Foundations of Nursing Exam #1 Infection and Control
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Results when a pathogen invades tissues and begins growing within a host
What is an infection?
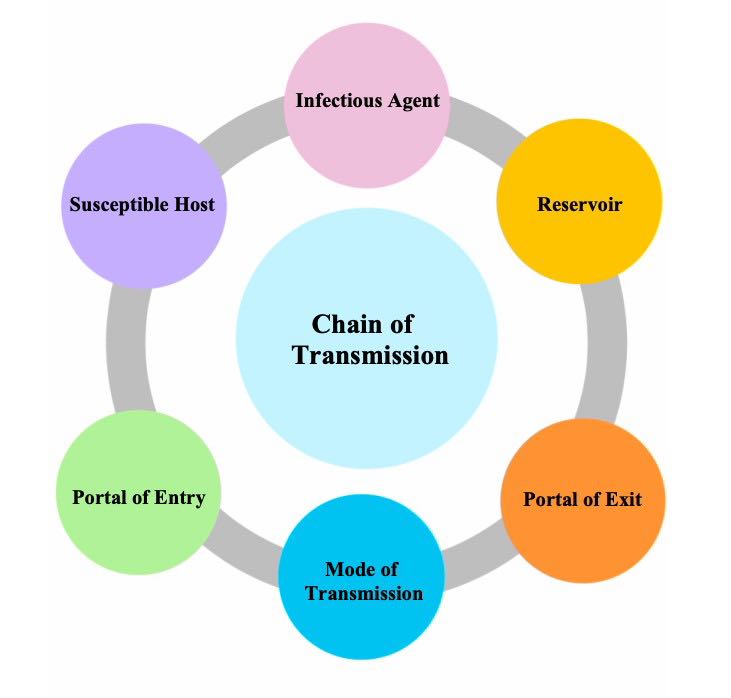
\-----------------------
* Infectious Agent
* Reservoir (food, oxygen, water, temperature, pH, and light
* Portal of Exit (skin and mucous membranes, respiratory tract, urinary tract, gastrointestinal tract, reproductive tract, blood
* Modes of transmission (contact, droplet, airborne
* Port of Entry
* Susceptible Host
* Normal Floras (exists in our gut)
* Body system defenses (our skin to help keep pathogens out)
* Inflammation
* Vascular and Cellular responses
* Inflammatory exudate
* Tissue repair
* Invasive procedures (surgical procedures)
* antibiotic administration
* Multi-drug-resistant organisms (MDROs)
* Breaks in infection prevention and control activities
* Sex
* Nutritional Status
* Stress
* Disease Process
* Past Experiences
* Knowledge of infection
* Risk factors
* Clinical appearance (do they appear tired?, do they have dry skin which might lead to an entry in for bacteria
* Status of defense mechanisms
* Medical Therapy
* Travel History
* Laboratory data
A term used to describe an infection that can be transmitted directly from one person to another
What is a Communicable Disease?
