Hearing Science Exam 2
1/277
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
278 Terms
what problem does middle ear polarization function fix?
how to allow for motion of the cochlear liquids inside closed capsule by having 2 windows to inner ear with mechanical stimulation at oval window
what does the round window reciprocating response in the middle ear allow for?
it allows for displacement of cochlear liquids causing wave action stimulated by rocking motion of footplate of stapes
what is the middle ear ventilation and pressurization problem and what is the solution?
problem is the tympanic cavity is closed, air-filled cavity and the solution is that periodically open airway via eustachian tube
what muscles are used during swallowing, yawning, and chewing?
both tensor veli palitini and levator veli palatini
what is the opening for swallowing, yawning, and chewing?
at toros tubarius in nasopharynx
what does swallowing, yawning, and chewing do?
places TM in proper position and prevents unhygienic environment
eustachian tube dysfunction may lead to
a lack of middle ear aeration
what can a lack of. middle ear aeration lead to?
tympanic membrane retraction, chronic otitis media, hearing loss with language delay in children, chronic tympanic membrane perforations, or cholesteatoma
what is a cholesteatoma?
an abnormal skin growth in the middle ear
if a cholesteatoma is allowed to increase in size what might happen?
it may destroy the ossicular chain and in rare cases may also result in a permanent hearing loss, dizziness, and facial muscle paralysis
what problem does the middle ear protection/distortion control function seek to solve and how does it solve it?
the problem is protect inner ear from mechanical overstimulation and the solution is to increase tension of ossicular chain in order to reduce the low frequency sound intensity that reaches the cochlea
what is the mechanism of middle ear protection/distortion control function
the acoustic reflex is stimulated by eating, talking, yelling, other vocalizations, and exposure to high-level sounds. primarily, the stapedius muscle is contracted which stiffens the ossicular chain and reduces the sound reaching the cochlea
what is the efferent acoustic reflex pathway?
descending path from brainstem to stapedial muscle via VIIth (facial) nerve
what is the afferent acoustic reflex pathway?
ascending path from cochlea to brainstem via VIIIth nerve?
what is the acoustic reflex pathway?
from the inner ear (cochlea) to the ventral cochlear nucleus to the superior olivary complex to the facial nerve to the stapedius
what are the x and y axis for measuring the acoustic reflex response?
x axis is time
y axis is admittance or flow of sound energy into the middle ear
why is the acoustic reflex threshold determined and why is it used?
it's determined to measure the function of the acoustic reflex pathways and is used in part to determine the site of lesion for auditory disorders
sound reduction is provided by
the acoustic reflex
are low or high frequency sounds more attenuated (reduced)?
low frequency
what is maximum benefit for low frequencies?
20-30 dB
after the experiment, the stapedius reflex was functional or not functional in response to the highest level sounds?
functional
in rabbits with one ear with and one ear without functioning midle ear muscles, the ear without functioning MEMs had more what than ear with functional MEMs?
extensive damage
exercise ___ the stapedial reflex and ___ the risk of a temporary threshold shift, resulting in what?
depresses, increases, temporary hearing loss
what happens for the stapedius reflex to kick in?
loud sound and mostly a low frequency
which frequency region is found at the base?
high frequencies
what is the middle of the cochleus?
modiolus
cochlea turns around the
modiolus
what neurons conect to the hair cells
afferent and efferent neurons
what are habenula perforatum
holes in the osseous spiral lamina
what attacks high frequency and can cause hearing loss?
noise exposure, old age, sometimes genetics, some cancer drugs are oditoxic
what covers the tops of the hair cells
reticular lamina (a thin layer of connective tissue)
tectorial membrane covers
stereocilia of the hair cells
what are some characteristics of inner hair cells?
pear or flask shaped
approximately 3,500
single row
centralized nucleus
organelles distributed throughout the cell body
no motility
what are stereocilia like in the inner hair cells?
they are not attached to the tectorial membrane and are in crescent shape
what are some characteristics of outer hair cells?
cylindrical shape
approximately 12,000
3 rows
nucleus found in base
organelles found along the outer walls
"stretch and shrink" OHC motility
what are stereocilia like in the outer hair cells?
they are attached under the tectorial membrane and are in W or V shape
what are neurons like in inner hair cells?
95% of the afferent neurons
many afferent neurons connect to each IHC
afferent neurons synapse with cell body while efferent neurons synapse with the afferent neurons
what are neurons like in outer hair cells?
