g) the ultrastructure of eukaryotic cells and the functions of the different cellular components
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are cells?
All living organisms are made up of cells
Understanding cell structure and function is a key concept in biology
The term cell was first coined by Robert Hooke in the 17th century
Advances in light microscopy and electron microscopy have improved understanding of cell structure and function
Improvements in microscopy have been essential to understanding cell ultrastructure
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Two main types of organism: prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Prokaryotic organisms consist of prokaryotic cells (single-celled organisms, e.g. bacteria)
Eukaryotic organisms are made of eukaryotic cells
Both types contain organelles
Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells
Organelles
Structures found within cells
Each organelle has a specific function
Can be seen using an electron microscope
The internal structure of organelles is known as cell ultrastructure
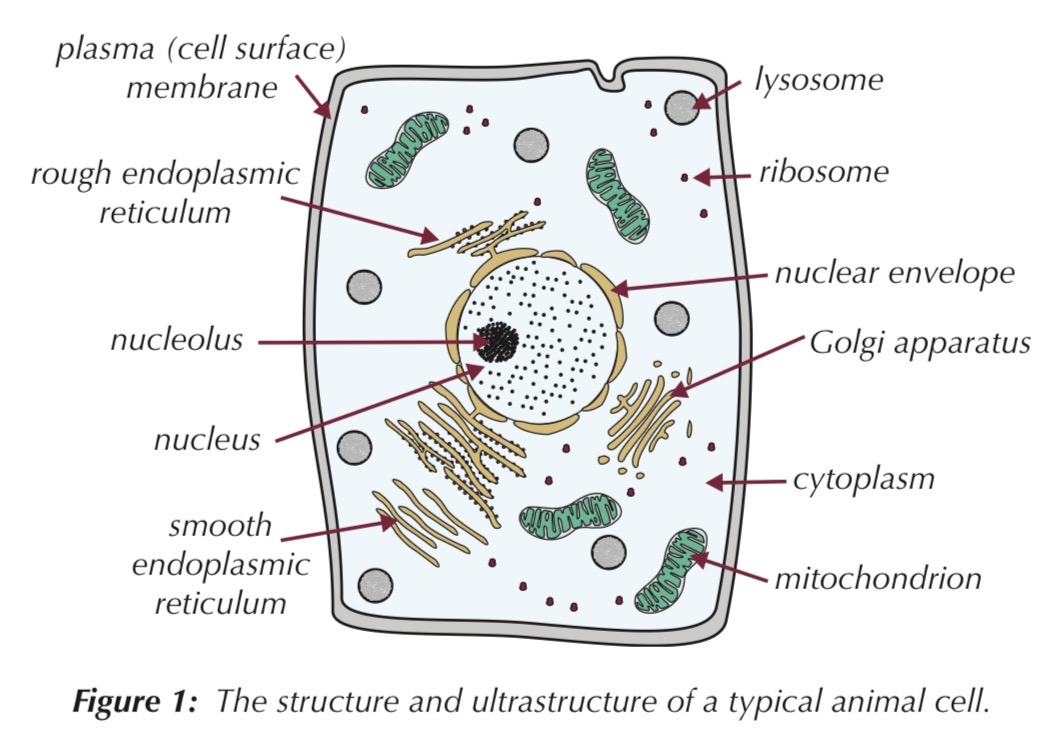
Animal cells organelles:

Plant cells organelles:
Are eukaryotic cells
Contain all organelles found in animal cells plus:
a cell wall with plasmodesmata (‘channels’ for exchanging substances
vacuole (compartment that contains cell sap),
and chloroplasts (the organelles involved in photosynthesis).

Plasma membrane (cell surface membrane)
Found on the surface of animal cells
Found just inside the cell wall of plant and prokaryotic cells
Made mainly of lipids and proteins
Function:
Regulates movement of substances into and out of the cell
Contains receptor molecules that respond to chemicals (e.g. hormones)
Cell wall.
