earth's geological processes & hazards (#3)
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
🍂
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
exogenic processes
these are external forces that operate and act on the Earth’s surface;
“destructive forces”
ex. weathering, mass wasting, soil erosion
weathering
EXOGENIC PROCESSES:
refers to breaking down of rocks & minerals near the Earth’s surface;
can be physical, chemical, or biological
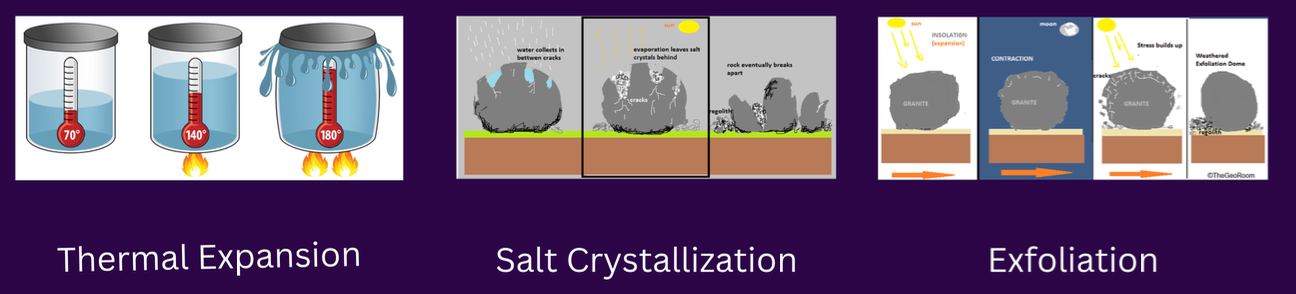
physical weathering
TYPES OF WEATHERING:
process of rock & mineral breakdown without altering their chemical composition;
causes: water, wind, gravity, temperature change
chemical weathering
TYPES OF WEATHERING:
process of rock & mineral breakdown due to chemical reactions;
causes: elements, mineral composition, acids
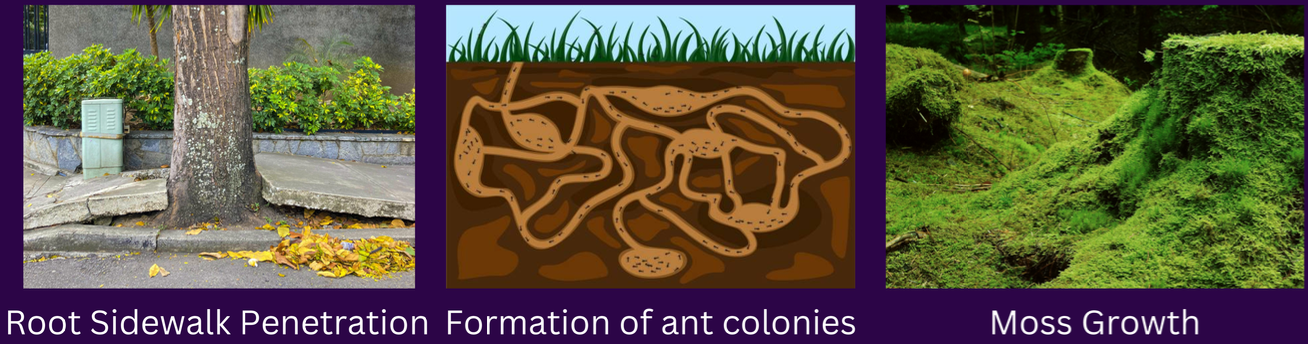
biological weathering
TYPES OF WEATHERING:
process of rock & mineral breakdown as a result of plant & animal activity;
causes: organisms
mass wasting
EXOGENIC PROCESSSES:
refers to the movement of rock and/or soil down a slope influenced by gravity;
ex. creep, debris flow, falls, slumps, solifluction
creep
TYPES OF MASS WASTING:
slow and gradual movement of soil and rocks down a slope;
barely noticeable due to its very slow movement
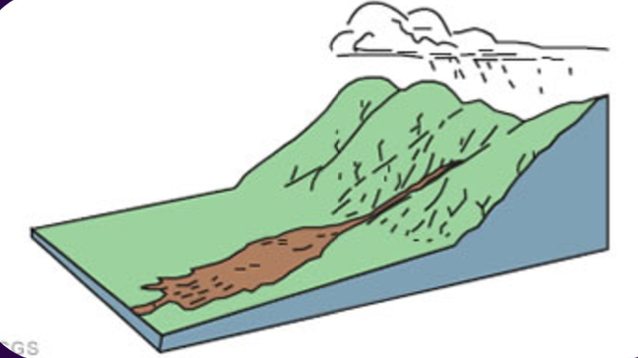
debris flow
TYPES OF MASS WASTING:
