Exam 4: Respiratory, GI, and Renal
4.0(1)
4.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcard set for Exam 4 of PCB 4701
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
1
New cards
What is the equation for blood flow?
Change in pressure / resistance
2
New cards
What is the equation for cardiac output?
mean arterial pressure / total peripheral resistance
3
New cards
How is systolic pressure measured when measuring blood pressure?
Pressure at which blood can first get past cuff (i.e. when blood is at highest pressure) gives systolic pressure
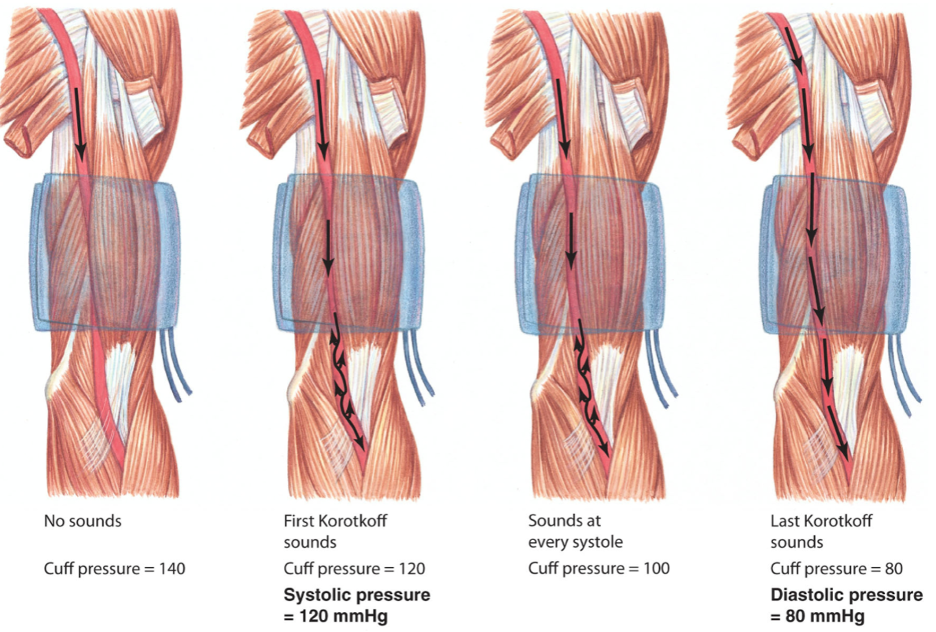
4
New cards
How is diastolic pressure measured when measuring blood pressure?
Pressure at which all blood can get past cuff (i.e. even when blood is at lowest pressure) gives diastolic pressure
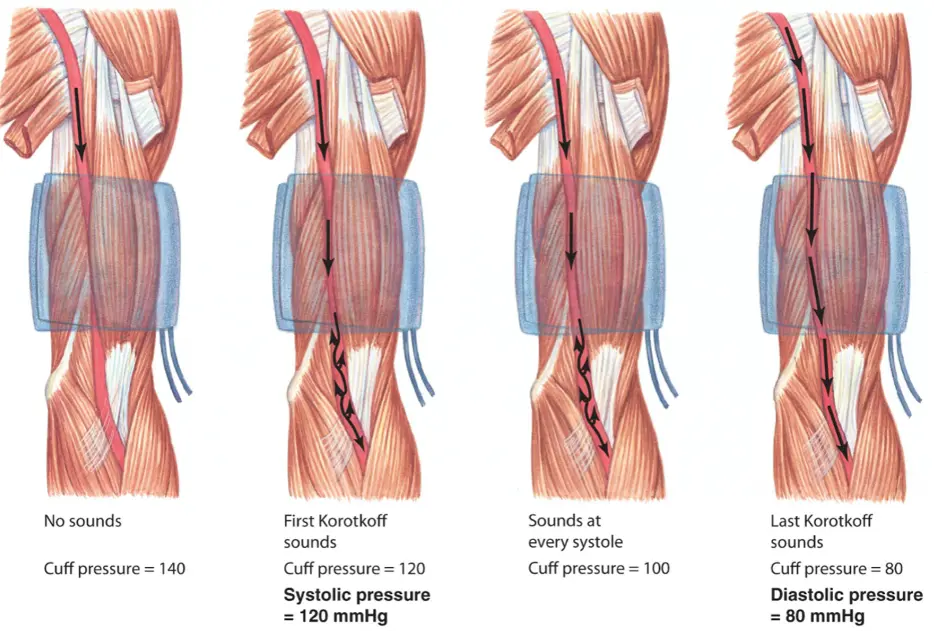
5
New cards
Where is oxygen concentration the highest?