* Impaired Nutritional Status: Deficient Food Intake
* Impaired Oral Mucus Membrane
* Social Isolation
* Impaired Tissue Integrity
* Preventing further exposure to infectious organisms
* Controlling or reducing extent of infection
* Maintaining resistance to infection
* Verbalizing understanding of infection prevention and control
\
* Setting Priorities
\- Establish priorities for each diagnosis and for related goals of care (ABCs Maslow Hierarchy of needs)
\
* Teamwork and Collboration
- Collaborate with patients and interprofessional team
* Hygiene
* Immunzation
* Adequate rest and exercise
* Support the patient’s defenses
* Cleaning
* Disinfection and sterilization
* Protection of the susceptible host
* Control and elimination of reservoir of infection
* Control portal of exit/entry (cough etiquette)
* Control of transmission (hand hygiene)
G- Gown
M- Mask
E- Eyewear
G- Gloves
* Anxiety and Depression
* Specimen collection
* Bagging trash or linen
* Transporting patients
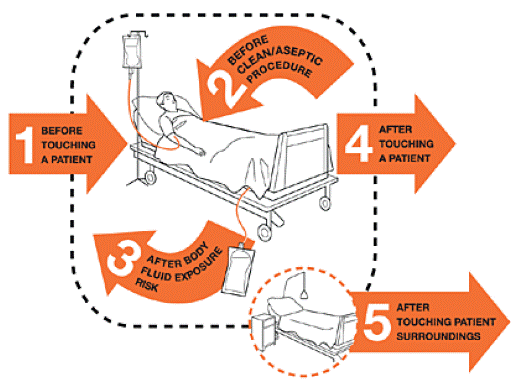
1. Before touching the patient
2. Before clean/aseptic procedure
3. After body fluid exposure risk
4. After touching a patient
5. After touching patient surroundings
* Have the patients expectations been met
* Patient outcomes
* Measure the success of the infection control techniques
* Compare the patient actual response with expected outcomes
* If goals are not achieved, determine what steps must be taken
* Eye Protection
* Gown
* Mask
* IF A PATIENT HAS C DIFF YOU MUST WASH YOUR HANDS WITH SOAP AND WATER
* Must had a gown and gloves
* Must have a gown, gloves, and surgical mask if we are making contact within 3 feet of the patient
* Droplet precautions are typically directed towards patients with (influenza, pertussis, group A step, rubella, and bacterial meningtitis
* MUST use a Gown, Gloves, N95 Respirator
Washing hands with Soap and Water
How would a nurse properly perform hand hygiene after caring for a patient with C.Diff?
Posion
Falls
Fire
Immunzations
Disasters
Transmission of Pathogens
Motor Vehicle Accidents
Car seat use, elderly
Physical Hazards
Often results in physical or psychological injury or death
Temperature
Extremes post safety risks to vulnerable populations
Nutrition
Requires knowledge about healthy food and food safety
Environmental Safety
A safe environment protects the staff to function optimally