Rigid structure surrounding plant cells
Made mainly of cellulose (a carbohydrate)
Function:
Supports plant cells
Fungal and bacterial cell walls are not made of cellulose
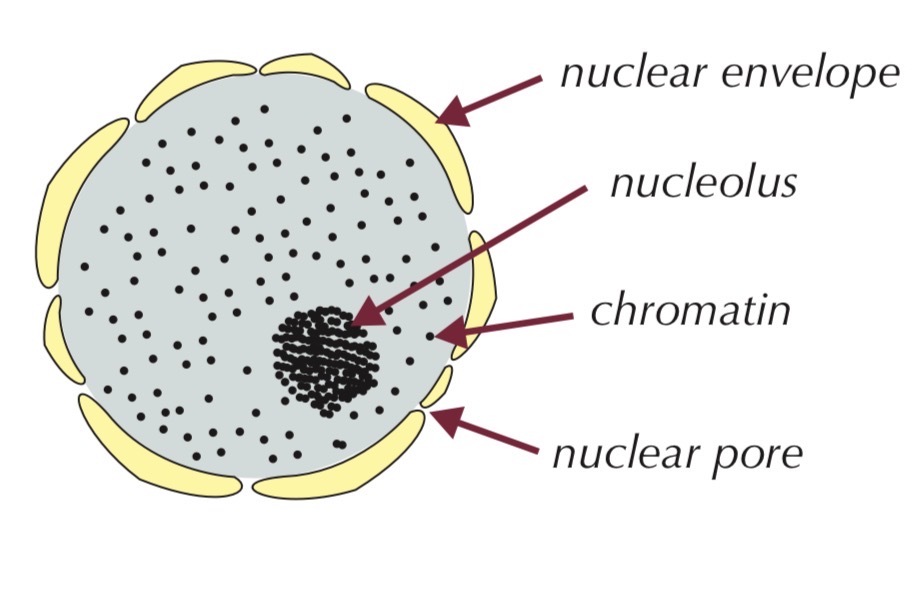
Nucleus
Large organelle surrounded by a double membrane (nuclear envelope)
Nuclear envelope contains pores
Contains:
Chromatin (DNA + proteins)
Nucleolus
Function:
Controls cell activities by controlling DNA transcription
DNA provides instructions to make proteins
Nuclear pores allow substances (e.g. RNA) to move between nucleus and cytoplasm
Nucleolus makes ribosomes
Lysosome
Round, membrane-bound organelle
No clear internal structure
Function:
Contains digestive enzymes
Digests invading cells
Breaks down worn-out cell components
Enzymes are kept separate from cytoplasm by the membrane

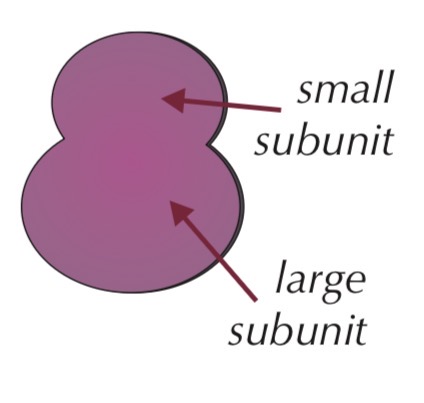
Ribosome
Very small organelle
Found free in cytoplasm or attached to rough ER
Made of proteins and RNA
Not surrounded by a membrane
Function:
Site of protein synthesis
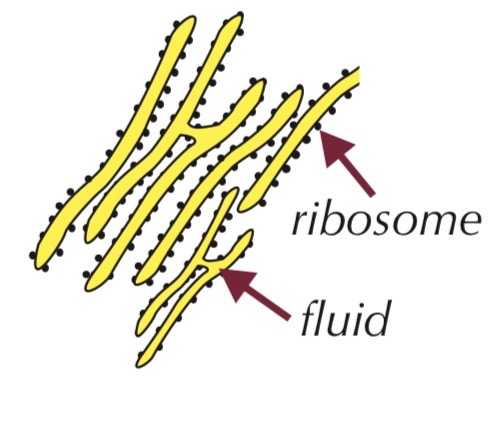
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