In the lungs
6
New cards
According to the Law of Laplace, pressure exerted by surface tension is decreased when 1________________. You learned this in the context of 2________________ and 3________________ is a detergent that helps combat their closure if they are coated with fluid.
1. Radius is increased
2. alveoli
3. surfactant
7
New cards
The volume of the intrapleural space of a normal human being is kept at a minimum by what?
Negative pressure relative to atmospheric pressure
8
New cards
Inspiration requires 1_____________of the diaphram, pressures of the intrapleural space to be 2_____than atmospheric pressures, and pressures of the intrapulmonary space to be 3________than atmospheric pressure.
1. Lowering
2. lower
3. lower
9
New cards
What are Type I alveolar cells responsible for?
* Allow for gas exchange between air and red blood cells
10
New cards
What are Type II alveolar cells responsible for?
* secrete surfactant
* reabsorb Na+ and H2O
* reabsorb Na+ and H2O
11
New cards
What are some examples of disorder of the surface tension of alveoli?
1. Lungs of premature babies = Haven’t started producing surfactant yet
2. Cystic Fibrosis = genetic defect causes problems with Cl- transporters, lack of secretion of surfactant
12
New cards
What causes the increase in respiratory rate?
* increase in blood PH
* lack of O2 does NOT cause increase in respiratory rate, is regulated based on PH
* lack of O2 does NOT cause increase in respiratory rate, is regulated based on PH
13
New cards
If blood pH is too high, then your body will compensate for this by breathing 1________ to retain C02 to convert it to 2__________ HCO3- and 3__________H+.
1. less
2. more
3. more
14
New cards
If blood pH is too high, then your body will compensate for this by breathing 1________ to retain 2_______ .
1. less
2. CO2
15
New cards
The difference between the tidal volume and vital capacity of your lungs is called:
reserve volume
16
New cards
Lung stretch receptors 1_______I motor neurons and 2_________E motor neurons.
1. inhibit
2. excite
17
New cards
If blood pH is high, then 1_____needs to be retained in order to produce more 2____________ because it dissociates to produce 3__________.
1. CO2
2. H2CO3
3. HCO3- and H+
18
New cards
During 1_______, a bolus of food stimulates sensory neurons. Interneurons then activate motor neurons which 2________in the esophagus behind the bolus and 3________ in the esophagus in front of the bolus.
1. Peristalsis
2. stimulate contractions
3. stimulate relaxation
19
New cards
Which of the following is not a cell type in the gastric glands?
a. Mucous cell
b. Parietal cell
c. Chief cell
d. Submucosa cell
e. All of the above are cells in gastric glands
\
a. Mucous cell
b. Parietal cell
c. Chief cell
d. Submucosa cell
e. All of the above are cells in gastric glands
\
d. Submucosa Cell
20
New cards
Pacemaker activity that coordinates 1_________ of the intestines is generated by 2____________.
1. Segmentation
2. Interstitial Cells of Cajal
21
New cards
________ is the product of chief cells that is an active enzyme that degrades ingested proteins.
Pepsin
22
New cards
What are some reasons that jaundice causes yellow skin colorization?
1. low functioning liver
2. gall bladder blockage
3. bile duct blockage
4. excess bilirubin in the blood
23
New cards
Glucagon and insulin are secreted from the 1_______ located in the 2_________.