Basic Human Needs
Sufficient oxygen, nutrition, and optimum temperature, influence a person’s safety
Oxygen
Supplemental poses fire risk
What are some contributing factors when it comes to ensuring patient safety and quality?
Patient’s developmental level
Mobility, Sensory, and Cognitive Status
Lifestyle choices
Knowledge of common safety pre-cautions
What are factors influencing patient safety?
Lifestyle
Impaired mobility
Sensory or communication impairment
Economic Resources
Lack of Safety Awareness
What are Individual Risk Factors to Patient’s Safety?
Medical Errors
TJC and CMC “Speak up Campaign”
National Quality Forum Mission
Serious reportable event (SREs)
Environmental Risks
Chemical Exposure
What are some risks in Healthcare Agencies?
Falls
Patient-inherent accidents
Procedure-related accidents
Equipment-related accidents
Workplace safety
What are some specific risks to a patient’s safety within the health care environment?
Successful critical thinking requires a synthesis of knowledge, experience, critical thinking attitudes, and intellectual and professional standards
Critical thinking allows nurses to anticipate the needs of particular patients and make conclusions about available data
On-going process
What is required from a nurse to have successful critical thinking skills
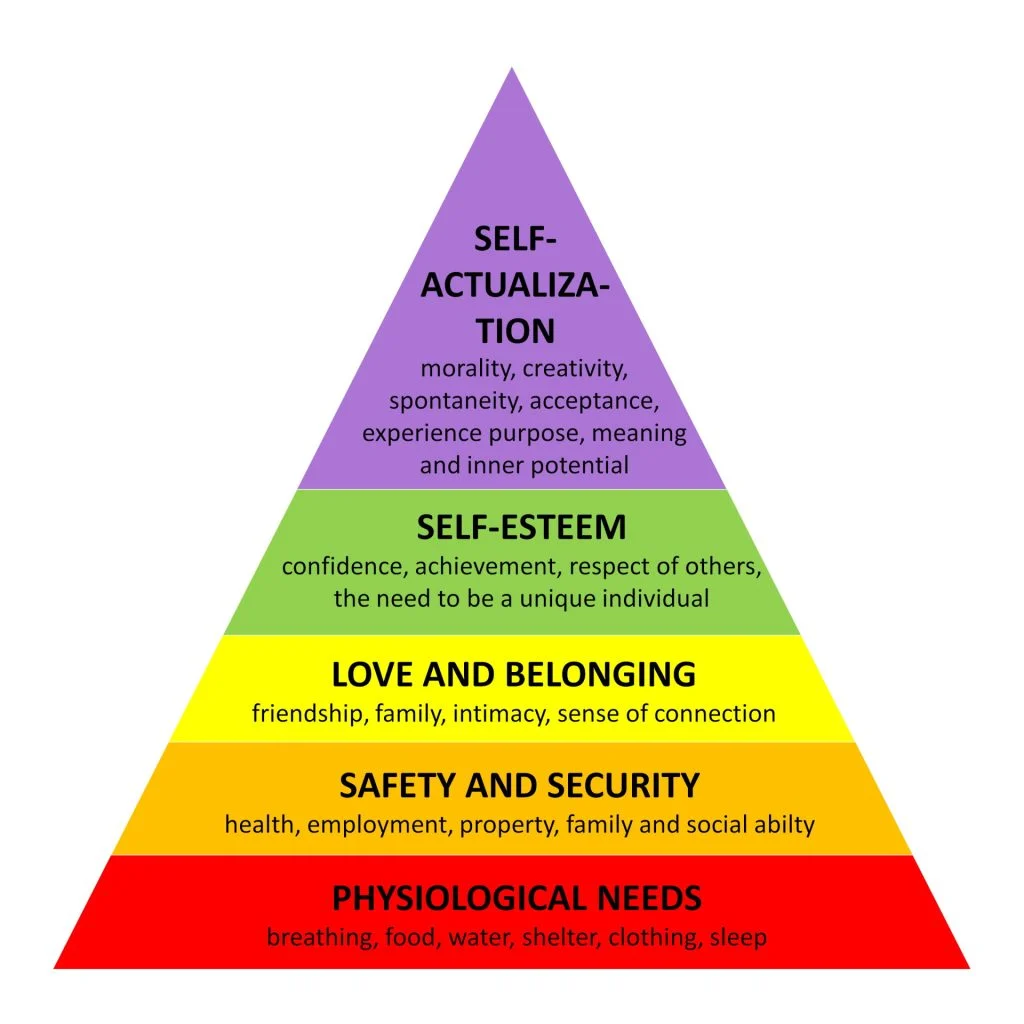
Self-Actualization (desire to become the most that one can be)
Self-Esteem (respect, self-esteem, status, recognition, strength, freedom)
Love and Belonging
(friendship, intimacy, family, sense of connection)
Safety and Security
(personal security, employment, resources, health, property)
Physiological Needs
(Air, water, food, shelter, sleep, clothing, reproduction)
What is Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
Environmental Interventions
Basic needs
Fall safety in the home
General Protective Measures
Lighting
Changing the environment
What are some Environmental Interventions and General Preventive Measures
Fall prevention
Follow fall protocols
Patient-centered care
Assistive Aids
Restraints
Physical
Chemical
Ongoing Assessment
Objectives
What are some examples of acute and restorative care
Fires
Electrical hazards
Seizures
Disasters
Preventing Workplace Violence
What are some examples of Acute Care Safety procedures?
Nurses must make accurate and appropriate
clinical decisions or judgments.
