ECO105 Ch. 8: Monopoly to competition and in between: Market Structure and Pricing power
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
1
New cards
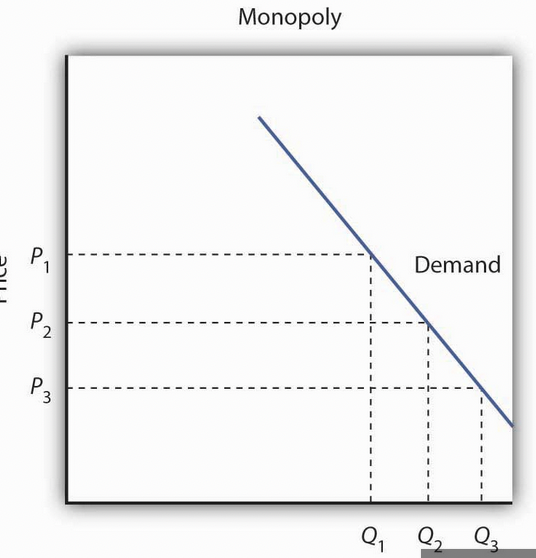
Monopoly
- Only seller of product and services
- No close substitutes available
- Demand is steep and inelastic
- No close substitutes available
- Demand is steep and inelastic
2
New cards
Market Power
Business's ability to set price
3
New cards
Price Maker
- Monopoly with maximum power to set price
- Business can set any price, but cannot force consumers to buy
- Even monopoly price makers must live by law of demand
- Business can set any price, but cannot force consumers to buy
- Even monopoly price makers must live by law of demand
4
New cards
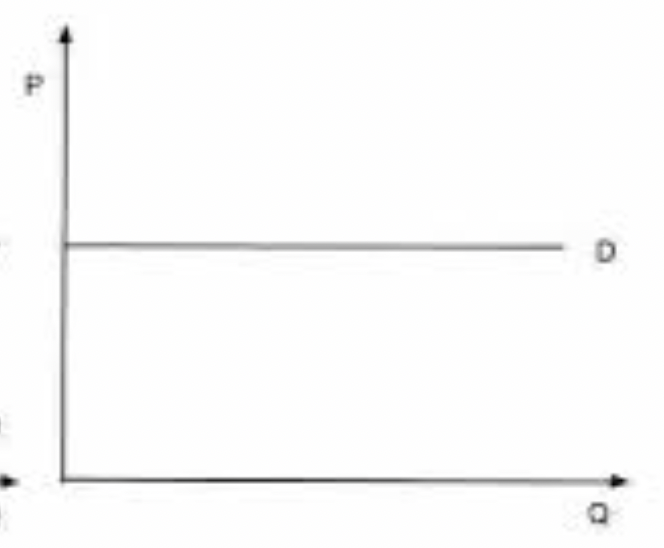
Perfect Competition
- Many seller producing identical products or services
- Demand is horizontal and perfectly elastic at market price
- Only change quantity but not price
- Demand is horizontal and perfectly elastic at market price
- Only change quantity but not price
5
New cards
Price taker
Business with ZERO power to set price
6
New cards
Market Structure
Characteristics affecting competition and pricing power
1) Available substitutes
2) Number of Competitors
3) Barriers to entry of new competitors
1) Available substitutes
2) Number of Competitors
3) Barriers to entry of new competitors
7
New cards
Barriers to entry
Legal or economic barriers preventing new competitors from entering a market
1) Legal barriers: Patent and copyrights are exclusive property rights to sell or license creations