1. Islet of Langerhans
2. Pancreas
24
New cards
If blood glucose levels fall, alpha cells release 1_________, but, if blood glucose levels rise, beta cells release 2__________.
1. glucagon
2. Insulin
25
New cards
Presence of fat and protein in the duodenum causes secretion of _______; which results in the secretion of pancreatic juices.
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
26
New cards
__________ digests starches to maltose and short chains of glucose molecules.
Amylase
27
New cards
The “filtration barrier” of the glomerular capsule prevents ______ from being filtered from the blood:
Red Blood Cells/ Protein
28
New cards
Anti-diuretic hormone is secreted from the 1______________ and causes 2__________.
1. Pituitary
2. Water retention
29
New cards
Aldosterone is secreted from the 1______________ and causes 2__________.
1. Adrenal Cortex
2. Sodium reabsorption
30
New cards
What is the body’s response to low blood pressure (kidney unit)
* Increased renin secretion
* Increased angiotensinogen conversion
* Increased aldosterone secretion
* Decreased urine production
* Increased angiotensinogen conversion
* Increased aldosterone secretion
* Decreased urine production
31
New cards
The general mechanism of diuretic drugs is to 1_________________, resulting in 2______________.
1. block solute reabsorption
2. increased urine volume
32
New cards
Which of the following is a major difference between the kidney cortex and kidney medulla?
1. blood flows in the cortex; urine collects in the medulla
2. the medulla is very hypertonic compared to the cortex
3. sodium is absorbed in the medulla; water is absorbed in the cortex
4. the nephron is in the cortex, not the medulla
5. the medulla is the outer layer of the kidney; the cortex is the inner layer
1. blood flows in the cortex; urine collects in the medulla
2. the medulla is very hypertonic compared to the cortex
3. sodium is absorbed in the medulla; water is absorbed in the cortex
4. the nephron is in the cortex, not the medulla
5. the medulla is the outer layer of the kidney; the cortex is the inner layer
2. the medulla is very hypertonic compared to the cortex.
33
New cards
Diabetes Insipidus is characterized by what?
Excessive urination
34
New cards
In the kidney, the enzyme 1_____________ aids in the reabsorption of 2____________.
1. Carbonic anhydrase
2. bicarbonate
35
New cards
“GFR” is a measure of what?
filtrate produced each minute by both kidneys
36
New cards
Common drugs to treat acid secretion in the stomach act by…
a. neutralizing stomach acid (antacids)
b. blocking the H+/K+ ATPase pump
c. blocking histamine receptors (antihistamines)
d. b and c
e. all of the above
a. neutralizing stomach acid (antacids)
b. blocking the H+/K+ ATPase pump
c. blocking histamine receptors (antihistamines)
