Cellular Respiration: Pathways and Processes Section 5: Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron Transport Chain & Chemiosmosis)
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biology
Biochemistry
A-Level Chemistry
AQA
Organic Chemistry
Cellular Respiration: Pathways and Processes Section 5: Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron Transport Chain & Chemiosmosis)
Section 5: Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron Transport Chain & Chemiosmosis)
Cellular Respiration: P&P Section 5: Oxidative Phosphorylation (ETC & C)
Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron Transport Chain & Chemiosmosis)
Bio-120-A
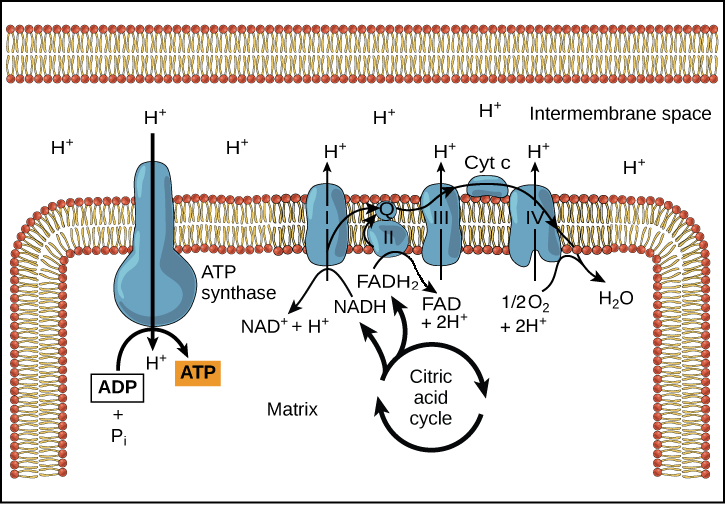
Electron Transport Chain
Module 8
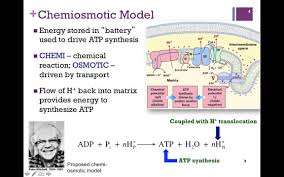
Chemiosmosis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
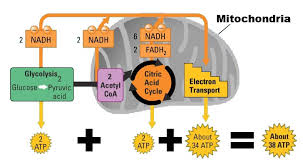
Oxidative Phosphorylation
ATP is produced via electron transport chain and chemiosmosis, powered by oxygen use.
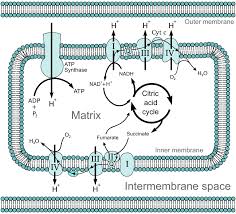
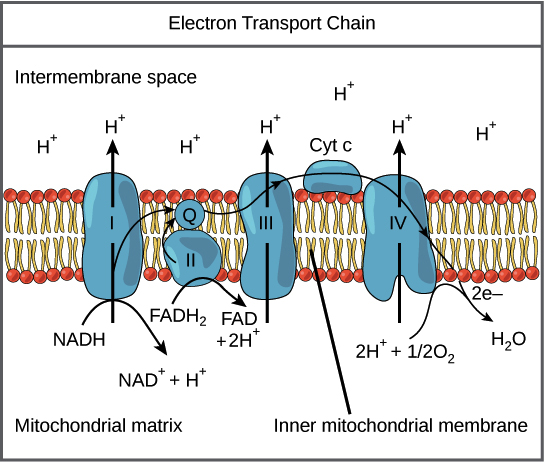
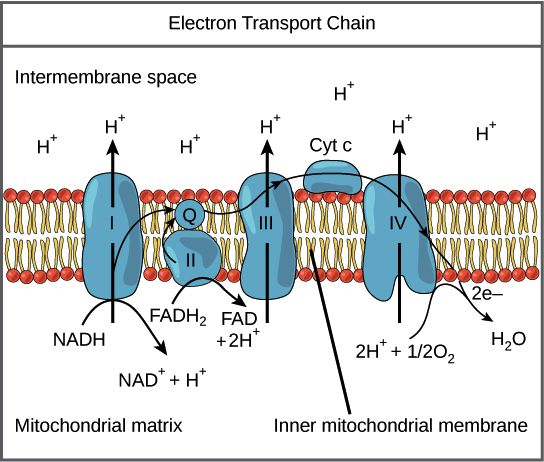
Electron Transport Chain
Proteins transfer electrons in mitochondrial respiration, pumping H+ and producing ATP efficiently.