Clinical judgment
Observed outcome of critical thinking and decision
making
Clinical decision making
Separates professional nurses from technicians or
other assistive personnel (AP)
What is the purpose of the Clinical Judgment Model (CJM)
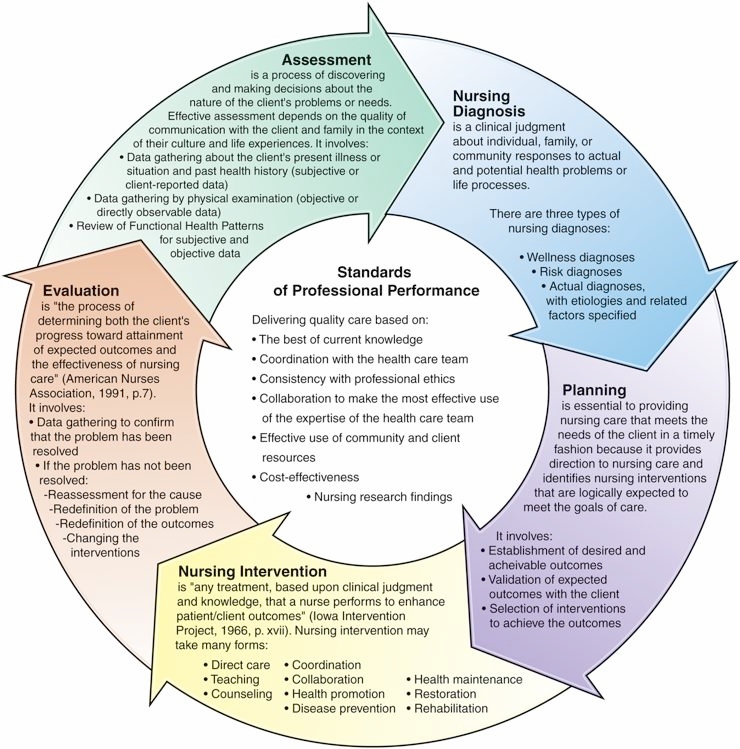
Assessment-
Diagnosis
Planning
Implementation
Evaluation
What is the correct order of the Nursing Process?
Critical thinking
The ability to think in a systematic and logical manner
with openness to question and reflect on the
reasoning process.
The aim of critical thinking is the ability to focus on the
important issues in any clinical situation and make
decisions that produce desired patient outcomes
What is Critical Thinking?
influences patients’ comfort, safety, and well-being
A variety of personal, social, financial and cultural factors influence hygiene practices
Use communication skills
When providing hygiene, integrate other nursing activities, including patient assessment and interventions
Always ensure privacy, convey, respect, and foster a patient’s independence, safety, and comfort
How does personal hygiene play a role in patient/nursing care?
During a bath
When is the best time to assess a patient’s skin or integumentary system?
The skin
Epidermis- Top layer of the skin, helps by preventing entrance of micro-organisms
What organ is classified as the largest organ in the body?
Tape scraping, or stripping, using dry razors, tape removal, or improper turning or positioning techniques
What are some possible actions that could potential damage or weaken the epidermis?
The skin
Sensory organ
Temperature Regulation
Excretion and Secretion purposes (oils may sometimes harbor microorganisms
The feet, hands, and nails
Requires special attention
Influences the ability for the patient to perform hygiene (if they can’t bear weight, they can’t ambulate)
Inadequate nutrition and disease can change the the shape and thickness of our nails or cause curvature
The oral cavity- Teeth (HUGE AREA RISK FOR INFECTION)
Increased risk for gingivitis (inflammation of the gums.
Medication, exposure to radiation, dehydration, and mouth breathing may impair salivary secretion
May cause Xerostomia- Dry mouth
The Hair
The way our hair grows is a indication of a patient’s health status (i.e an individual who has cancer may begin to see the lost or thinning of the hair)
Hormonal changes, stress, nutrition, aging
The eyes, ears, and nose - Don’t get soap in the eyes
Eyes have their own mechanisms to clean itself (i.e tears)
Cerebrum that we excrete in our ears help trap foreign bodies
Scientific Knowledge Base
Social Practices
Personal Preferences
Body image
Socioeconomic status
Health benefits and motivation
Cultural Variables
Development Stages
Skin
Feet and Nails
The mouth
Hair
Eyes, ear, and nose
Physical Condition
Describe factors that influence personal hygiene practices.
Teeth/dentition
What is classified as a huge area of infection for patients?
