Bones and Skeletal Tissue in Human Anatomy
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Hyaline cartilage
Provides support, flexibility, and resilience; most abundant type; contains collagen fibers only.
Elastic cartilage
Similar to hyaline cartilage, but contains elastic fibers; found in external ear and epiglottis.
Fibrocartilage
Contains thick collagen fibers with great tensile strength; found in menisci of knee and vertebral discs.
Perichondrium
Layer of dense connective tissue surrounding cartilage that helps resist outward expansion and contains blood vessels for nutrient delivery.
Hematopoiesis
Blood cell formation that occurs in red marrow cavities of certain bones.
Osteocalcin
Hormone secreted by bones that helps to regulate insulin secretion, glucose levels, and metabolism.
Axial skeleton
Consists of the long axis of the body, including the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage.
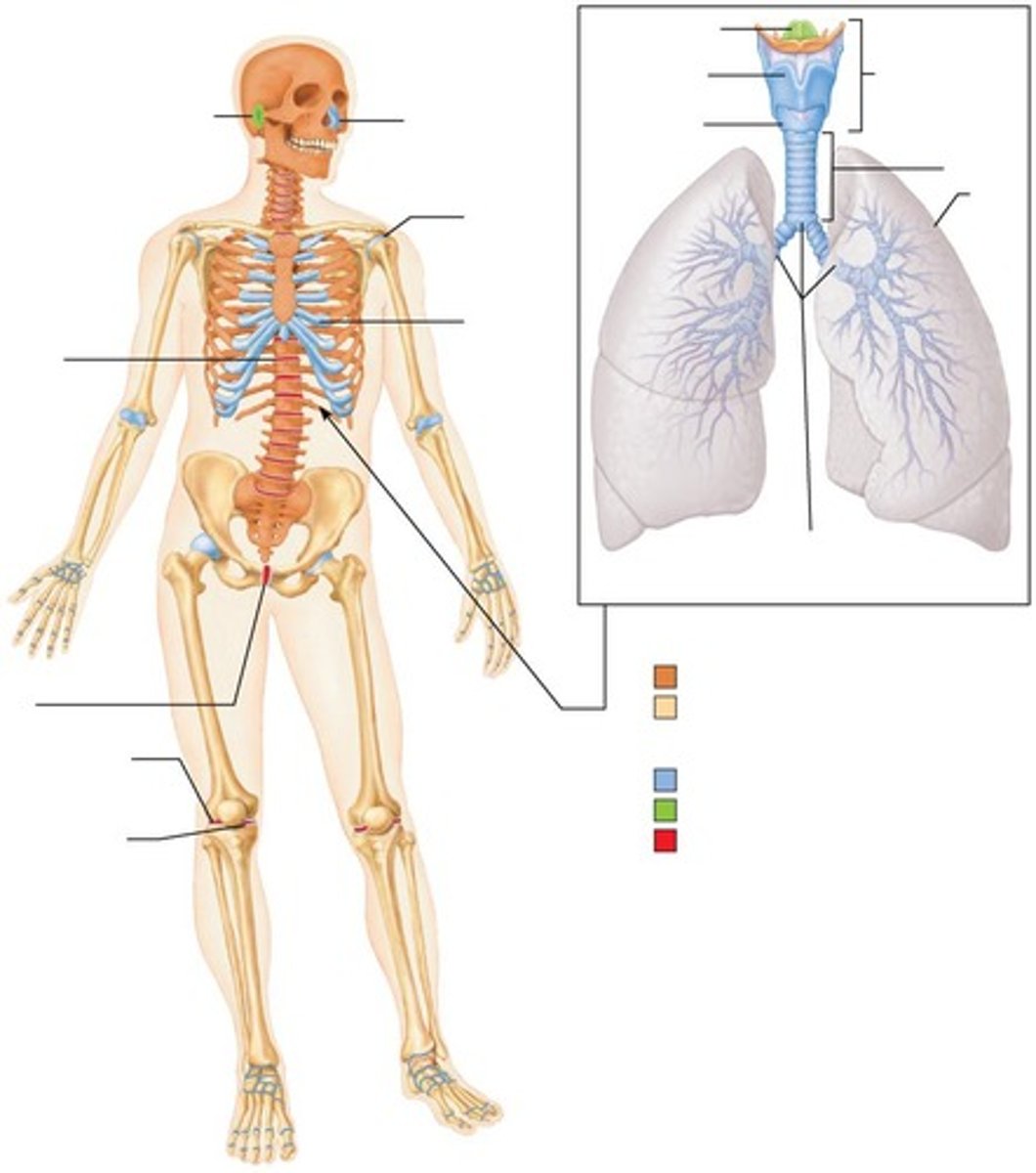
Appendicular skeleton
Includes bones of the upper and lower limbs and girdles attaching limbs to the axial skeleton.
