Chapter #8- Joints
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Joints
Areas where two or more bones join together
aka- articulations
function of joints
give skeleton mobility and hold skeleton together
2 classifications of joints
structure and function
3 structural classifications of joints
1. Fibrous
2. Cartilaginous
3. Synovial
3 functional classifications of joints
synarthroses, amphiarthroses, diarthroses
3 types of fibrous joints
sutures, syndesmoses, gomphoses
Syntharoses joints
immovable joints
amiphiarthroses joints
slightly movable joints
Diarthroses
freely movable joints
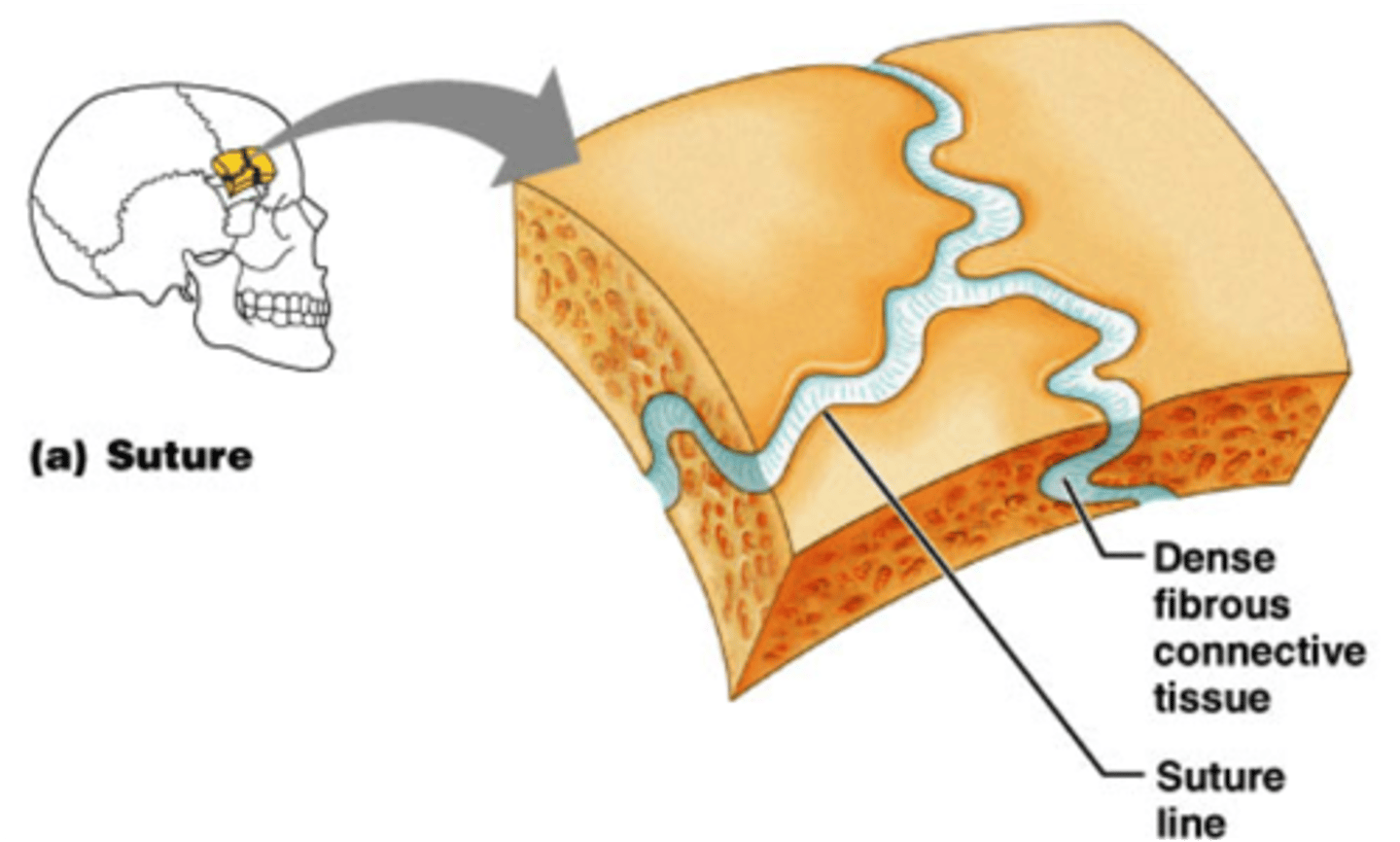
Fibrous Joints: Sutures
Rigid, interlocking joints
Immovable joints for protection of brain
Contain short connective tissue fibers
Allow for growth during youth
In middle age, sutures ossify and fuse
Called Synostoses
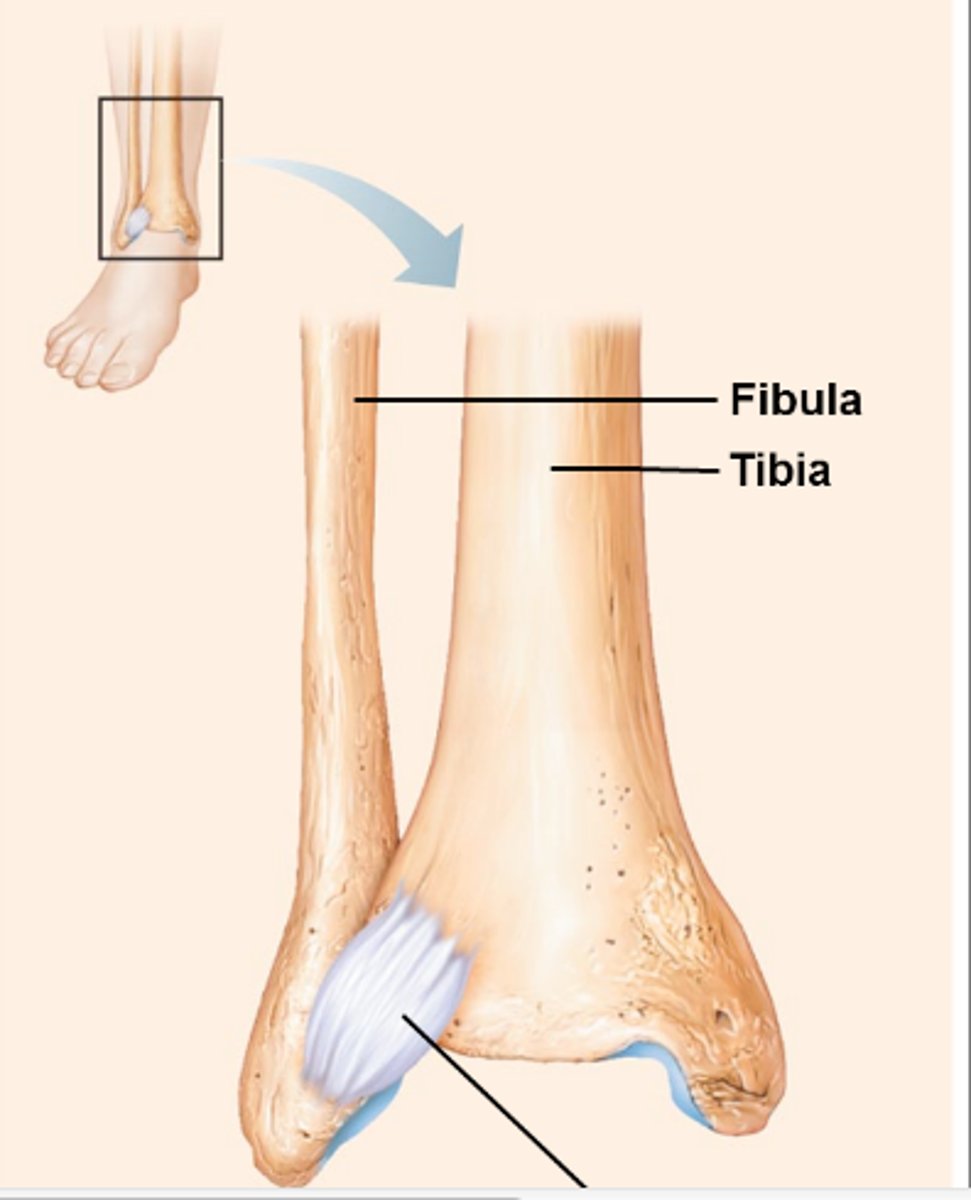
fibrous joints: syndesmoses
Bones connected by ligaments (bands of fibrous tissue)
Movement varies from immovable to slightly movable
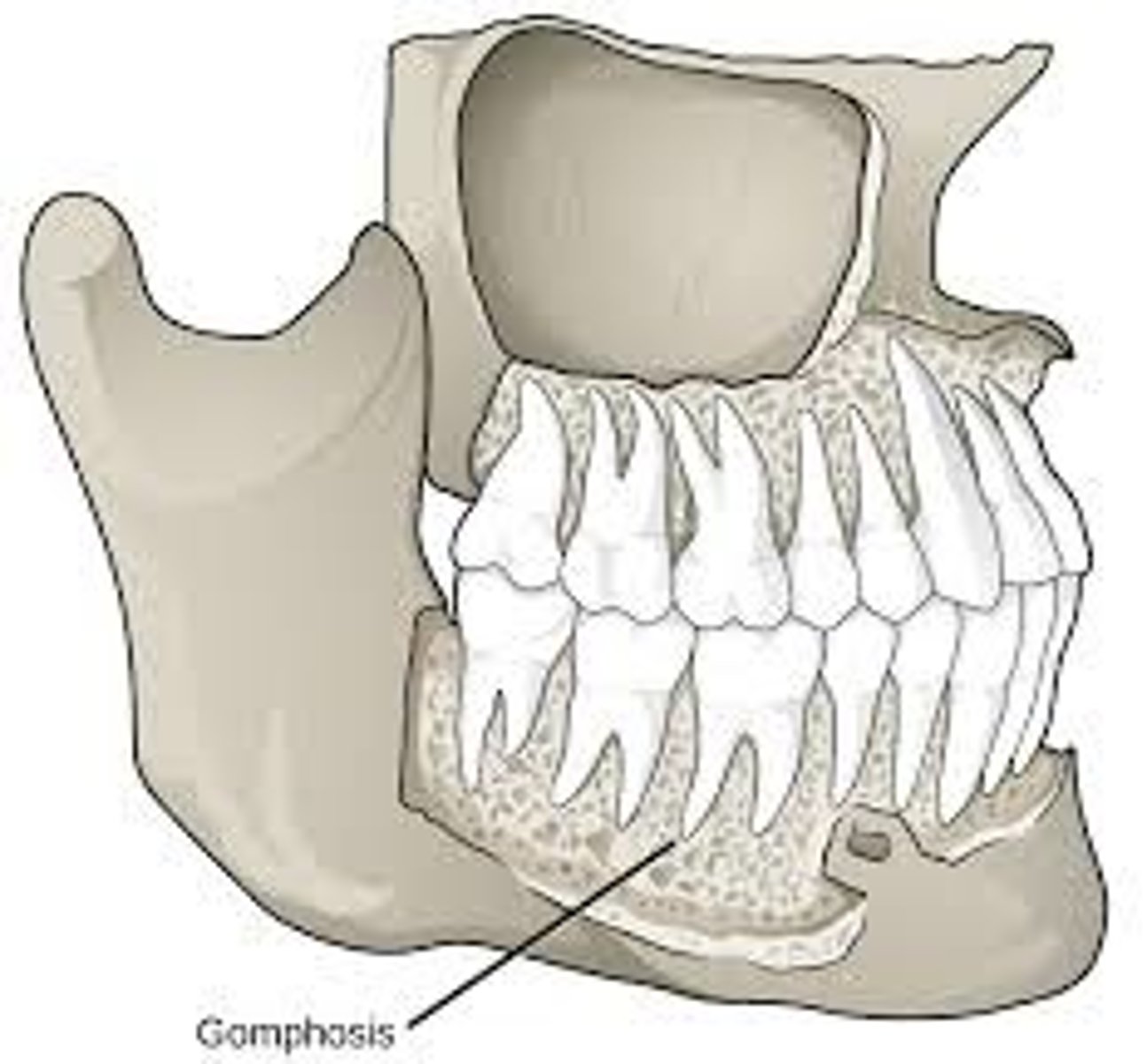
Fibrous Joint: Gomphoses
attachment of a tooth to its socket
cartilaginous joints
allow only slight movement and consist of bones connected entirely by cartilage
2 types of cartilaginous joints
synchondroses and symphyses
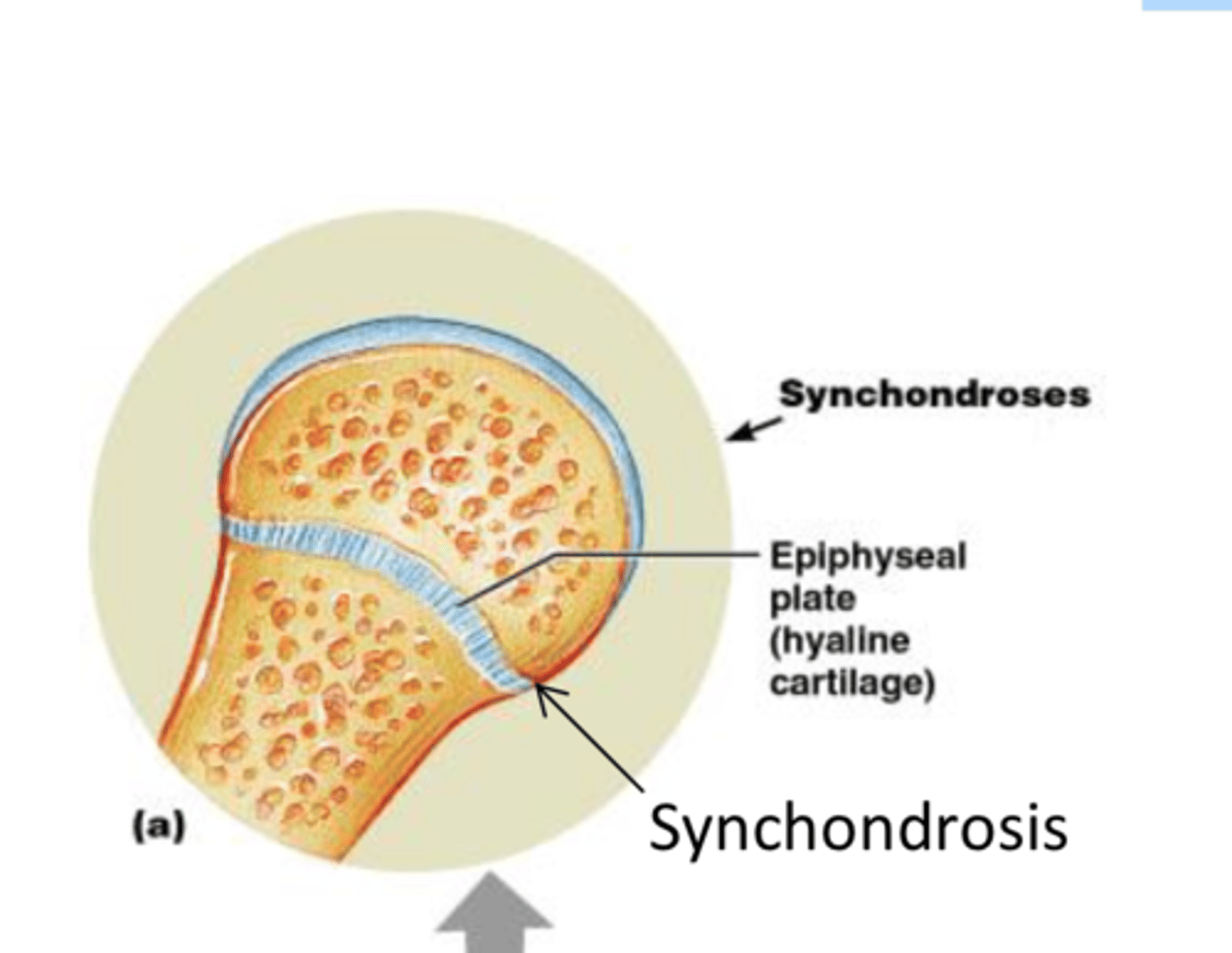
Cartilaginous Joints: Synchondroses