Chemiosmosis
ATP production through H+ gradient-driven synthesis process.
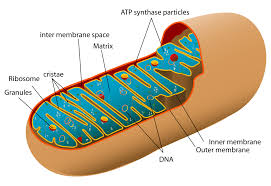
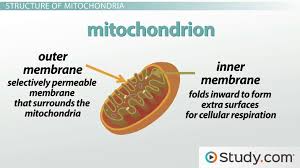
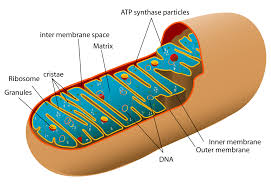
Mitochondria
Site of cellular respiration in eukaryotic cells (location of oxidative phosphorylation).
Prokaryotes
Organisms where respiration occurs in plasma membrane (location in prokaryotes).
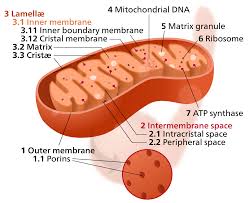
Inner Membrane
Location of electron transport and chemiosmosis in mitochondria.
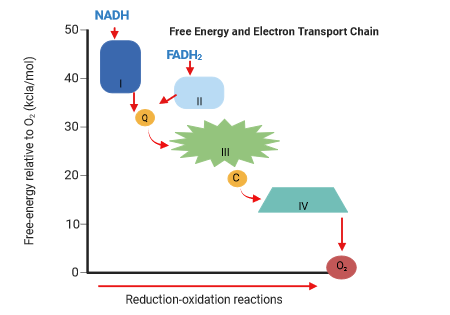
Oxygen
Final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain.
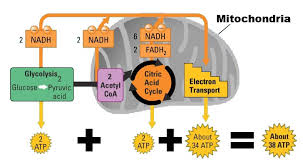
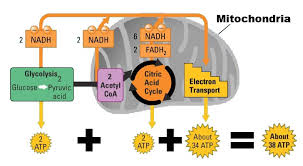
ATP Yield
Almost 90% of ATP generated by oxidative phosphorylation.
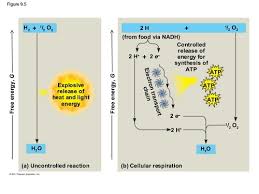
Energy Release
Occurs in steps to prevent explosive reactions (in the ETC).
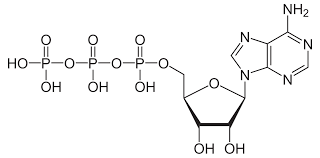
ATP
Energy currency of the cell, 7.3 kcal/mol (produced by oxidative phosphorylation).
Mitochondrial membrane
Membrane site for ATP synthesis and electron transport, utilizing chemiosmosis for energy production.
Proton-Motive Force
Proton gradient drives ATP synthesis in mitochondria for energy production.
Cristae
Folds of the inner mitochondrial membrane (increasing surface area for ETC).
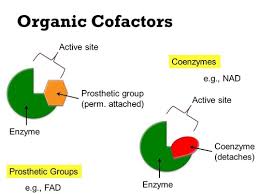
Prosthetic groups
Nonprotein components essential for enzyme function (in ETC proteins).
Redox reactions
Electron transfer processes involving oxidation and reduction (driving the ETC).
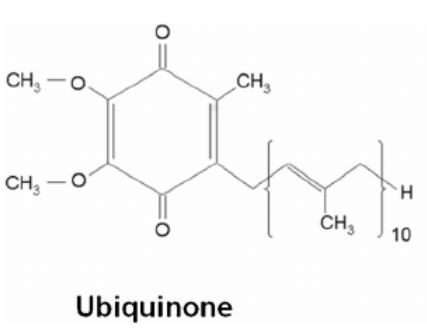
Ubiquinone
Mobile electron carrier in the membrane (ETC).
Cytochromes
Proteins in electron transport with heme groups (ETC).
Cyt a3
Last cytochrome transferring electrons to oxygen (ETC).
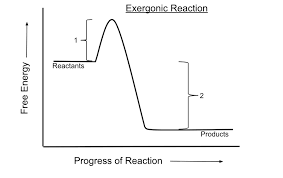
Free energy drop
Electrons lose energy moving through the chain (ETC).
ATP synthesis
synthesizes ATP from ADP using a proton gradient.