refers to the material flow caused by rainfall or seismic activity
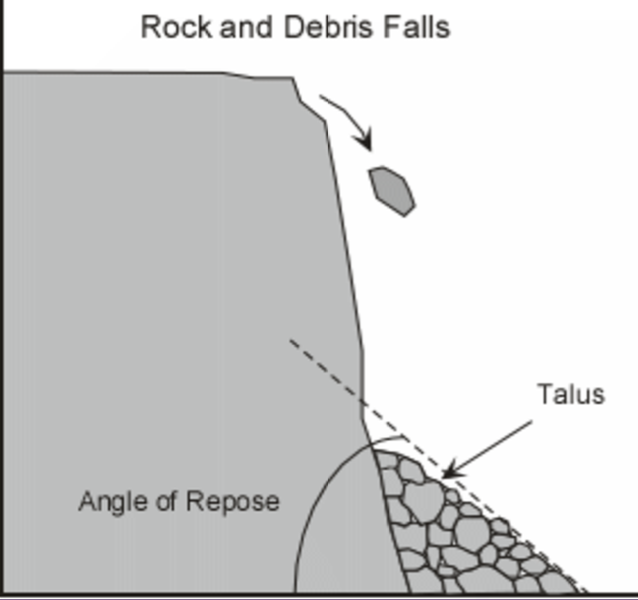
falls
TYPES OF MASS WASTING:
occur when rocks or rock masses rapidly move down a slope
slumps
TYPES OF MASS WASTING:
occur when soil and/or rock debris move downhill along a curved plane in a rotational manner
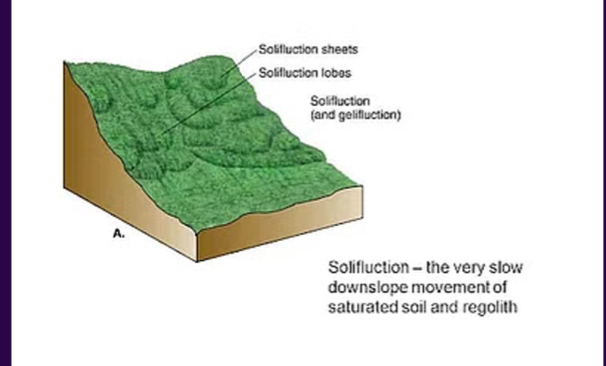
solifluction
TYPES OF MASS WASTING:
sluggish flow of saturated soil down a slope related to freeze-thaw activity
soil erosion
EXOGENIC PROCESSES:
gradual wearing away of the soil’s surface;
water erosion, wind erosion, gravitational erosion
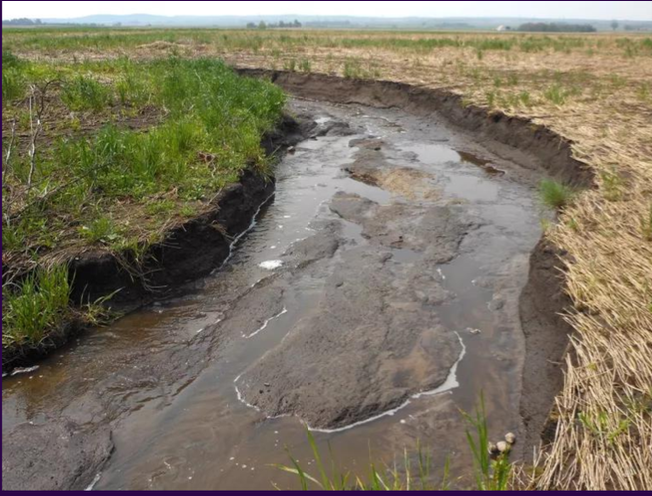
water erosion
TYPES OF EROSION:
degradation of soil due to flow of water from nearby bodies of water

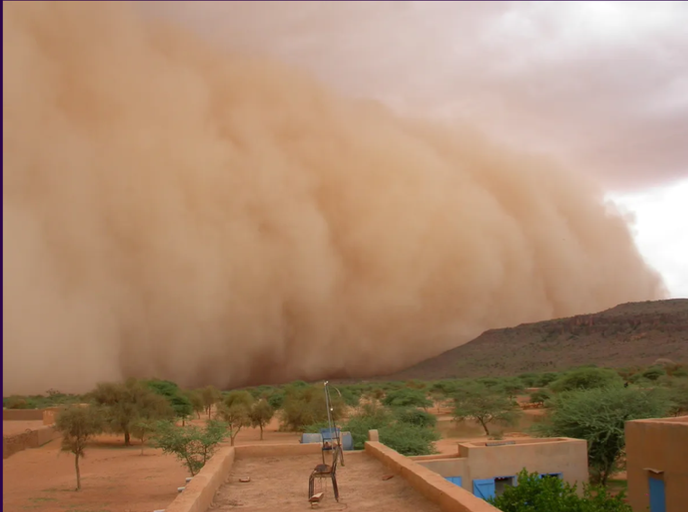
wind erosion
TYPES OF EROSION:
natural process that moves soil from one place to another by wind power

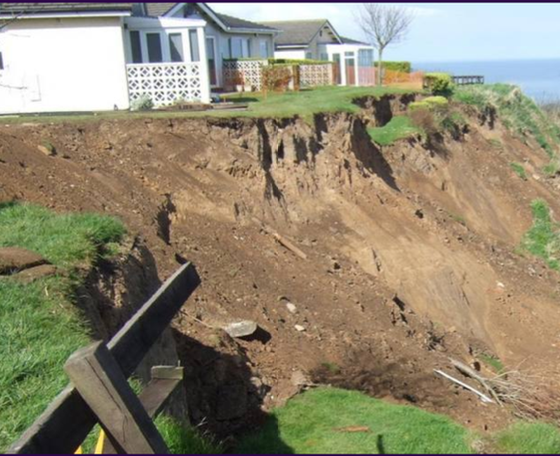
gravitational erosion
TYPES OF EROSION:
erosion wherein rocks & sediments move under gravity’s influence

True
TRUE OR FALSE:
In erosion, nutrient depletion in the soil could be observed due to the loss of minerals.
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
In erosion, issues regarding water purity arise as eroded sediments become mixed with water.
endogenic processes
these are internal forces that exist deep inside the Earth
ex. tectonic plates, faults, earthquakes, volcanoes