A bar or plate of hyaline cartilage unites the bones
All are synarthrotic
EX: epiphyseal plate, joint between rib and sternum
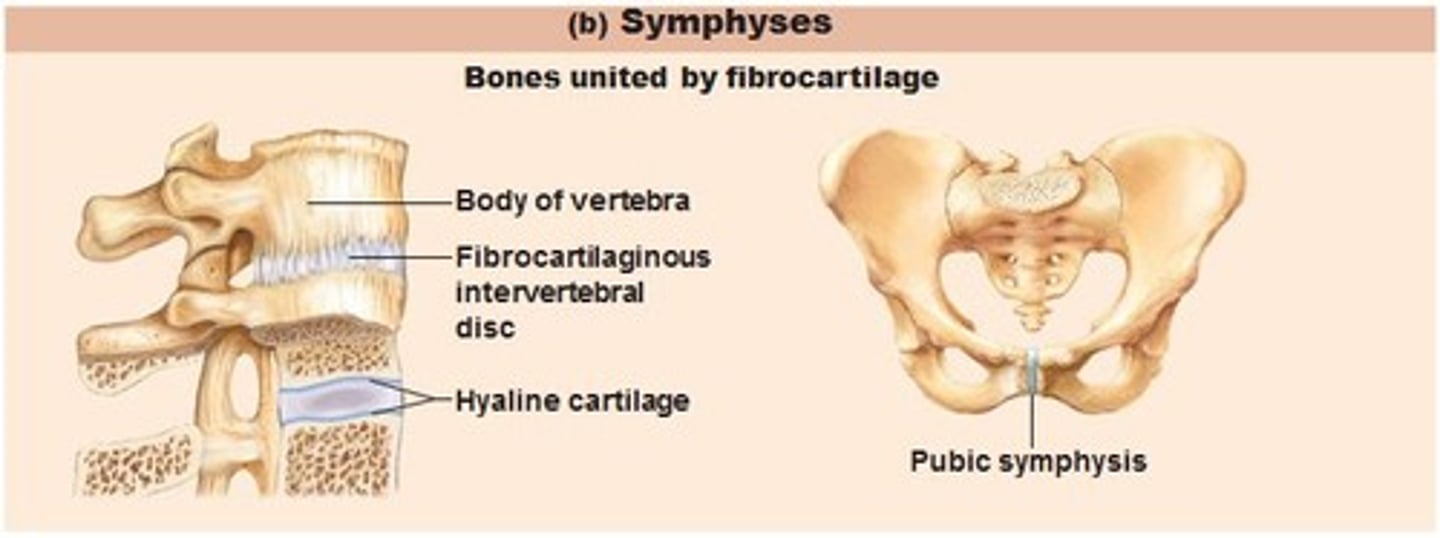
Cartilaginous Joints: Symphyses
Fibrocartilage unites bone
Hyaline cartilage present as articular cartilage
Strong, flexible amphiarthroses
EX: intervertebral joints, pubic symphysis
synovial joints
freely movable joints
-bones that separated by fluid-filled joint cavities
-all are diarrhetic
-include almost all limb joints
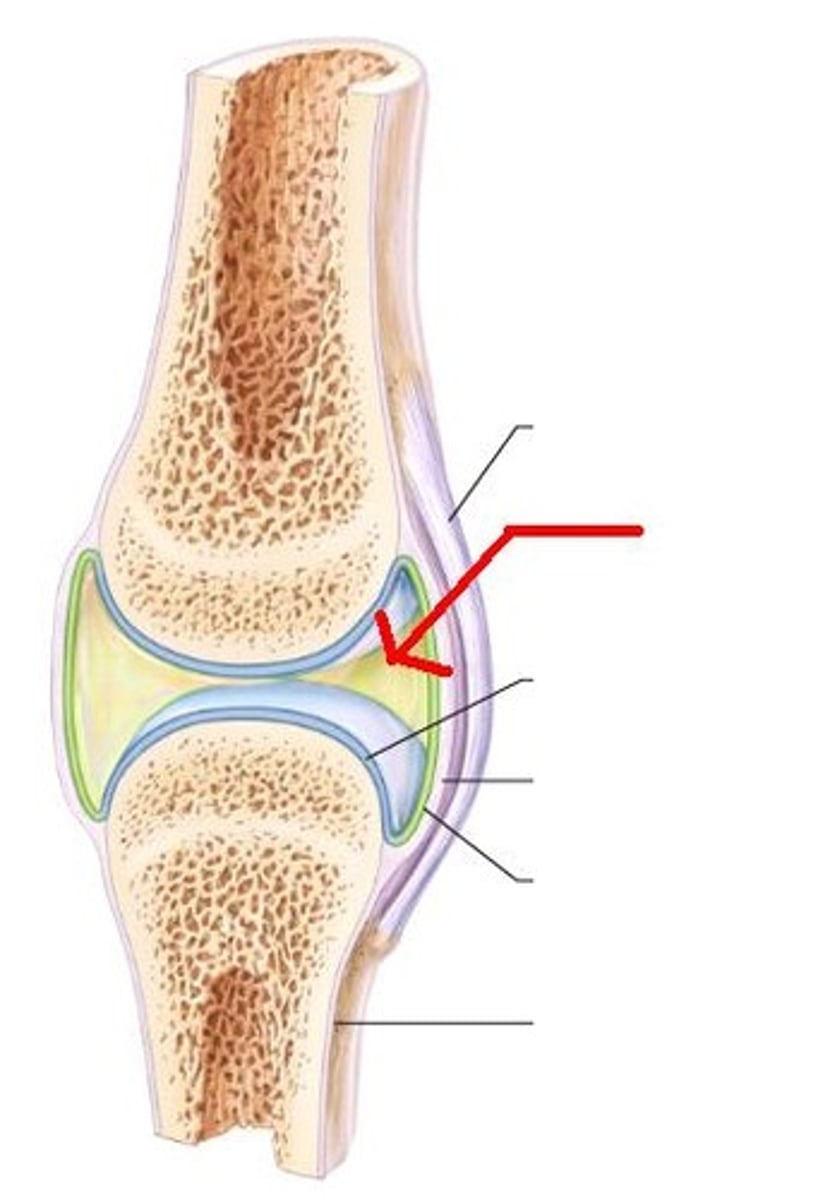
5 characteristics of synovial joints
1. have six general features
2. have bursae and tendon sheaths
3. stability is influenced by three factors
4. allow several movements
5. classified into six different types
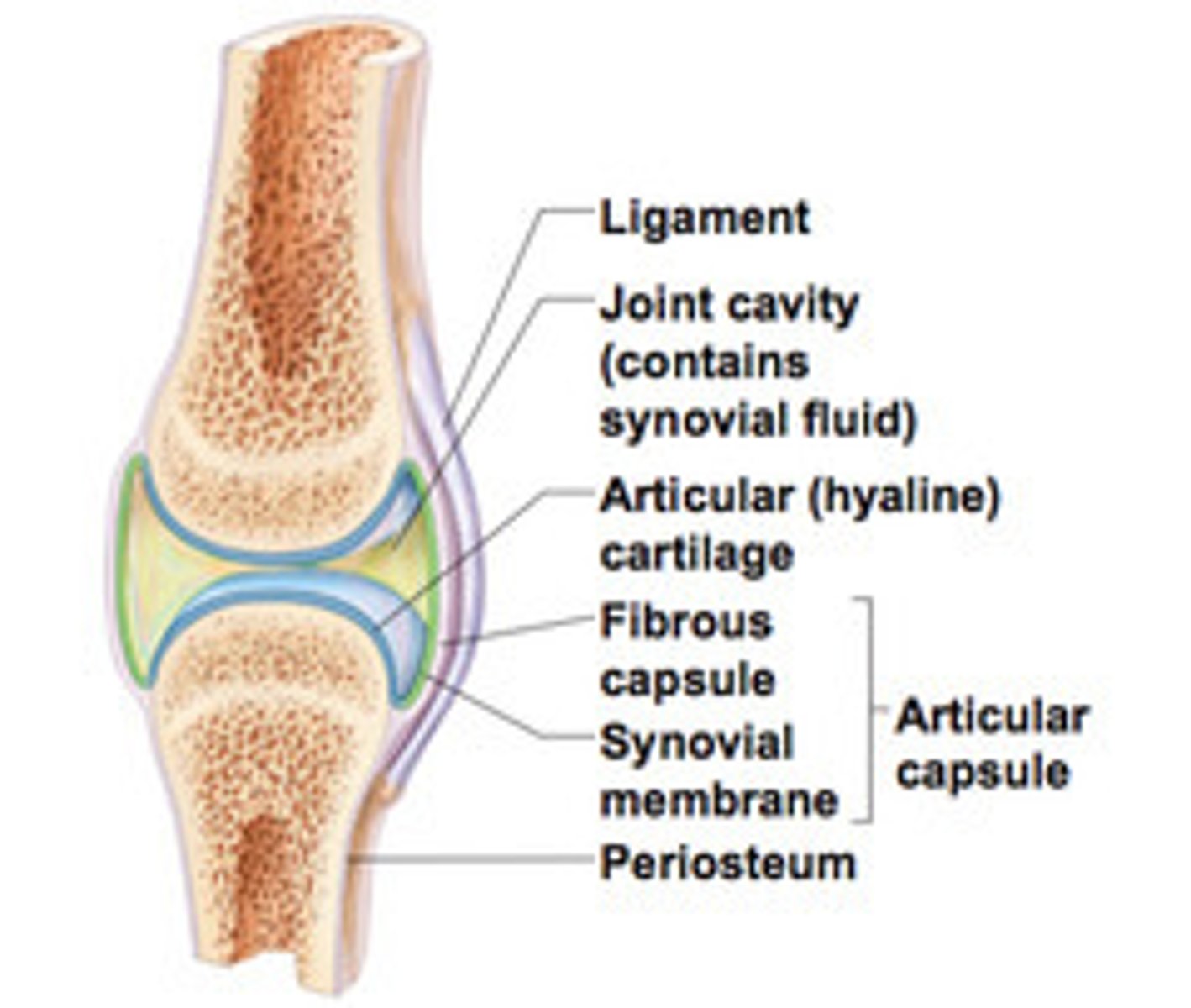
6 features of synovial joints
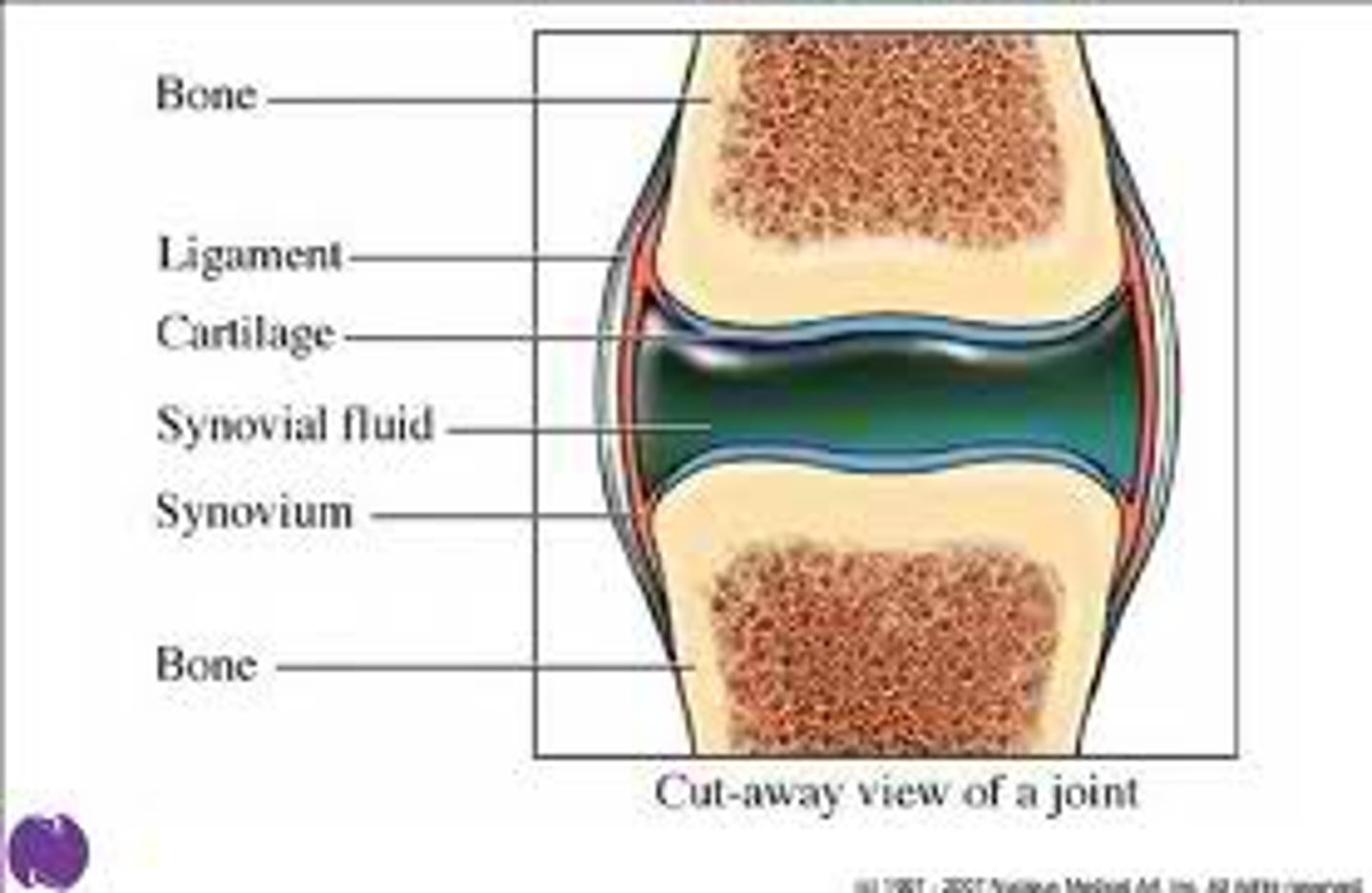
1. articular cartilage
2. joint cavity
3. articular capsule
4. synovial fluid
5. reinforcing ligaments
6. nerves and blood vessels
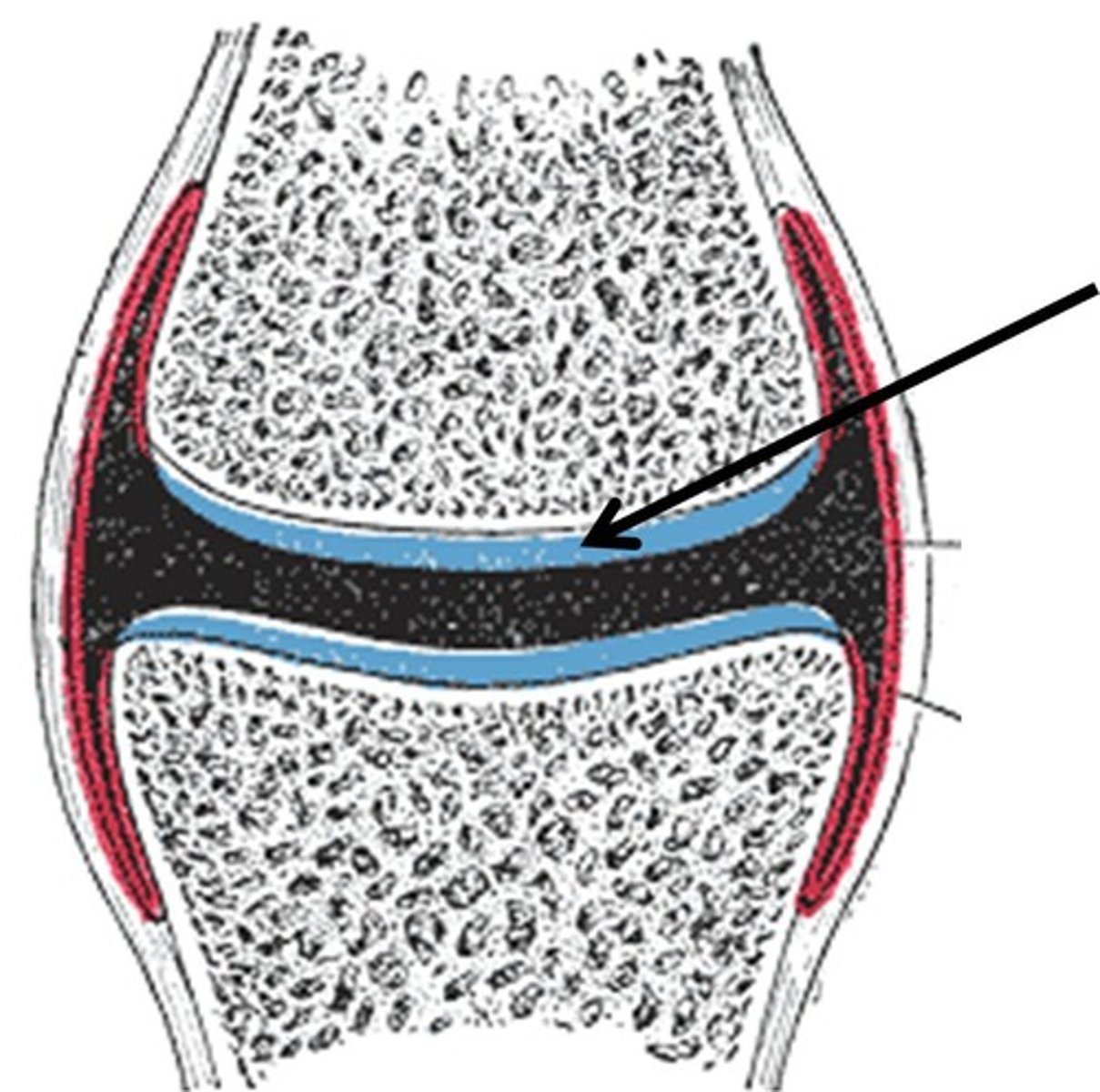
articular cartilage
Hyaline cartilage attached to articular bone surfaces
prevents crushing of bones
joint cavity
the space between two connecting bones
fluid-filled space that is unique to the synovial joint
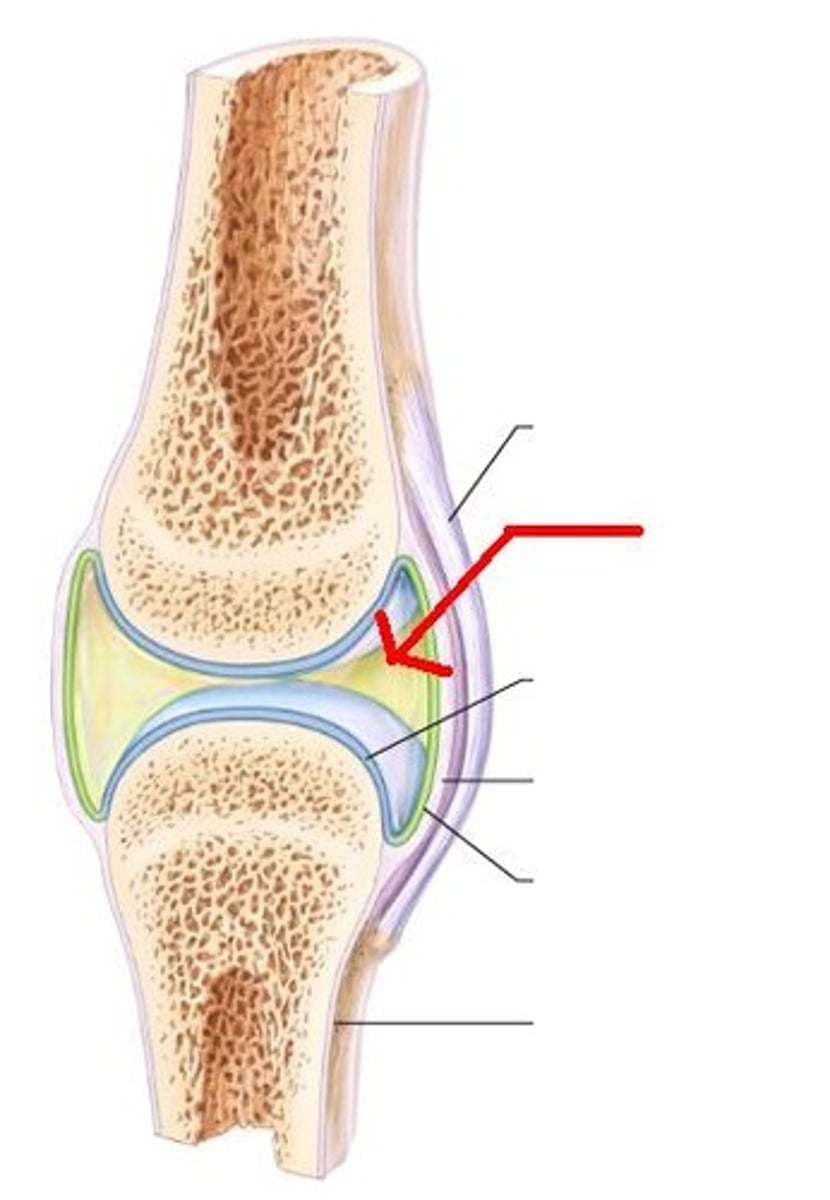
articular capsule
2 layers thick
-external fibrous layer: dense irregular connective tissue