2) Economic Barriers: Economies of scale = average total cost of producing decrease as quantity (scale) of production increases
- Average total cost: total cost per unit of output
- Small = average cost higher
1) Legal barriers: Patent and copyrights are exclusive property rights to sell or license creations
2) Economic Barriers: Economies of scale = average total cost of producing decrease as quantity (scale) of production increases
- Average total cost: total cost per unit of output
- Small = average cost higher
8
New cards
Broader definition of market
- More substitutes and competitors
- More elastic demand
- less pricing power
- More elastic demand
- less pricing power
9
New cards
Narrower definition of market
- Fewer substitutes and competitors
- More inelastic demand
- More pricing power
- More inelastic demand
- More pricing power
10
New cards
Product differentiation
- Attempt to distinguish product or service from those of competitors
- Reduce competition and substitutes
- Increasing pricing power
- Can be actual differences or perceived differences (Don't need to be real)
- Reduce competition and substitutes
- Increasing pricing power
- Can be actual differences or perceived differences (Don't need to be real)
11
New cards
Relationships between pricing power and number of competitors
- Fewer competitors = more price power
- More competitors = less price power
- More competitors = less price power
12
New cards
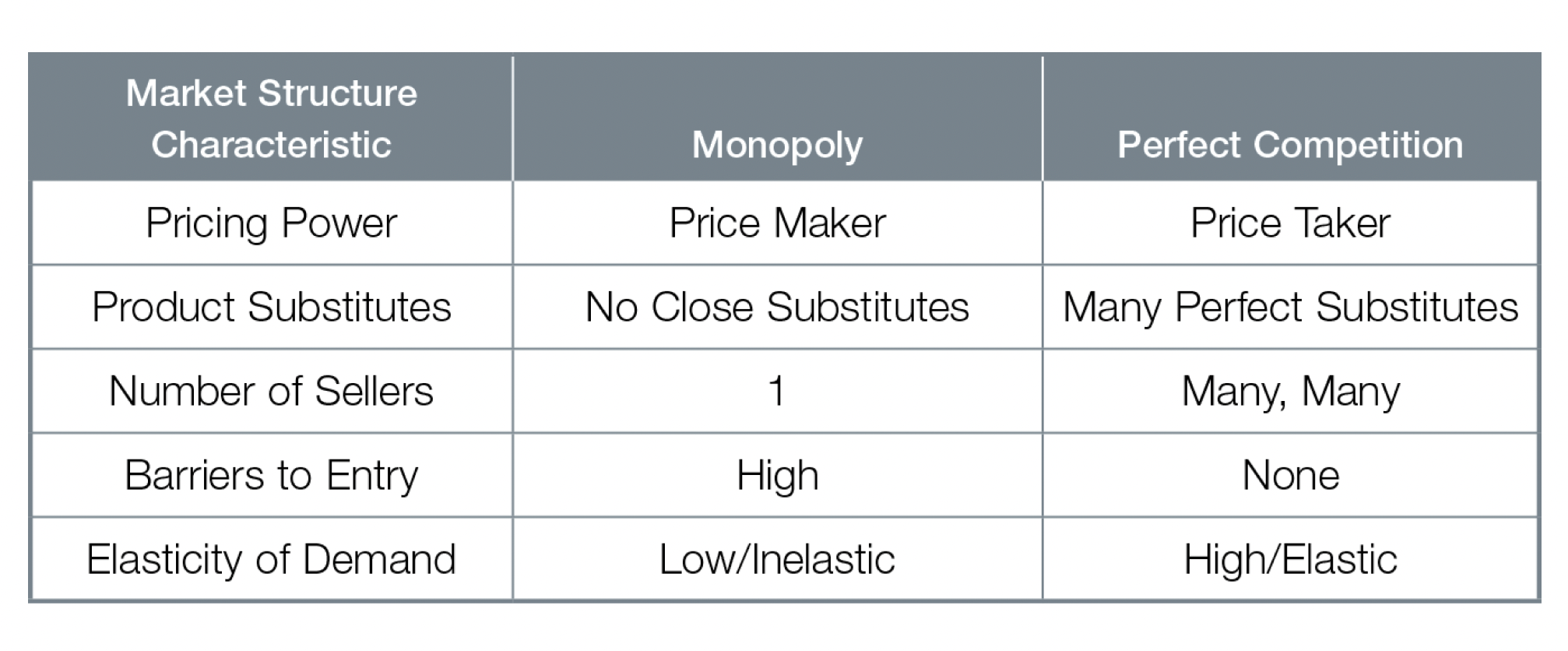
Relationships between pricing power and demand
- Higher pricing power = more inelastic demand
- consumers have few substitutes or strong brand loyalty
