Insulin + Care
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Short duration
Regular
Intermediate
Long duration
types of insulin
LAG
lispro (Humalog)
aspart (NovoLog)
glusiline (Apidra)
Rapid Short duration: drugs
Onset: 15 - 30 mins
Duration: 3 - 6 hr
SQ or via insulin pump
faster than reg insulin but shorter duration
5 - 10 min B4 meals
Rapid Short Duration: Dose + Route
Humulin R
Novolin R
Reg duration: drugs
Check BG b4 admin @ 8, 12, 9
can be mixed w/ NPH
NR 2 RN
ONLY one given as IV
Reg insulin Implications
SQ, IM, & Oral inhalation (not currently used)
Onset: 30 - 60 min
Peak: 1 - 5 hr
Duration: up to 10 hr
clear solution
Reg duration: dose + route
Injected 2 - 3X DAILY & btwn meals and during night
ONLY one that can be mixed w/ short acting
Allergic Rxs possible
Cloudy
SQ only
NPH insulin Considerations
glargine (Lantus)
detemir (Levemir)
Onset: 1.5 hr
Peak: Peakless
Duration: up to 24 hr
Long duration: Drugs
refrigeration
Unopened vials should be stored under
frozen
insulin SHOULD not be
the expiration date if kept in the fridge
insulin can be used until
1 month w/out losing effectiveness
how long can insulin be kept up to?
direct sunlight and extreme heat
Insulin needs to avoid?
Mixtures of insulin in vials are stable for 1 month at room temp, and for 3 months under refrigeration
mixtures in prefilled syringes should be stored in a refrigerator for at least 1 week; they should be stored vertically w/ the needle pointing up
how long can mixed insulins be effective?
Required by all pts w/ T1DM and many pts w/ T2DM
IV insulin for DKA
Gestational diabetes
Hyperkalemia
aids in the diagnosis of growth hormone (GH) deficiency
Indications of insulin
Hypoglycemia: BG < 70 mg/dL
D/I: rapid Tx mandatory
Conscious Pts: fast acting oral sugar (eg, glucose tablets, OJ, sugar cubes, non-diet soda).