-inner synovial membrane: loose connective tissue that makes synovial fluid
synovial fluid
Viscous, slippery filtrate of plasma and hyaluronic acid
-Lubricates and nourishes articular cartilage
-Contains phagocytic cells to remove microbes and debris
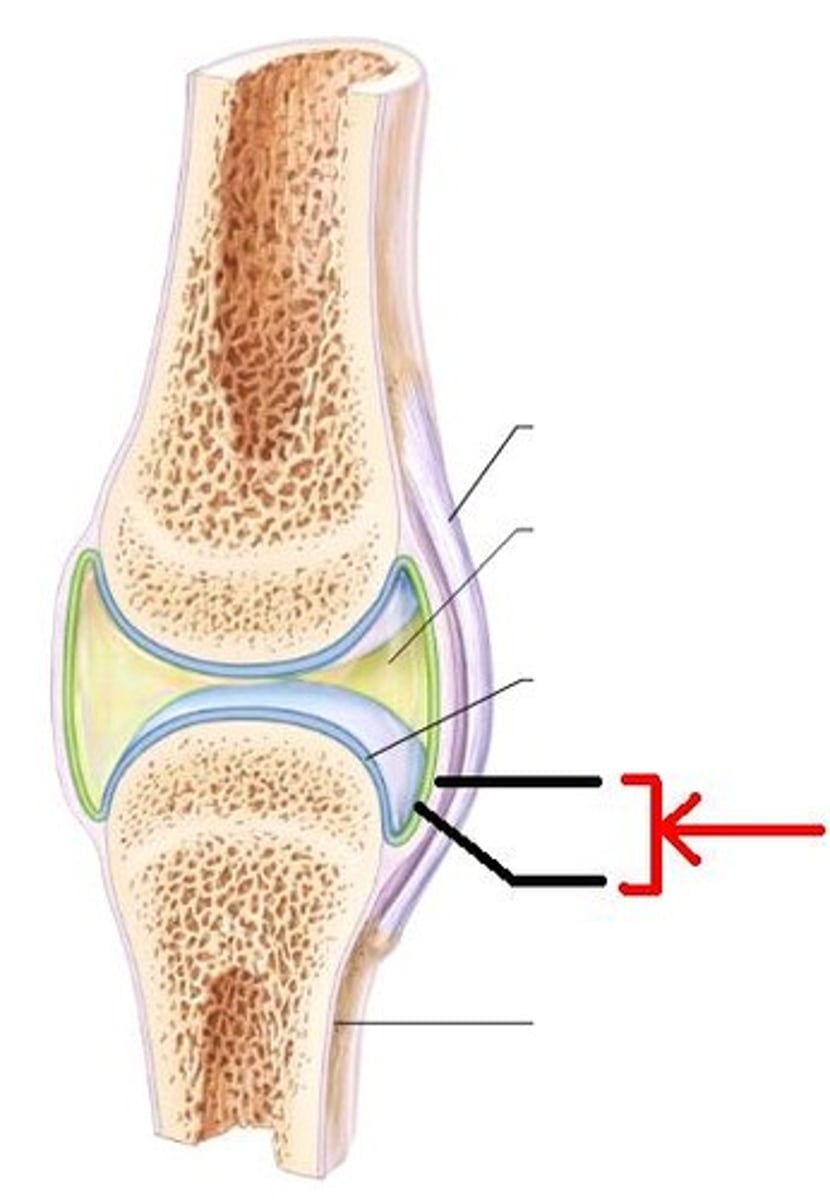
3 types of reinforcing ligaments
capsular, extracapsular, intracapsular
capsular
thickened part of fibrous layer of synovial joints
extracapsular ligaments
outside the capsule
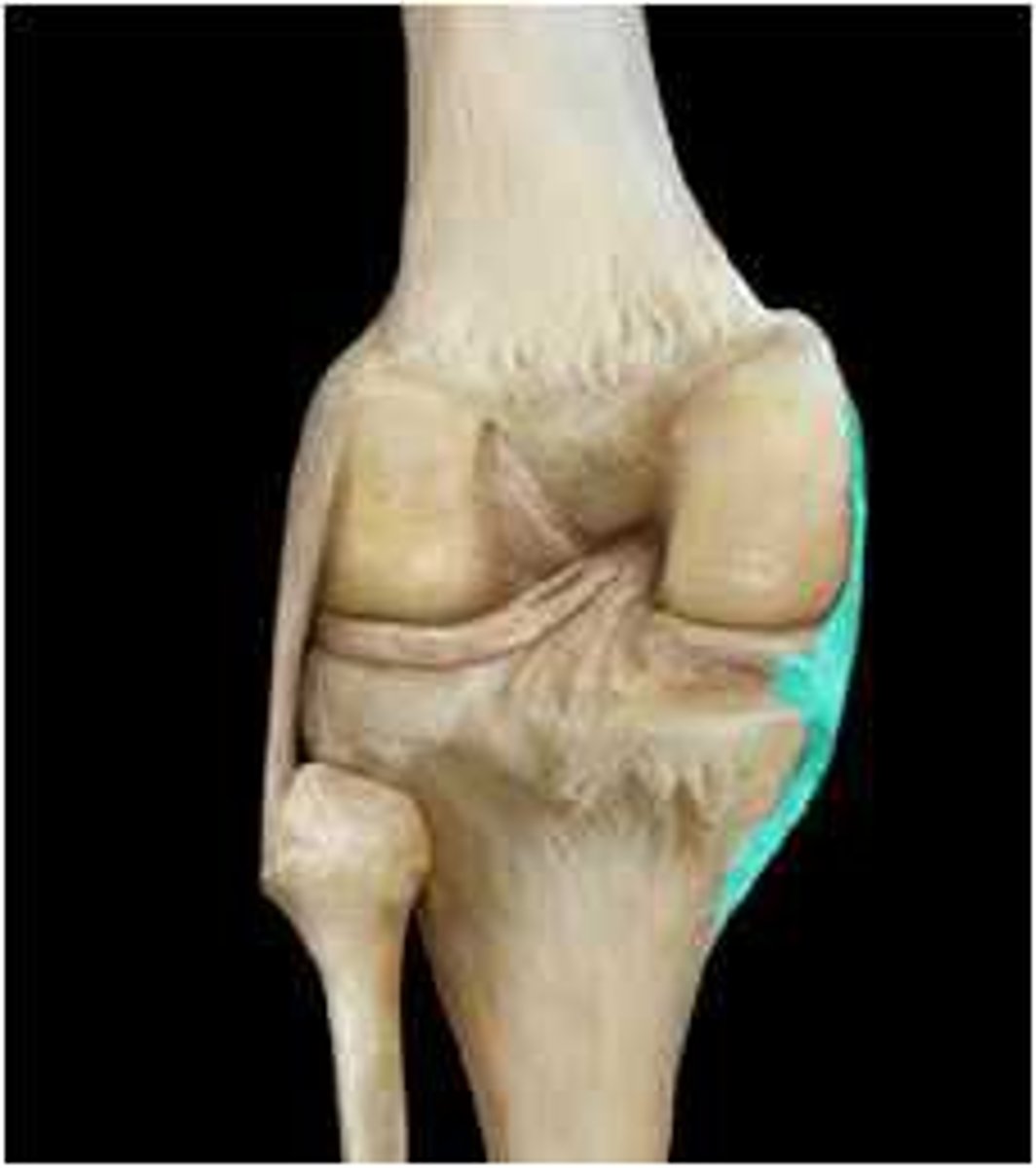
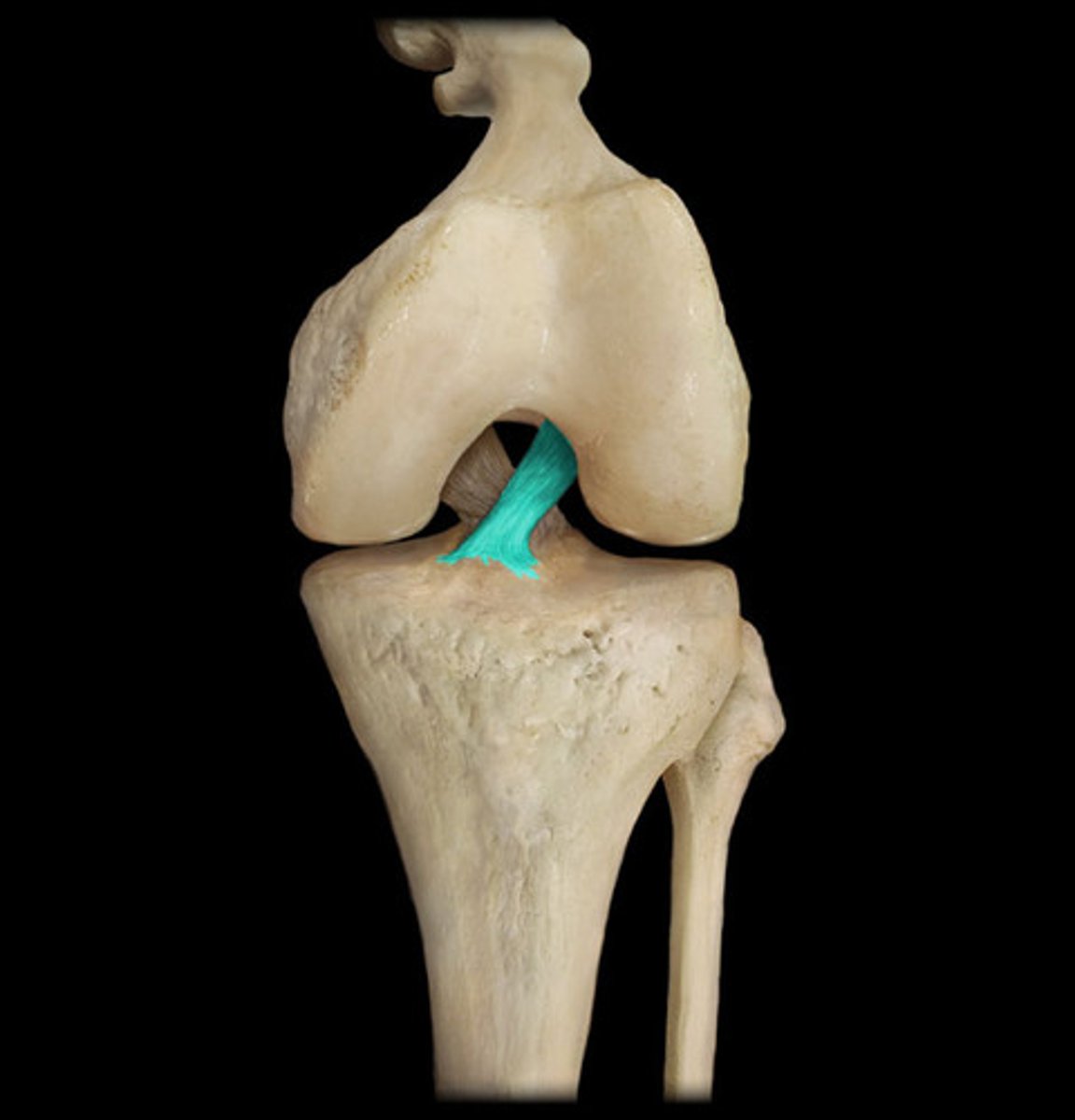
intracapsular ligaments
stabilizing ligaments located inside joint capsule
nerve and blood vessels
-detect pain; monitor joint position and stretch
-capillary beds supply filtrate for synovial fluid
Fats pads
cushioning between fibrous layer of capsule and synovial membrane or bone
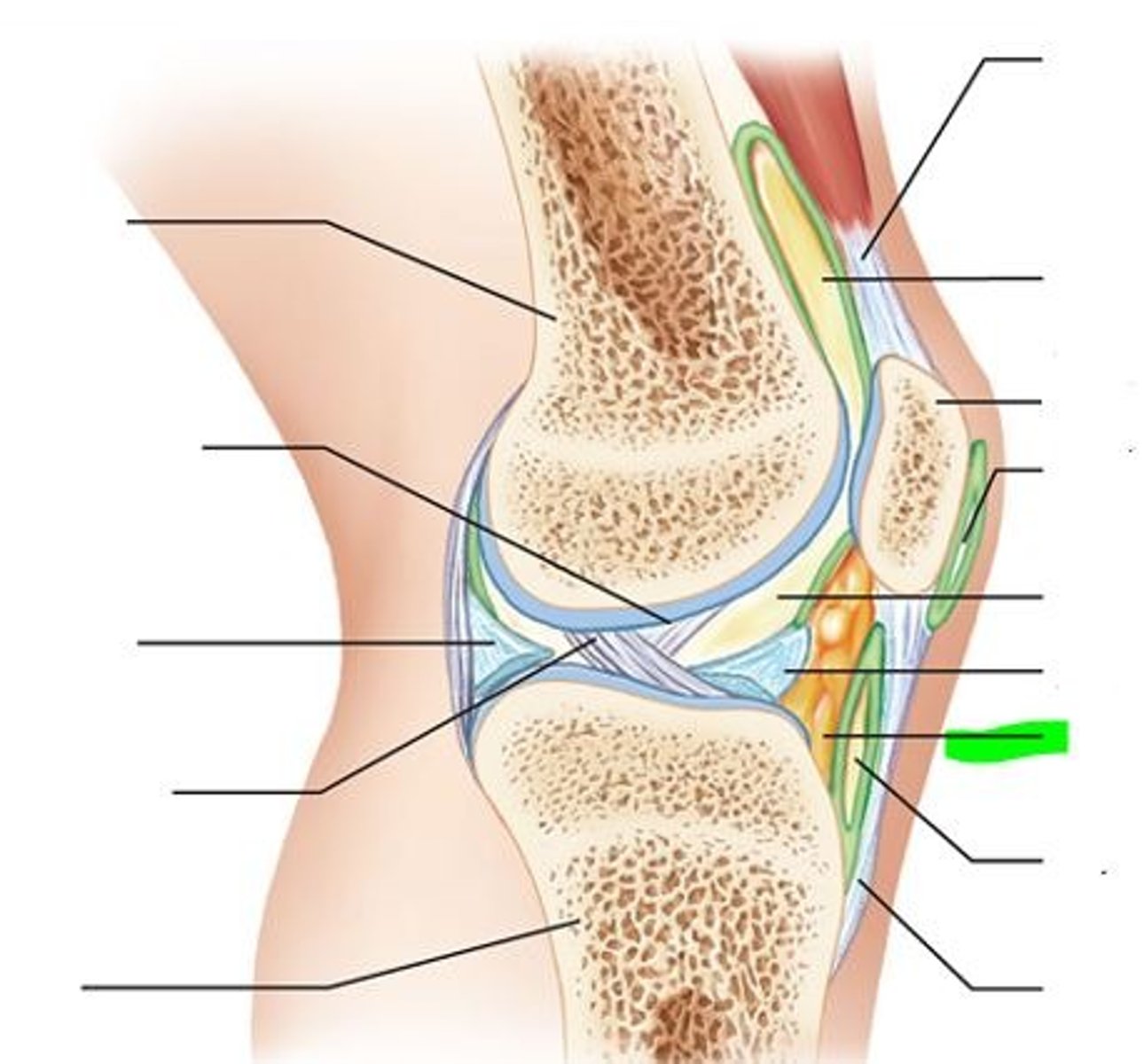
articular discs
fibrocartilage that separates articular surfaces of bones and minimizes wear and tear
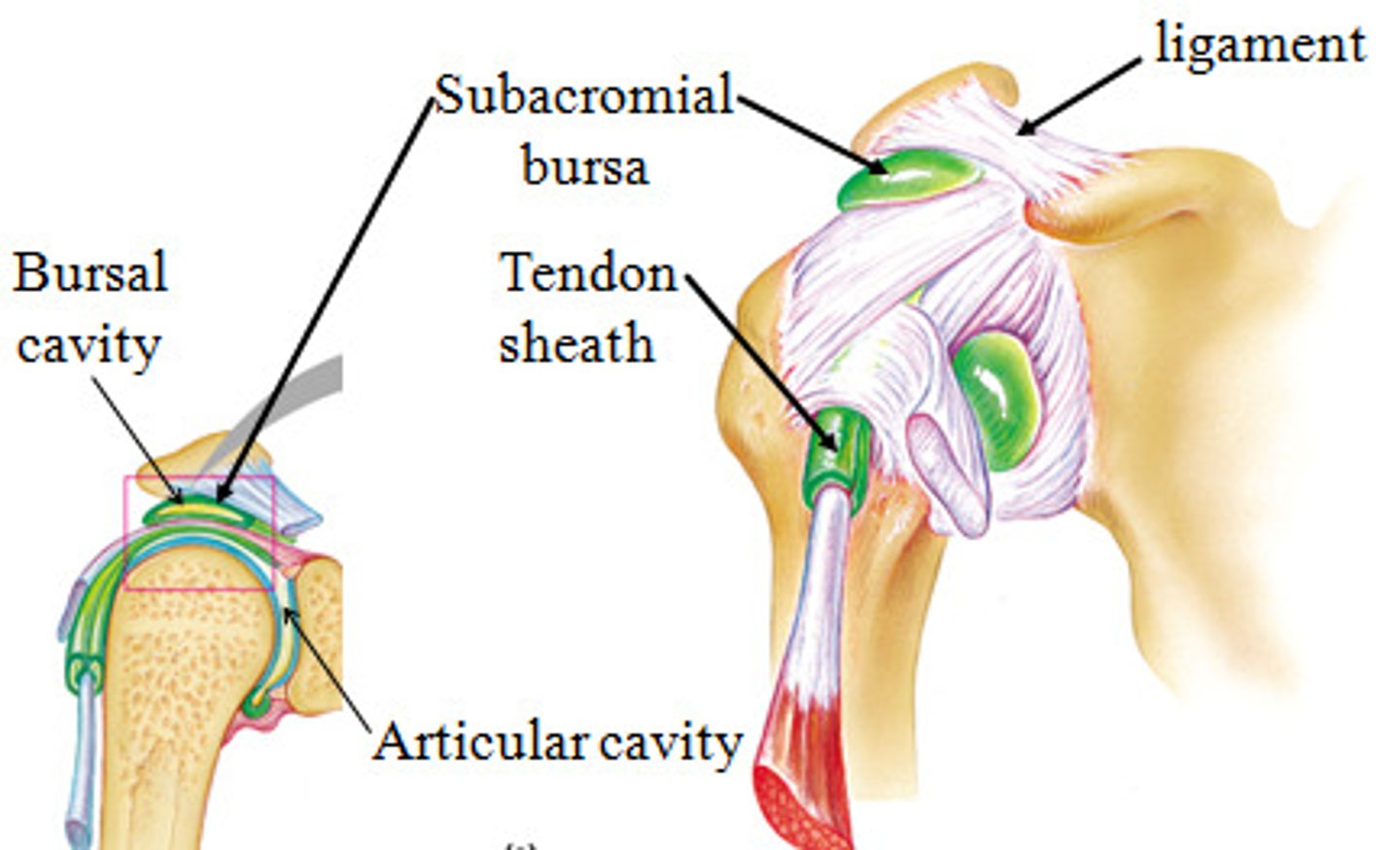
Bursae
reduce friction where ligaments, muscle, skin, tendons or bones rub together
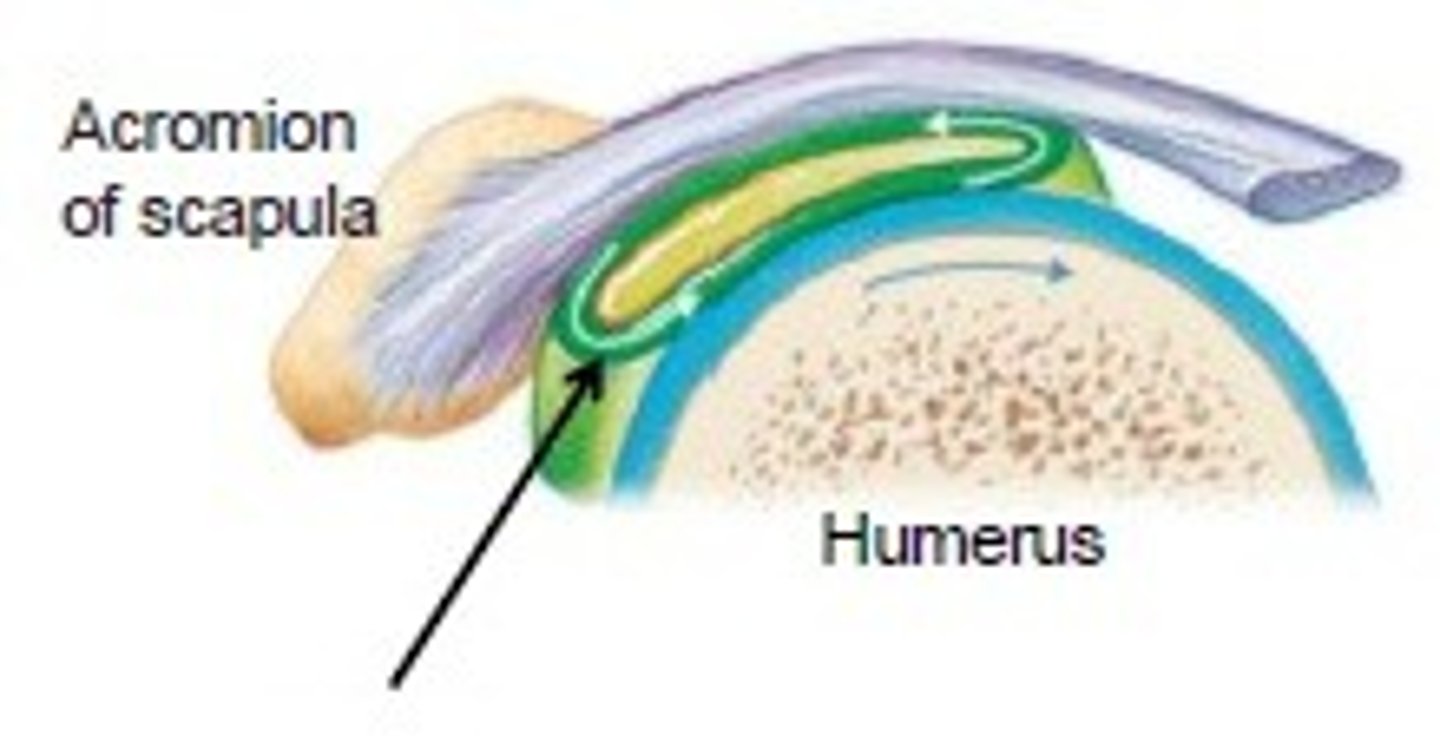
Tendon sheaths
Elongated bursa wrapped completely around tendon subjected to friction
3 factors of synovial joint stability
1. shape of articular surface (shallow surface less stable than ball-and-socket)
2. ligament number and location (more ligaments=more strength)