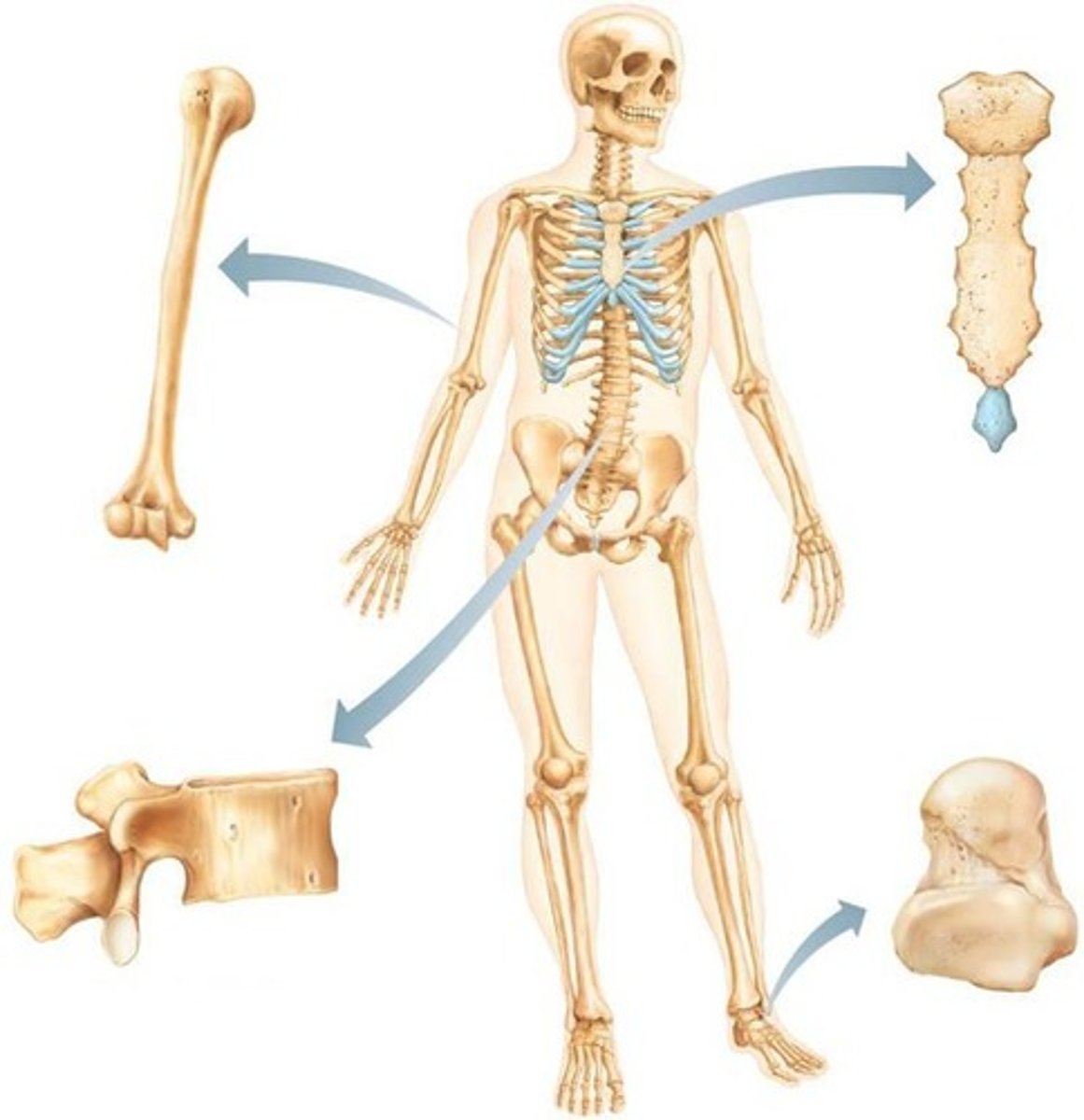
Long bones
Bones that are longer than they are wide, such as limb bones.
Short bones
Cube-shaped bones found in the wrist and ankle; sesamoid bones form within tendons (e.g., patella).
Flat bones
Thin, flat, slightly curved bones such as the sternum, scapulae, ribs, and most skull bones.
Irregular bones
Bones with complicated shapes, such as vertebrae and hip bones.
Spongy bone
Bone that has a mesh of bony spines called trabeculae.
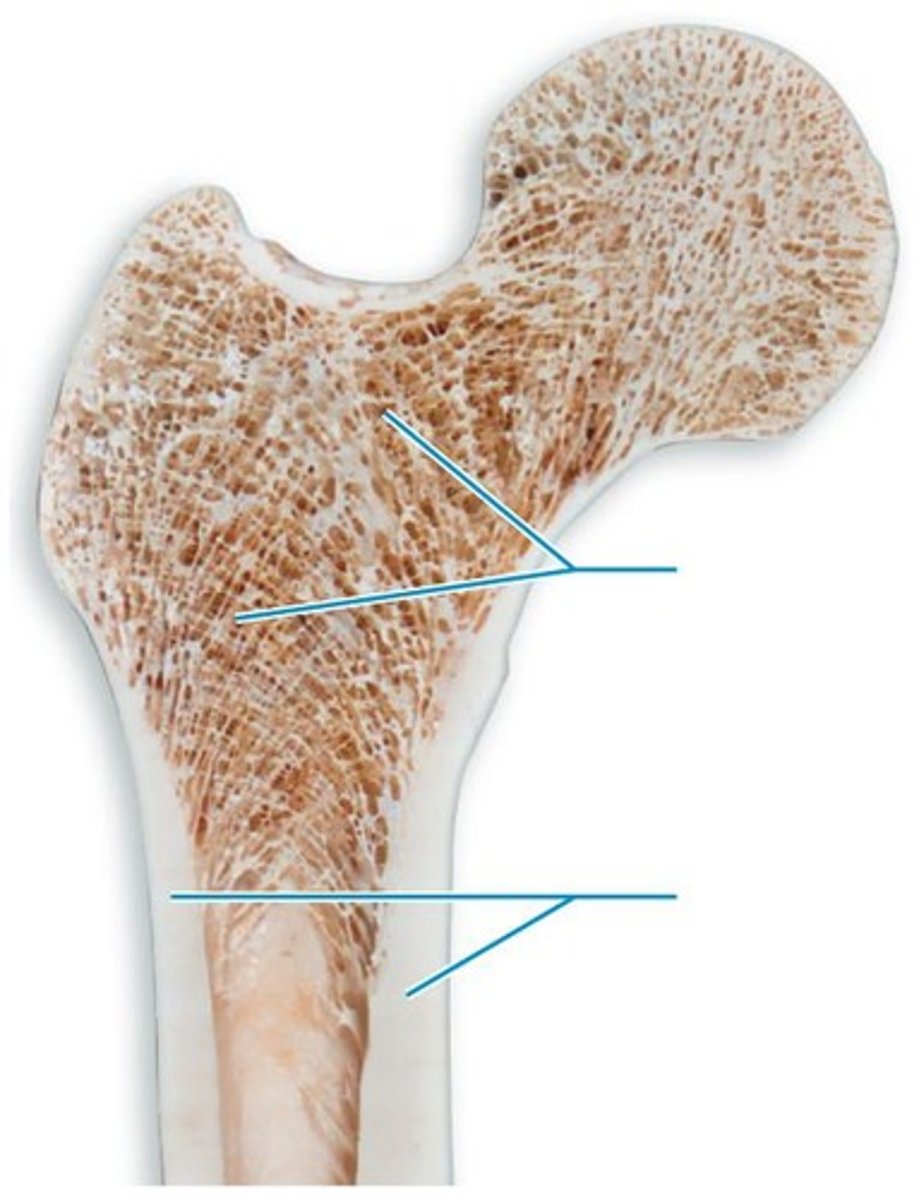
Compact bone
Bone that looks smooth and solid.