Integrate nursing knowledge
Consider developmental and cultural influences
Think creatively
Be non-judgemental and confident
Draw on your own experiences
Rely on professional standards
Discuss how to apply critical thinking when providing hygiene.
o Use correct handwashing techniques before and after entering the room.
o Wear gloves and gown when changing the client's brief.
o Change gloves between procedures.
o Hand hygiene with antimicrobial soap and water after removing gloves
A healthcare student is assigned to a client who is on isolation precautions and needs
assistance with hygiene and elimination. The client is 47 years old, diagnosed with
clostridium difficile (C.Diff.) and wears an adult brief due to incontinence of stool.
The client has requested assistance with bathing and changing their brief.
o Perform hand hygiene using antimicrobial soap and water due to C.Diff.
diagnosis.
o Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) as outline by the
facility.
o Maintain hygiene practice to decrease the risk of spreading infections to
visitors
What infection prevention education should be shared with
the client and their family?
o The client may feel neglected due to the limited interaction with others.
This may cause mixed emotions from the client, for example, feeling
lonely, depressed, or angry. It is important to provide optimal, holistic care
and continue to assess client's physical, psychosocial, and emotional well-
being
The client is on isolation precautions, how may this impact the client?
Coming in contact with: nonintact skin, mucous membrane, secretions, excretions, or blood
A nurse should use clean gloves when?
Assessment-
Diagnosis
Planning or outcome identification
Implementation
Evaluation
What is the mnemonic ADPIE
Demographics
Social Determinants of Health
Health Disparites
Physical
Functional
Psychosocial
Emotional
Cognitive
Sexual
Cultural
Age-related
Environmental
Spiritual/Transpersonal
Economic
What are some information the nurse will collect from a patient when conducting an assessment
Focuses on the patient’s response to health problems
Collecting Data
Identifying Cues and making inferences
Validating Data
Clustering related data and identifying data
Reporting and recording data
What is the main purpose of conducting the Assessment Portion of the Nursing Process?
Identifying how the patient reacts to actual or potential health and life processes
Identify the factors that contribute or cause health problems (etiology)
Identify resources or strengths the patient can rely on to prevent or resolve problems
What is the main purpose of conducting the Diagnosis Portion of the Nursing Process?
Create a list of suspended problems (diagnosis)
Ruling out Similar problems and diagnosis
Naming actual and potential problems
Determining risk factors
Identifying resources, strengths, and areas for health promotion
How do we develop a diagnosis?
Establish priorities
Identify expected outcomes
Select evidence-based nursing interventions
Communicate the plan of care
What is the main purpose of outcome identification and planning
Identify and select nursing-initiated interventions
Desired patient outcomes
Characteristics of the nursing diagnosis
Acceptability of the patient
Capability of the patient
Research base for the intervention
Carry out the plan
Continue data collection
Document the care
What is the purpose of Implementation in the Nursing process?
Identify expected patient outcomes
Collect Data
Interpret and Summarize your findings
Document your judgement
Terminate, continue or modify plan of care
What is the purpose of Evaluation in the Nursing Process
Support soft tissues of the body
Protects crucial components of the body
Furnishes surfaces for the attachment of muscles, tendons, and ligaments
Provides storage areas for minerals and fat
Produces blood cells
What is the main function of the Skeletal System?
Cardiovascular
Increased efficiency of our heart
Decreased heart rate and blood pressure
Increased blood flow to all body parts
Improved Venous Return
Increased circulating fibrolysin (substance that breaks up small clots)
Respiratory
Improved Alveolar ventilation
Decreased work of breathing
Improved diaphragmatic excursion
Gastrointestinal
Increased appetite
Increased Intestinal Tone
Urinary
Increased blood flow to the kidneys
Increased efficiency of acid-base balance
Efficiency in excreting body waste
Musculoskeletal
Increased muscle efficiency and flexibility
Increased efficiency and of nerve impulse transmission
Reduced bone loss
Increased Coordination
Intregumentary
Improved Tone, Color, Tugor
Improved Skin Circulation
How does exercise effect our body systems?