Unconscious: swallowing/gag reflex is suppressed: NPO, give IV glucose or parenteral glucagon for TX
Hypokalemia
complications of Insulin
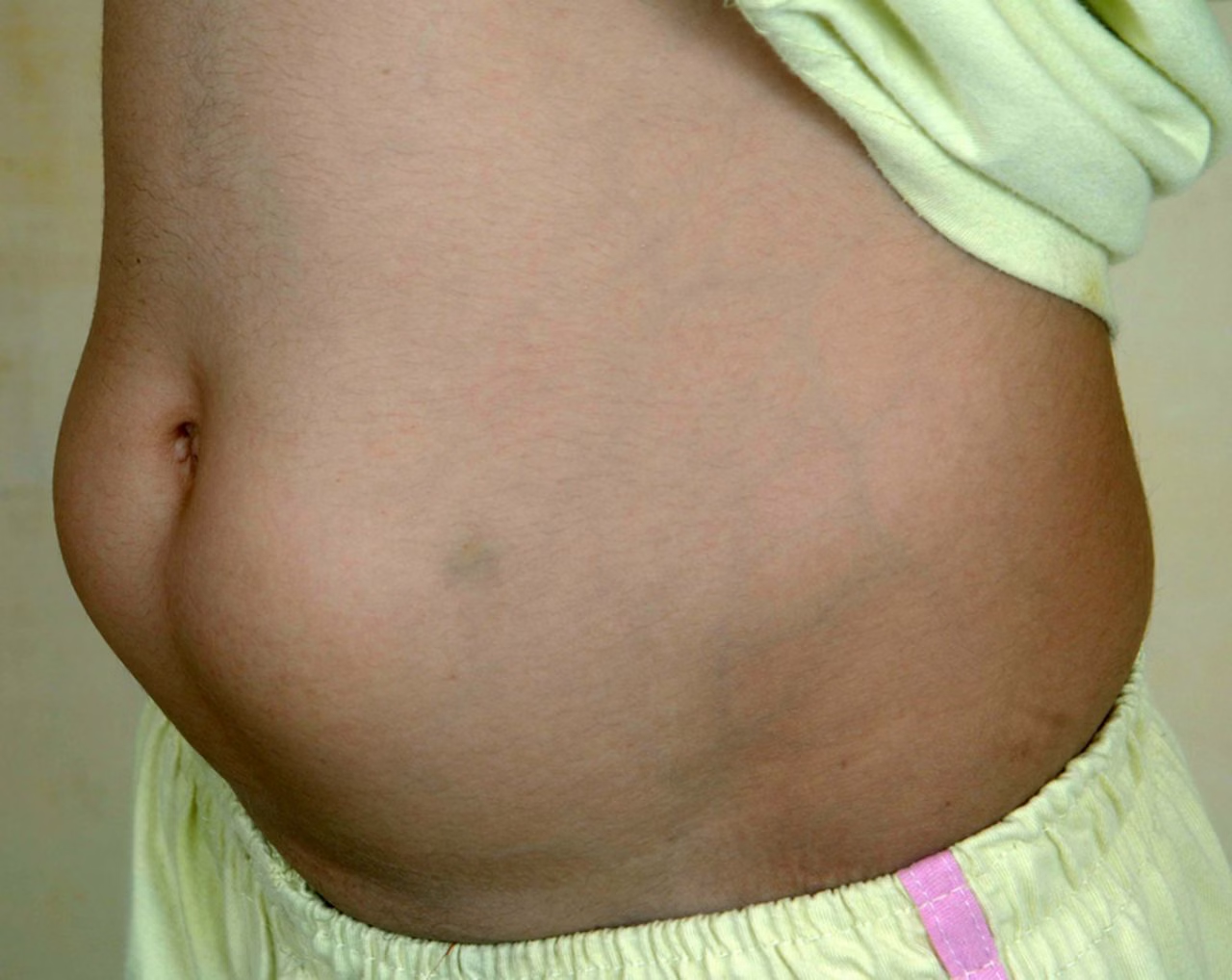
where fat tissue builds up under the skin at insulin injection sites, causing lumps or bumps.
Prevention: rotate injection sites
Lipohypertrophy
DKA
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS)
both are life-threatening
Acute complications of Poor glycemic control
Hyperglycemia is more severe than HHS
ketoacidosis characteristic of DKA absent in HHS
Which acute complication is more severe
severe sx’s of insulin deficiency
sx’s evolve quickly w/in hrs or days
most common complication in peds pts and leading cause of death
hyperglycemia, ketoacids, hemoconcentration, acidosis, coma
DKA sx’s
insulin replacement
BIcarbonate for acidosis
Water & sodium replacement
K replacement
Normalization of glucose levels
DKA TX
can evolve slowly: changes w/in a month or 2 b4 s’s & sx’s become apparent
large amount of glucose excreted in urine
results in dehydration and loss of blood volume
occurs frequently w/ T2DM w/ acute infx, acute illness, or some other stress
HHS
No sweet or acetone-like smell to urine or breath
blood “thickens” and becomes sluggish
little or no change in ketoacid levels and pH
If left untreated, it can lead to coma, seizures, and death
Characteristics of HHS
correct hyperglycemia and dehydration w/ IV insulin, fluids, and electrolytes
HHS Tx
Preferred Tx is IV glucose
Glucagon immediately raises BG levels
Can be used if BG is not available
Delayed elevation of BG
CANNOT correct hypoglycemia Resulting starvation bc there is nothing for glucagon to break down in the liver
Promotes glycogen breakdown and the malnourished have little glycogen left
Glucagon Tx of Sev Hypoglycemia