Articular cartilage
Cartilage found at joints.
Costal cartilage
Cartilage that connects ribs to the sternum.
Intervertebral disc
Cartilage found between vertebrae.
Meniscus
Padlike cartilage in the knee joint.
Trabeculae
Bony spines that form the mesh structure of spongy bone.
Red marrow
Bone marrow responsible for blood cell production.
Yellow marrow
Bone marrow primarily involved in fat storage.
Calcium and phosphorus
Minerals stored in bones, serving as a reservoir for the body.
Flat Bones
Consist of a layer of spongy bone sandwiched between two thin layers of compact bone.
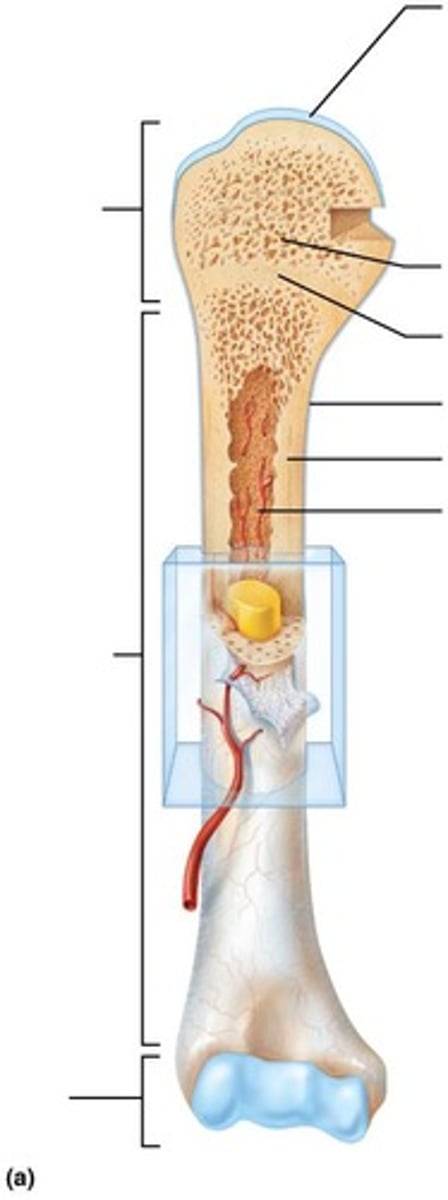
Diaphysis
Tubular shaft that forms long axis of bone.
Epiphyses
Ends of long bones that consist of compact bone externally and spongy bone internally.
Articular cartilage
Covers articular (joint) surfaces.
Epiphyseal line
Remnant of childhood epiphyseal plate where bone growth occurs.