d. b and c
e. all of the above
e. all of the above
37
New cards
Match the exchange surface with the function
1. kidney glomerulus
1. lipid absorption
2. water & Na+ reabsorption
3. nutrient absorption
4. oxygen absorption
5. plasma filtration
1. kidney glomerulus
1. lipid absorption
2. water & Na+ reabsorption
3. nutrient absorption
4. oxygen absorption
5. plasma filtration
e. plasma filtration
38
New cards
Match the exchange surface with the function
1. vasa recta
1. lipid absorption
2. water & Na+ reabsorption
3. nutrient absorption
4. oxygen absorption
5. plasma filtration
1. vasa recta
1. lipid absorption
2. water & Na+ reabsorption
3. nutrient absorption
4. oxygen absorption
5. plasma filtration
b. water & Na+ reabsorption
39
New cards
Match the exchange surface with the function
1. villus
1. lipid absorption
2. water & Na+ reabsorption
3. nutrient absorption
4. oxygen absorption
5. plasma filtration
1. villus
1. lipid absorption
2. water & Na+ reabsorption
3. nutrient absorption
4. oxygen absorption
5. plasma filtration
c. nutrient absorption
40
New cards
Match the exchange surface with the function
1. lacteal
1. lipid absorption
2. water & Na+ reabsorption
3. nutrient absorption
4. oxygen absorption
5. plasma filtration
1. lacteal
1. lipid absorption
2. water & Na+ reabsorption
3. nutrient absorption
4. oxygen absorption
5. plasma filtration
a. lipid absorption
41
New cards
Match the exchange surface with the function
1. alveoules
1. lipid absorption
2. water & Na+ reabsorption
3. nutrient absorption
4. oxygen absorption
5. plasma filtration
1. alveoules
1. lipid absorption
2. water & Na+ reabsorption
3. nutrient absorption
4. oxygen absorption
5. plasma filtration
d. oxygen absorption
42
New cards
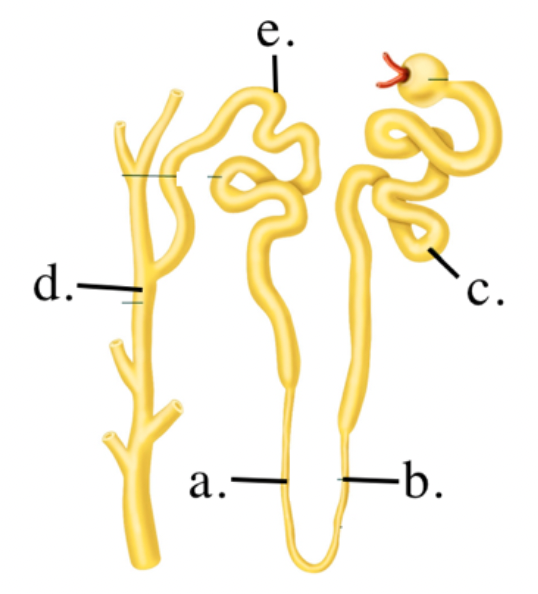
Identify the different parts on the diagram
a. ascending limb of loop of Henle
b. descending limb of loop of Henle
c. proximal convoluted tubule
d. collecting duct
e. distal tubule
b. descending limb of loop of Henle
c. proximal convoluted tubule
d. collecting duct
e. distal tubule
43
New cards
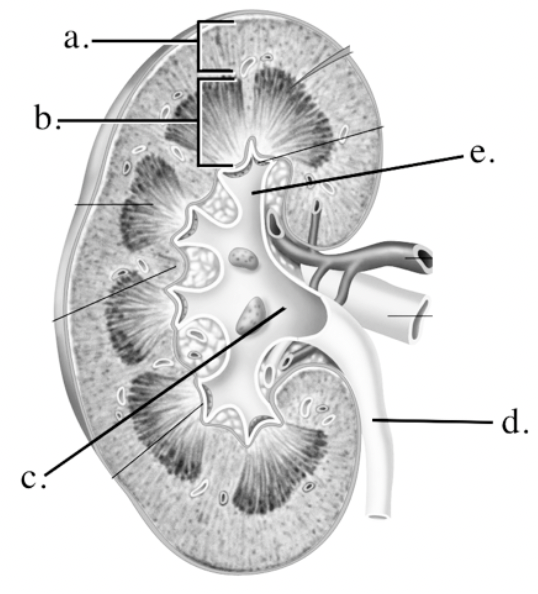
Identify the different parts of the kidney
a. cortex
b. medulla
c. renal pelvis
d. ureter
e. major calyx
b. medulla
c. renal pelvis
d. ureter
e. major calyx
44
New cards
If a person drinks too much water, how is blood volume kept more or less constant?
ADH levels will fall, resulting in less re-uptake of water from the urine
45
New cards
How can you distinguish diabetes mellitus from diabetes insipidus?
* an increase in glucose in urine of diabetes mellitus
* could be lacking a specific hormone (insulin or ADH)
* could be lacking a specific hormone (insulin or ADH)
46
New cards
What parts of the nephron contribute to sodium reabsorption?
