PL SCI 221 - Midterm
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
middle lamella
non-living area b/w cells
pectin
a complex set of polysaccharides (plant glue)
pectinases
secreted into middle lamella, breaking down pectin. Results in fruit softening
plasma membrane
forms a continuum throughout the plant. Semi-permeable
symplast
continuum of living material
Apoplast
non-living portions of plant tissues
Lipids (40%)
arranged in bilayer so polar portions of molecules face out, while non-polar are in internal region of the membrane
phospholipids
contains a charged, polar head group and 2 hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails
protein (40%)
most are enzymes that transport metabolites across the membrane, some extend through membrane, some confined to either inside or outside of membrane
carbohydrates (20%)
linked to proteins & lipids
nucleus
surrounded by nuclear envelope. Contains chromosomes & one or more nucleoli
chromosomes
genetic material of cell
nucleoli
masses made of protein & nucleic acids involved in RNA synthesis
endoplasmic reticulum
network of continuous tubules & flattened sacs that course through cytoplasm & connect to nuclear envelope
Dictyosomes
assemble complex carbs for the cell wall, synthesize carb side chains for glycoproteins in membrane, cell wall, & vacuole
Vacuoles
stores water, sugars, proteins, organic acids, & pigments. Digestion. pH & ionic homostasis. Defence against microbial pathogens & herbivores.
amyloplasts
unpigmented plastids that contain starch granules
leucoplasts
colourless plastids involved in synthesis of monoterpenes
chromoplasts
synthesize & accumulate carotenoid & xanthophyll pigments making them yellow, orange, or red
etioplasts
plastids where development from proplastids to chloroplasts has been arrested by absence of light
chloroplasts
photosynthetic plasids responsible for energy capture. Bonded by a double membrane
thylakoid
membrane bound compartments inside chloroplasts. Site of light dependant reactions of photosynthesis
grana thylakoids
PSII - capture of light energy & electron transport
unstacked stroma thylakoids
PSI - electron transport & ATP synthesis
Stroma
fluid surrounding thylakoids. Site of dark reactions
light reaction
capture of light energy & its conversion to chemical bond energy. ATP & NADPH
dark reaction
enzymatic fixation of CO2 into carbohydrate utilizing the ATP & NADPH
gymnosperms
cone bearing plants
angiosperms
flowering plants
meristem
tissue that contains actively dividing cells
apical meristem
area of cell division/growth. Can give rise to leaves, buds, stem, and sometimes flowers
intercalary meristem
found b/w two differentiated tissues. Can increase growth of plant
vascular cambium & cork cambium
two types of secondary (lateral) meristem
vascular cambium
produces additional vascular tissue (secondary xylem & phloem) in plants undergoing secondary growth, pericycle generates…
cork cambium
produces outer bark (woody plants). add to stem & root girth. econdary meristem in wood. Species develop a diff bark b/c of differences in this. part of periderm
protoderm
forms epidermis or outer protective covering of growing root or shoot
ground meristem
forms cortex or main bulk of plant
parenchyma cells
cells that provide support & cellular respiration. thin cell wall
sclerenchyma cells
cells that provide support. Thick cell walls. Dead at maturity
collenchyma cells
cells that provide support. Thin cell walls, Alive at maturity
procambium
produces vascular tissue that consists of xylem & phloem. found in apical meristem
pith
cells in the centre of a tissue
root cap, apical meristem, elongation, maturation
regions of development in roots (bottom to top)
root cap
protects apical meristem. derived from protoderm
region of cell division
includes apical meristem. If damaged, root will no longer grow
region of cell maturation
region where primary tissues mature into secondary tissues & differentiate into their functions
cortex
large thin walled parenchyma cells found to the inside of epidermis. Occupies greatest area in primary roots. Stores nutrients.