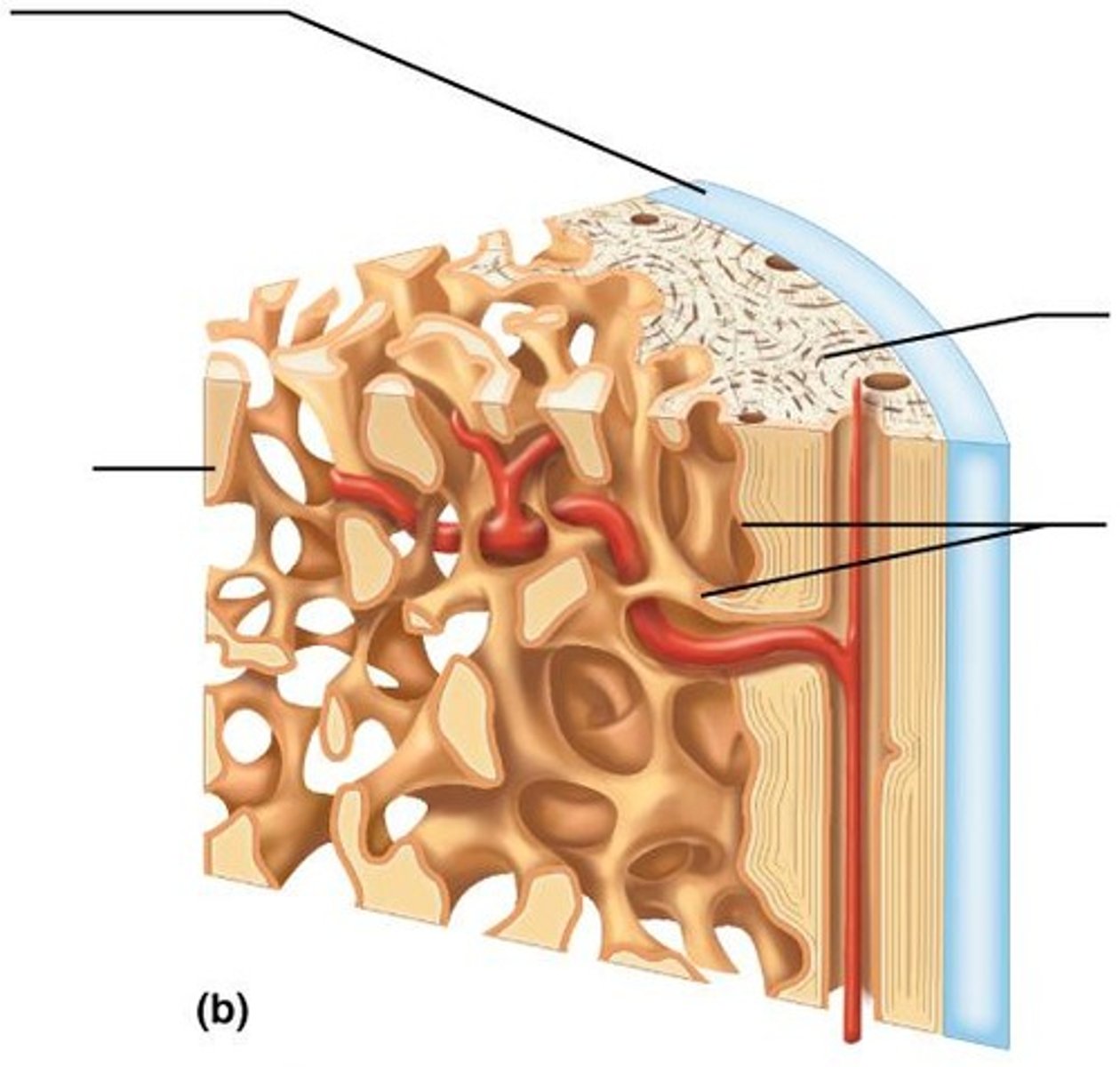
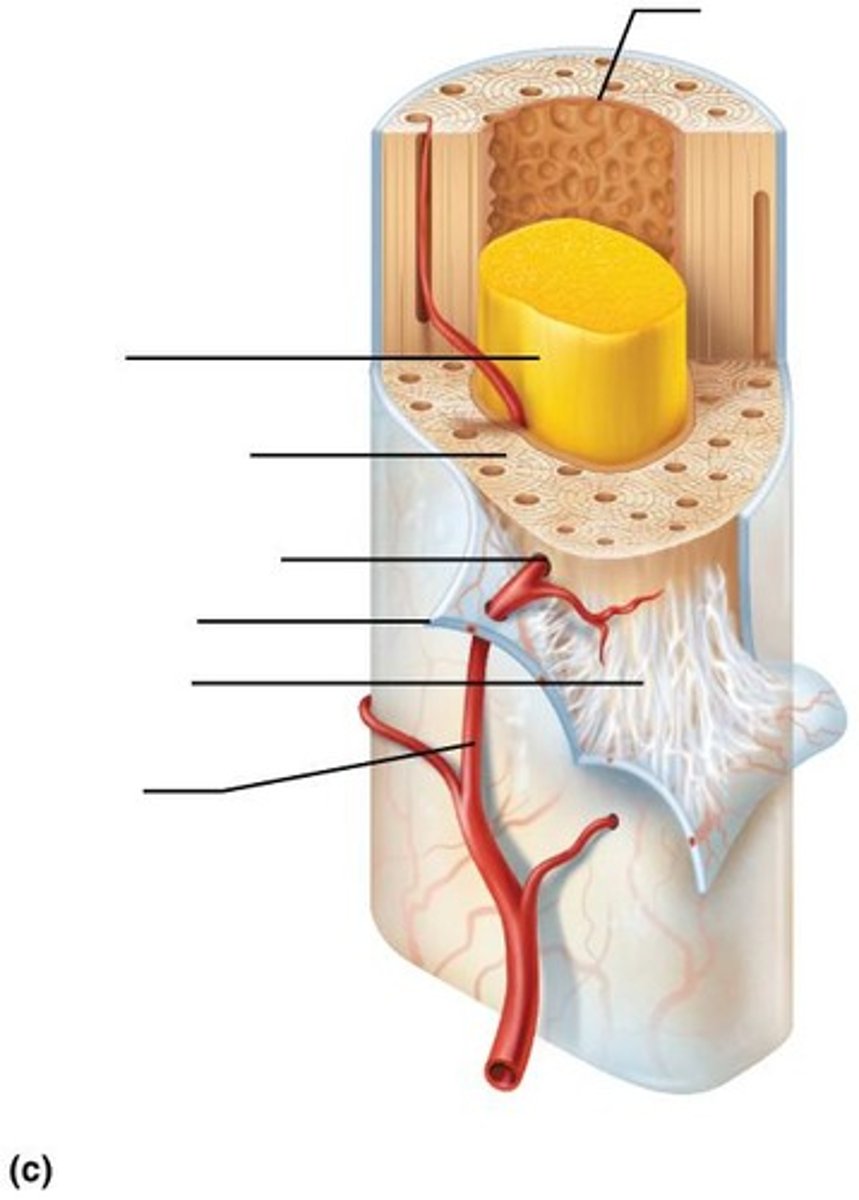
Periosteum
White, double-layered membrane that covers external surfaces except joints.
Fibrous layer
Outer layer of periosteum consisting of dense irregular connective tissue with Sharpey's fibers that secure to bone matrix.
Osteogenic layer
Inner layer of periosteum abutting bone that contains primitive osteogenic stem cells that give rise to most all bone cells.
Endosteum
Delicate connective tissue membrane covering internal bone surface.
Hematopoietic tissue
Red marrow found within trabecular cavities of spongy bone and diploë of flat bones.
Red marrow
Found in newborns' medullary cavities and all spongy bone, and in adults located in heads of femur and humerus.
Yellow marrow
Can convert to red if a person becomes anemic.
Bone markings
Sites of muscle, ligament, and tendon attachment on external surfaces.