5% of afferent neurons
each afferent neuron (outer spiral fibers) connects to many OHCs
efferent and afferent neurons synapse directly with cell body
efferent neurons synapse with the _______, while afferent neurons synapse with ____
afferent neurons, IHC
efferent and afferent neurons synapse directly with
the OHC
each afferent neuron (outer spiral fibers) connects to many
OHCs
type 2 fibres synapse with up to
50 OHCs
many type 1 fibres synapse with ______ directly opposite their habenular opening
one IHC
the features of the cochlea imply a complex systen that is
mechanical (vibrator motion)
hydraulic (wave motion)
chemo-electrical (nerve energy)
what is the role of the semicircular canal?
to sense movement of the head, both speed and direction
how many semi circular canals are there?
3
what are the two parts parts of the vestibule?
the saccule and utricle
where is the utricle located?
superior to the saccule
what are the utricle and saccule used for?
to detect the orientation of the head, ex. tipped down or up, or tilted to one side
what is the cochlea?
it's closed, labryrinthine capsule, filled with fluid
where is the cochlea?
inner ear in petrous portion of temporal bone; it's the most anterior structure
what is the cochlea named for?
the sea snail that its shape resembles
what is the auditory branch of the 8th nerve?
large bundle of nerve cells that enters the center of the cochlea
how many turns is the bony labrynth?
2 5/8th turns
are schematic of the cochlea stretched or coiled?
stretched, note the tube inside the canal
what are the 3 major anatomical components of the inner ear?
semi circular canals, vestibule, and the cochlea
what is the bony canal?
it's like a spiral staircase that turns around the modiolus
what is the modiolus?
the center of the cochlea with solid bone walls
auditory nervefibers from the hair cells enter the
modiolus
what is the line that passes through the modiolus?
the center of the cochlea
what does Reissner's membrane separate?
the scala vestibuli and the scala media
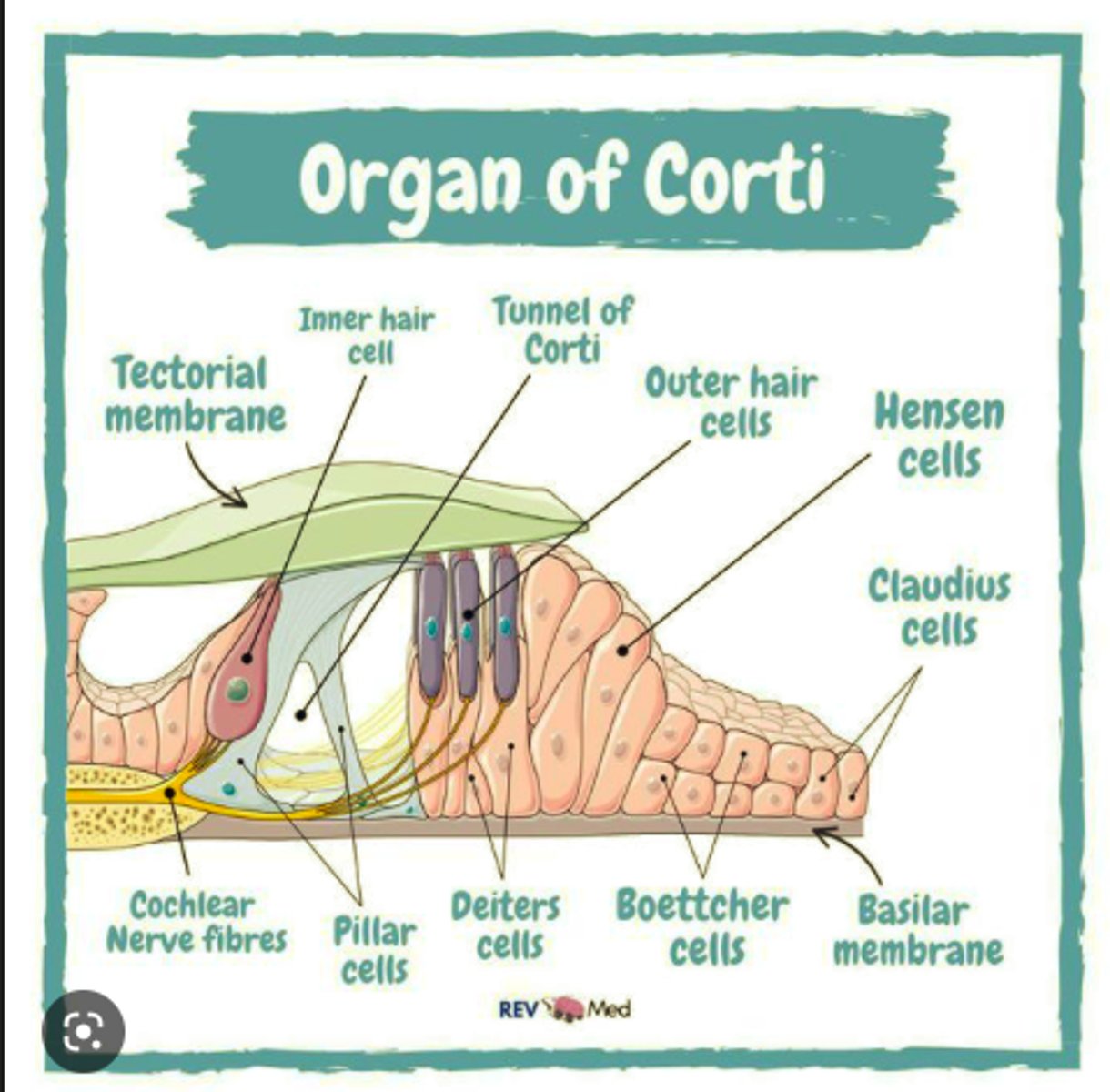
what is the organ of corti?