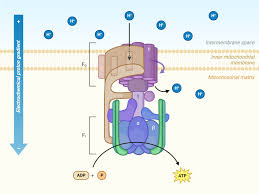
Hydrogen ions
Protons involved in forming water from oxygen (at the end of ETC).
Energy yield
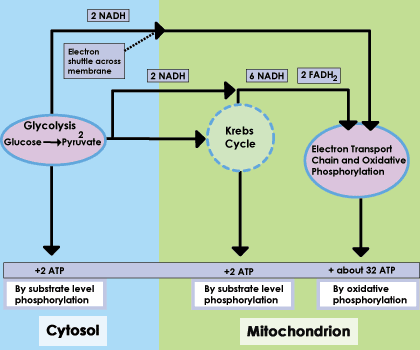
Total ATP from glucose is 38 ATP (majority from oxidative phosphorylation).
Electron carriers
Molecules that transfer electrons in respiration (NADH, FADH2, and within the ETC).
Lower energy level
FADH2 enters electron transport at a lower state (than NADH).
Hydrophobic molecule
Ubiquinone's property allows mobility in membranes (ETC).
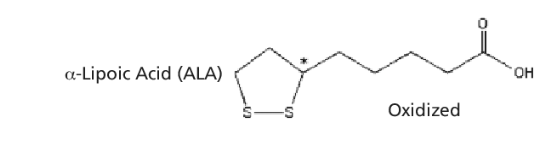
Oxidized form
State of a molecule after losing electrons (in the ETC).
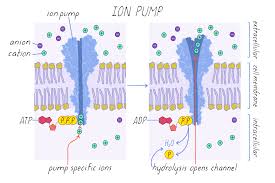
Ion Pump
Transports ions against gradients using ATP (conceptually related to proton pumps).
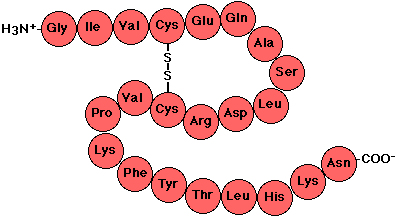
Polypeptides
Protein subunits making up ATP synthase structure.
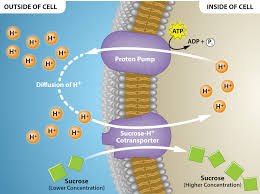
Nutrient Pumping
Prokaryotic use of H+ gradients for nutrient transport (related concept).
Flagella Rotation
Movement mechanism powered by proton-motive force (related concept in prokaryotes).
H+ Diffusion
Movement of protons down their concentration gradient (through ATP synthase)
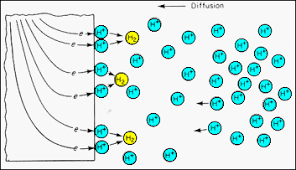
Intermembrane Space
Area where H+ accumulates during electron transport.
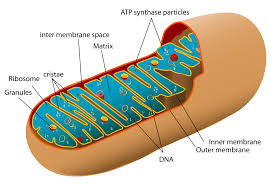
Mitochondrial Matrix
Space inside mitochondria where ATP synthesis occurs (where ADP and Pi are).
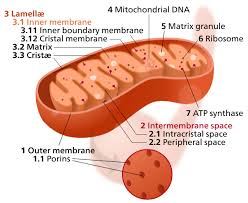
Efficiency of Respiration
Calculated as 34% for energy conversion, significantly influenced by oxidative phosphorylation processes.