- Lower pricing power = more elastic demand
- consumers have many substitutes or no brand loyalty
- consumers have few substitutes or strong brand loyalty
- Lower pricing power = more elastic demand
- consumers have many substitutes or no brand loyalty
13
New cards
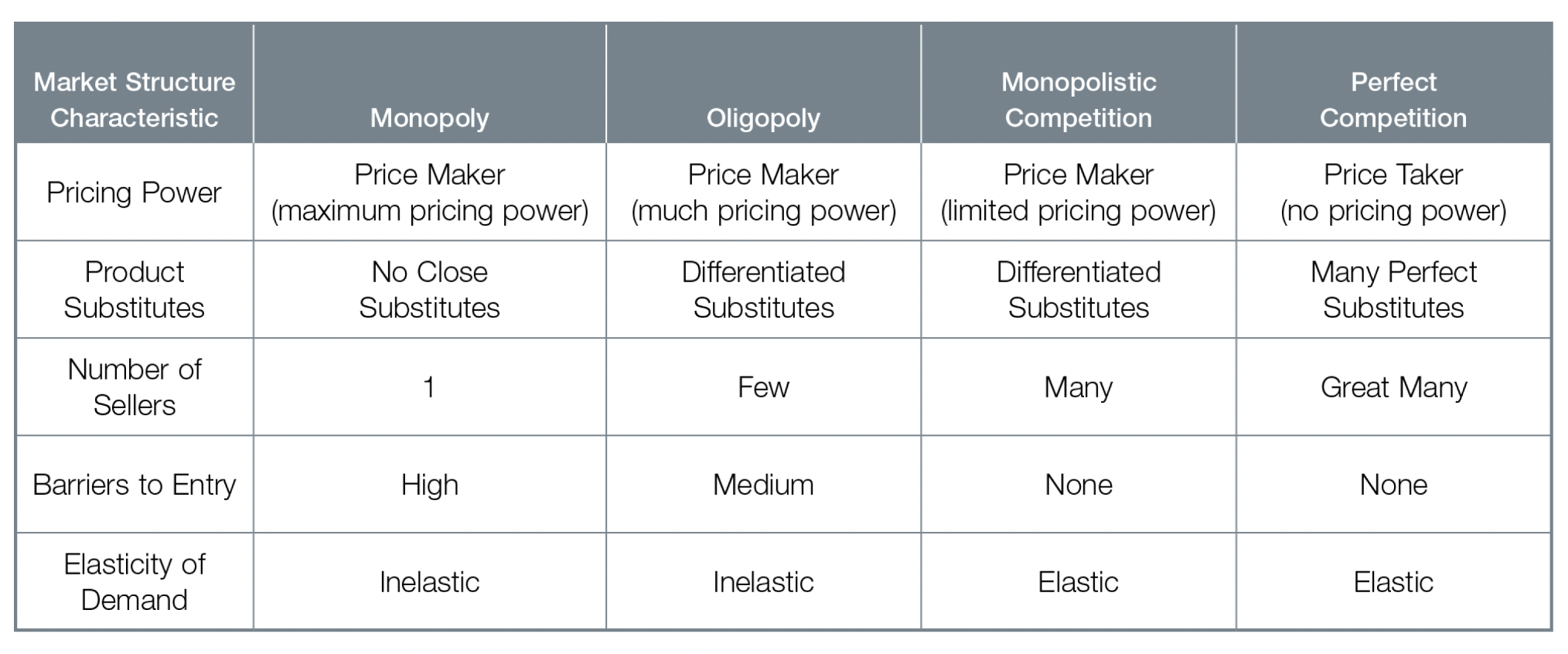
Four main market structures
1) Monopoly
2) Oligopoly
3) Monopolistic competition
4) Perfect competition
2) Oligopoly
3) Monopolistic competition
4) Perfect competition
14
New cards
Oligopoly
- Few big sellers control most of the market
- Eg. Coke and Pepsi
- Eg. Coke and Pepsi
15
New cards
Monopolistic Competition
- Many small businesses make similar but slightly differentiated products or services
- Eg. Dry cleaning and restaurant
- Eg. Dry cleaning and restaurant
16
New cards
Competition
- Active attempt to increase profit
- Gain market power of monopoly
1) Cutting cost
2) Improving quality and product innovation
3) Advertising and brand loyalty
4) Eliminating competition
5) Building barrier to entry
- Gain market power of monopoly
1) Cutting cost
2) Improving quality and product innovation
3) Advertising and brand loyalty
4) Eliminating competition
5) Building barrier to entry
17
New cards
Shrinkage
- Employee stealing
- happens in retail a lot
- happens in retail a lot
18
New cards
Creative destruction (Schumpeter theory )
- Competitive business innovations generate economic profits for winner, improving living standards for all
- But destroy less productive or less desirable products and production methods
- But destroy less productive or less desirable products and production methods