System of membranes enclosing fluid-filled spaces
Surface covered with ribosomes
Function:
Folds and processes proteins made at ribosomes
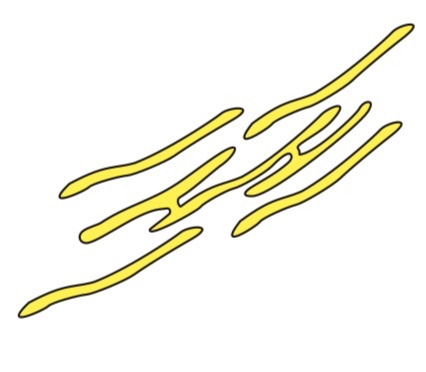
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
Similar structure to RER
Does not have ribosomes
Function:
Synthesises and processes lipids
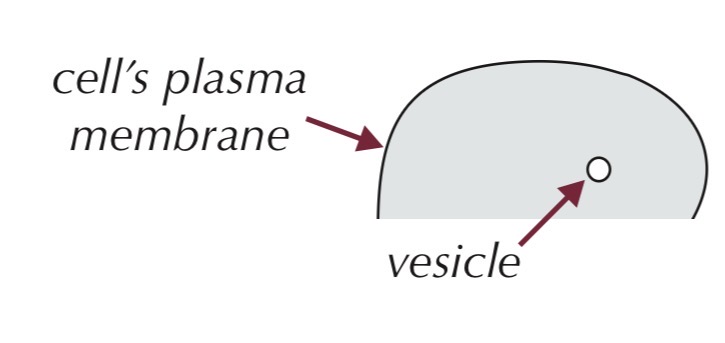
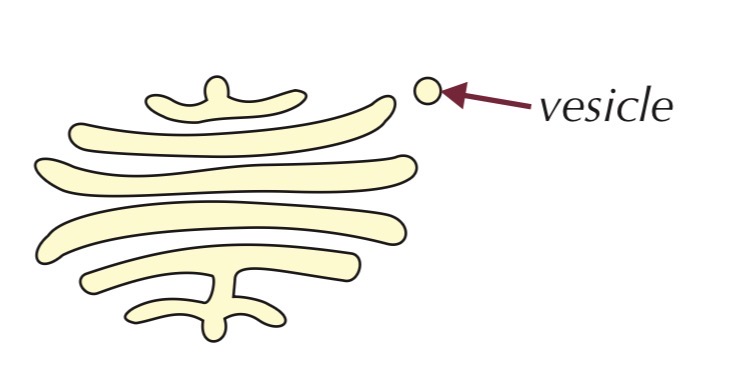
Vesicle
Small, fluid-filled, membrane-bound sac in cytoplasm
Function:
Transports substances:
In and out of the cell (via plasma membrane)
Between organelles
Formed by Golgi apparatus, ER, or plasma membrane
Golgi apparatus
Group of flattened, membrane-bound sacs
Vesicles often seen at edges
Function:
Processes and packages proteins and lipids
Forms lysosomes
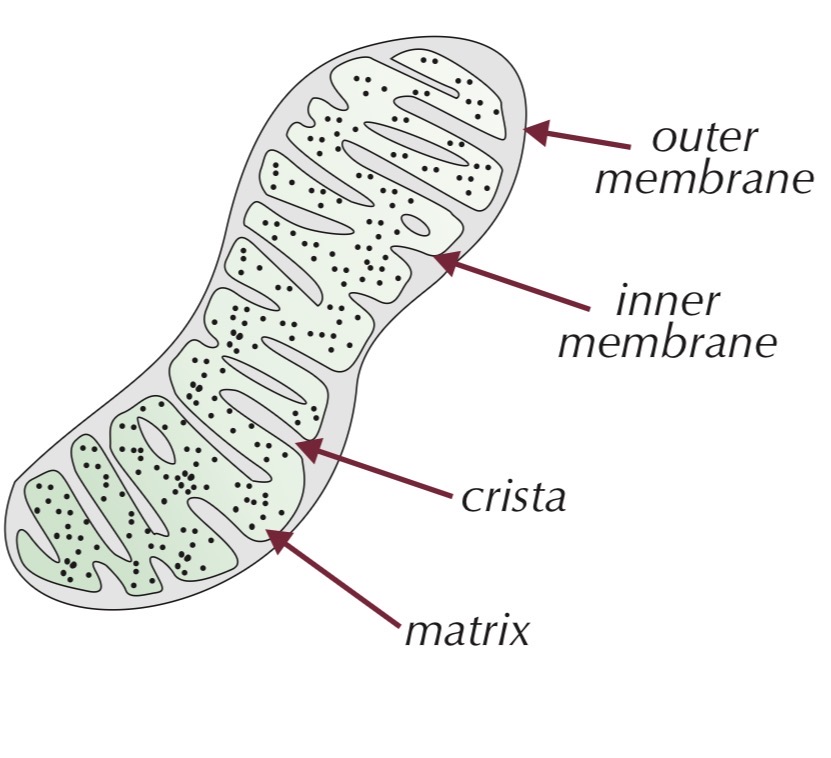
Mitochondrion
Oval-shaped organelle
Double membrane:
Outer membrane
Inner membrane folded into cristae
Inside is the matrix containing respiration enzyme
Function:
Site of aerobic respiration
Produces ATP
Found in large numbers in energy-demanding cells
Exam Tip: Never say mitochondria “produce energy” – they produce ATP