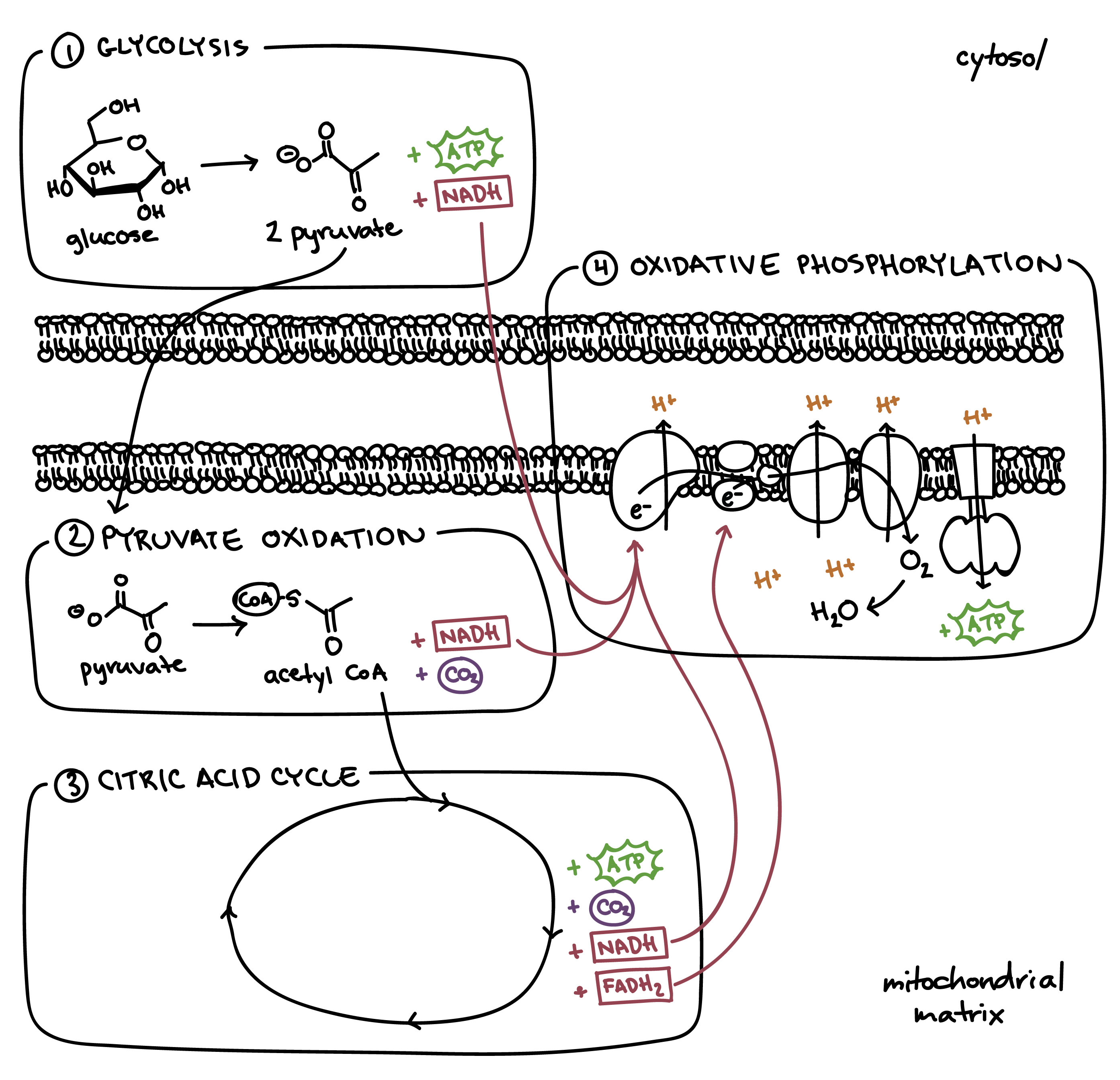
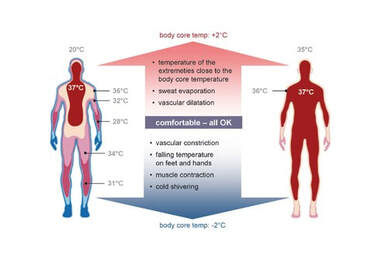
Heat Loss
Energy not converted to ATP, released as heat (some occurs in ETC).
Brown Fat
Tissue generating heat without ATP during hibernation (involves uncoupling in mitochondria).
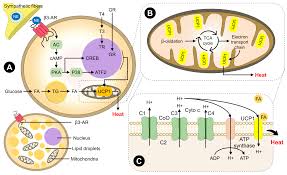
Uncoupling Protein
Allows protons to flow, generating heat instead of ATP (in mitochondria)
ATP Yield Variation
Depends on electron shuttle type used in cells (affecting NADH entry to ETC).
Body Temperature Maintenance
Heat generated helps maintain 37°C internal temperature (related to metabolic heat).
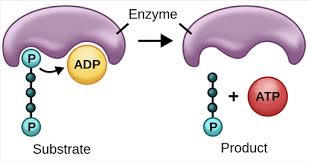
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
Direct ATP production from a substrate without electron transport (contrasting with oxidative phosphorylation).