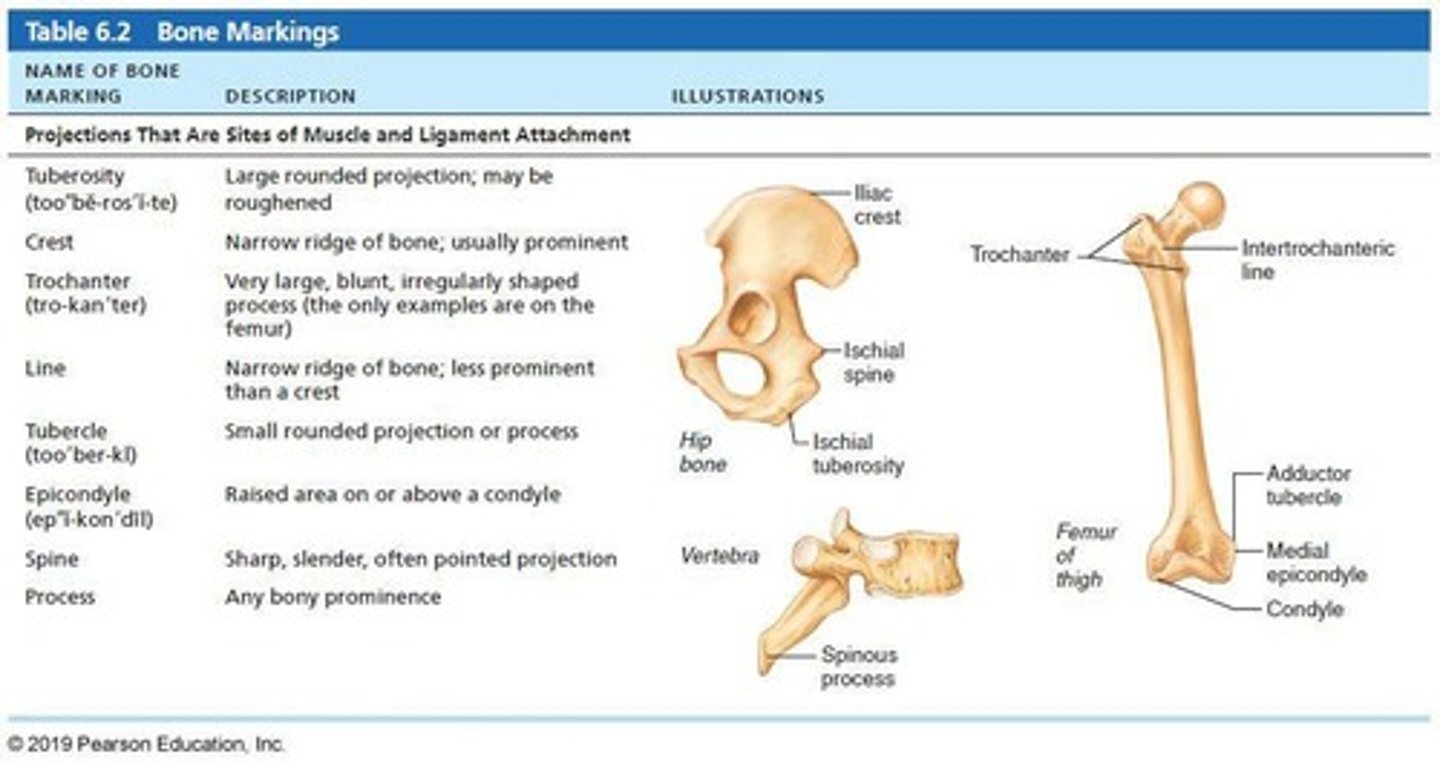
Projection
Outward bulge of bone, may be due to increased stress from muscle pull or is a modification for joints.
Depression
Bowl- or groove-like cut-out that can serve as passageways for vessels and nerves, or plays a role in joints.
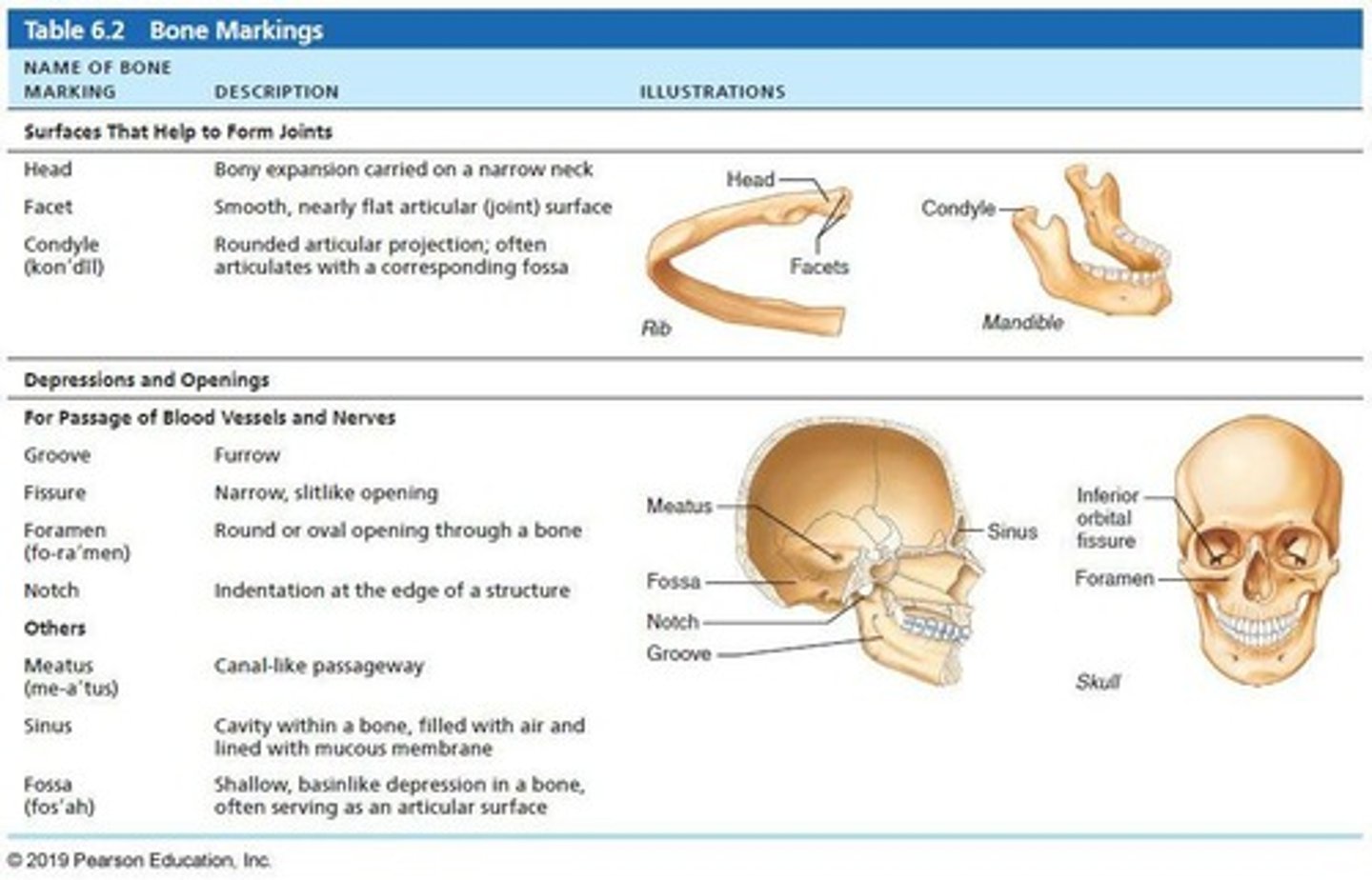
Opening
Hole or canal in bone that serves as passageways for blood vessels and nerves.
Osteoprogenitor cell
Mitotically active stem cells in periosteum and endosteum that can differentiate into osteoblasts or bone-lining cells.
Osteoblast
Matrix-synthesizing cell responsible for bone growth.
