ATP & Cellular Respiration
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts in ATP and cellular respiration.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Cellular respiration
involves the production of ATP energy
Mitochondrion
The mighty energy producer of the cell, responsible for generating ATP.
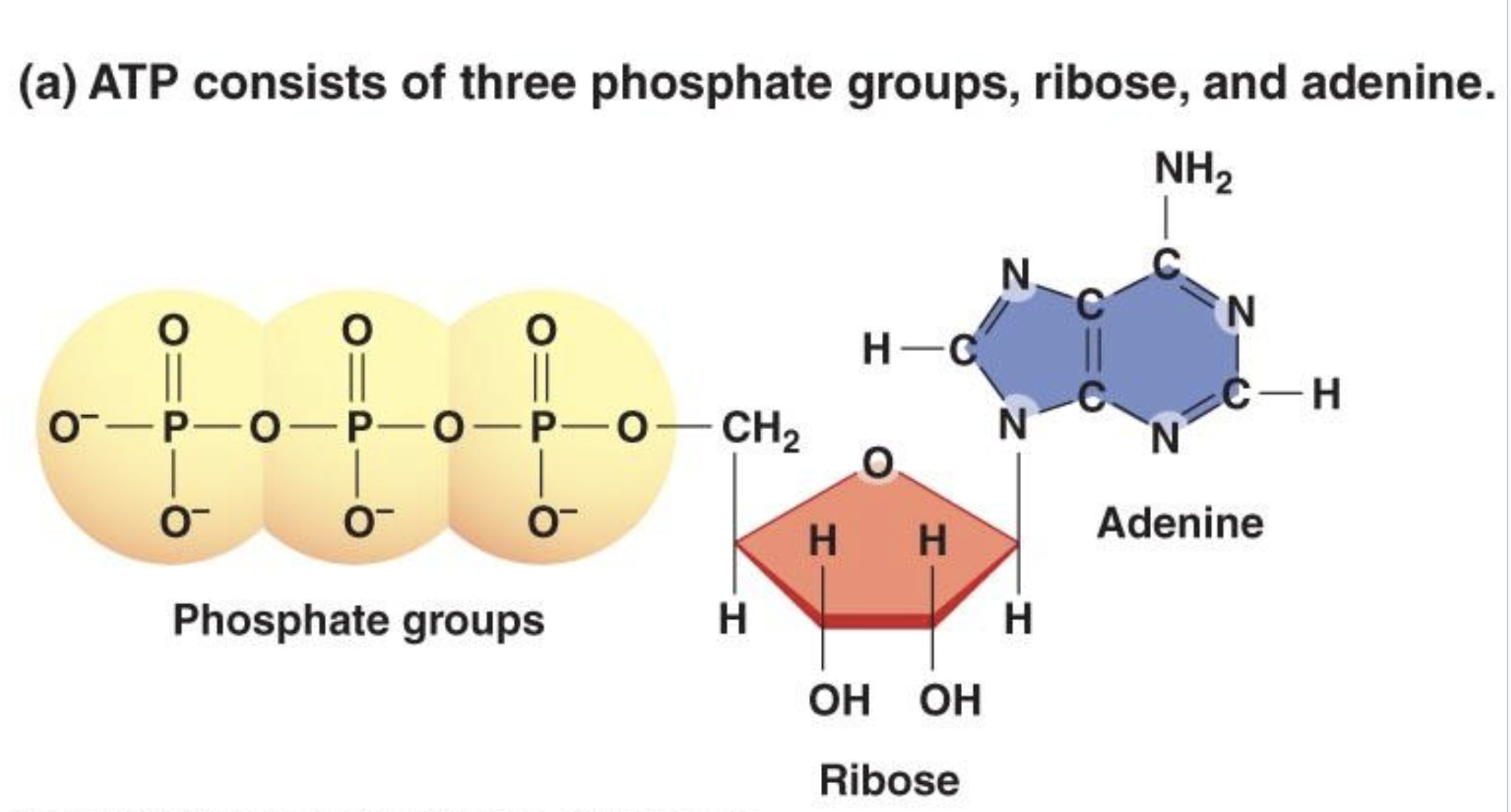
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate; the primary energy carrier in cells.
Glycolysis
The first step in cellular respiration, breaking glucose into two pyruvate molecules.
Aerobic respiration
Type of respiration that requires oxygen and occurs in the mitochondria, producing a large amount of ATP.
Anaerobic respiration
Type of respiration that occurs without oxygen, typically resulting in fermentation. It happens in the cytoplasm. It produces less ATP energy and doesn't completely break down glucose
Fermentation
A metabolic process that converts sugar to acids, gases, or alcohol in the absence of oxygen.