* proximal convoluted tubule
* loop of Henle
* collecting duct
* NOT glomerulus
* loop of Henle
* collecting duct
* NOT glomerulus
47
New cards
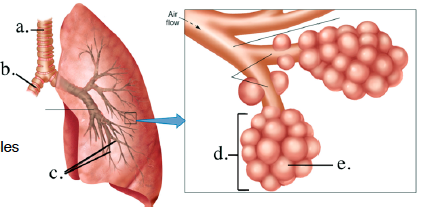
Label the respiratory structures
a. Trachea
b. bronchus
c. terminal bronchioles
d. alveolar sack
e. alveola
b. bronchus
c. terminal bronchioles
d. alveolar sack
e. alveola
48
New cards
Which enzyme triggers the release of most of the enzymes secreted from the pancreas?
enterokinase
49
New cards
normal GFR is \~200L/day, when normal plasma volume is typically 3 L. About how much filtrate volume is reabsorbed?
99% of filtrate
50
New cards
What is the "gateway" that regulates gastric emptying into the intestine?
pyloric sphincter
51
New cards
You attempt to treat two patients with diabetes mellitus, by transfusing blood between them (so that they share a blood supply). What outcomes would indicate that one has Type I diabetes and the other has Type II diabetes?
the blood transfusion normalizes plasma glucose levels in one patient but not the other.
52
New cards
What is the major cause of stomach ulcer?
Helicobacter pylori
53
New cards
What occurs during respiration?
* intrapleural pressure drops
* size of thoracic cavity increases
* intrapulmonary pressure drops
* diaphragm contracts and flattens
* size of thoracic cavity increases
* intrapulmonary pressure drops
* diaphragm contracts and flattens
54
New cards
What is angiotensin’s impact on…
1. arterioles
2. adrenal cortex
3. blood stream
4. pancreas
1. arterioles
2. adrenal cortex
3. blood stream
4. pancreas
1. arterioles → contraction
2. adrenal cortex → decreased Na+ in urine
3. blood stream → increased BP
4. pancreas → no impact
55
New cards
What is CCK’s impact on…
1. arterioles
2. adrenal cortex
3. blood stream
4. pancreas
1. arterioles
2. adrenal cortex
3. blood stream
4. pancreas
1. arterioles → no impact
2. adrenal cortex → no impact
3. blood stream → gall bladder contraction
4. pancreas → enzyme secretion
56
New cards
Why would a perforation of the chest wall cause a problem with breathing?
* lung would collapse, making it difficult to reinflate
* equalizing air pressure b/w chest cavity and atmosphere would prevent breathing
* equalizing air pressure b/w chest cavity and atmosphere would prevent breathing
57
New cards
What is blue light therapy a treatment for?
inability to conjugate bilirubin (treats infantile jaundice)
58
New cards
What does spraying surfactant into the lungs treat?
elevated surface tension
59
New cards
What is a treatment for a patent oval foramen?
heart surgery
60
New cards
What is a treatment for central diabetes insipidus?
ADH injections
61
New cards
Match the exchange surface with the compound(s) that move across that surface.
Answers may be used once, more than once or not at all.
1. placenta
2. villi
3. collecting duct
4. gastric pits
5. alveoli
1. CO2
2. fatty acids
3. H20
4. H+
5. bilirubin
Answers may be used once, more than once or not at all.
1. placenta
2. villi
3. collecting duct
4. gastric pits
5. alveoli
1. CO2
2. fatty acids
3. H20
4. H+
5. bilirubin
1. placenta → CO2
2. villi → fatty acids
3. collecting duct → H20
4. gastric pits → H+ (to make HCl)
5. alveoli → CO2
62
New cards
The enzyme 1_____ aids in the reabsorption of 2_____ from the urine.
1. Renin
2. Sodium
63
New cards
What is the main function of myoglobin?
Store oxygen to be used in muscles
64
New cards
If the chest wall is punctured and air enters the intrapleural space, the lung may collapse. This condition is called what?
pneumothorax
65
New cards
The primary metabolic waste that is ultimately eliminated via the urine is what?
Nitrogen/Ammonia
66
New cards
After a meal, blood glucose levels increase and stimulate the secretion of which hormone?