Osteocyte
Mature bone cell that monitors and maintains the mineralized bone matrix.
Osteoclast
Bone-resorbing cell derived from the same hematopoietic cells that become macrophages.
Ossification (osteogenesis)
The process of bone tissue formation.
Bone remodeling
Occurs throughout life as part of bone development and repair.
Endochondral ossification
Process where bone collar forms around the diaphysis of the hyaline cartilage model.
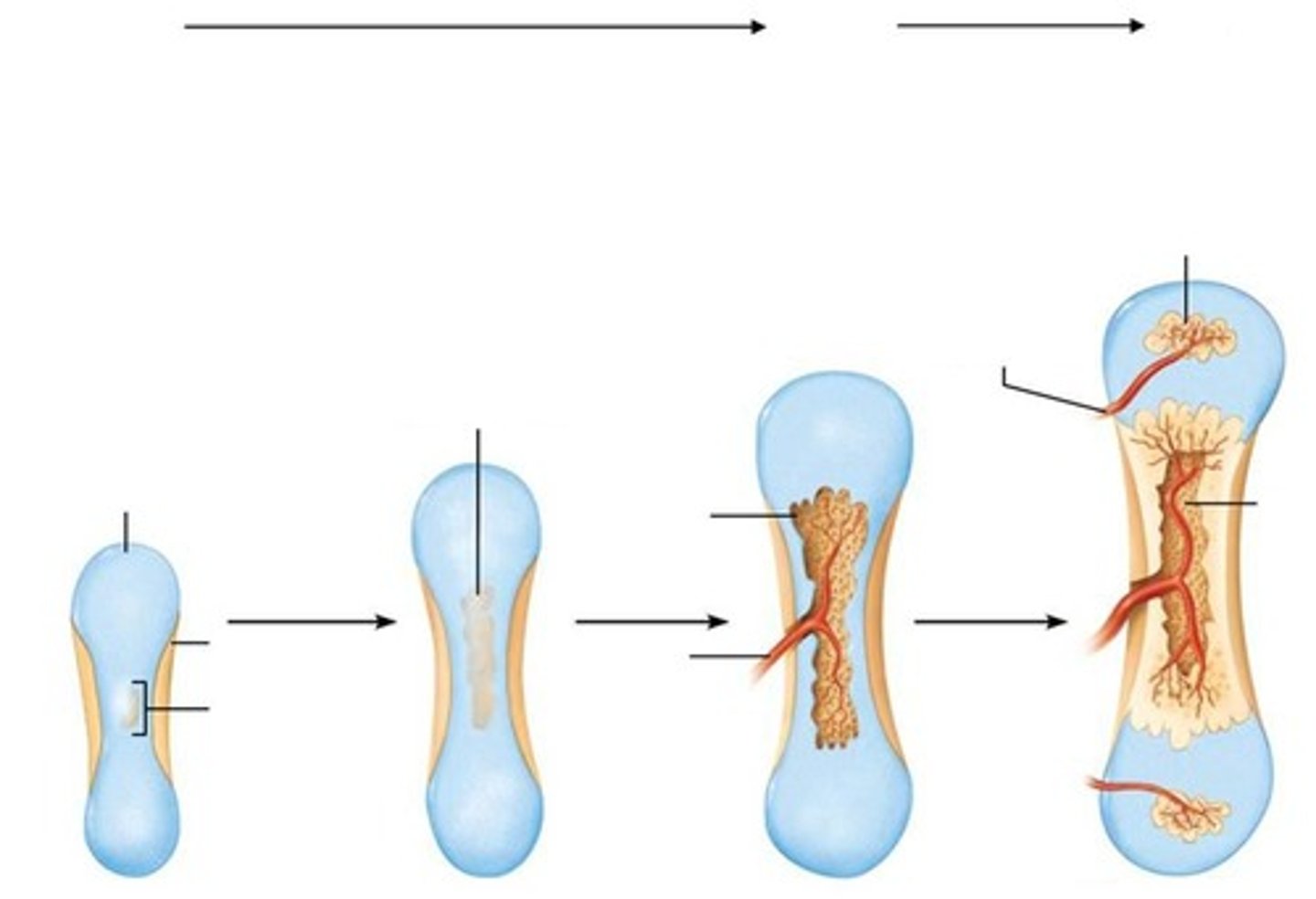
Endochondral Ossification
The process where cartilage is replaced by bone in the development of long bones.