Lactic acid fermentation
A type of anaerobic respiration occurring in some bacteria and animal cells, producing lactic acid.
Alcoholic fermentation
A type of anaerobic respiration occurring in yeasts and bacteria, producing CO2 and alcohol.
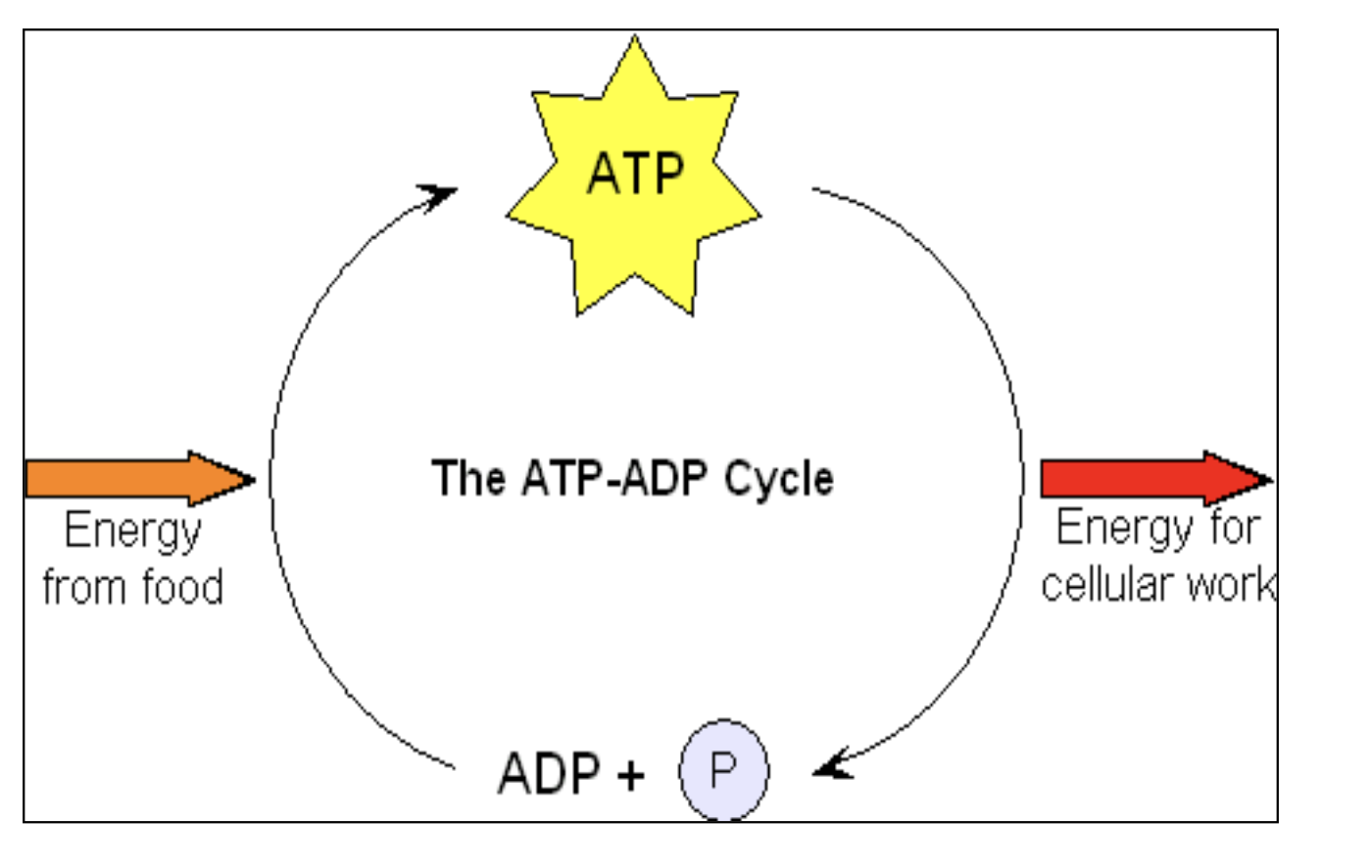
ADP
Adenosine diphosphate; a molecule that is formed when ATP loses one phosphate group.
Respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy; represents the overall process of cellular respiration.
Photosynthesis Equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (sunlight) → C6H12O6 + 6O2 (Glucose); represents the overall process of photosynthesis.