Insulin
67
New cards
A subject is instructed to breath in and out of a closed volume with CO2 filter attached, so that she is re-breathing the same volume of air but expired CO2 is removed. After a few minutes what happens?
she breathes at a normal rate until the air runs out of oxygen (dies)
68
New cards
Why is glucagon prescribed to treat hypoglycemia?
It stimulated gluconeogenesis in the liver to put glucose back into the blood and increase glucose levels.
69
New cards
What is the trigger for insulin to release from pancreatic cells?
Elevated ATP levels
70
New cards
In the ascending limb of the loop of Henle 1_____ occurs, so that 2_____ can occur in the descending limb.
1. Active transport of Na+
2. Osmosis into the medulla
71
New cards
Atmospheric PO2 is 150 mmHg; PO2 in the pulmonary artery is 40 mmHg. If you are suddenly exposed to a low oxygen environment with a PO2 of only 30 mmHg, what would happen?
Breathing rate would not change because your body is unaware of changes in O2 levels, only CO2 via the measurement of PH.
72
New cards
What is a major difference between peristalsis and segmentation?
Peristalsis is a reflex responds to distension by food and segmentation is controlled via pacemakers cells (ICC)
73
New cards
Why is it that an acetylcholine agonist (e.g. muscarine) could stimulate both acid and bicarbonate secretion into the gastrointestinal tract?
Because parasympathetic nerve activation induces both gastric and pancreatic secretion.
74
New cards
The apneustic center promotes 1_____, while the pneumotaxic center promotes 2_____.
1. inspiration
1. expiration
75
New cards
The "Renal Plasma Threshold" of glucose is the level at which…
a. more glucose is filtered by the kidney from the plasma than can be reabsorbed
b. glucose appears in the urine
c. glucose transporters in the proximal tubule become saturated
d. a potential indicator of diabetes mellitus (Type I or Type II)
e. all of the above
a. more glucose is filtered by the kidney from the plasma than can be reabsorbed
b. glucose appears in the urine
c. glucose transporters in the proximal tubule become saturated
d. a potential indicator of diabetes mellitus (Type I or Type II)
e. all of the above
e. All of the above
76
New cards
What is NOT stored in some tissue reservoir of the body for use or recycling when it is not being breathed in or eaten?
Sodium
77
New cards
How does Angiotensin II help increase blood pressure (2 ways)?
vasoconstriction and sodium reabsorption
78
New cards
When acting on its target tissues, what is the effect of insulin?
insertion of glucose transporters on the plasma membrane
79
New cards
Which of the following factors generally increases respiratory rate and depth?
a. increase in blood bicarbonate
b. breathing into a sealed container
c. decrease in blood CO2
d. decrease in blood pH
e. decrease in O2 but not CO2 levels in the environment
a. increase in blood bicarbonate
b. breathing into a sealed container
c. decrease in blood CO2
d. decrease in blood pH
e. decrease in O2 but not CO2 levels in the environment
d. decrease in blood PH
80
New cards
In hemoglobin, the 1_____ at the center of heme binds 2_____.
1. Iron
2. Oxygen
81
New cards
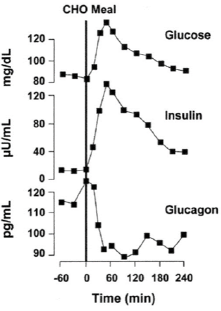
The figure represents glucose, insulin, and glucagon levels in the blood of a healthy subject after a meal rich in carbohydrates (CHO meal). Which statement does NOT describe what is happening after this meal?
a. alpha cells of the pancreas release glucagon
b. after the meal, blood glucose level rises and beta
cells of the pancreas release insulin into the blood
c. liver takes up glucose and stores it as glycogen
d. insulin increases glucose uptake in muscles and adipocytes
e. beta cells and acinar cells of the pancreas are
activated by the vagus nerve to produce gastric juices and insulin
a. alpha cells of the pancreas release glucagon
b. after the meal, blood glucose level rises and beta
cells of the pancreas release insulin into the blood
c. liver takes up glucose and stores it as glycogen
d. insulin increases glucose uptake in muscles and adipocytes
e. beta cells and acinar cells of the pancreas are
activated by the vagus nerve to produce gastric juices and insulin
a. alpha cells of the pancreas release glucagon
82
New cards
Sensory neurons do NOT detect changes in one of these physiological variables of the plasma. Which one is not well-regulated?