plate tectonics theory
though it remains a theory, this aims to explain how major landforms are created as a result of Earth’s subterranean movements
tectonic forces
ENDOGENIC FORCES:
these refer to the energy that causes a change in the Earth’s crust
compressional, tensional, & shear stress (CTS)
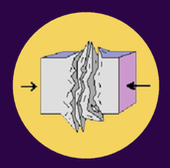
compressional stress
3 TYPES OF STRESS:
occurs when tectonic plates are pushed together, resulting in a shorter but thicker crust
ex. Sierra Madre
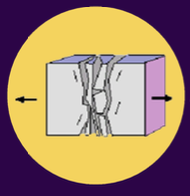
tensional stress
3 TYPES OF STRESS:
occurs when tectonic plates are pulled apart, resulting in a thinner crust
ex. East African Rift (or rift valleys in general)
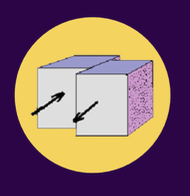
shear stress
3 TYPES OF STRESS:
occurs when parallel plates move in opposite directions, commonly leading to formation of faults
ex. San Andreas Fault
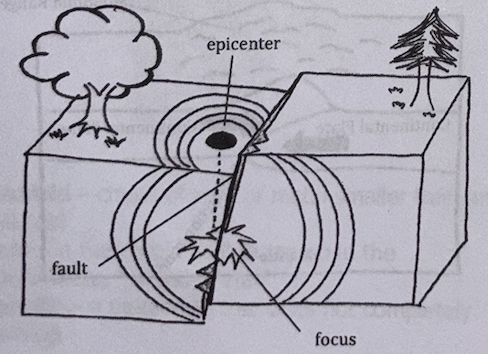
fault
ENDOGENIC PROCESSES:
refers to the fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rocks or 2 tectonic plates
normal, reverse, strike-slip (NRS)
normal fault
3 TYPES OF FAULT:
this forms when the Earth’s surface moves apart due to tensional stress;
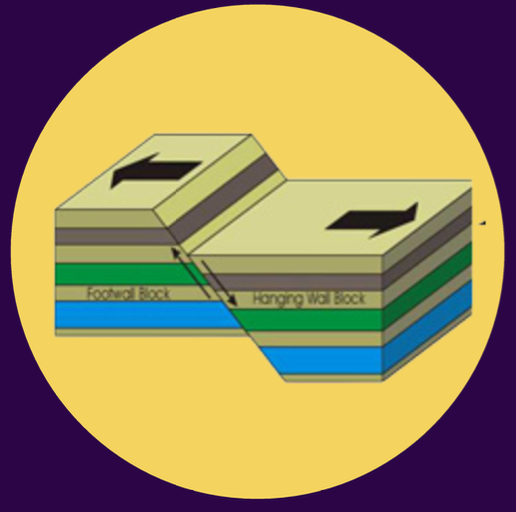
normal fault
3 TYPES OF FAULT:
this occurs when the hanging wall moves down relative to the foot wall
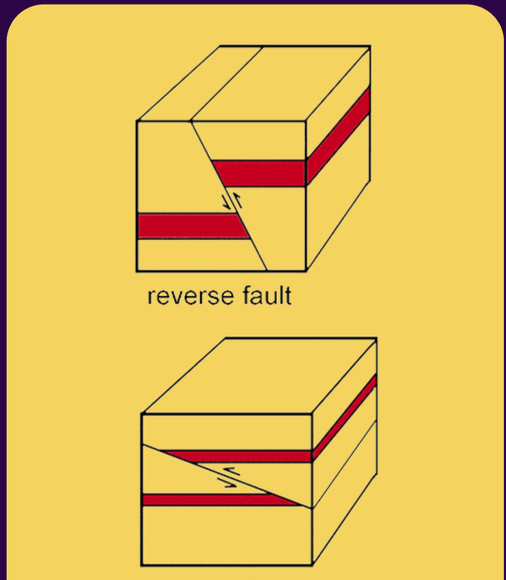