ATP/ADP cycle
The process by which ATP is converted to ADP and back, involving the transfer of energy and phosphate groups. Energy is released when a phosphate bond is broken.
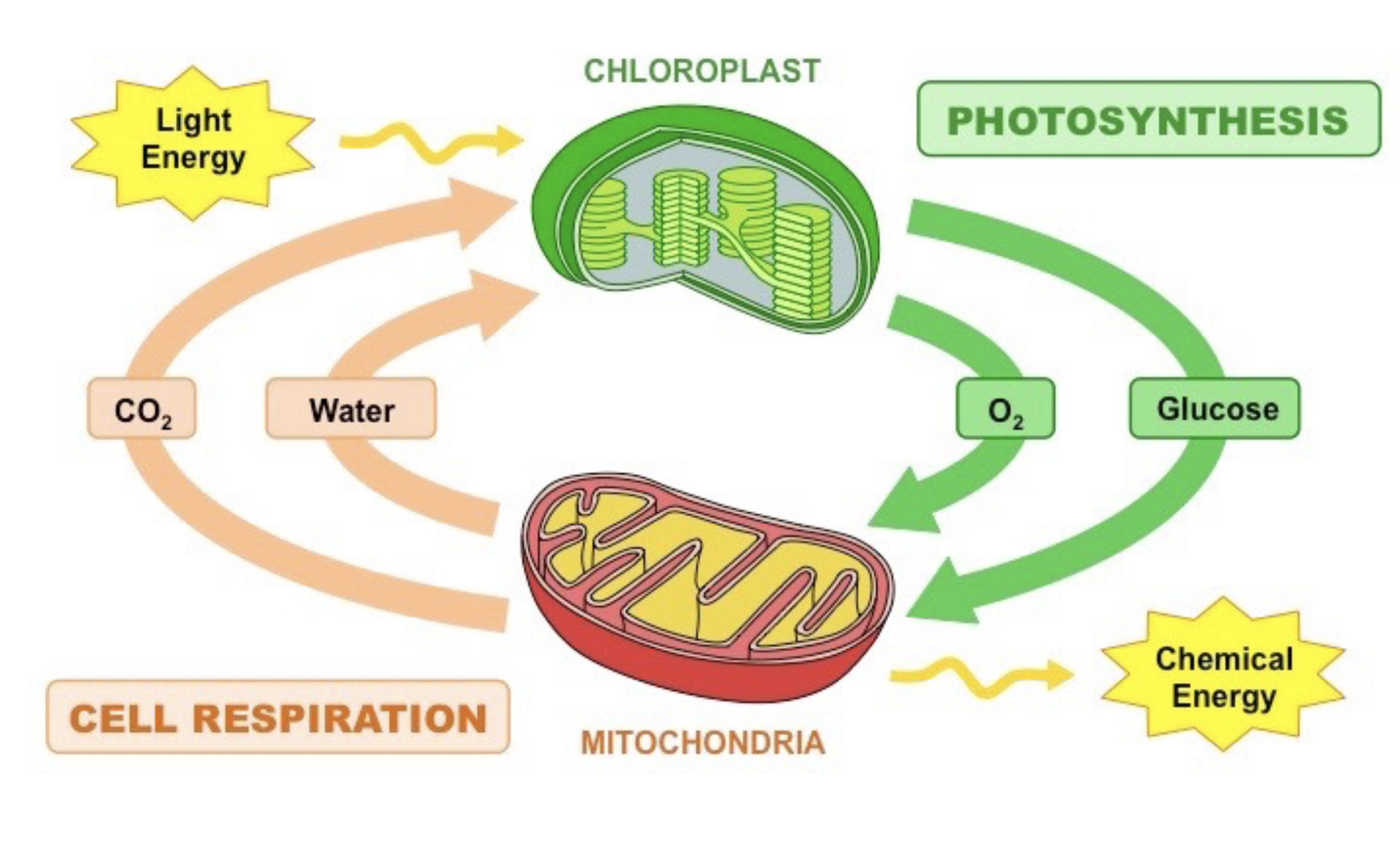
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy (glucose) using chloroplasts.
Cellular respiration
The process by which cells break down glucose to produce ATP.
Carbon cycle
The ecological cycle that involves the transformation of carbon among various environmental reservoirs.
Phosphate bond
A high-energy bond in ATP that, when broken, releases energy for cellular activities.
Net gain of ATP in glycolysis
2 ATP; the total amount of ATP made during the glycolysis stage of cellular respiration.
Respiration Aerobic and Anaerobic Pathways
Image

Cellular Carbon Cycle
Plants do both respiration and photosynthesis