
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
Adaptations
Inherited traits that increase an organism's probability of survival and reproduction.
natural selection
-favors individuals with advantageous traits, leading to an increase in those traits over generations
-organisms with better adaptations leave more offspring, causing favorable traits to accumulate
MRSA bacteria resistance
bacteria's resistance to methicillin occurred because resistant strains survived antibiotic treatment and reproduced (when attacked)
do individuals evolve?
NO, populations evolve, not individuals
-organisms cannot decide to mutate; beneficial mutations occur randomly and are selected over time
directional selection
favors one extreme phenotype (e.g., dark-colored mice surviving better than light-colored ones)
-ONE DIRECTION
disruptive selection
favors both extreme phenotypes over intermediate ones (e.g., both very dark and very light mice survive better than medium-colored mice)
-disrupt EVERYTHING expect “middle” one
stabilizing selection
favors the intermediate phenotype, reducing variation (e.g., medium-colored mice surviving better than extremes)
-MIDDLE is to “equalize” not distinction in change (reducing variation)
genetic drift is a
random change in allele frequencies due to chance, affecting small populations more
founder effect
small group leaves a population and starts a new one, leading to different allele frequencies
bottleneck effect
population's size is dramatically reduced (TYPICALLY by disaster), changing allele frequencies by chance
gene flow is
movement of alleles between populations via immigration or emigration
-movement of genes from one population to another!
genetic drift vs gene flow
genetic drift = random and affects small populations
gene flow = actual movement of genes between populations typically on larger populations
conditions for natural selection
variation in traits = differential reproduction (some traits lead to more offspring)
heritability of traits = more offspring produced than the environment can support
Cladograms & Phylogenetic Trees
Organisms that share a more recent common node are more closely related.
derived character
trait appears in recent lineages but not older ones
Extinct vs. extant organisms
Extinct lineages end before reaching the present, while extant organisms reach the top of the tree.
hardy-weinberg equilibrium
population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium if allele frequencies remain constant because:
- No mutations
- Random mating
- No natural selection
- Extremely large population size
- No gene flow.
Hardy-Weinberg equations
p² + 2pq + q² = 1 (genotype frequencies), p + q = 1 (allele frequencies).
homologous structures are
similar anatomical structures inherited from a common ancestor (e.g., human arm, bat wing).
Vestigial structures are
reduced structures that serve little or no function but existed in ancestors (e.g., human appendix).
molecular homologies contain similar
DNA and protein sequences showing shared ancestry
convergent evolution
unrelated species evolve similar traits due to similar environments (e.g., dolphins and sharks)
-UN is CON is SIM
analogous structures
similar structures in unrelated organisms (e.g., wings of birds and insects)
-ANA-not
artificial selection
human-driven selection for desirable traits (e.g., breeding dogs, modifying crops).
how antibiotic resistance evolves…
genes survive antibiotics and reproduce, leading to a resistant population
allopatric speciation
population is geographically separated, leading to divergence into new species
sympatric speciation
new species arises within the same geographic area (e.g., due to polyploidy in plants)
-NE SYM SAME
geographic isolation:
physical barriers prevent breeding
prezygotic isolation:
prevents fertilization:
-behavioral isolation
-habitat isolation
-gametic isolation
-temporal isolation
behavioral isolation:
differences in mating behaviors
habitat isolation:
live in different areas
gametic isolation:
-sperm cannot fertilize egg
temporal isolation:
different breeding times
Postzygotic isolation
Hybrid offspring cannot survive or reproduce:
-Reduced hybrid viability
-Reduced hybrid fertility
-Hybrid breakdown
reduced hybrid viability:
hybrid dies early
reduced hybrid fertility:
hybrid is sterile (e.g., mule)
-ILI ILE
hybrid breakdown:
offspring of hybrids are weak or sterile
-WEAK breaksDOWN
taxonomic levels
Hierarchy:
Domain → DO
Kingdom → KIDS
Phylum → PREFER
Class → CANDY
Order → OR
Family → FRIED
Genus → GREEN
Species → SNAKES
-how they show relatedness: Organisms in the same genus are more closely related than those only sharing a kingdom.
what is mechanical isolation?
prezygotic barrier: morphological differences prevent successful mating
hybrid breakdown vs. reduced hybrid viability vs. reduced hybrid fertility
- hybrid breakdown:
first-generation hybrids are viable and fertile, but their offspring are weak or sterile
- reduced hybrid viability:
hybrid offspring fail to develop properly or survive to reproductive age
- reduced hybrid fertility:
hybrids are sterile and cannot produce offspring (ILI ILE)
what are the two primary modes of speciation?