reverse fault
3 TYPES OF FAULT:
this forms when the Earth’s surface moves towards one another & is associated with compressional stress
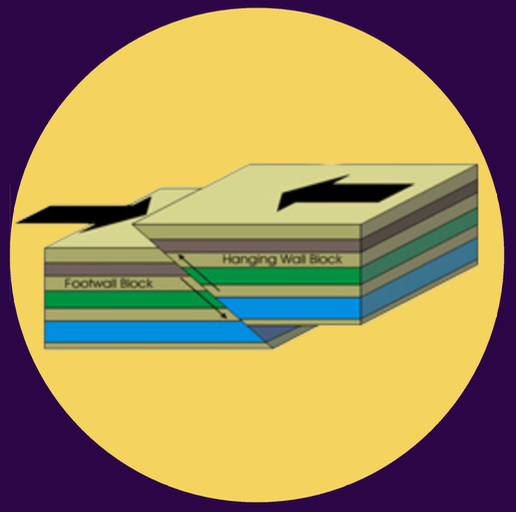
reverse fault
3 TYPES OF FAULT:
occurs when the hanging wall moves up or is thrust over the foot wall
thrust fault
this a form of reverse fault in which the dip is less than 45 degrees
strike-slip fault (transcurrent fault)
3 TYPES OF FAULT:
this is formed due to the sideways movement of blocks/plates
can be right lateral strike-slip fault or left lateral strike-slip fault
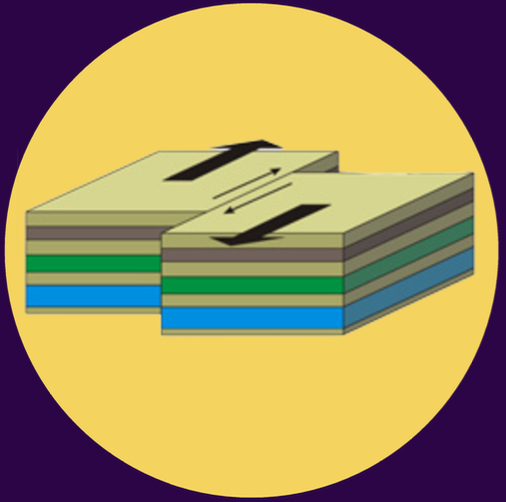
strike-slip fault (transcurrent fault)
3 TYPES OF FAULT:
in this fault, the block moves laterally in opposite directions relative to a reference point
right lateral strike-slip fault and left lateral strike-slip fault
2 classification of strike-slip fault
False; tsunamis should be earthquakes
TRUE OR FALSE:
Normal, reverse, and strike-slip faults result in tsunamis and the alteration of Earth’s crust.
normal and reverse faults, strike-slip fault
What types of fault form these geographical formations?
rifts, valleys, & mountains
valleys or undersea canyons
earthquakes
ENDOGENIC PROCESSES:
these are caused by the movement of tectonic plates due to tectonic forces;
also produce seismic waves;
seismograph is used to detect/record seismic waves
seismic waves
ENDOGENIC PROCESSES:
these are vibrations that transmit energy & occur during seismic activities (like earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, & man-made explosions)
primary & secondary waves
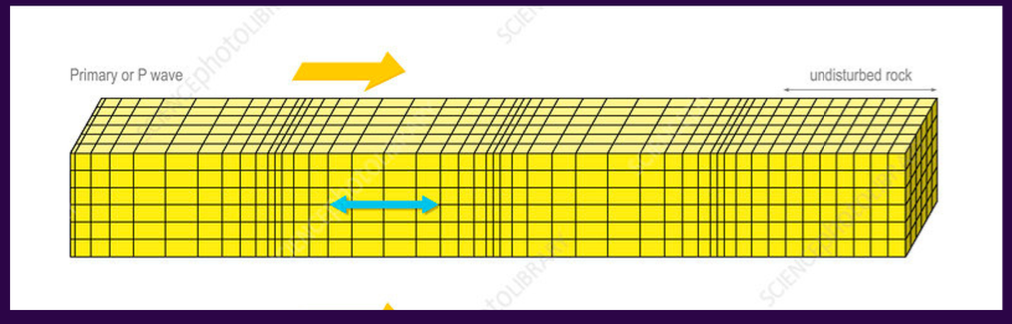
primary waves (p-waves/pressure waves)
these are longitudinal waves, which means that the direction of motion & propagation are the same
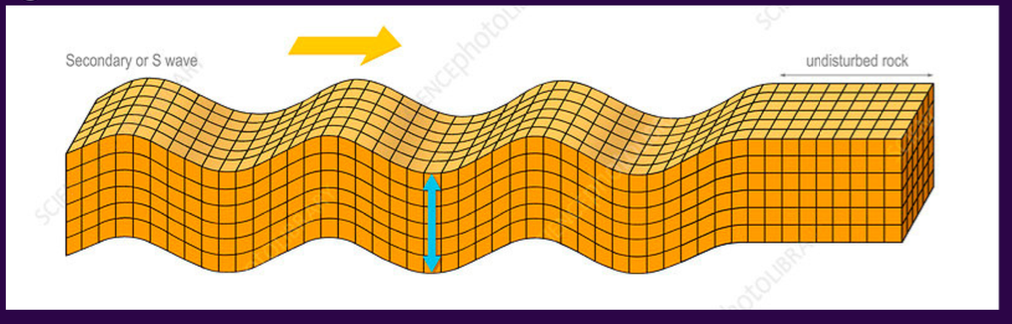
secondary waves (s-waves)
these are transverse waves, which means that the motion is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation
subduction
ENDOGENIC PROCESSES:
volcanoes form from the process of _______, wherein either an oceanic plate descends below another oceanic plate or an oceanic plate descends under a continental plate
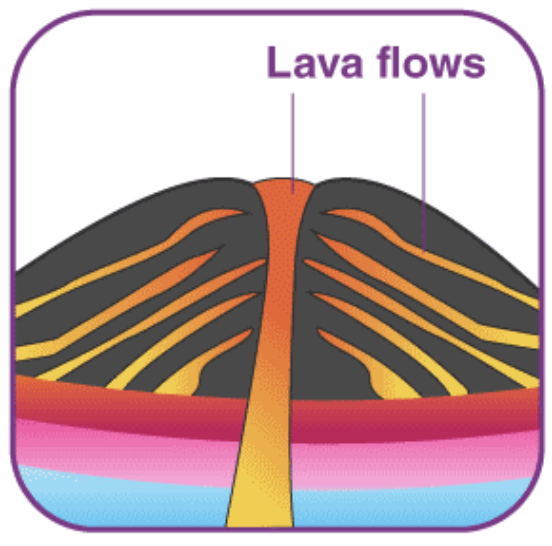
shield volcano
TYPES OF VOLCANO:
this is shaped as a bowl with long gentle slopes made by basaltic lava flows;
formed by eruption of low-viscosity lava that can flow a great distance from a vent
ex. Mauna Kea (Hawaii)
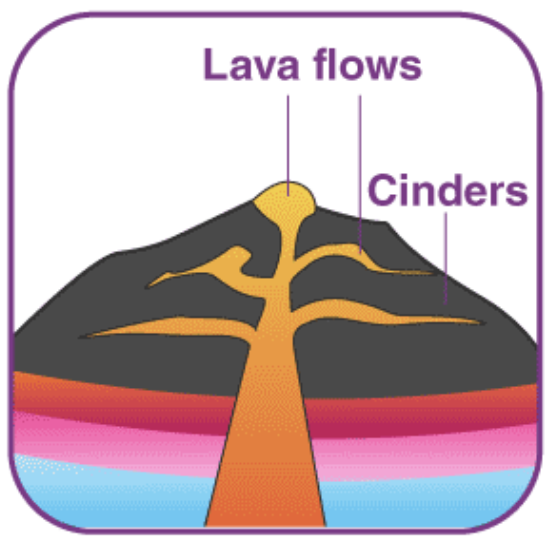
stratovolcano (composite volcano)
TYPES OF VOLCANO:
is a steep-sided volcano composed of many layers of volcanic rocks, usually made from high-viscosity lava, ash, & rock debris
ex. Mount Mayon (Bicol)
cinder volcano
TYPES OF VOLCANO:
this is circular or oval made up of small fragment of lava from a single vent that have been flown up;
low-viscosity lava;
results from eruptions of mostly small pieces of scoria and pyroclastic that build up around the vent
ex. Smith Volcano (Babuyan Island)
magmatic eruptions
3 MAIN MECHANISMS OF VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS:
these are caused when gas releases under decompression

phreatic eruptions
3 MAIN MECHANISMS OF VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS:
these are caused when an ejection of entrained particles during steam eruptions happen

phreatomagmatic eruptions
3 MAIN MECHANISMS OF VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS:
these are caused when a thermal contraction from chilling on contact with water happens

natural hazards
RS BETWEEN GEOLOGIC PROCESSES & NATURAL HAZARDS:
refer to natural events that threaten lives, property, and other assets;
both endogenic & exogenic influence the occurence of _______ _______
tectonic hazards, geomorphological hazards, hydrometeorological hazards
3 TYPES OF NATURAL HAZARDS:
during earthquakes & volcanic eruptions
during landslides & soil erosion
during storms & flooding
cascading effect
RS BETWEEN GEOLOGIC PROCESSES & NATURAL HAZARDS:
this is a chain reaction where one geological event leads to multiple secondary consequences;
ex. volcanic eruptions causing climate change that leads to extreme weather; deforestation causes soil erosion and leads to landslides.