3. muscle tone(keeps tendons taut as they cross joints)
origin
attachment of a muscle that remains relatively fixed during muscular contraction
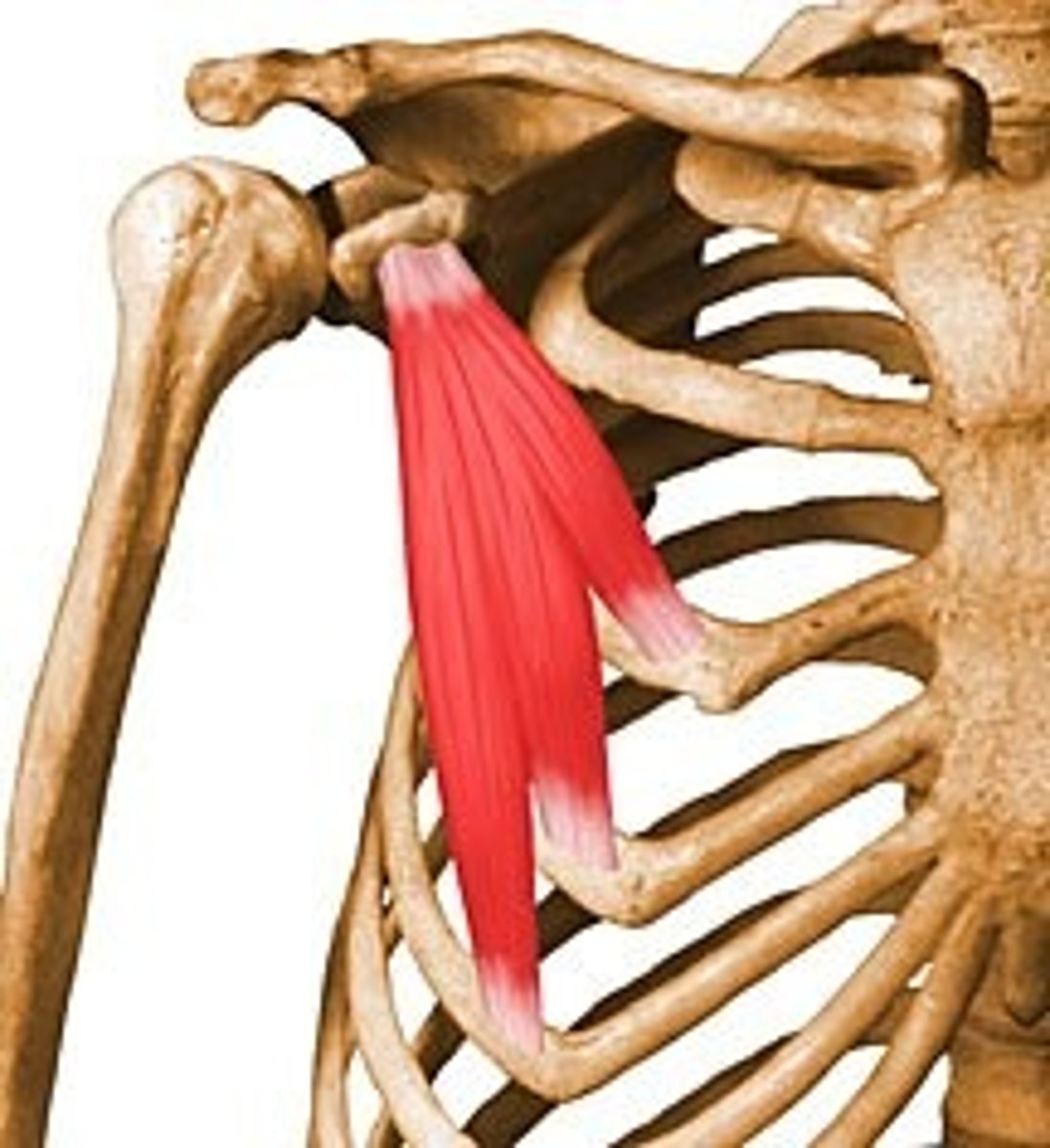
Insertion
attached to the movable bone
4 ranges of motion
nonaxial, uniaxial, biaxial, multiaxial
Non-axial motion
slipping movement
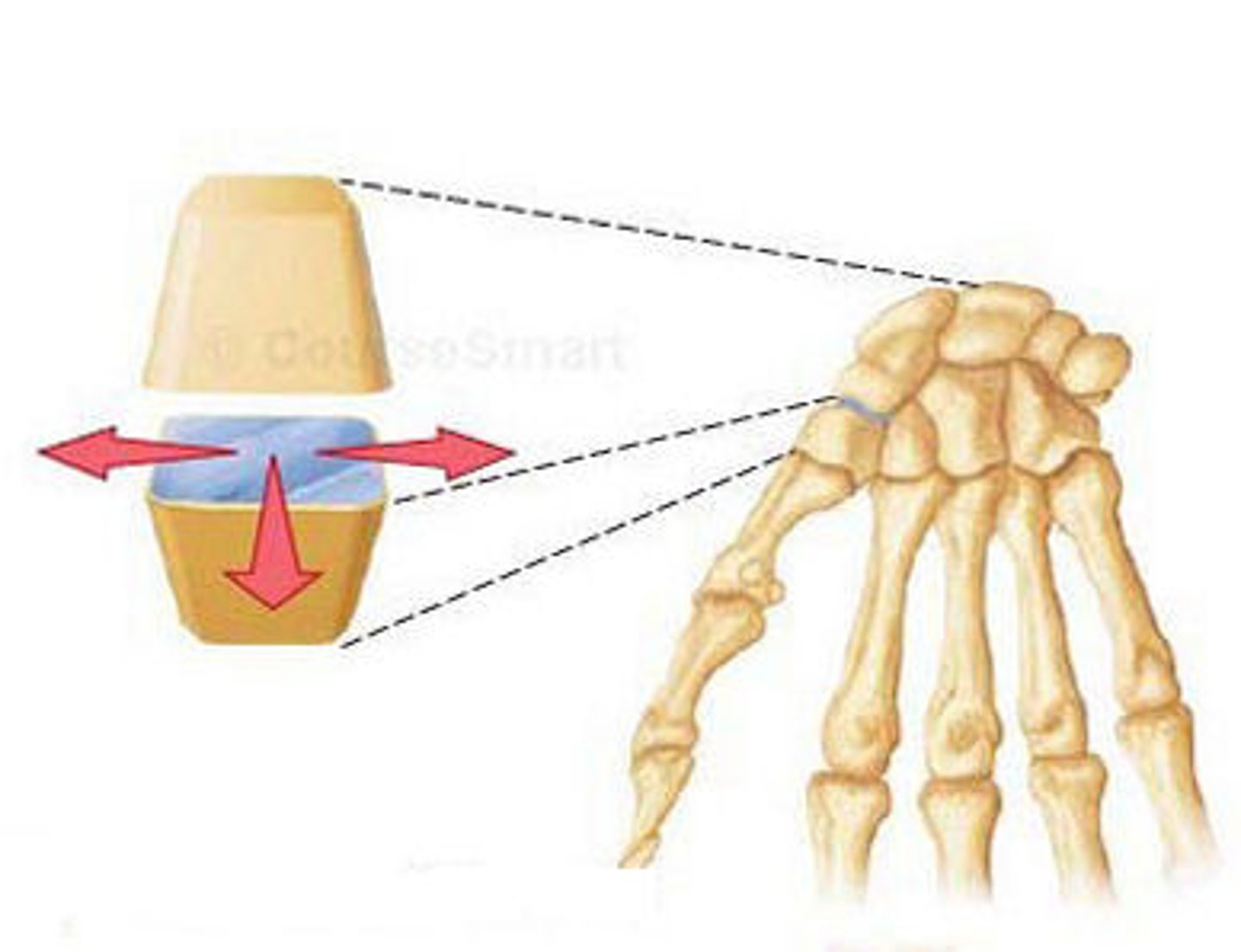
uniaxial motion
movement in one plane
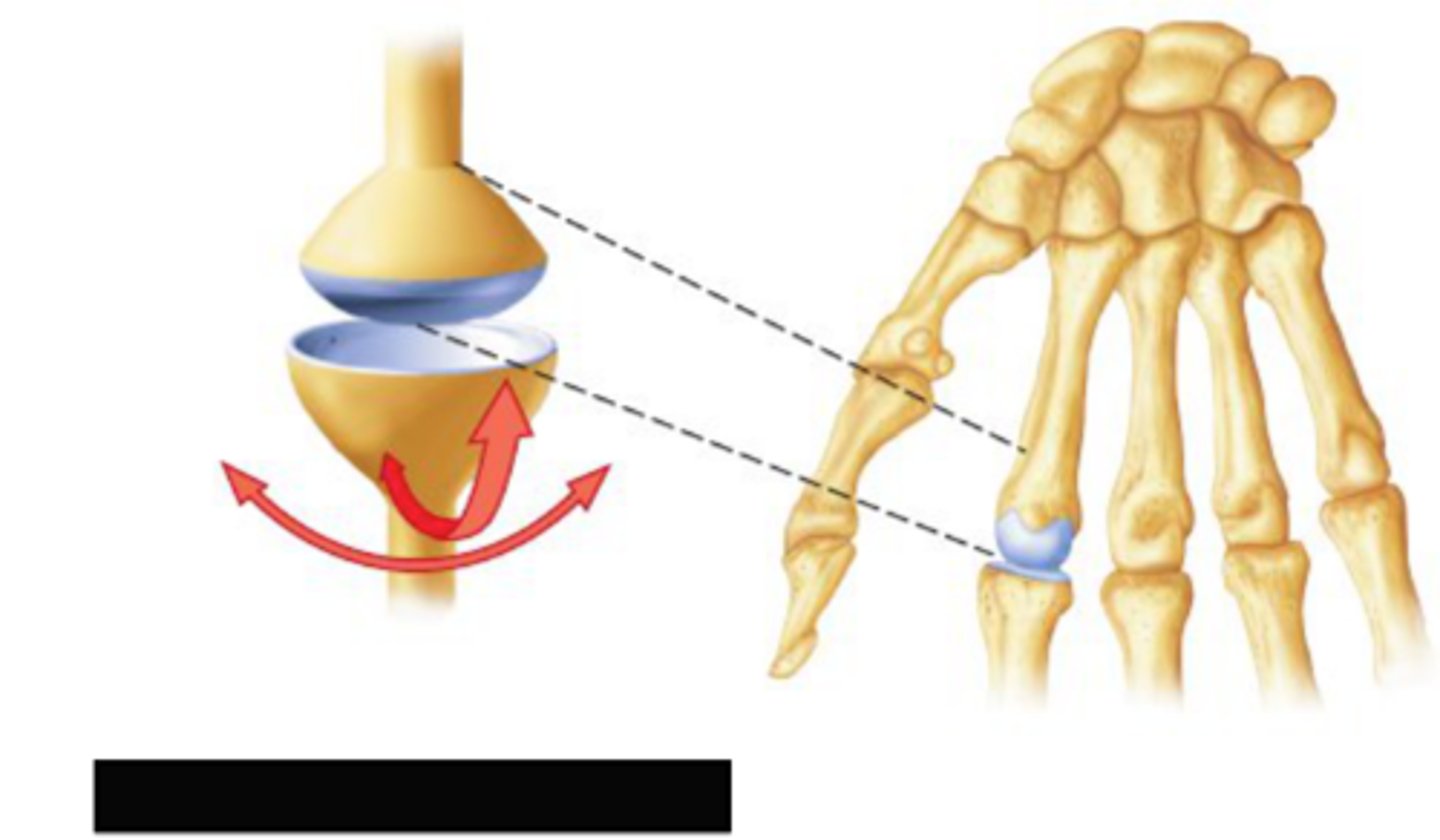
biaxial motion
movement in two planes (metacarpophalangeal joint, occipital condyles to atlas)
multiaxial motion
movement in or around all three planes
3 movements of synovial joints
1. Gliding
2. Angular
3. Rotation
gliding movement
one flat bone surface glides or slips over another similar surface
EX: inter carpal joints, intertarsal joints,
angular movements
increase or decrease the angle between two bones
movement along side the sagittal plane
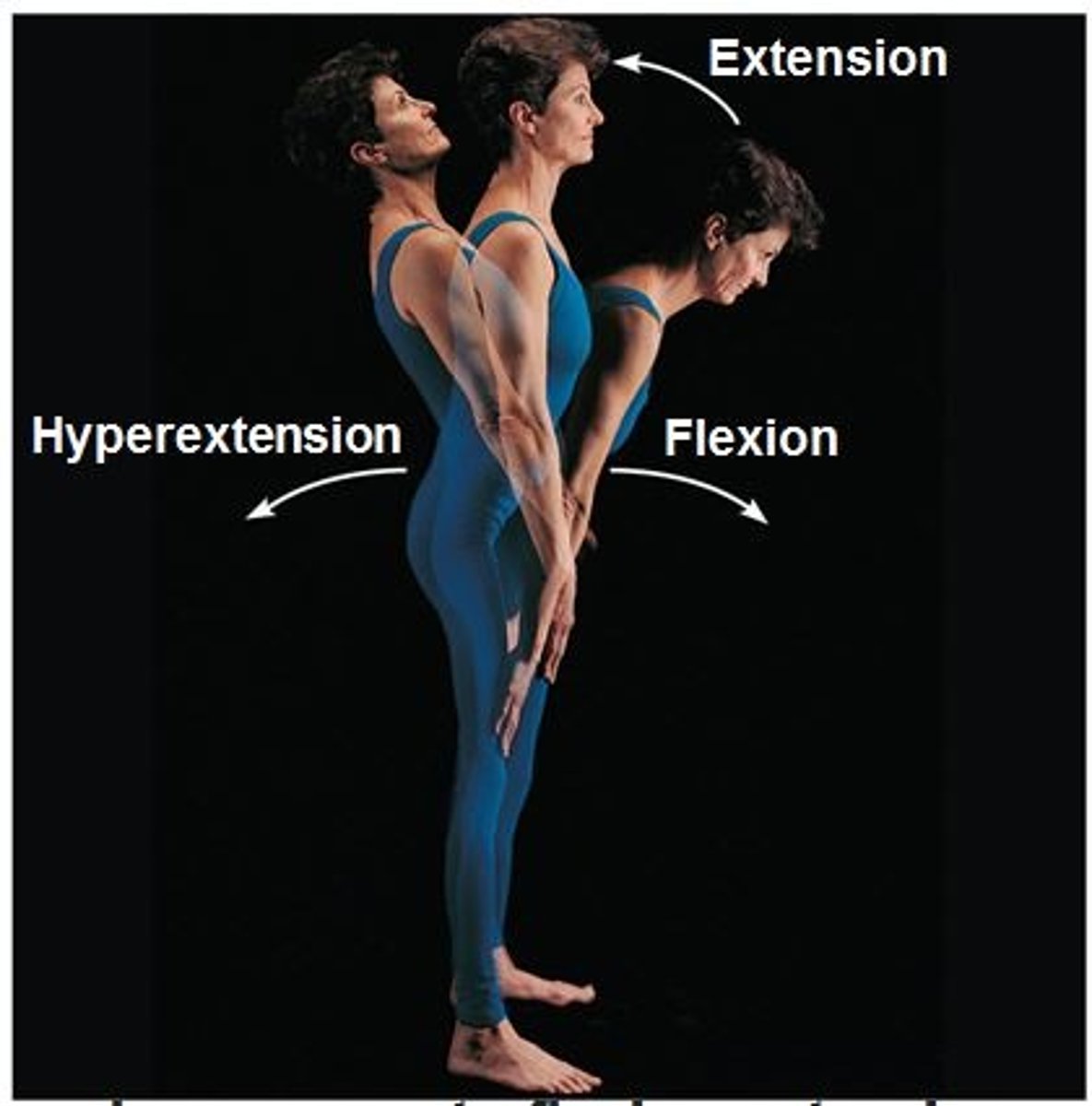
3 types of angular movements
flexion, extension, hyperextension,
Flexion
decrease in the angle between articulating bones
extension
increases the angle of a joint
Hyperextension
extension beyond anatomical position
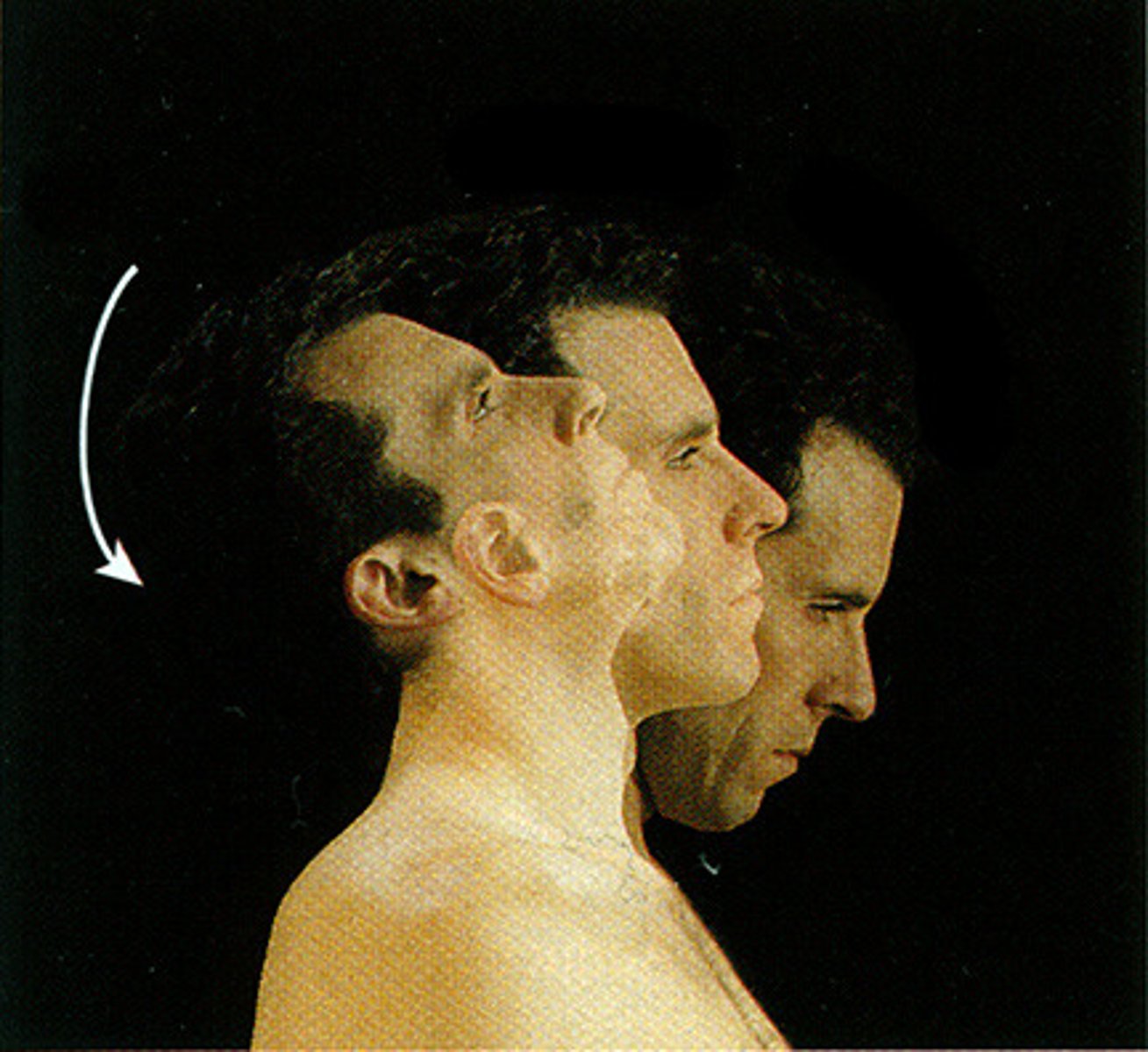
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
Circumduction
circular movement of a limb at the far end
Rotation
Turning around an axis or center point.
