CP1 W1 Mod 1, 2, 8, 9, 3
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What are the 4 ergonomic hazards for dental hygienists?
Awkward Positions
Static postures
Force/forceful exertion
Repetitive Movements
Injury to the musculoskeletal system can cause…
Loss of strength
Impairment of motor control
Tingling
Numbness
Pain
Definition and Cause(s): Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Compression of the brachial nerve plexus causing painful disorders of the fingers, hand and/or wrist
Cause:
Tilting the head forward
Hunching the shoulders forward
Continuously reaching overhead
Definition and Cause(s): Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
Inflammation of the muscle tendons in the shoulder region causing pain in the shoulder
Cause:
Holding elbow above waist level
Holding upper arm away from the body
Definition and Cause(s): Pronator Syndrome
Compression of the median nerve by the pronator muscle causing pain in the wrist and hand.
Cause:
Holding the lower arm away from the torso of the body
Definition and Cause(s): Extensor Wad Strain
Injury to the extensor muscle causing pain to the fingers
Cause:
Extending the fingers independently of each other
Definition and Cause(s): Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Compression of the median nerve in the wrist causing pain in the wrist and hand.
Cause:
Repeatedly bending the hand up, down, or from side to side at the wrist
Pinch-gripping an instrument without resting the muscles
Definition and Cause(s): Ulnar Nerve Entrapament
Compression of the ulnar nerve at the wrist causing pain to the lower arm and wrist.
Cause:
Repeatedly bending the hand up, down, or from side to side at thwr ist
Holding the little finger a full span away from the hand
Definition and Cause(s): Tenosynovitis
Inflammation of the tendons on the side of the wrist and the base of the thumb causing pain
Cause:
Hand twisting
Forceful gripping
Bending the hand back or to the side
Definition and Cause(s): Tendinitis
Inflammation of the tendons of the wrist causing pain.
Cause:
Repeatedly extending the hand up or down at the wrist
What is the ideal neutral neck position? What should we avoid to maintian it?
Head tilt of 0-15 deg
Avoid:
head tilting too far forward or to one side
What is the ideal neutral back position? What should we avoid?
Leaning foward slightly from the waist or hips of 0-20 deg
Avoid:
Curved back
What is the ideal neutral upper arm position? What should we avoid?
Elbows at waist level held slightly away from the body up to 20deg
Avoid:
Elbows held above waist level
What should you avoid for neutral hand position?
Avoid palms parallel to the floor
What are the 3 healthy curves of the spine?
Cervical (inward curve)
Lumbar (inward curve)
Thoracic (slight outward curve)
What is the light position for the maxillary/mandibular arch?
Max = position will vary from over oral cavity or over the neck
Mand = position light directly over the oral cavity
*always position light arms length away
What is the 4 steps to establish Easy Neutral Position?
Sit alongside pt
Arm at your side
Arm crossed across your waist
Lower pt chair until pt’s mouth is below the point of your elbow
What is coaxial illumination?
Spectacle mounted light that is parallel to the clinicians line of vision
What are the 4 things for the ideal handle design of DH tools?
Large handle diameter
Light weight (hollow handle)
Handle tapers near shank
Raised texturing on the handle
Why is instrument balance important?
Ensures that finger pressure applied against handle is transferred to the working end
What is the difference between simple shank and complex shank?
Simple (aka straight shank):
Bent in one plane
Primarily used on anterior teeth
Complex (aka angled or curved shank):
Bent in 2 or more plantes
Primarily used on posterior teeth
Shank diameter determines what?
Strength that can be applied to remove heavy, medium, or small deposits.
Thicker shanks are more ridgid and used to remove heavy deposits
What is the advantage of flexible shanks?
Flexible shanks can transmit vibrations from the working end as it runs over irregular tooth surfaces. It is important for detecting deposits beneath the gingival margin
Draw an instrument shank and label the working end, terminal shank, and functional shank
working end = tip
terminal shank/lower shank= portion nearest to the working end
functional shank = portion of the shank that allows working end to be adapted to the tooth surface
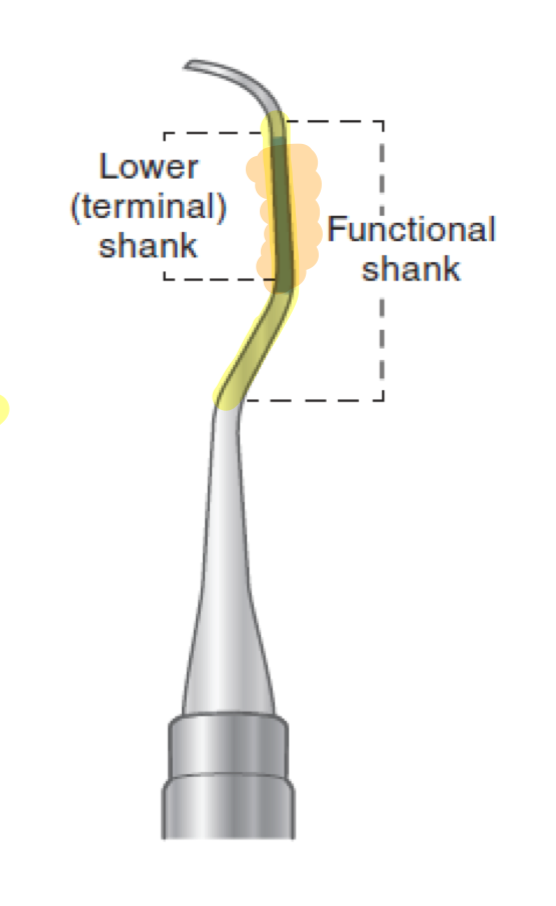
What shank length would be best suited for SUPRAgingival?
SHORT functional shank length
What shank length is best suited for SUBgingival use?
LONG functional shank length
Instruments with extended lower shanks are used for?
Reaching the middle and apical-third of root surface.
What is the difference between a paired and un-paired working end?
Unpaired = dissimilar working ends
Paired = mirror image working ends
What are the 5 parts of the working end?
Face
Back
Lateral surfaces
Cutting edges
Toe or tip
The _____ is formed where face and lateral surfaces on instruments meet. (hint: working end)
Cutting edge
What is the signifcance of the cross-section of a working end?
It determines whether the tool can be used subgingivally.
Semi-circle = ok
Triangle = not ok
What are the 2 classifications of Periodontal Instruments?
Assessment Instruments
Calculus removal instruments (Debridement)
Use: Periodontal Probe
Evaluate health of periodontal tissue
Use: Explorer
Locate calculus deposits, tooth irregularities and defective restoration margins
Use: Sickle scalers
Used to remove SUPRAgingival calculus
*pointed tip, triangular xs
Use: Curets
Used to remove calculus both supra/sub gingivally
*semi-circular xs, round toe
Use: Periodontal file
Used to crush large calculus deposits
How should you be positioned for Standing work?
Shoulders relaxed
Elbow of dominant hand at waist level
Torso in neutral position
Why is proper glove fit important?
To avoid muscle strain (too tight = unnecessary tension)
Tactile sensitivity is enhanced with THIN gloves and good fit at the finger tip area
Nitrile glove provide more grip friction than latex = better grasp
What does proper glove fit look like ?
Loose fitting across palm and wrist area
Index finger of other hand should be able to slip under wrist area of gloved hand.
Gloves should not be overly tight
Define Proprioception
A persons ability to sense their body and its position and movement through 3D space. (ex. you know where to touch your nose even though your eyes are closed)