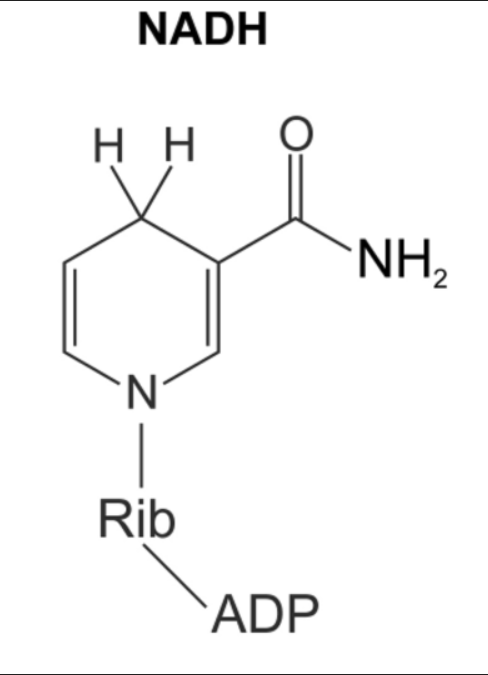
NADH
Reduced form of NAD+, carries electrons to electron transport.
Proton Gradient
Difference in H+ concentration across membranes (driving chemiosmosis).
Exergonic Reactions
Reactions releasing energy, driving H+ pumping (in the ETC).
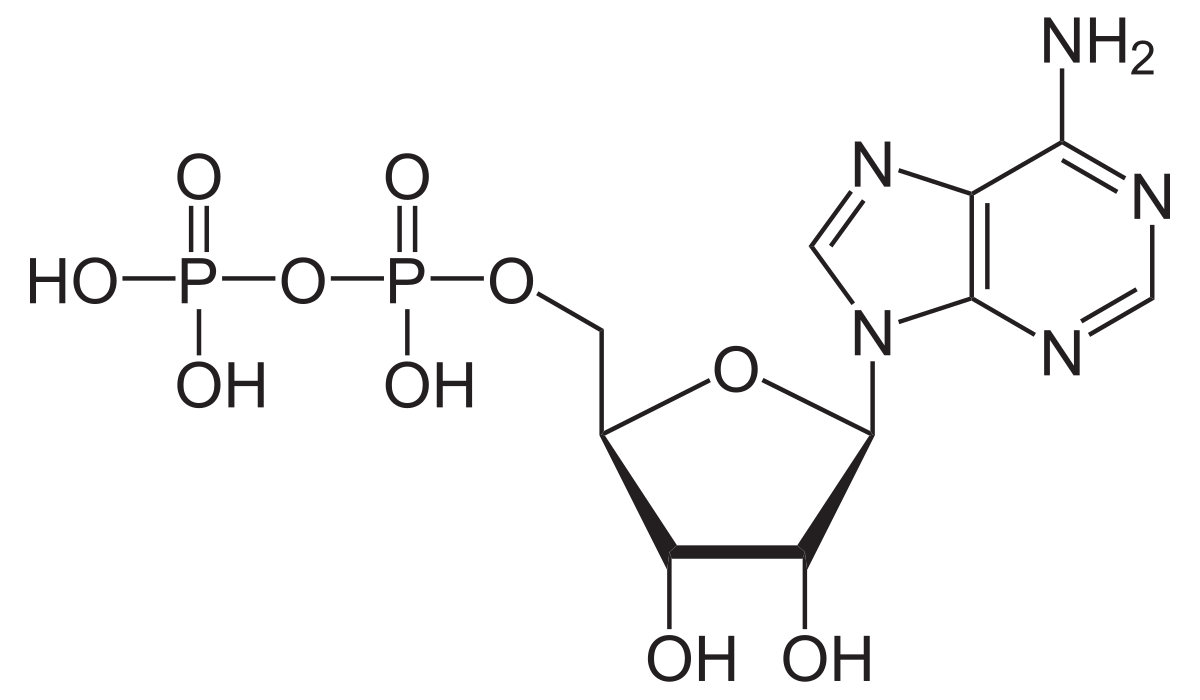
ADP
Adenosine diphosphate, precursor to ATP.
