Types of Organic Chemistry Reactions
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Addition Reaction (Definition)
One in which two substances react to form a single substance
Where do addition reactions always occur?
Double/triple bond
How does the geometry/bondage of a molecule change due to an addition reaction?
Planar unsaturated to tetrahedral saturated
Does benzene undergo addition reactions?
No
Why does benzene not undergo addition reactions?
Delocalised electrons make it very stable and unreactive
Uses of addition reactions (2)
Hydrogenation of vegetable oils to form margarine. Make plastics
Explain the hydrogenation of vegetable oils to form margarine
H2 with Ni catalyst added to unsaturated oils to partially saturate them. This is also reduction due to the addition of hydrogen
Explain the production of plastics using addition reactions
Polymerisation reactions form long carbon chains which we know as plastics
Ethene to ethane reaction
…
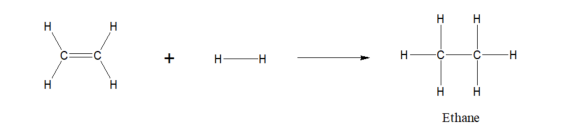
Ethene to 1,2-dichloroethane reaction
…
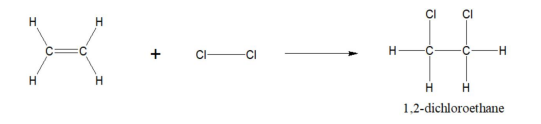
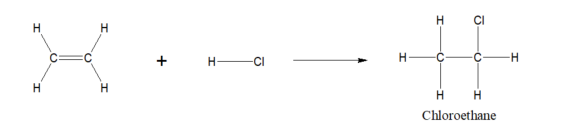
Ethene to chloroethane reaction
…
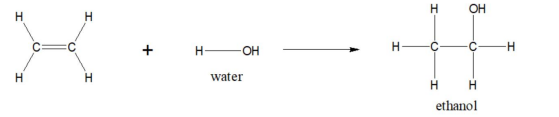
Ethene to ethanol reaction
…
Ethene to 1,2-dibromoethane reaction
…
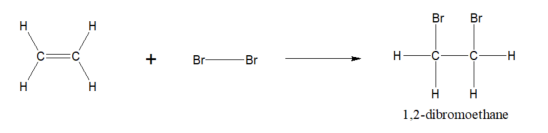
The bromination of ethene is what type of reaction?
Ionic Addition
Mechanism (Definition)
The detailed step-by-step description of how the reaction occurs.
Name the 4 steps of the bromination of ethene
Polarisation. Heterolytic Fission. Carbonium Ion Formation. Ionic Attack
Explain Polarisation (Bromination of Ethene)
Double carbon bond in Ethene has a high concentration of negative charge. As Br2 approaches Ethene electrons are replelles away from Ethene and polarising Br2
Draw a diagram of polarisation (Bromination of Ethene)
…
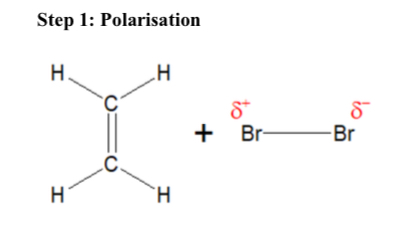
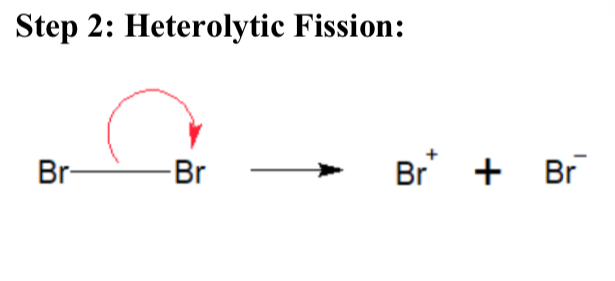
Explain Heterolytic Fission (Bromination of Ethene)
Polarisation becomes great enough to split Br2 into Br+ and Br-