discovered by Alfonzo Corti, in the middle scala of the ear, the actual hearing apparatus
what does the organ of corti hold?
outer and inner hair cells and tectorial membrane
labeled organ of corti
the human ear is not sensitive to sounds outside
20-20,000 Hz
what is the tectorial membrane
part of the scala media that covers the inner and outer hair cells along the basilar membrane
nerve cells attach to the
cell body
how many turns is the bony labyrinth
2 5/8ths
how long is the base to the apex of the bony labrynth
35 mm (about 1' long)
where does the labyrinth of the cochlea end?
at the helicotrema in the apex
the base of the cochlea is near the ____ while the apex is where?
stapes footplate, apex is at the other end of the bony labyrinth
what is paralymph?
fluid in both the oval and round windows
what happens at the helicotrema?
the scala tympani and scala vestibuli meet
what is the osseous spiral lamina?
bony extension of the medial wall of the bony labyrinth, runs continuously along the medial wall
what are the holes in the osseous spiral lamina called?
habenulae perforata
the width of the osseous spiral lamina ____ between the base and apex of the cochlea
decreases
by the time the cochlea reaches its third turn, the osseous spiral lamina has nearly
disappointed/disappeared
3 sections/scalas of the mebranous labyrinth
scala vestibuli, scala media, scala tempani
characteristics of the scala vestibuli
bounded inferiorly by Reissner's membrane
ends at helicotrema
contains perilymph
where are the spinal ganglion and what does it do?
in the modiolus and houses lots of cell bodies together
where does the 8th nerve come out of?
the spiral lamina and then goes into the internal auditory meatus
outer hair cells are on the ____ side of the scala media of the basiliar membrane of the cochlea
lateral
what is the auditory nerve and where does it attach?
the 8th nerve which is a bunch of nerve cells together attached to the cochlear nucleus
what do neurons, nerve cells, and nerve fibers attach to
inner and outer hair cells
what is a vestibule
a small entrance hole
what is the scala vestibuli bounded by?
inferiorly by Reissner's membrane
what is the scala tympani bounded by?
bounded superiorly by basilar membrane
where does the scala tympani end?
at the helicotrema
what does the scala tympani contain?
perilymph
does the width of the basilar membrane increase or decrease between the base and the apex of the cochlea?
increase
what does the increase in width (and in mass) of the basilar membrane correspond with?
the decrease in the width of the osseous spiral lamina (to which the basilar membrane is attached to on its medial surface)
damage at the cochlea can cause
low frequency hearing loss and voiceless fricative hearing problems
noise exposure, old age, odotoxic medications can damage what part of the cochlea?
high frequencies (at the base)
what is the scala media bounded by?
bounded superiorly by Reissner's membrane and inferiorly by basilar membrane
what does the scala media contain?
the organ of corti and endolymph
is the osseuous spiral lamina closer to the inner or outer hair cells?
closer to inner hair cells
how do the scala vestibuli and scala tympani share perilymph and what keeps the endolymph in the scala media?
Reissner's superiorly and basilar membrane inferiorly
perilymph is shared at
helicotrema
what are the attachments for the basilar membrane
spiral ligament on lateral side, osseous spiral lamina on medial side
what are on top of the osseous spiral lamina?
fibrous stiff cells