Inorganic Phosphate
Phosphate used in ATP synthesis with ADP.
Rotary Motor
ATP synthase's mechanism for ATP production.
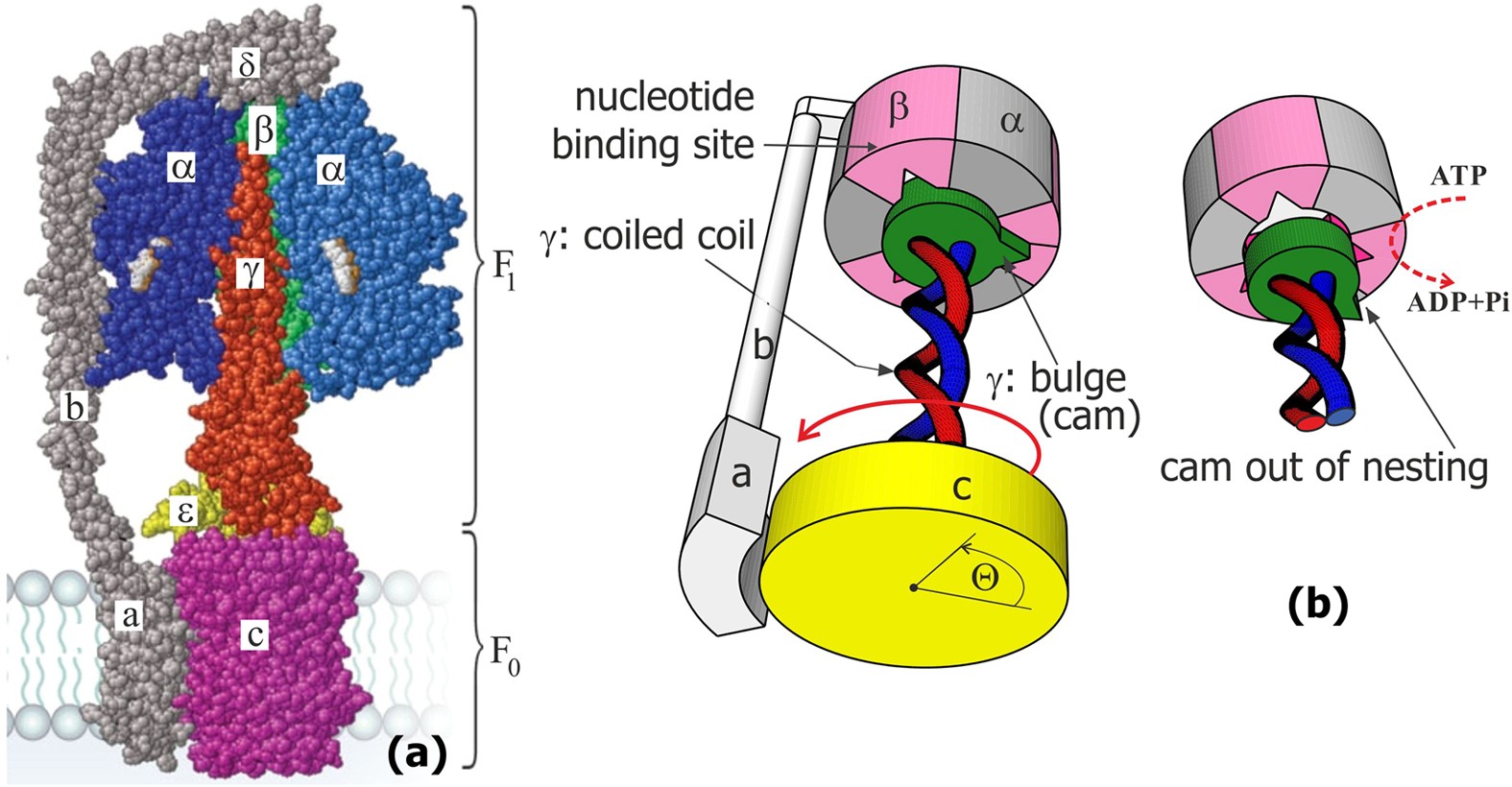
H+ Channels
Specific pathways for protons to re-enter mitochondria (through ATP synthase).
Binding Sites
Locations on ATP synthase for H+ entry.
Osmosis
Flow of H+ across a membrane driving ATP synthesis (though "chemiosmosis" is the specific term).