apoplastic
path of water goes around the cells
symplastic
path of water through the cells
endodermis
located at end of cortex next to the vascular cylinder. Last chance to filter water
pericycle
location where lateral roots arise
xylem
transport tissue, moves water & minerals from roots to leaves
tracheids
elongated w/ tapered ends, hollow, non-living at maturity
vessel elements
large, lack end walls, form continuous pipeline for transport, hollow, non-living at maturity
pit pairs
secondary cell wall regions where no secondary cell wall was deposited
pit membrane
this has openings in it that water can freely flow through. It is too thick to let anything pass through
torus
secondary cell wall projections over pit area & a swollen central region of the pit membrane
transpiration
pulling of water up through the xylem of a plant utilizing energy of evaporation
Phloem
transport tissue that conducts organic nutrients from leaves to roots (source tissue to sink tissue)
perocity
ability to induce fruitfullness w/o need for completing juvenile phase of a plant
stolons
horizontal stem. new plants produced where nodes touch the ground
tendrils
branch capable of clinging to structures to provide supports. modified stem or leaf
rhizomes
horizontal stems roots & shoots develop from nodes. stores food
bulbs
compressed stem surrounded w/ fleshy leaflike structures called scales. outer scales protect the ___ and inner scales store food
tubers
swollen fleshy stems, functions as storage organ
corms
short swollen fleshy stem, structures form axillary bud. dies at season end. found in some monocots
periderm
contains, cork, cork cambium, & phelloderm
axial wood elements
transport water w/ dissolved mineral nutrients up from the soil to the leaves (vessels & tracheids) Woody plants
radial wood elements
mostly living cells. used to transport nutrients b/w growth rings & storage of metabolites
cross (transverse)
plane of cut of wood. perpendicular to the axis
tangential longitudinal
plane of cut of wood. parallel to growth rings
radial longitudinal
plane of cut of wood. perpendicular to growth ring (bricks in wall)
resin ducts (canals)
present on some conifers, can be formed in response to injury. Produces resin to fight insect/pathogen invasion or to cover wounds
Auxin
triggers cell division at the shoot apical meristem forming the leaf primordium
leaf primordium
natural protrusions determined by phyllotaxy of the plant
guard cells
regulates the opening/closing of the stomata
stomata
opening that allows gases in for photosynthesis to occur. Water vapour can also enter/leave through these openings
mesophyll tissues
palisade layer & spongy layer
palisade layer
upper region of elongated cells vertically arranged in 1-2 compact layers
spongy layer
lower region of irregular shaped cells loosely arranged. contains fewer chloroplasts
intercellular space
abundant in spongy mesophyll layer as a result of the irregular shaped, loosely packed arrangement of cells. large # of air spaces in the leaf increase surface area available for gas exchange
Braccicaceae Brassica oleracea
broccoli, brussellese sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, collards, kale
receptacle
region where floral parts are attached
sepals
outermost whorl of floral parts. may resemble leaves or floral parts. protects inner flower from damage before it opens. collectively called a calyx
apetalous
no petals
sympetalous
petals are partially or completely fused
choripetalous
petals are separate
stamen
pollen bearing structure includes anther & filament
pistil
includes ovary, stigma, & style
complete flower
contain all floral components including sepals, petals, stamens, & carpels
incomplete flower
missing one or more floral components
perfect flower
have both female & male reproductive structures
imperfect flower
have only female or only male reproductive structures
peduncle
stalk below a inflorescence
pedicels
small stalk below each individual flower in an inflorescence
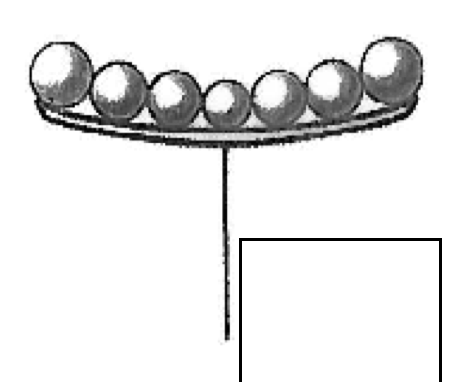
spike-unbranched
flowers attached directly to the central axis
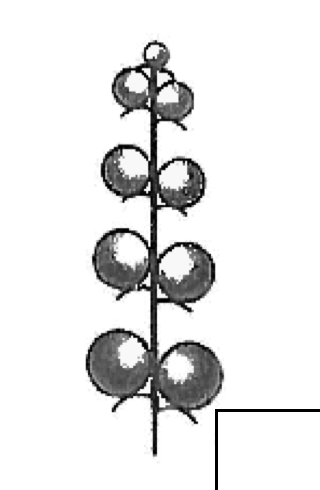
raceme-unbranched
flowers are attached by pedicels to the central axis
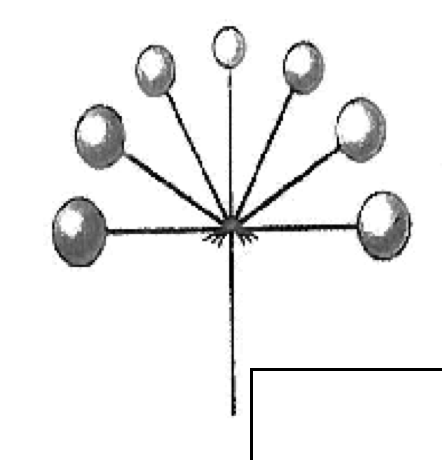
umbel-flowers
attached by pedicels which arise from a common point (simple or compound)
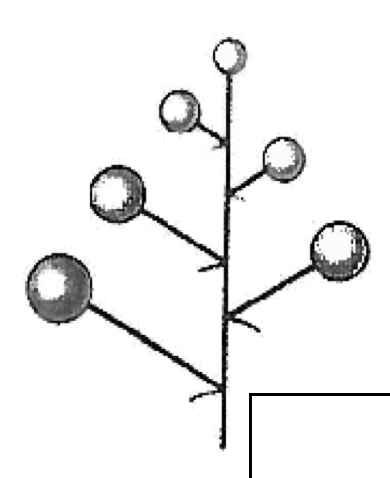
corymb-unbranched
pedicure of unequal length alternately attached along central axis
head
peduncle w/ flowers attached directly to a broad receptacle (ray & disk flowers)