medial and lateral rotation
Supination
movement that turns the palm up
Pronation
turning the palm downward
Dorsiflexion
bending of the foot or the toes upward
plantar flexion
bending of the sole of the foot by curling the toes toward the ground
Inversion
Turning the sole of the foot inward
Eversion
turning the sole of the foot outward
2 types of movement in lateral plane
protraction and retraction
Protraction
mandible juts out
Retraction
mandible is pulled toward neck
Elevation
lifting a body part superiorly
Depression
lowering a body part
oppoisition
movement of thumb
EX: touching thumb to tip of fingers on the same hand... grasping movements
6 types of synovial joints
1. plane
2. hinge,
3. pivot
4. condyloid
5. saddle
6. ball and socket
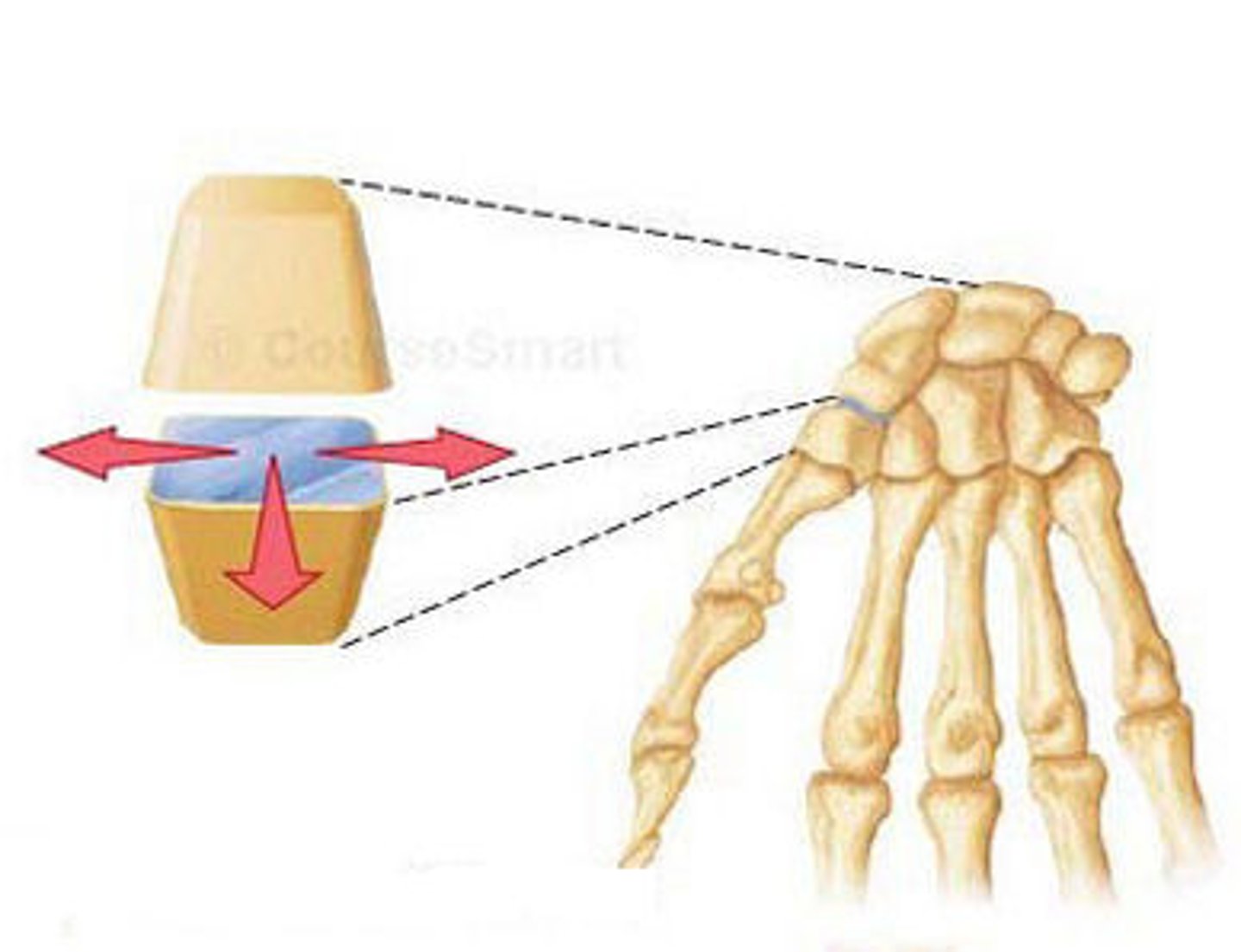
plane joint
Non-axial The flat surface of one bone slides in many directions along the flat surface of another bone.
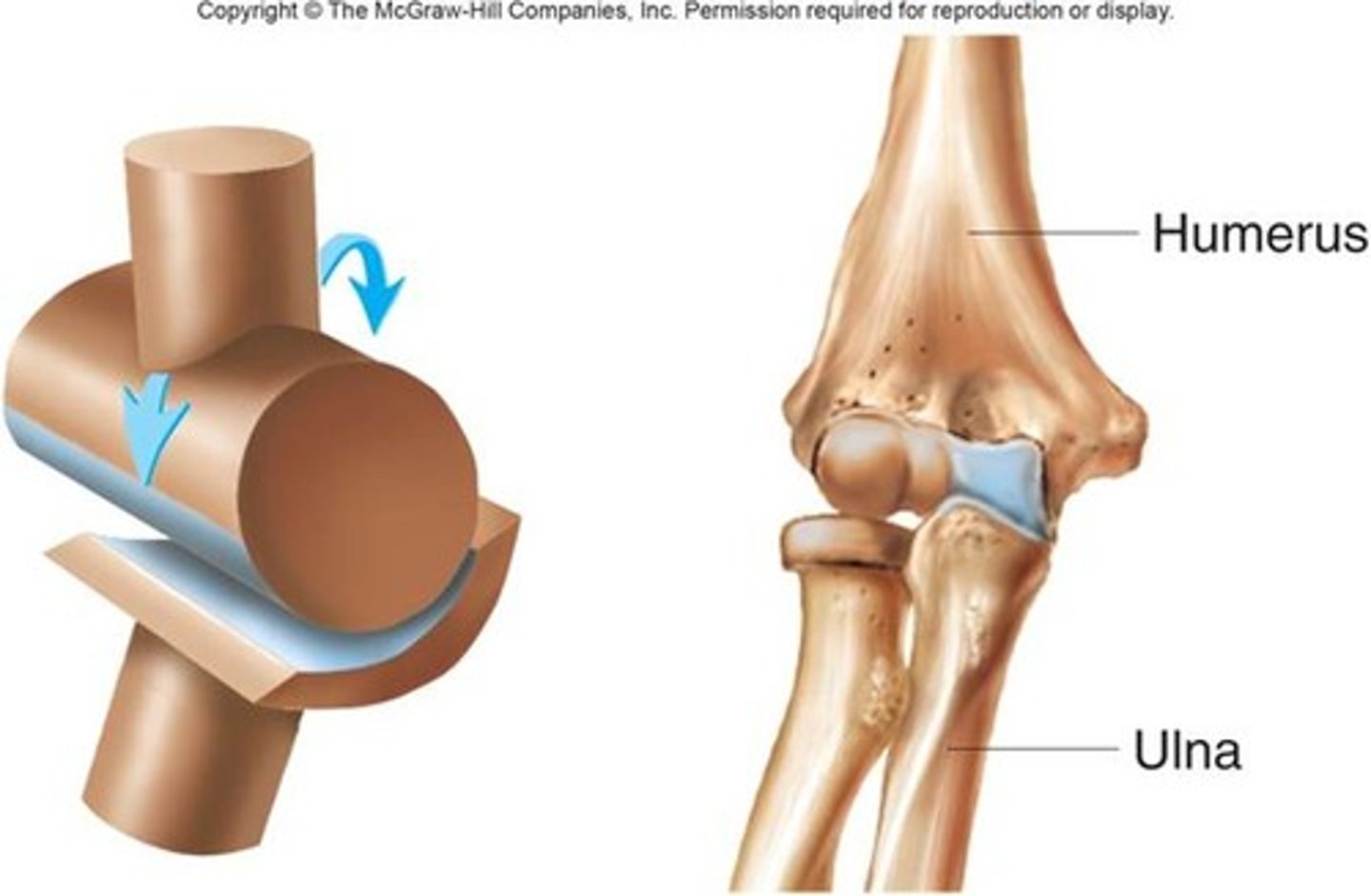
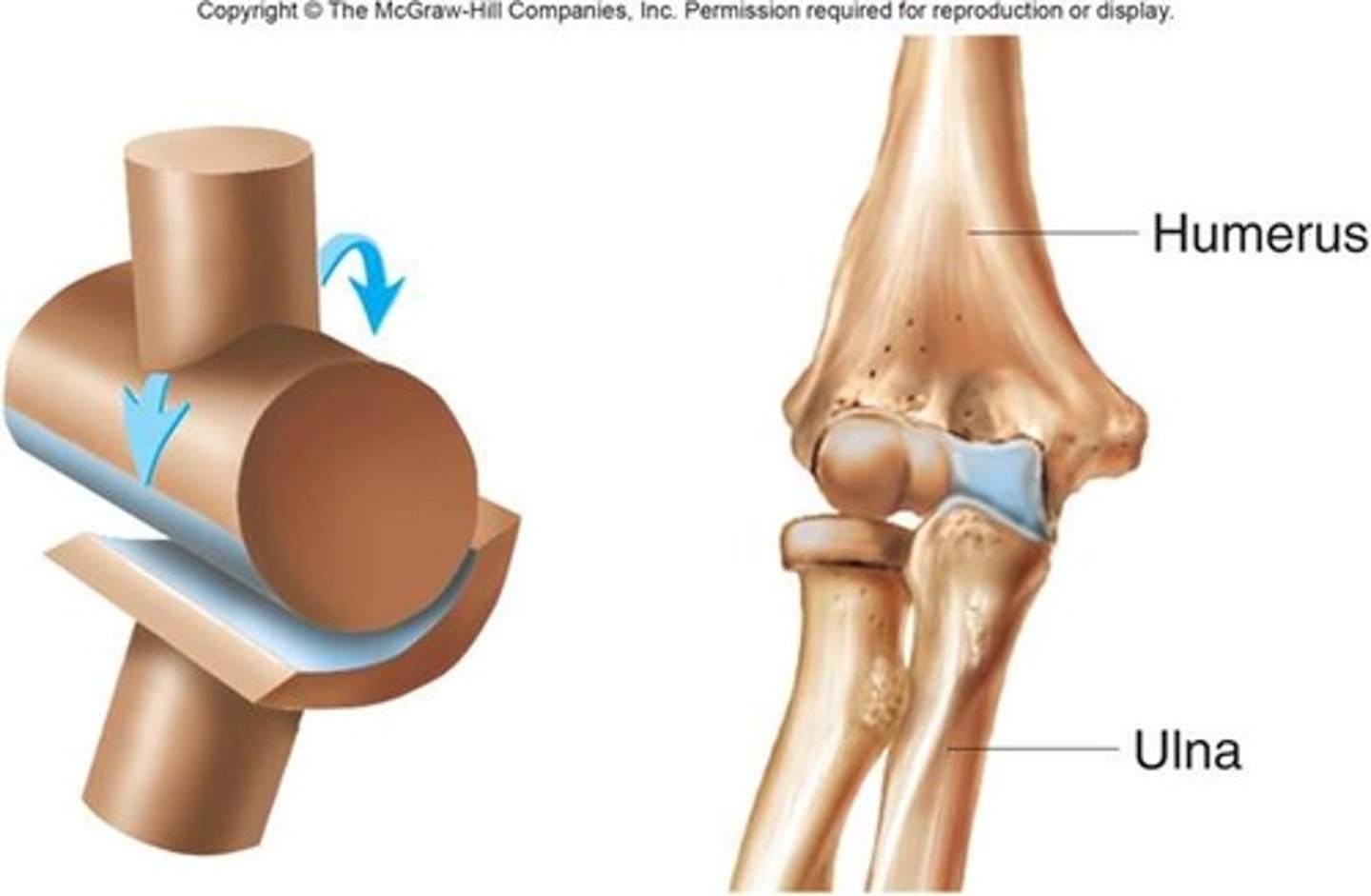
hinge joint
uniaxial, flexion and extension
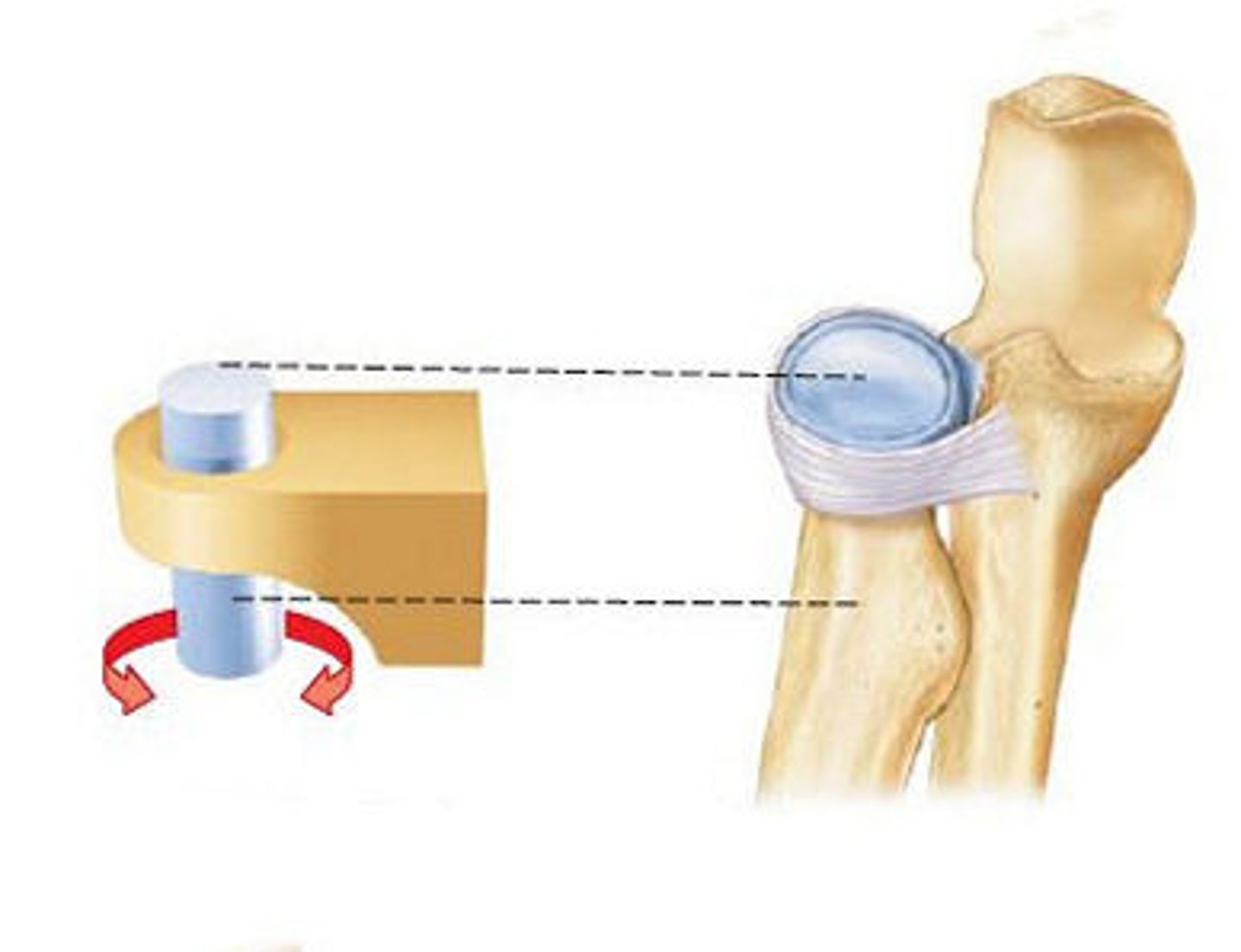
pivot joint
rotating bone turns around an axis; i.e. connection between radius/ulna and humerus
uniaxial
condylar joint