Primary ossification center
The region in the center of the diaphysis where cartilage calcifies and cavities develop.
Bone collar
A layer of bone that forms around the diaphysis of the hyaline cartilage model.
Secondary ossification center
The area where ossification occurs in the epiphyses after birth.
Medullary cavity
The central cavity of bone shafts where red marrow is stored.
Epiphyseal plate
The area of hyaline cartilage that remains between the epiphysis and diaphysis during growth.
Articular cartilage
Hyaline cartilage that covers the ends of bones in joints.
Intramembranous ossification
The process of bone development from fibrous connective tissue membranes.
Osteoblast
A cell that secretes the matrix for bone formation.
Osteoid
The unmineralized organic component of bone matrix secreted by osteoblasts.
Osteocyte
A mature bone cell that maintains the bone matrix.
Collagen fiber
A protein that provides strength and structure to bones.
Ossification center
The site in the bone where ossification begins.
Fibrous periosteum
The outer layer of connective tissue surrounding the bone.
Compact bone
The dense outer layer of bone that provides strength.
Immature spongy bone
The initial form of spongy bone that is later remodeled into mature spongy bone.
Diploë
The spongy bone found between the inner and outer layers of compact bone in flat bones.
Red marrow
The tissue found in the medullary cavity that produces blood cells.
Vascularized mesenchyme
Mesenchymal tissue that contains blood vessels and contributes to bone formation.
Trabeculae
The small rod-like structures in spongy bone that provide support.
Hyaline cartilage
A type of cartilage that is glossy and provides support and flexibility.
Spongy bone formation
The process of creating spongy bone from cartilage or other tissues.
Interstitial growth
Requires presence of epiphyseal cartilage in the epiphyseal plate.
Epiphyseal plate
Maintains constant thickness.
Rate of cartilage growth
On one side balanced by bone replacement on the other.
Zones of the epiphyseal plate
Consists of five zones: Resting (quiescent) zone, Proliferation (growth) zone, Hypertrophic zone, Calcification zone, Ossification (osteogenic) zone.
Resting zone
Zone in the epiphyseal plate where cartilage cells are quiescent.
Proliferation zone
Zone where cartilage cells undergo mitosis.
Hypertrophic zone
Zone where older cartilage cells enlarge.
Calcification zone
Zone where matrix becomes calcified; cartilage cells die; matrix begins deteriorating.
Ossification zone
Zone where new bone is forming.
Bone remodeling
About 5-7% of bone mass is recycled each week.
Spongy bone replacement
Replaced approximately every 3-4 years.
Compact bone replacement
Replaced approximately every 10 years.
Bone remodeling process
Consists of both bone deposit and bone resorption.
Remodeling units
Packets of adjacent osteoblasts and osteoclasts coordinate the remodeling process.
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Produced by parathyroid glands in response to low blood calcium levels.
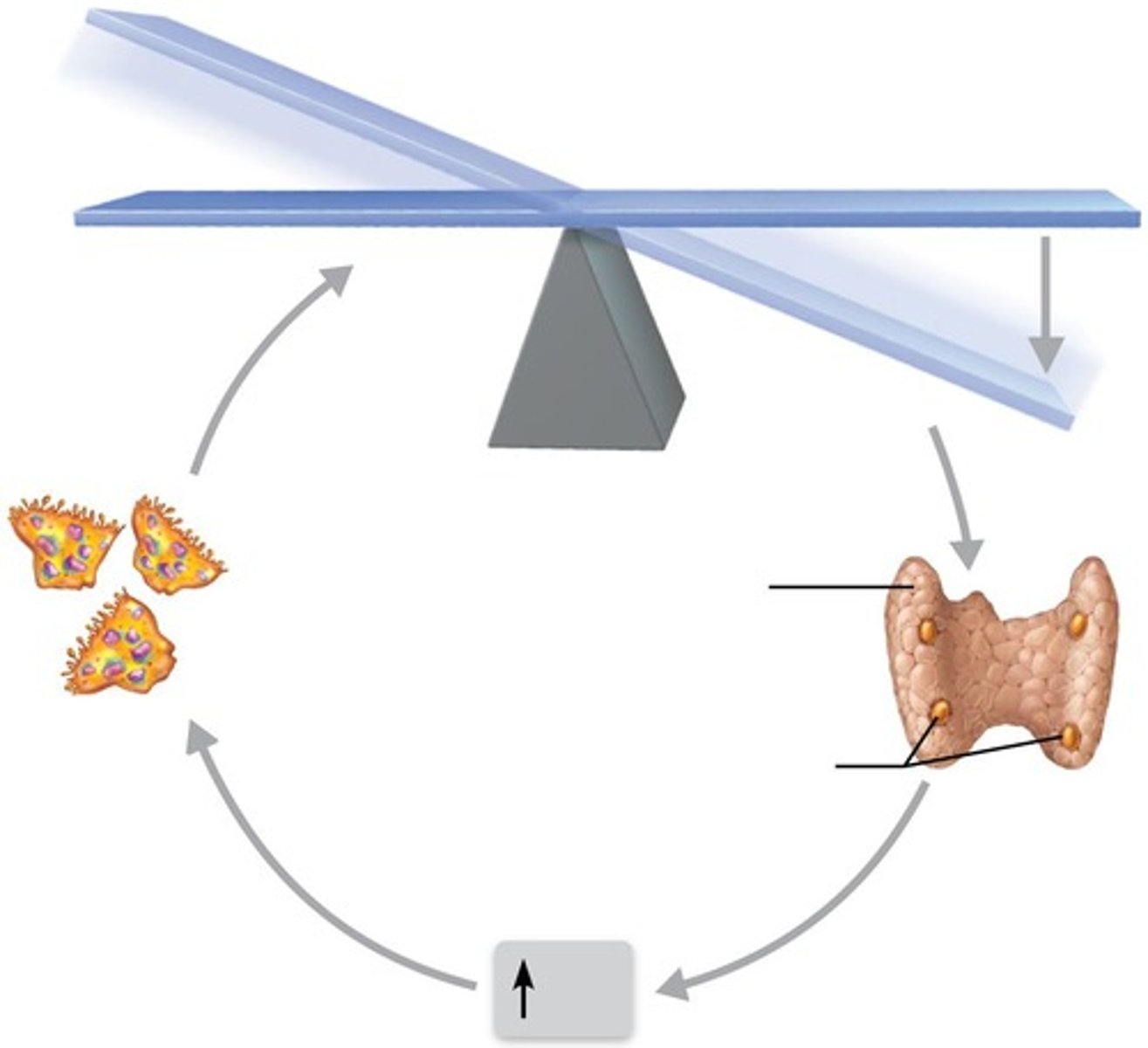
Calcitonin
Produced by parafollicular cells of thyroid gland in response to high levels of blood calcium levels.