a. glucose
b. osmotic concentration
c. plasma pH
d. blood pressure
e. bilirubin
a. glucose
b. osmotic concentration
c. plasma pH
d. blood pressure
e. bilirubin
e. bilirubin
83
New cards
The relatively toxic metabolite 1_____ is derived from 2_____ and secreted in the 3_____.
1. Urea
2. Amino Acids
3. Kidneys
84
New cards
Which of the following organs does NOT secrete digestion juices or enzymes?
a. kidneys
b. liver
c. stomach
d. pancreas
e. all of the above secrete either digestion juices or enzymes
a. kidneys
b. liver
c. stomach
d. pancreas
e. all of the above secrete either digestion juices or enzymes
a. kidneys
85
New cards
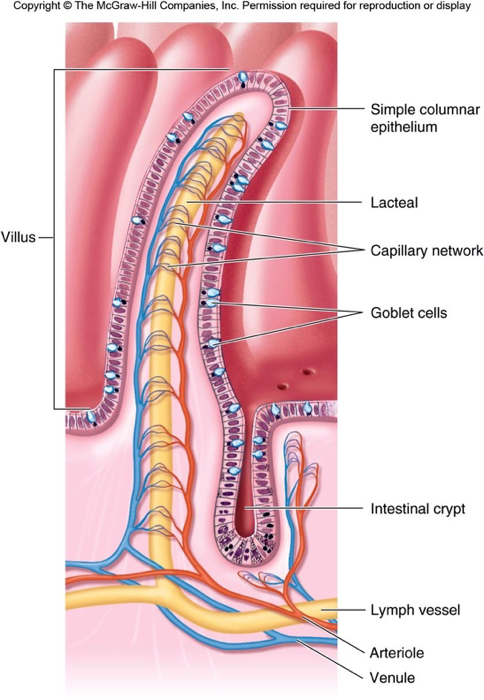
Parts of the villi
86
New cards
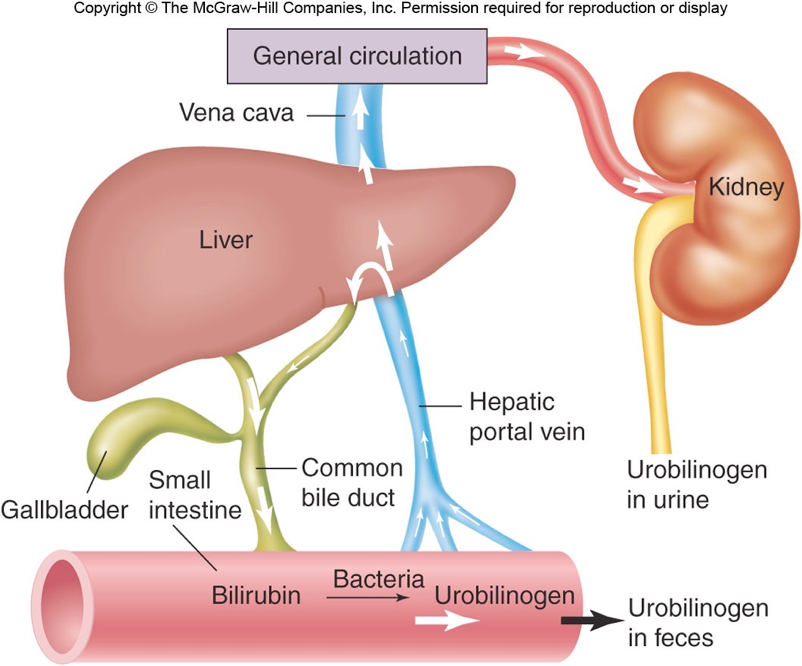
Enterohepatic Circulation