feedback loop
RS BETWEEN GEOLOGIC PROCESSES & NATURAL HAZARDS:
this occurs when an initial geological process reinforces itself, either increasing or decreasing an event’s intensity
positive feedback loop
TYPES OF FEEDBACK LOOP:
this relates to amplifying effects
ex. Glacial melting causing crustal rebound that leads to more earthquakes
negative feedback loop
TYPES OF FEEDBACK LOOP:
this relates to stabilizing effects
ex. after a volcanic eruption volcanic, ash enriches the soil with minerals that lead to fertile lands encouraging plant growth that stabilizes the soil with vegetation that prevents further erosions
geological processes
these shape Earth’s landscapes but also contribute to hazards like earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, landslides, and floods;
these interactions amplify hazard risks, making them harder to predict and control.
ex. Earthquake (endogenic) causing a landslide (exogenic) leading to a river blockage that causes flooding
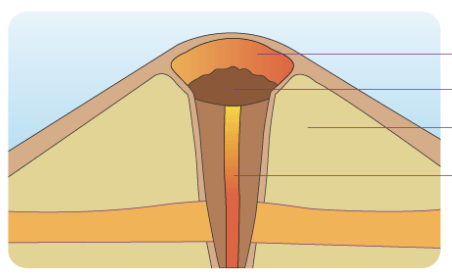
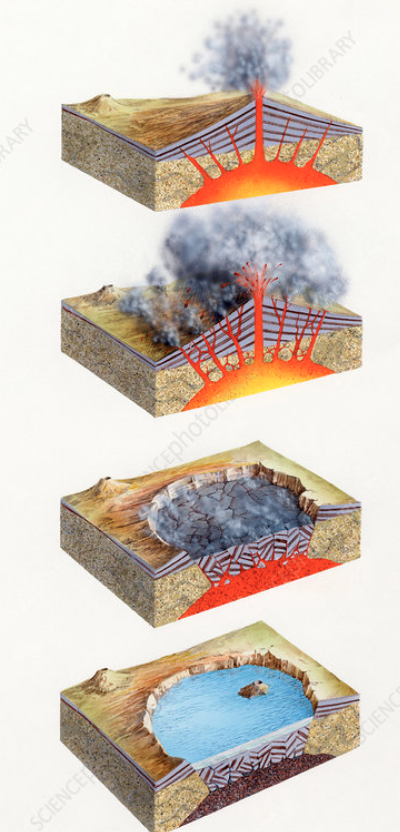
caldera
refers to the large depression formed when a volcano erupts and collapses;
during a volcanic eruption, magma present in the magma chamber underneath the volcano is expelled, often forcefully
Richter scale
UNDER EARTHQUAKES:
measures the strength/magnitude of earthquakes;