a shallow ball-and-socket joint with limited mobility
biaxial
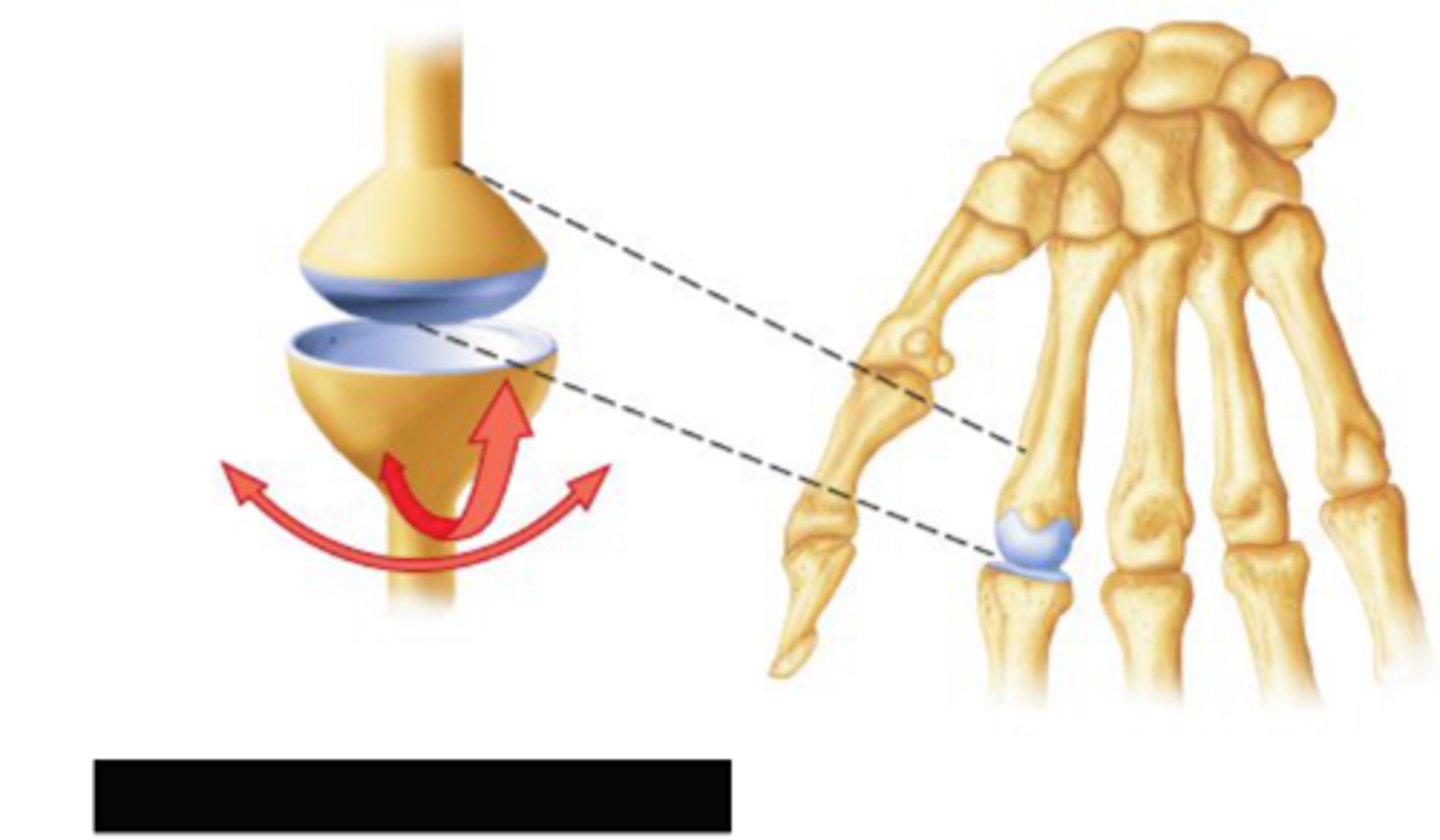
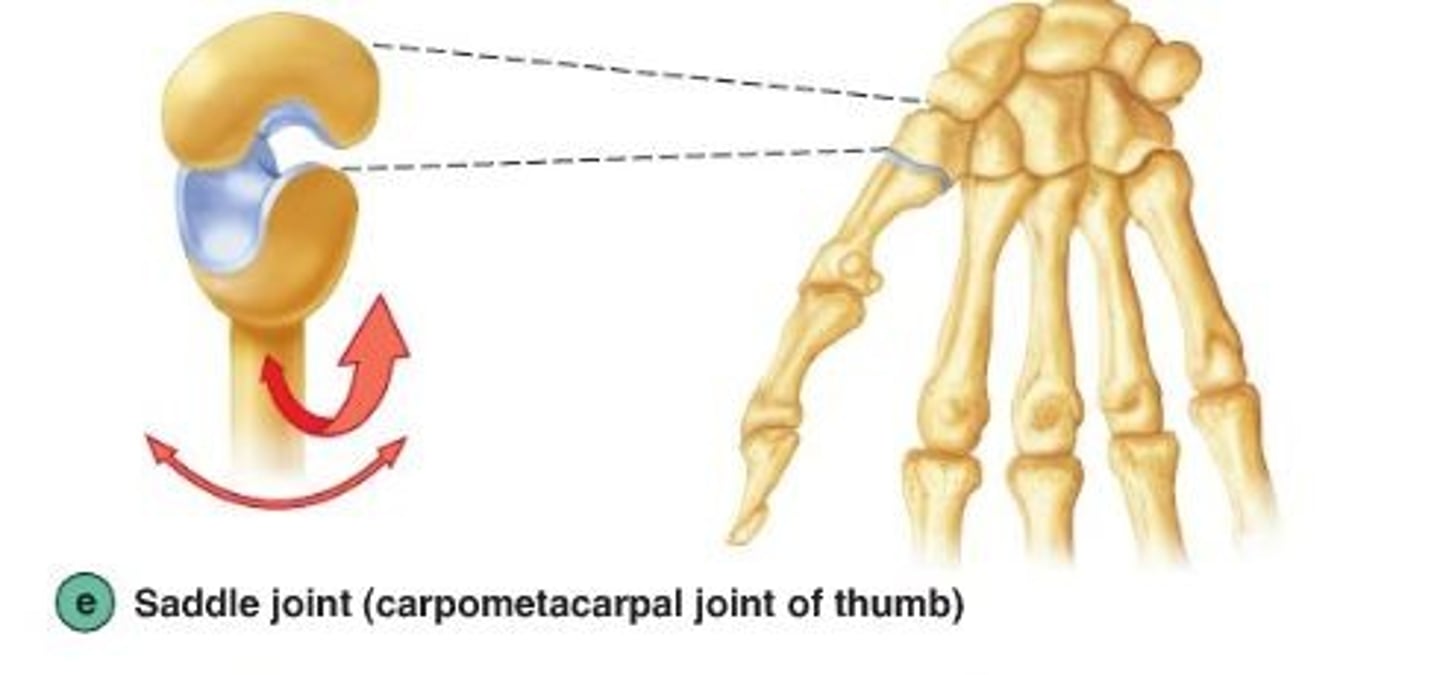
saddle joint
type of joint found at the base of each thumb; allows grasping and rotation
biaxial
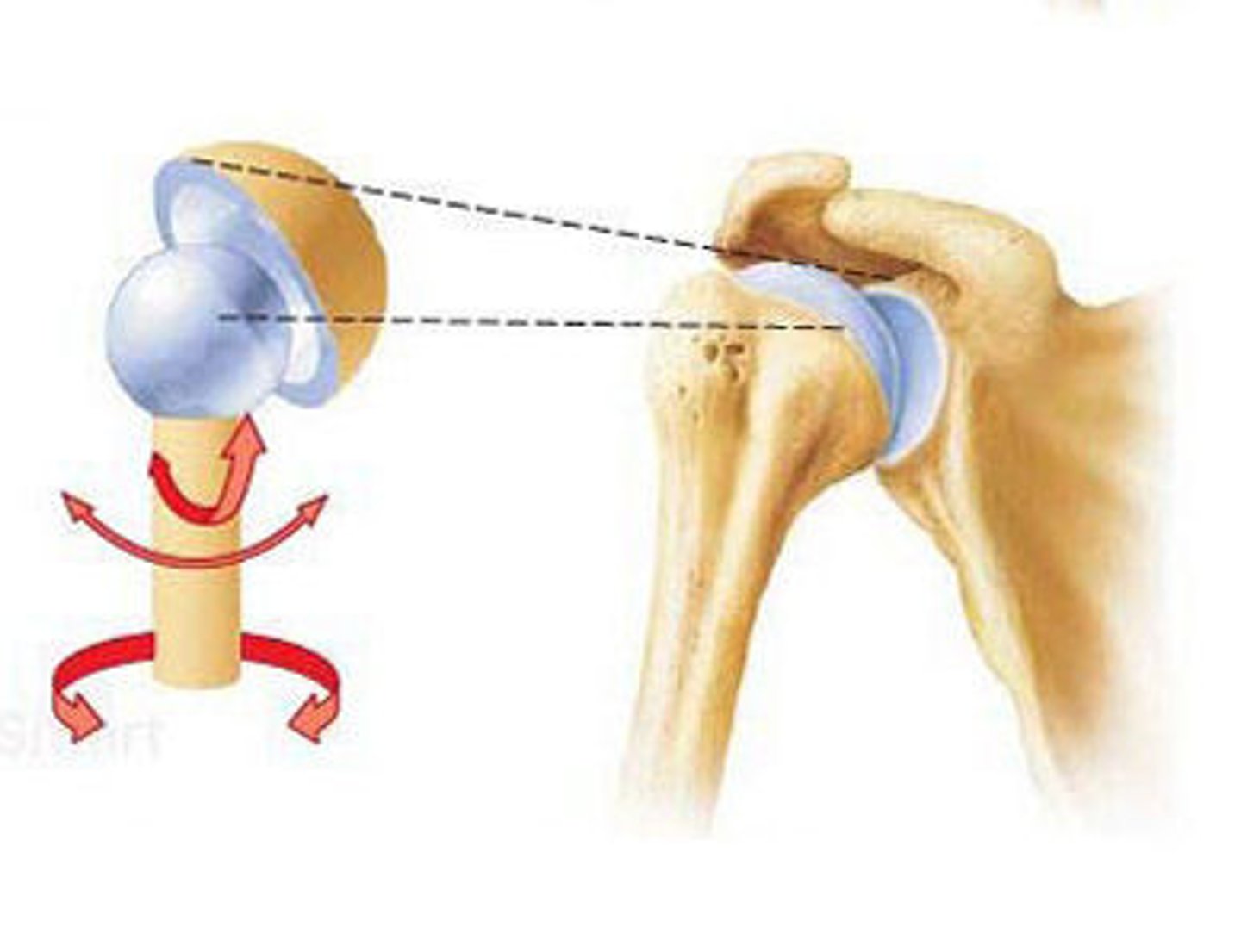
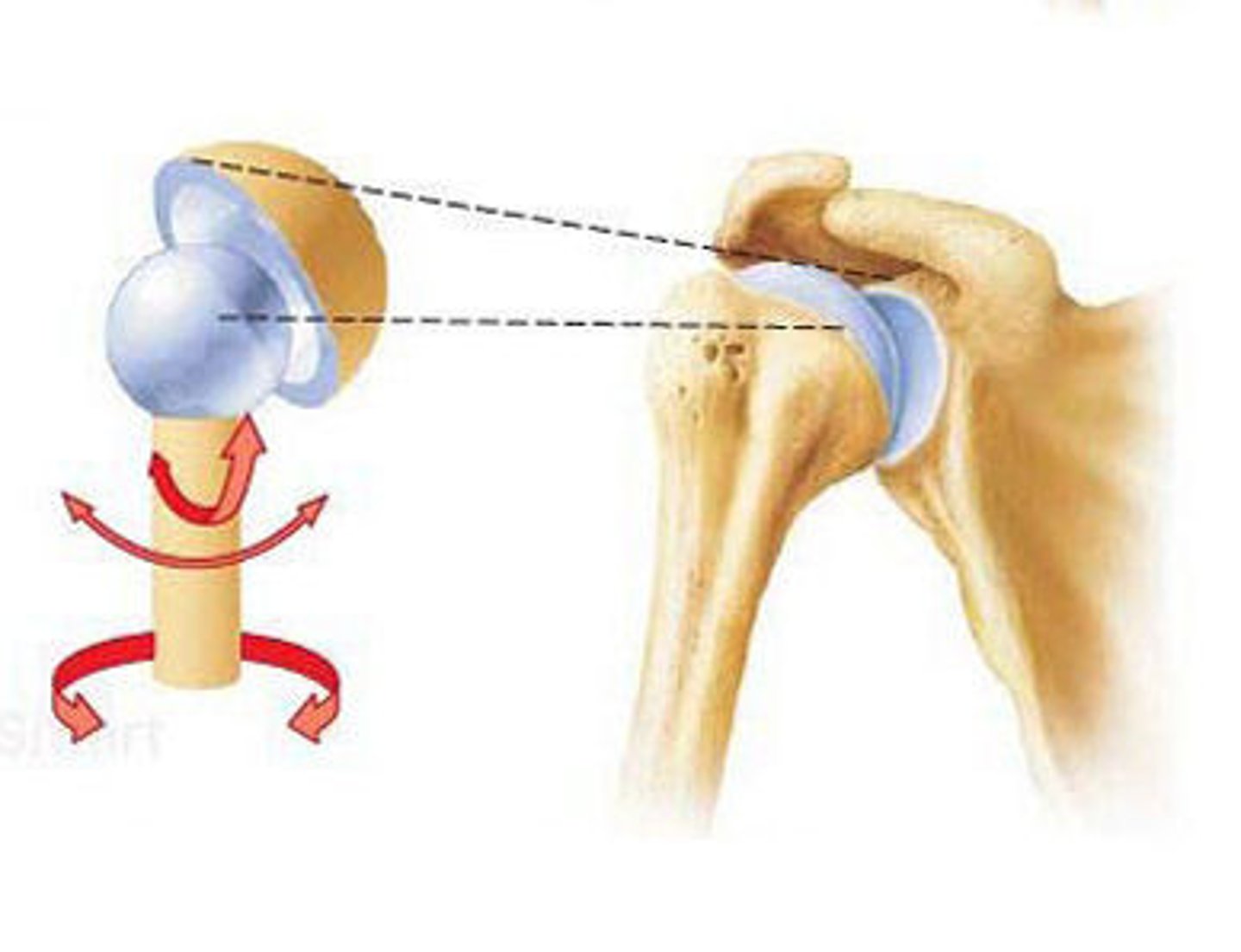
ball and socket joint
hip and shoulder joints
Main synovial joints
knee, shoulder, elbow, hip, jaw
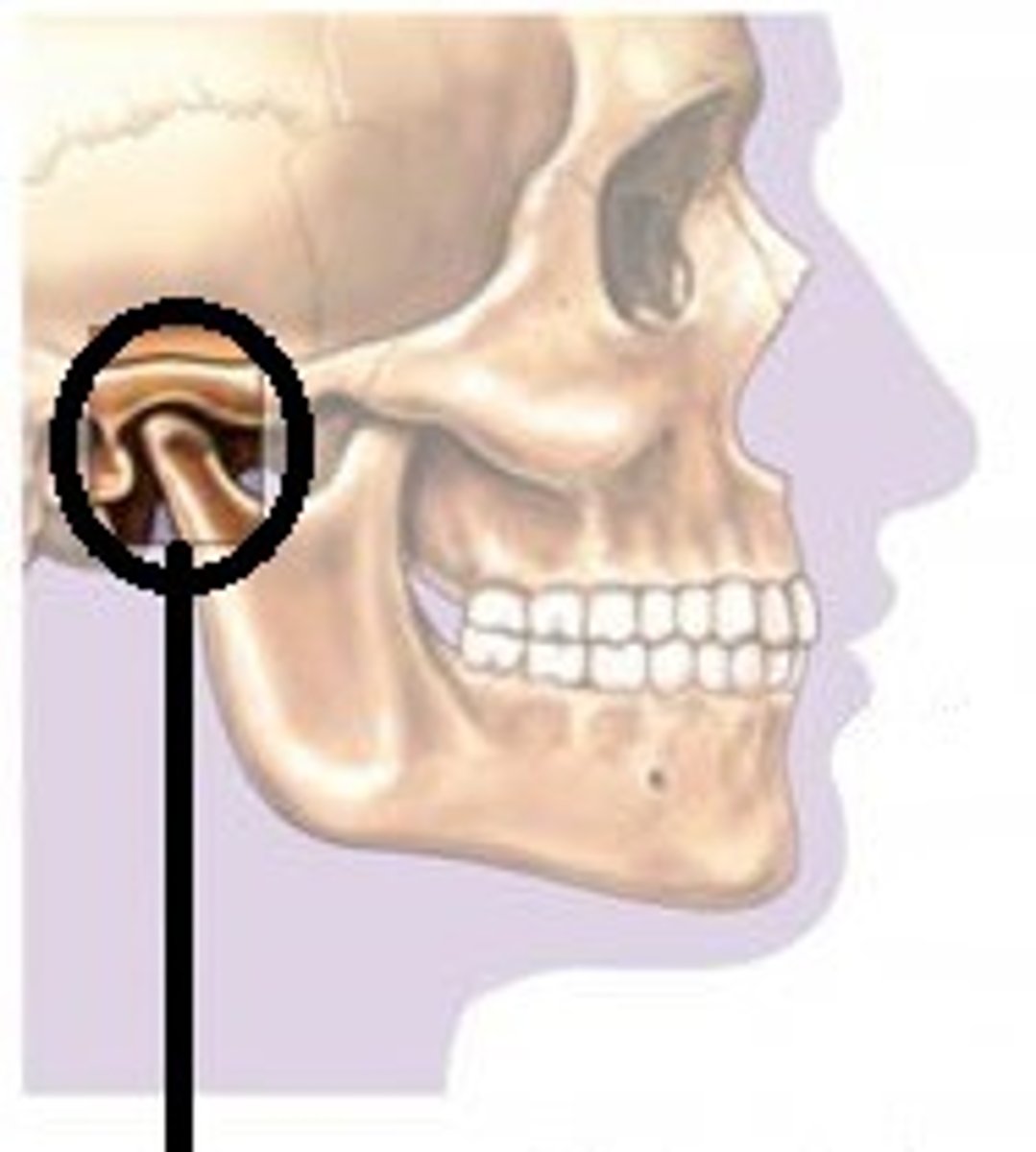
temporomandibular joint
jaw joint; modified hinge joint
-mandibular condyle articulates with temporal bone
-posterior temporal bone forms mandibular fossa, while anterior portion forms articular tubercle
-articular capsule thickens into strong lateral ligament
shoulder joint
-mostly freely moving joint in the body
-stability is sacrificed for freedom of movement
-ball-and socket joint
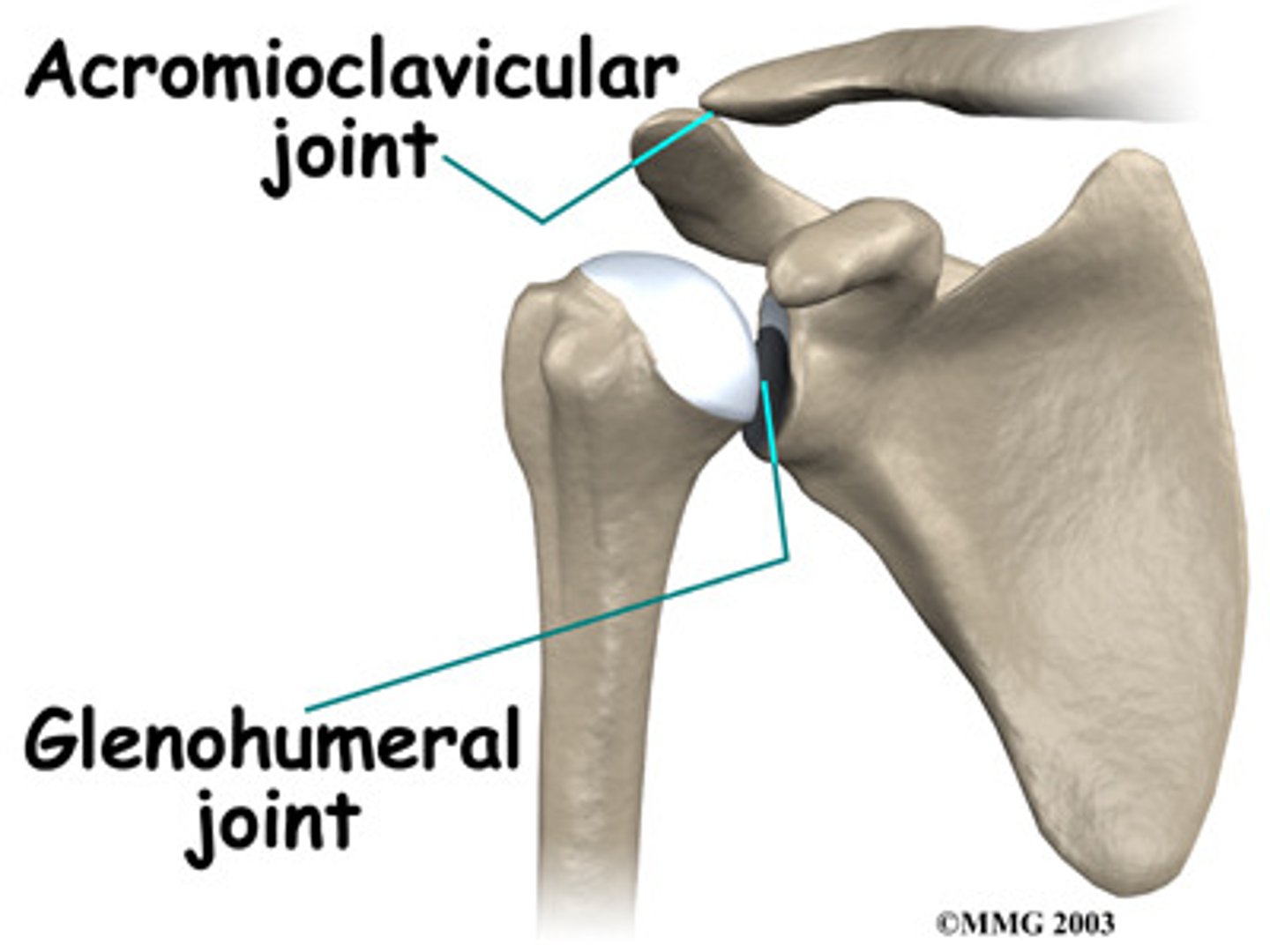
Reinforcement of shoulder joint
gelnoid labrum: fibrocartilaginous rim around glenoid cavity, adds depth to shallow cavity
coracohumeral ligament: helps support weight of the upper limbs
3 glenohumeral ligaments: strengthen anterior capsule, but are weal support
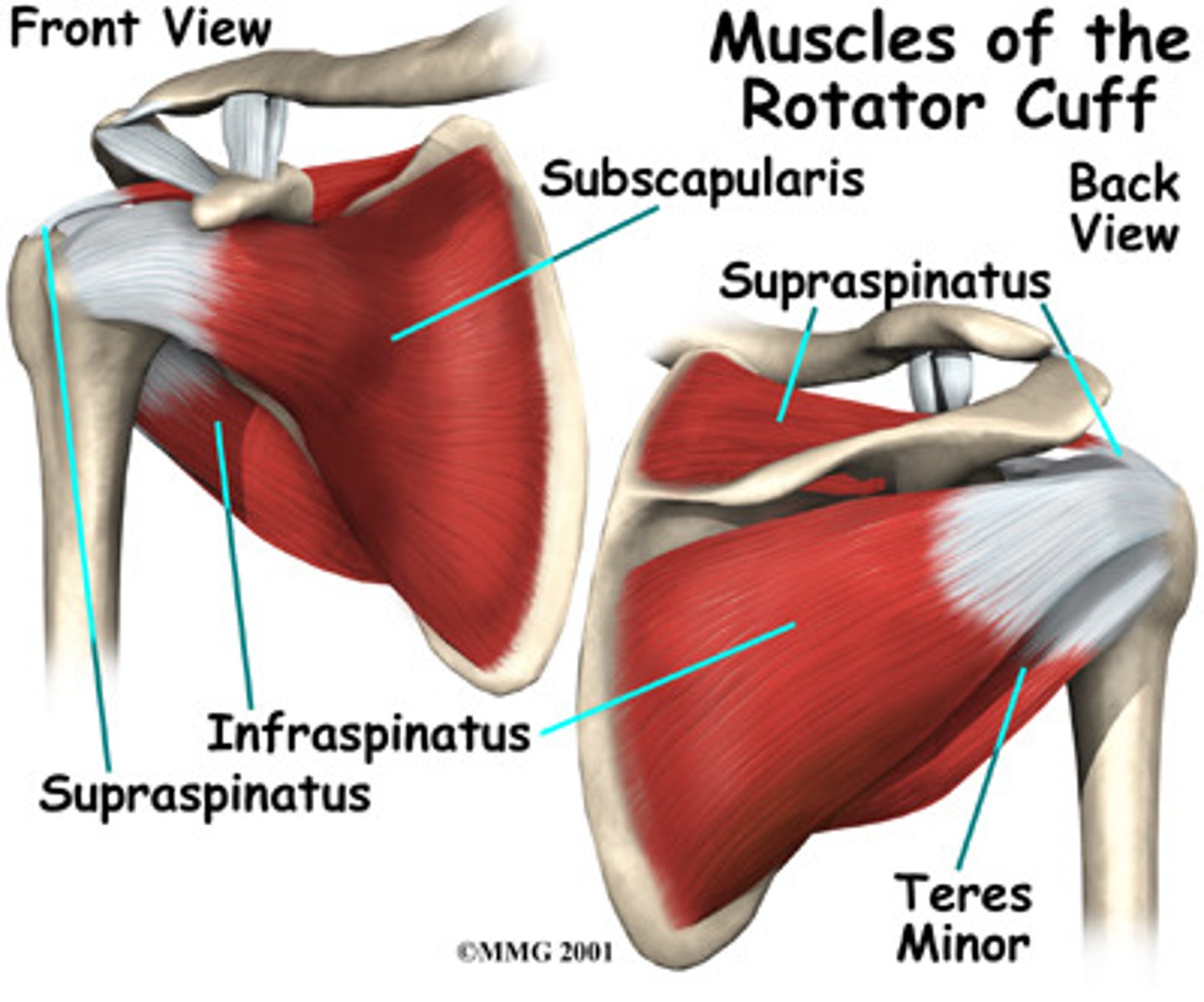