- allopatric:
a population is geographically divided, leading to reproductive isolation and divergence(LL)
- sympatric:
occurs within the same geographic area due to factors like polyploidy, sexual selection, or habitat differentiation (S=SAME)
what are the conditions necessary for reproductive isolation to lead to speciation?
- lack of gene flow
- genetic divergence
- accumulation of reproductive barriers (prezygotic and postzygotic)
how does gene flow impact speciation?
it counters speciation by mixing genetic material between populations, preventing divergence (accumulation of genetic/structural differences)
can two species interbreed and produce viable offspring?
In most cases, NO
-however, some closely related species can hybridize, though hybrids often have reduced viability or fertility
why is reproductive isolation important in speciation?
prevents gene flow between populations, allowing them to evolve independently into distinct species
what are analogous structures evidence of
NATRUAL SELECTION - not common ancestry
* arise due to convergent evolution
what is selective breeding
(artificial selection) - humans intentionally breed organisms with desirable traits to enhance or modify specific characteristics in future generations
homolgous structures contain
- same structure
- different function
- recent common ancestor
- CLOSLEY related
vestigial structues contain
- reduced function
- past use
- distant common ancestor
- DISTANTLY related
molecular structures contain
- similar DNA, proteins
- most precise relation
- VERY RECENT common ancestor
what increases genetic variation when animals move from one population to another?
gene flow
artificial selection can be represented as:
recognized breeds of dogs
five factors that can lead to evolution are
-gene flow (GF)
-genetic drift (GD)
-mutation (M)
-natural selection (NS)
-sexual selection (SS)
why is genetic variation important in helping a species survive?
environment changing = some species will have adaptations that enable them to survive and reproduce
in stabilizing selection, what occurs in a population?
intermediate phenotype’s become more common
a bird that can easily outcompete other birds for food and that can produce many eggs has a high:
fitness
the observable change in the allele frequencies of a population over time is called:
microevolution
a feature that allows an organism to survive better in its environment
adaptation
hardy-weinberg equation is used to
predict the frequencies of genotypes and alleles in a population
seals and the penguins both have streamlined, fishlike bodies with a layer of insulating fat, but aren’t closely related…. this similarity results from:
convergent evolution
adaptive radiation is
the evolution from one common ancestor of many different species of organisms living in different environments and being exposed to different selection pressures
-MASTER moved to new reproductive site
what is co-evolution
evolution that results from two species interacting with one another and influencing each other’s adaptations over time (ex. pollinators and flowers)
-one spec + one spec CO-workers
what is parallel evolution
two organisms have ancestors that were closely related and over time the two origins were subjected to the same selection pressures
- now resemble one another
what is the smallest unit that can evolve
populations
what does inducing mutations in a population do
increases the genetic variation in the population
-induce = increase!
what does it mean for an organism to have high fitness
organisms in an environment can survive and reproduce
what is suggested by the similarity of early embryos of different species of vertebrates
evolution from a distant common ancestor
individuals is likely to be most successful in an evolutionary sense where
the organism that dies after five days of life but leaves 10 offspring, all of whom survive to reproduce
a mutation introduces a new skin color in a lizard population, which factor might determine whether the frequency of the new allele will increase
whether the mutation makes some lizards more fit for their environment than other lizards
natural selection that changes the distribution of a trait to favor one extreme phenotype is called
directional selection
-DIRECT contact with an EXTREME
which is not a cause for the actual proportions of homozygotes and heterozygotes to differ from Hardy-Weinberg predictions
natural selection acting on genotypes
which of the following describes natural selection
acts on existing physical traits
small number of birds, blown off course during migration, find an island and colonize it
-these are the first of this bird species on this island
-this population will most likely experience genetic drift as a result of the….
founder effect
actual allele frequencies in a population do not match genotype frequencies predicted by the Hardy-Weinberg equation, the population is
evolving
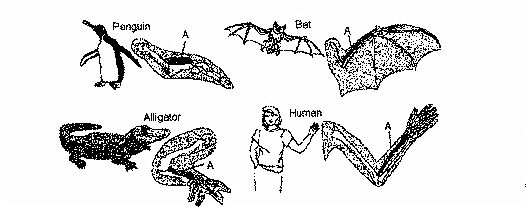
similarity of these structures suggests that the organisms
have a common ancestor
what makes up scientific name
genus + species
natural selection decreases what
genetic variability
allopatric =
geographical isolation
genetic drift does not involve what
mutations or selection (only randomness)
allopatric vs sympatric
ALLO = barrier
SYM = NO barrier (prezygotic)
H-W
q² = bb - homozygous reccesive
p² = BB - homozygous dominant
2pq = Bb heterozygous
the evolution of similar features in distantly related groups that live similar lifestyles is..
convergent evolution
Evolution ....
happens when the conditions for H-W equilibrium are not met