Calcium homeostasis of blood
Normal range is 9-11 mg/100 ml.
Fractures
Breaks in bones.
Nondisplaced fracture
Ends retain normal position.
Displaced fracture
Ends are out of normal alignment.
Complete fracture
Broken all the way through.
Incomplete fracture
Not broken all the way through.
Open (compound) fracture
Skin is penetrated.
Closed (simple) fracture
Skin is not penetrated.
Fracture treatment
Involves reduction, the realignment of broken bone ends.
Closed reduction
Physician manipulates to correct position.
Open reduction
Surgical pins or wires secure ends.
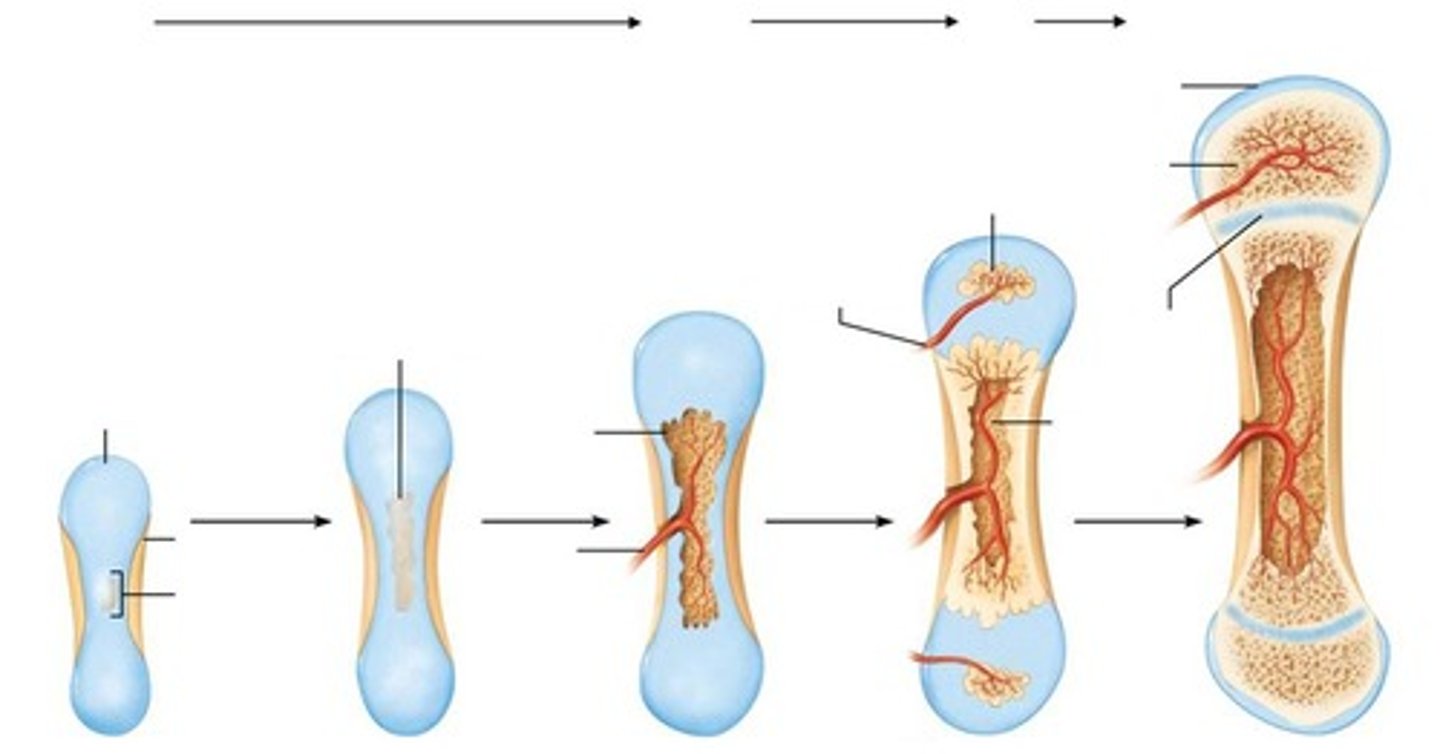
Stages of bone fracture repair
Includes hematoma formation, fibrocartilaginous callus formation, bony callus formation, and bone remodeling.
Classification of bones
Based on their shape, including long, short, flat, and irregular.