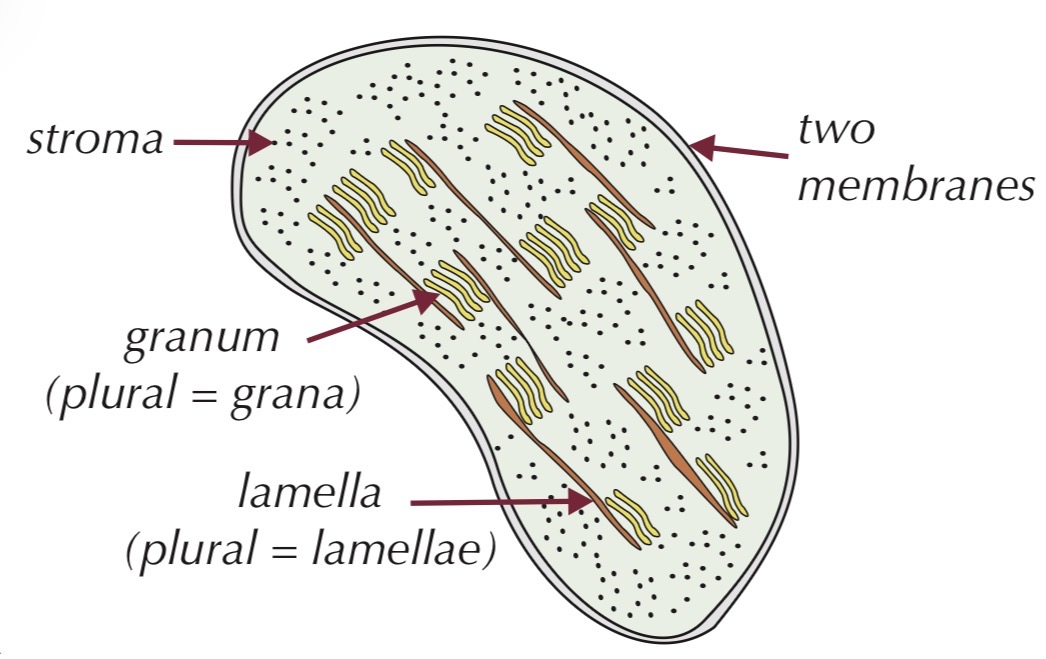
Chloroplast
Found in plant cells
Small, flattened organelle
Surrounded by a double membrane
Contains:
Thylakoid membranes
Grana (stacks of thylakoids)
Lamellae (link grana)
Stroma
Function:
Site of photosynthesis
Light-dependent reactions occur in grana
Light-independent reactions occur in stroma
Centriole
Small, hollow cylinders
Made of microtubules
Found in animal cells and some plant cells
Function:
Involved in chromosome separation during cell division

Cilia
Small, hair-like structures on surface of some animal cells
Structure:
Outer membrane
9 pairs of microtubules surrounding 2 central microtubules (9 + 2)
Function:
Movement of substances along cell surface
Tip: In trachea, cilia move mucus and dirt out of lungs

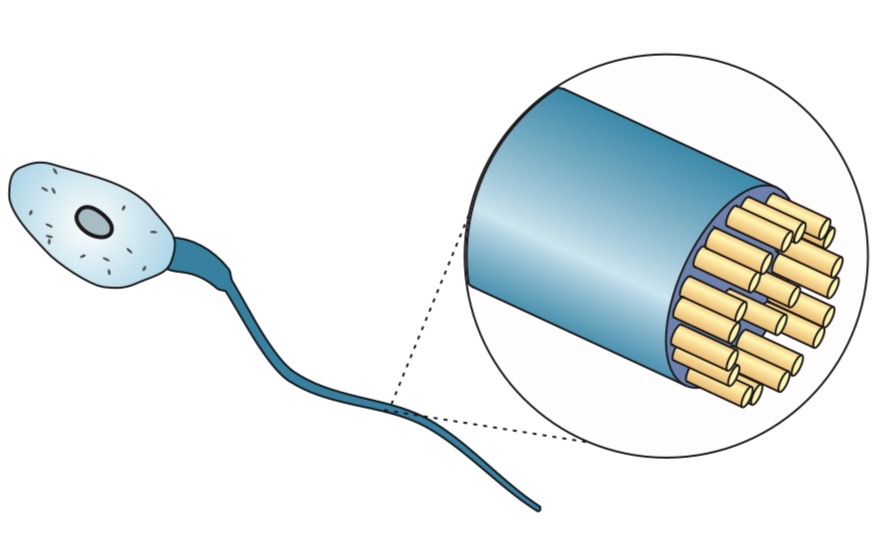
Flagellum
Longer than cilia
Surrounded by plasma membrane
Same 9 + 2 microtubule arrangement as cilia
Function: microtubles contract to make flagellum move
Propels cells forward (e.g. sperm cells)
Tip: In humans, only sperm cells have flagella
Tip: Singular = flagellum / plural = flagell