4 rotator cuff tendons
1. subscapularis
2. supraspinatus
3. infraspinatus
4. teres minor
shoulder dislocations
-common due to mobility in shoulder
-structures reinforcing this joint are weakest anteriorly and inferiorly
-head of humerus can easily dislocate forwards and downward
-glenoid cavity provides poor support when humerus is rotated laterally and abducted
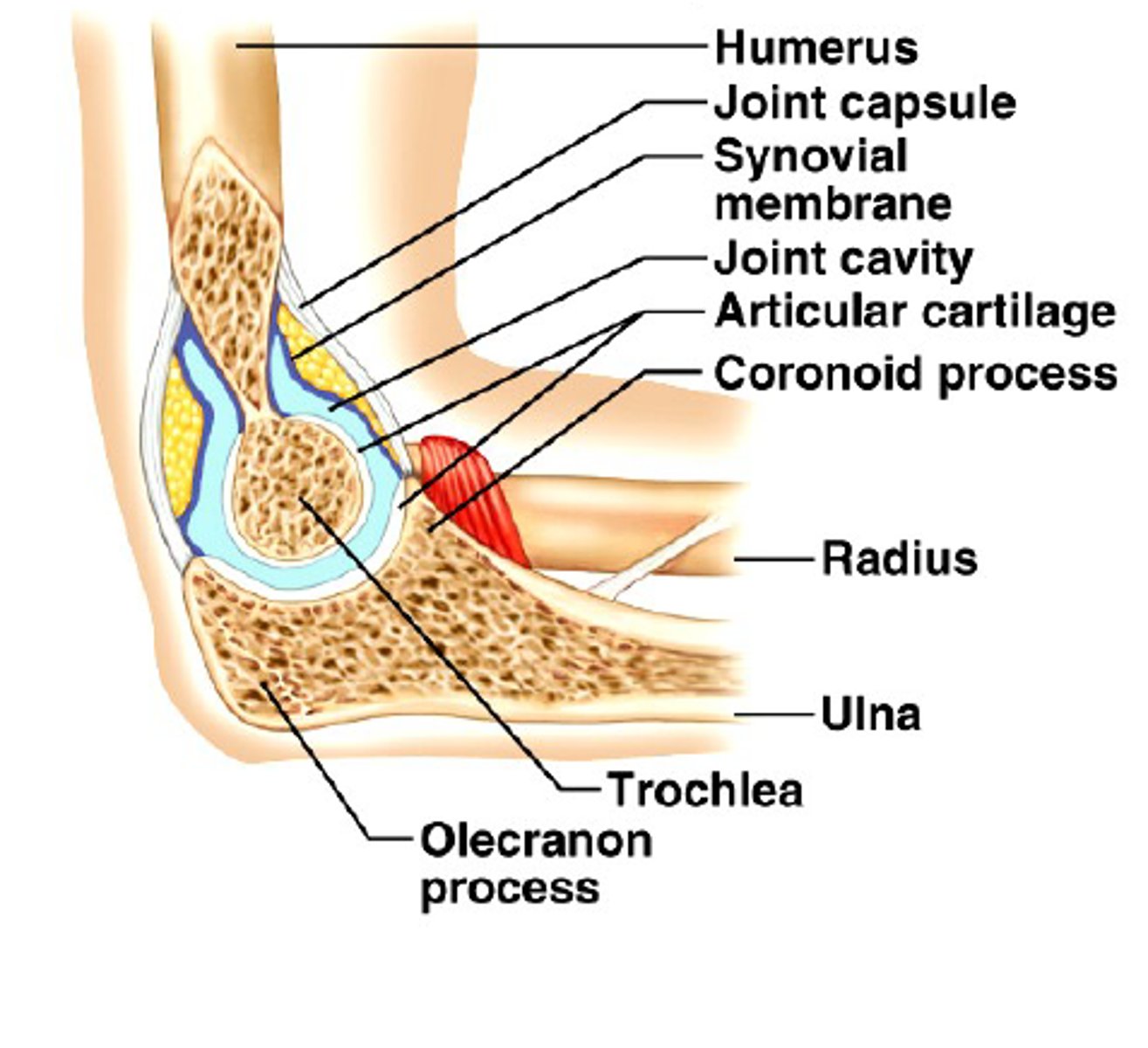
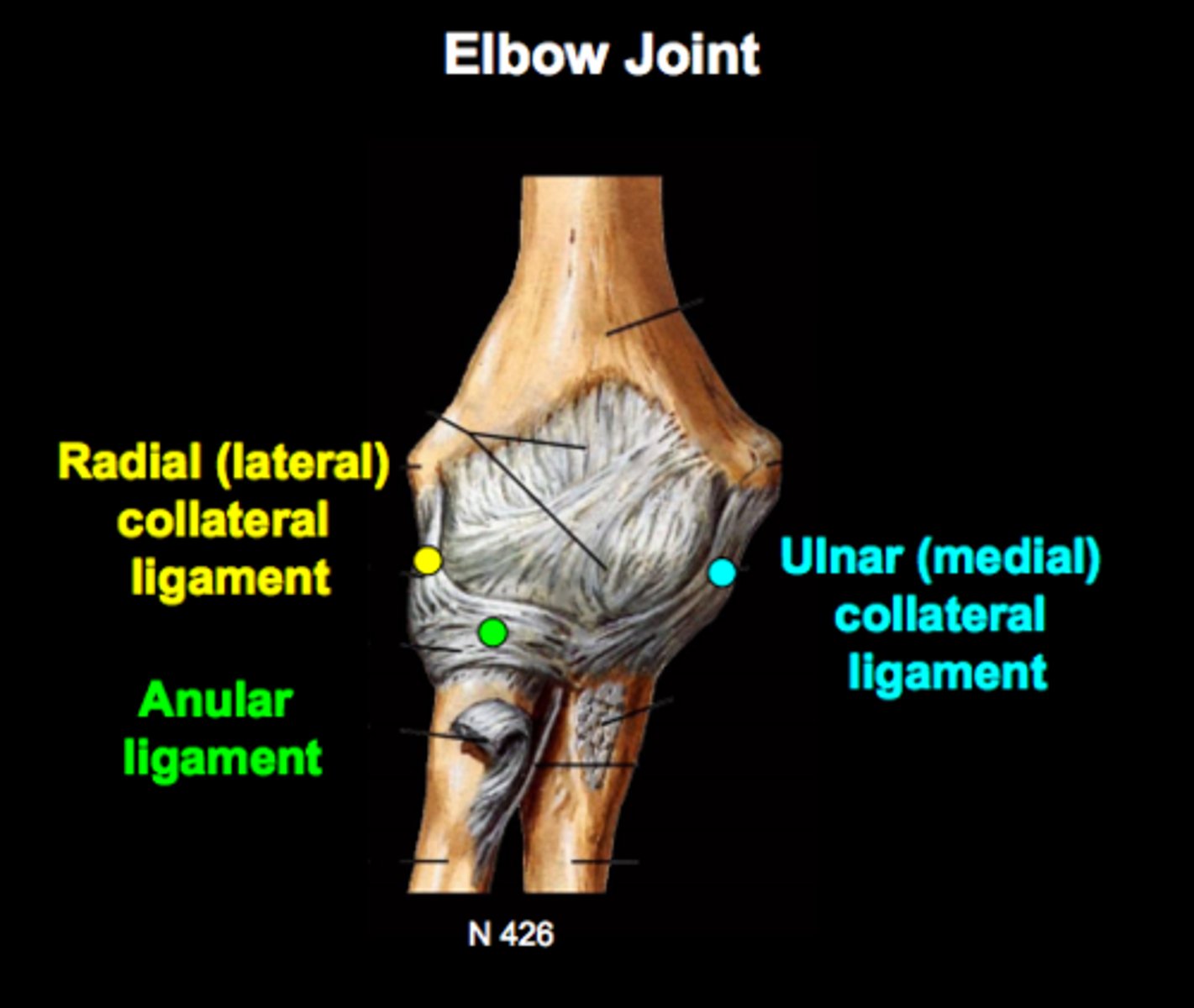
elbow joint
hinge joint formed by humerus, ulna, and radius
allows flexion and extension only
3 elbow ligaments
1. Radial collateral
2. anular ligament
3. Ulnar collateral
hip joint
-ball and socket joint
-large, spherical head of the femur articulates with deep cup-shaped acetabulum
-allows good range of motion, but is limited by deep socket
acetabular labrum
rim of fibrocartilage that enhances depth of socket (hip dislocations are rare)
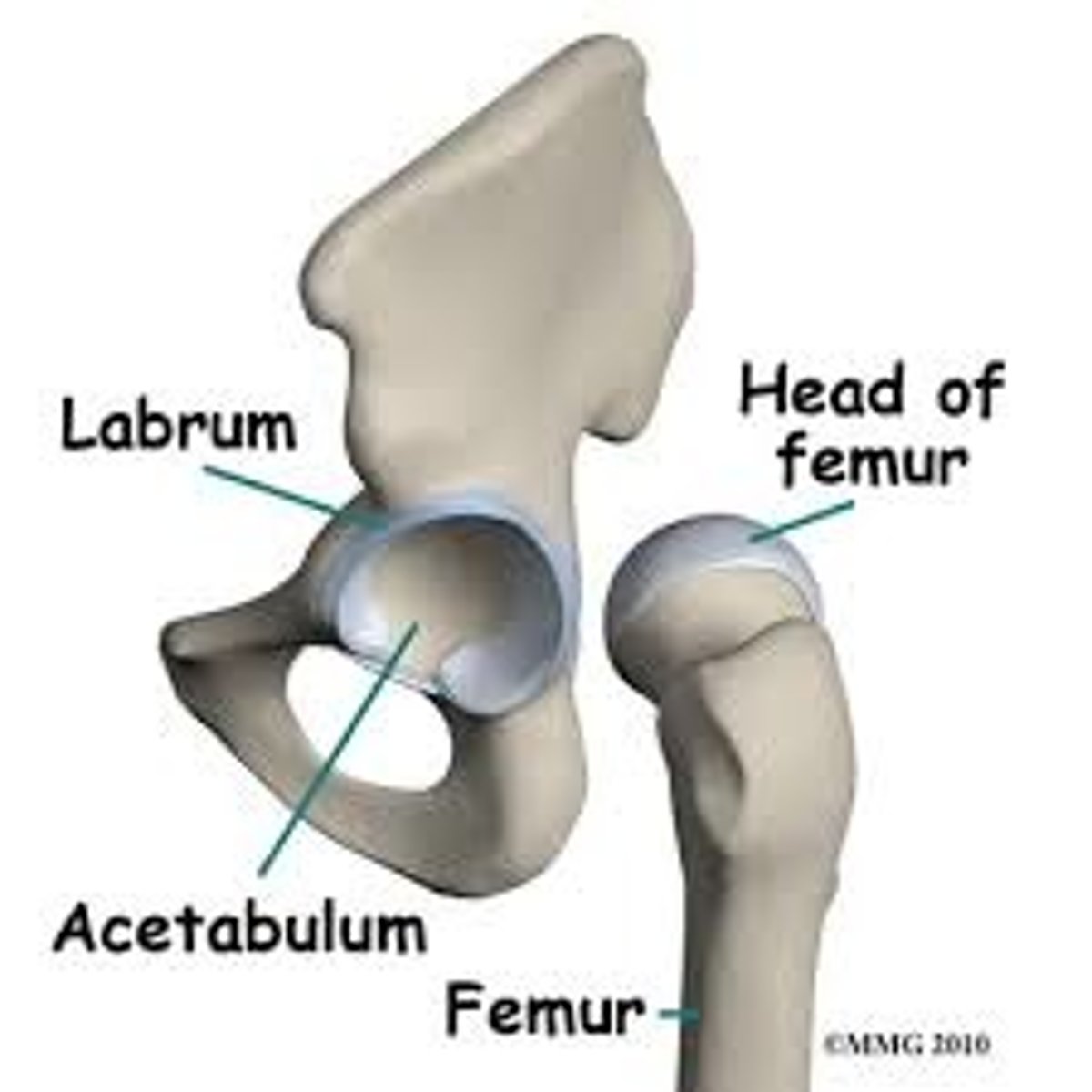
4 hip ligaments
1. iliofemoral
2. pubofemoral
3. ischiofemoral
4. ligaments of the head of the femur
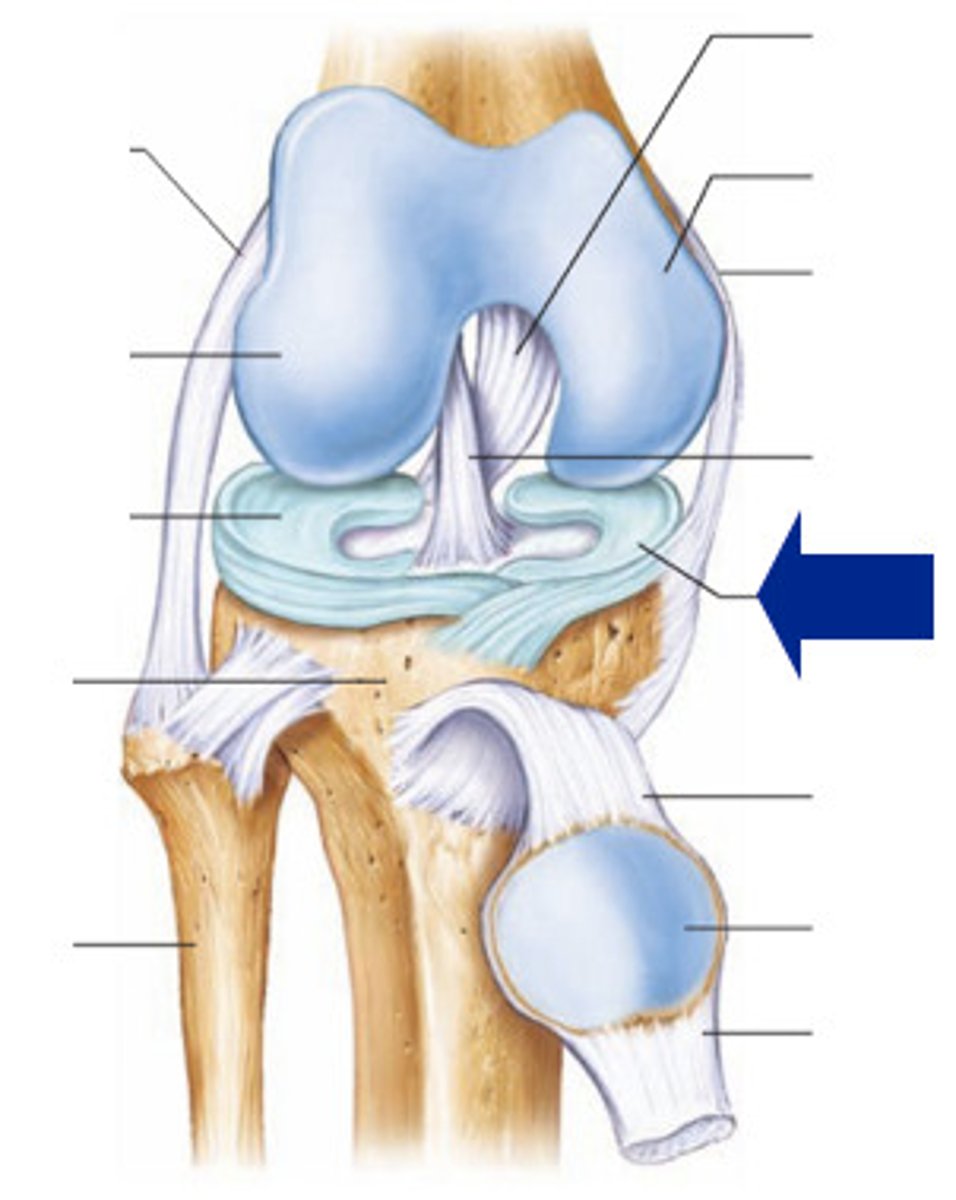
knee joint
-largest, most complex join of the body
hinge joint that allows flexion, extension, and some rotation when it is partly flexed
