro
first to propose things we can't see cause disease
Ignaz Semmelweis
physician
problem: spread of disease between patients
- he instituted hand washing between patients (reduced spread)
Joseph Lister
surgeon
problem: post-surgical infections
solved by:
- hand washing pre-surgery (5% phenol solution)
- cleaning surgical equipment with phenol solution
- cleaning the site of the incision
Robert Koch
developed postulates to determine the cause of disease (what microbe caused it) that validated the germ theory of disease
John Snow
father of epidemiology
- wanted to figure out why people got cholera
- discovered that everyone who got it used 1 of 2 water pumps (dirty water)
- discovered that people in brewery next to pump did not get sick because they were only drinking beer
Endosymbiotic Theory
theory that eukaryotic cells formed from a symbiosis among several different prokaryotic organisms
1. infoldings in plasma membrane of an ancestral cell gave rise to membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus and ER
2. in a first endosymbiotic event, the ancestral eukaryote consumed aerobic bacteria that evolved into mitochondria
3. in a second endosymbiotic event, the early eukaryote consumed photosynthetic bacteria that evolved into chloroplasts
4. ends up as modern photosynthetic eukaryote
Nomenclature
Genus species (ex. Escherichia coli)
Abbreviation= G. species (E. coli)
Genus spp.- when talking about multiple species in a genus
Genus sp.- when species is unknown or not needed