uses Arabic numbers (1 to 10), wherein magnitude 2 is 10x stronger than magnitude 1, & so on;
Moment magnitude scale (now more commonly used bc of higher precision)
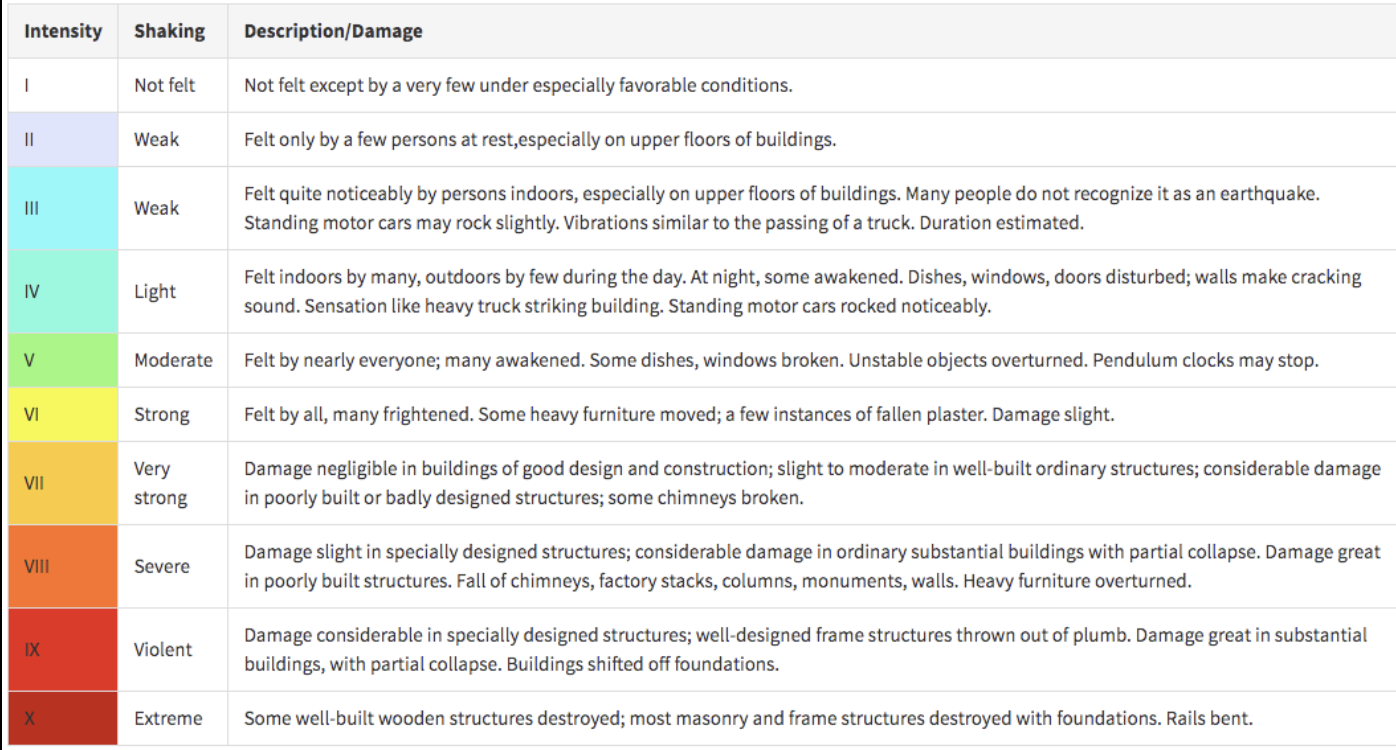
Mercalli scale
UNDER EARTHQUAKES:
intensity is measured using this (Roman numerals, I to X)
focus/hypocenter
UNDER EARTHQUAKES:
earthquake’s point of origin inside the earth
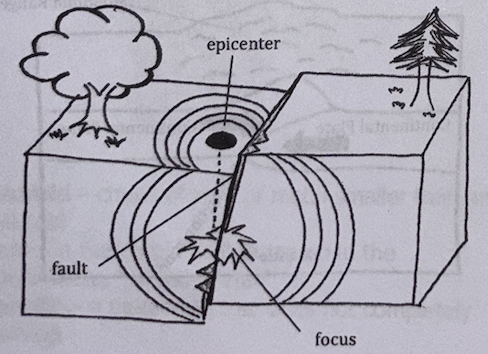
epicenter
UNDER EARTHQUAKES:
point on earth’s surface directly above the focus
magnitude, intensity
UNDER EARTHQUAKES:
the size of an earthquake or energy released
amount of damage caused by an earthquake
Continental Drift Theory by Alfred Wegener (1912)
UNDER TECTONICS:
theory of the movement of the continents relative to each other;
some evidences are:
fossils in Africa & South America
positions of mountain ranges
glacial striations - scratches in rock caused by movement of glaciers
tillites - glacial sediments buried in rock
tillites
refers to glacial sediments buried in rock
UNDER PLATE TECTONICS:
the "supercontinent" that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras; broke up into Laurasia in the north and Gondwanaland in the south during the Mesozoic era
UNDER PLATE TECTONICS:
started breaking up into Asia, Europe, and North America during the Cenozoic era
UNDER PLATE TECTONICS:
started breaking up into Africa, Australia, Antarctica, and South America during the Mesozoic era