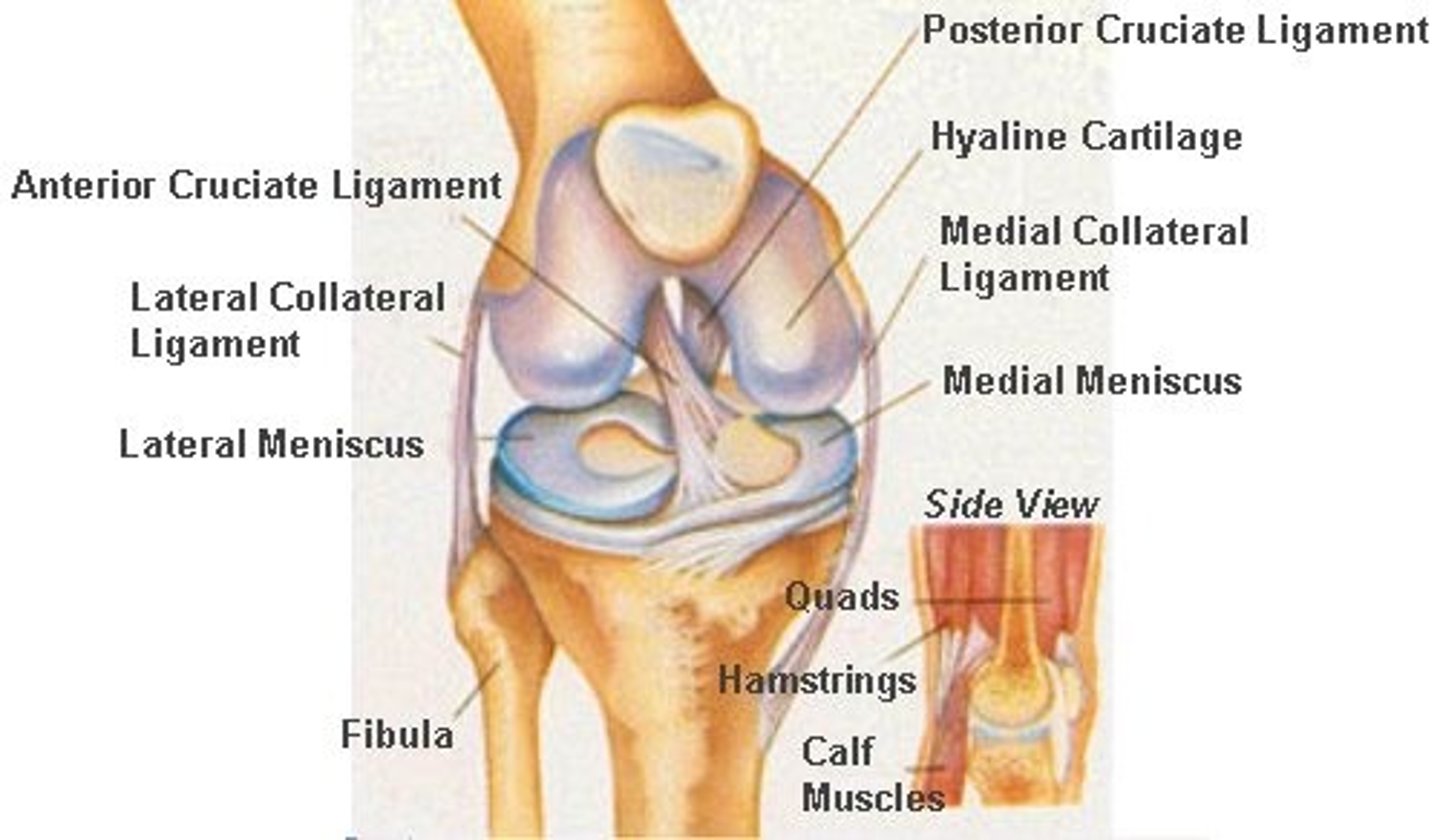
Three joints of the knee joint
- all three are within a single synovial cavity
1. Laterally: a tibiofemoral joint - a modified hinge joint
2. Medially: a second tibiofemoral joint - also a modified hinge joint.
3. An intermediate patellofemoral joint - a planar joint.
3 broad ligaments of knee joint
- patellar ligament
- Lateral and medial patellar retinaculum
joint capsule ligaments of knee
-capsular, extra capsular or intracapsular ligaments (stabilize knee joint)
-capsular & extracapsular ligaments (prevent hyperextension)
-fibular and tibial collateral ligaments
-fibular and tibial collateral ligaments (prevent rotation when knee is extended)
-oblique popliteal ligament (stabilizes posterior knee joint)
-arcuate popliteal ligament (reinforce joint capsule posteriorly)
intracapsular ligaments joints of knee
-within capsule but outside synovial cavity
-prevent anterior posterior displacement
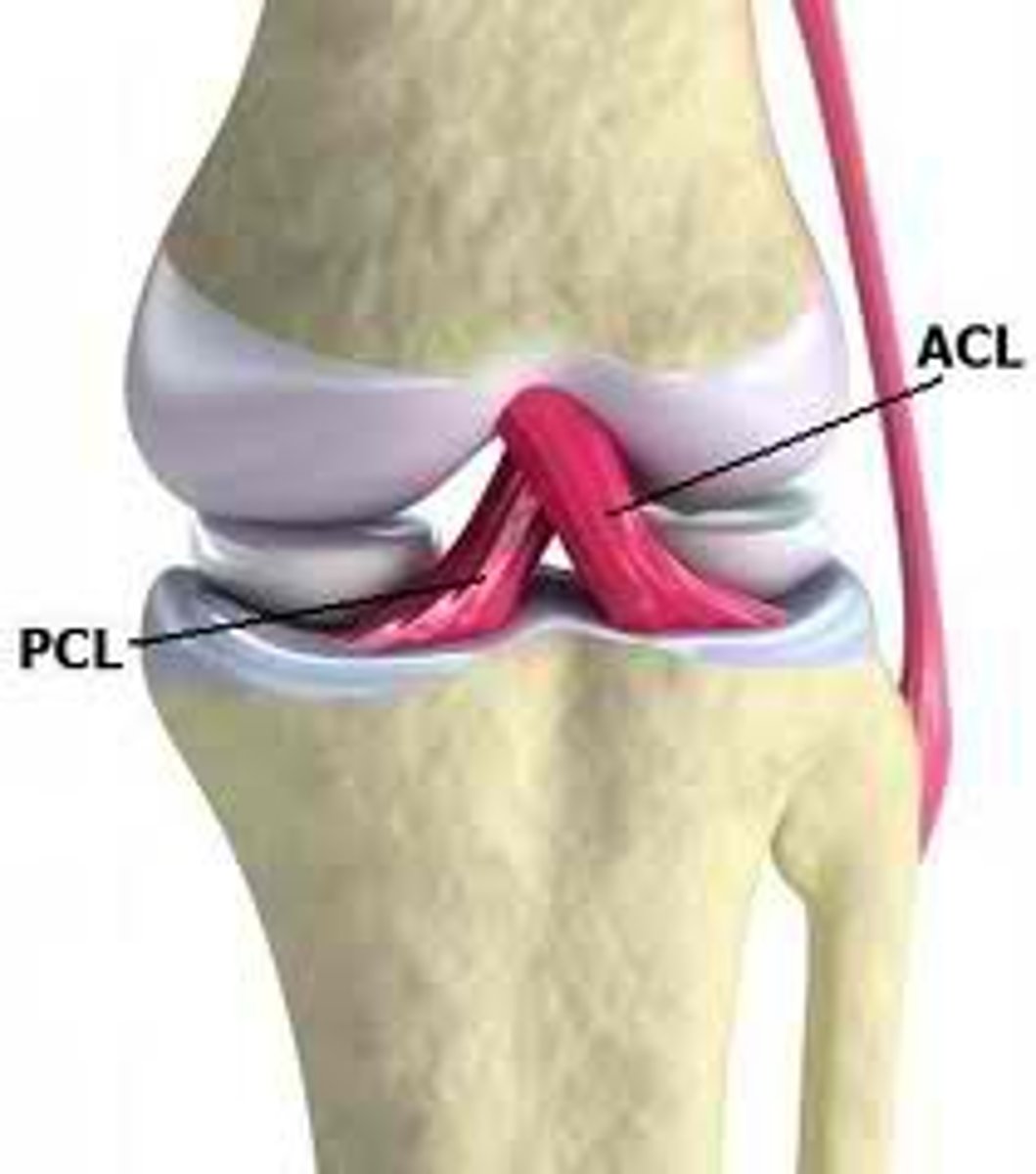
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
A ligament in the knee that attaches to the anterior aspect of the tibial plateau. restricting anterior movement of the tibia on the femur... stops hyperextension
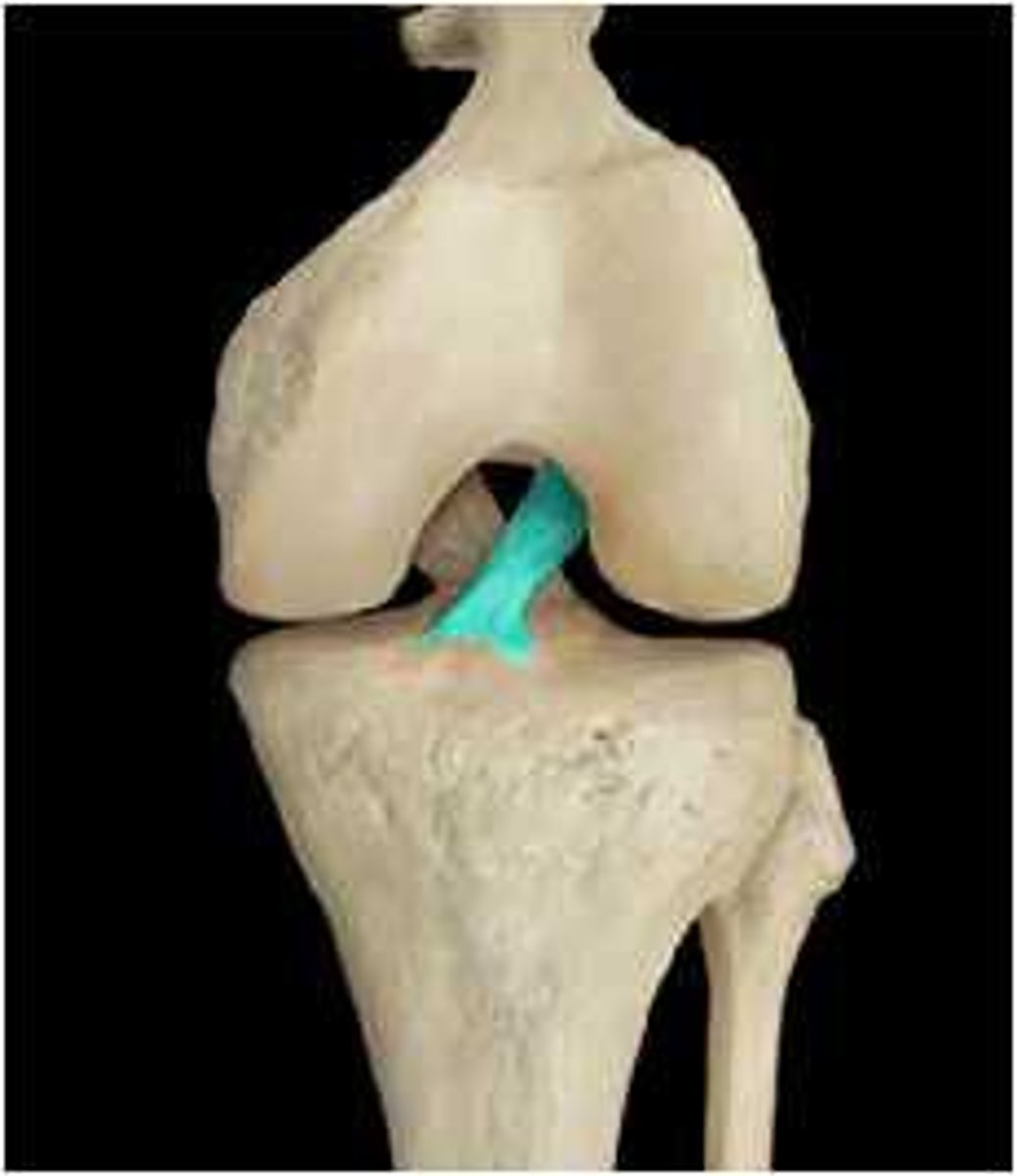
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
A ligament in the knee that attaches to the posterior aspect of the tibial plateau, restricting posterior movement of the tibia on the femur
3 C's of knee injuries
1. collateral ligaments
2. cruciate ligaments
3. cartilages (menisci)
cartilage tears
Caused by compression and shear stress (especially of menisci); rarely repairs itself
-fragments may lead to locking or binding of joint
-requires arthroscopic surgery
Sprains
ligaments reinforcing a joint are stretched or torn
-poorly vascularized therefor recovery is very slow
3 options of completely sprain
1. end of ligament is sewn together
2. replaced with graft
3. allow time and mobilization for healing
Dislocation
displacement of a bone from its joint
aka... luxations
7 Inflammatory and Degenerative Conditions
1. bursitis
2. tendonitis
3. arthritis
4. osteoarthritis
5. rheumatoid arthritis
6. gouty arthritis
7. lyme disease
burstisis
inflammation of bursa, usually caused by blow or friction
treatment: ice, and anti0inflammatory drugs
Tendonitis
inflammation of tendon sheaths typically caused by overuse
arthritis
-inflammatory or degenerative disease that damages the joints
symptoms: pain, stiffness, swelling of joint
acute form: caused by bacteria, treated with antibiotics
chronic forms: osteoarthiritis, rheumatoid arthritis and gouty arthritis
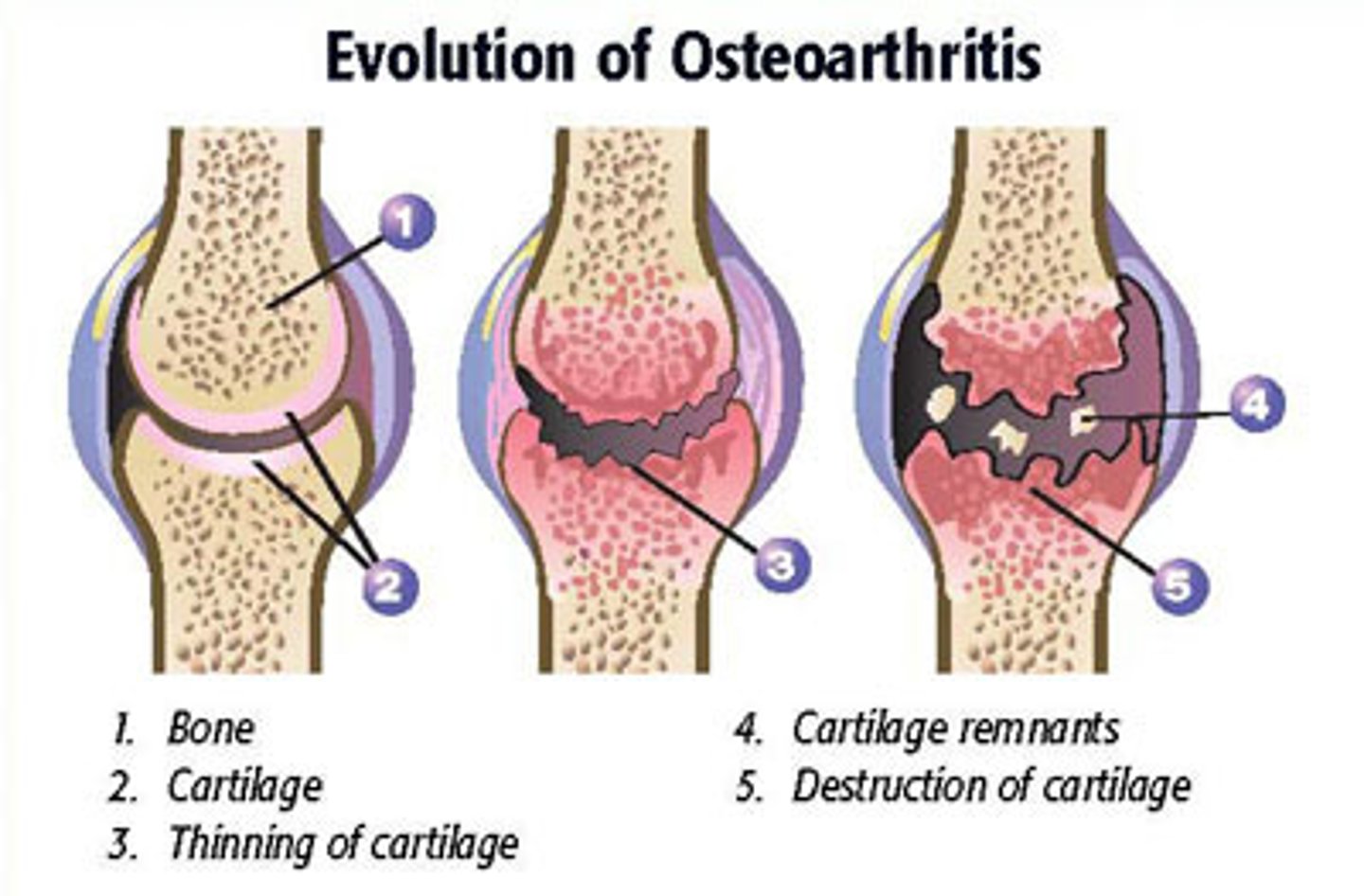
Osteoarthritis (OA)
-Most common type of arthritis
-Irreversible, degenerative ("wear-and-tear") arthritis
-May reflect excessive release of enzymes that break down articular cartilage
-Cartilage is broken down faster than it is replaced
-Bone spurs (osteophytes) may form from thickened ends of bones
-By age 85, half of Americans develop OA, more women than men
rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Chronic, inflammatory, autoimmune disease of unknown cause
-inflimation of synovial membrane of affected joints, blood cells migrate to the joint and release inflammatory chemicals that destroy tissues
-synovial fluid accumulates, causing swelling
treatments: steroids, NSAID, immunosuppressants
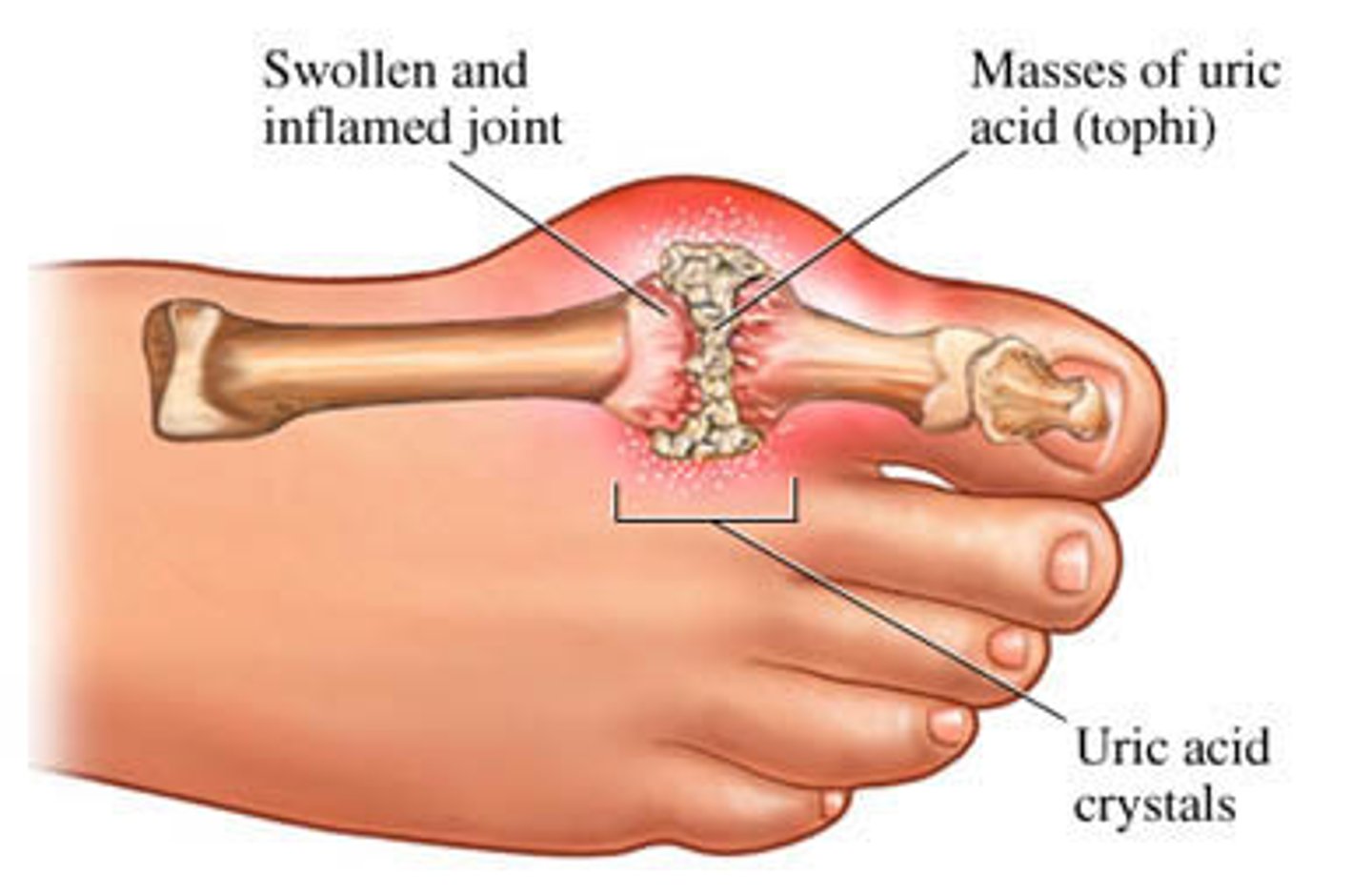
gouty arthitis (gout)
-deposition of uric acid crystals in joints followed by inflammation
-affects base of big toe
-if untreated bone ends fuse and immobilize joints
treatment: drugs, water, avoidance of alcohol and foods high in purines (liver, kidney, sardines...)