Why is heterolytic fission named heterolytic fission (Bromination of Ethene)
Br- took all 2 electrons from the Br-Br bond
Draw a diagram of heterolytic fission (Bromination of Ethene)
…
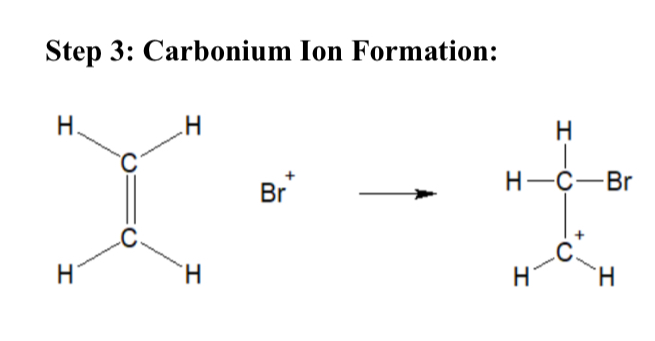
Explain Carbonium Ion Formation (Bromination of Ethene)
Br+ attacks electron rich C=C double bond. Forms a carbonium ion (C+)
Draw a diagram of carbonium ion formation (Bromination of Ethene)
…
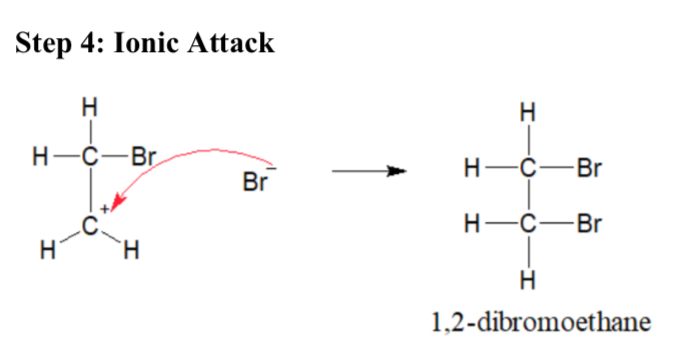
Explain ionic attack (Bromination of Ethene)
The Br- ion attacks the carbonium ion, forming 1,2-dibromiethane
Draw a diagram of ionic attack (Bromination of Ethene)
…
Evidence for the Bromination of Ethene mechanism
If the reaction is carried out in bromine water with Cl- ions added, 1,2-bibromoethane is produces along with 1-bromo-2chloroethane and 2-bromoethanol. These form due to the Cl- or OH- and can replace the Br- in ionic attack
Where does the OH- ion come from in the Bromination of Ethene
Water’s self-ionisation
How to write the mechanism for the addition of Cl2 or HCL?
Replace the Br2
What is polymerisation?
A type of addition reaction
Polymers (definition)
Long chain molecules made by joining many small molecules (monomers)
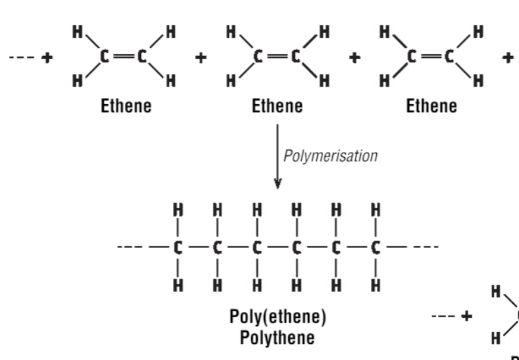
Draw the polymerisation of ethene
…
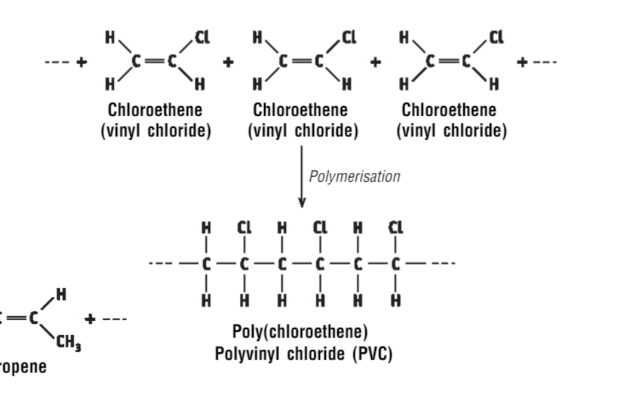
Draw the polymerisation of chloroethene
…
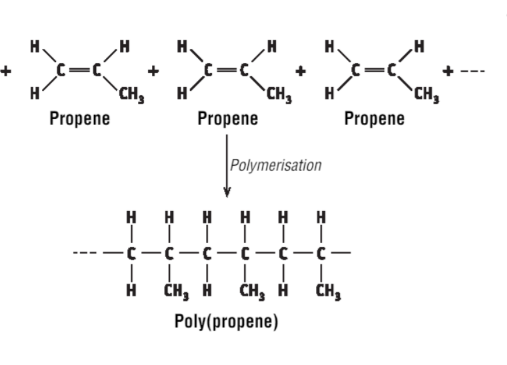
Draw the polymerisation of propene
…
What is chloroethene also known as?
Vinyl chloride
What is Poly(Chloroethene) also known as?
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Elimination reaction (Definition)
One in which a small molecule is removed from a larger molecule, leaving a double bond on the larger molecule
How does the geometry of a molecule change in an elimination reaction?
Tetrahedral to planar because a double bond is formed
What is removed during elimination reactions?
Removal of a water molecule
What are reactions that remove a water molecule also known as?
Dehydration reactions
Draw the reaction