Developmental considerations
Physical Health
Mental Health
Lifestyle
Attitude and Values
Fatigue and Stress
External Factors
What are some psychological benefits of exercise for a patient?
General ease of movement and gait
Alignment
Joint Structure and Function
Muscle mass, tone, and strength
Endurance
Describe the use of safe patient handling techniques during transfers and ambulation.
Gait Belt
Stand-assist and repositioning aids
Lateral-assist devices
Friction-reducing sheets
Mechanical lateral-assist devices
Transfer chairs
Powered stand-assist
Sedentary and immobile patient
Equipment and and Assistive Devices
Low or Semi Fowlers: 30 degrees
Fowlers: 45-60 degrees
High Fowlers: 90 degrees
Supine position= 0
What are fowlers positions?
Tripod/4 prong: Poor Balance
Half Circle: minimal balance
Straight handles:
If mild balance needed
Easier to hold with hand weakness
Axillary Crutches: Short term use
Be cautious to avoid axillary nerve injury
Walkers: Full Support
Mechanical Aids to Walking:
Walker and Canes
Take home message:
Support foot in correct anatomical position
Heel Support
What are the protective positioning for drop foot?
Holds hand in functional assessment position
Prevents claw-hand deformities
What are the protective positioning for Hand Rolls
Skin
Epidermis
Top Layer
Dermis
Inner layer of collagen
Dermal- epidermal junction
Separates dermis and epidermis
What are the different layers of the skin?
Pressure Injuries
Pressure Ulcer, decubitus ulcer, or bed sore,
Pathogensis
Pressure Intensity
Tissue ischemia
Blanching
Pressure Duration
Tissue Tolerance
Scientific Knowledge Base (2 of 9)
Impaired sensory perception
Impaired mobility
Alteration in LOC
Shear Friction
Moisture
What are the risk factors for pressure ulcer development?
Stage 1: Non-Blanchable erythema of intact skin
Stage 2: Partial-Thickness skin loss with exposed dermis
Stage 3:Full Thickness skin loss
Stage 4: Pressure Injury: Full thickness skin and tissue loss
What are the classifications of pressure injuries?
Either covered with slough (yellowish) or may be covered with eschar which is dark, usually dark brown to black, very thick and hard layer to cover.
How can unstagable wounds be identified?
Granulation Tissue
Slough
Eschar
Exudate
What are some key components in identifying deep-tissue injuries
When the wound begins to heal from the the inside out
What is Secondary Intention?
Wound healing when you get scar tissue to form
i.e surgical wound
What is Primary Intention?
Inflammatory Response, epithelial proliferation, and migration re-establishment of the epidermal layers
What is the Wound Repair Process for Partial thickness wounds?
Hemostasis- The even leveling of our tissues going back to normal,
inflammatory- WBC and phagocytes begin to attack and prevent any wound infection,
proliferation- The tissue begins to start growing and regenerating
maturation- Forms into the dermis and epidermal layers
What is the wound repair process for full-thickness wounds?
Hemmorhage
Infection
Dehiscense
Evisceration
What are some complications of wound healing?
Turning our patients frequently
offloading the pressure
making sure we keep our patients clean and dry
How do we prevent pressure injuries?
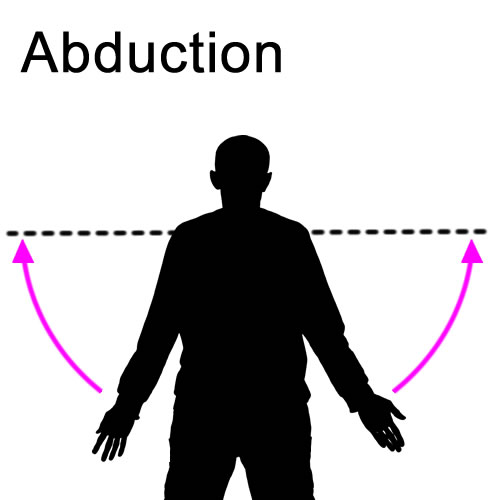
the motion of a limb or appendage away from the midline of the body
What is Abduction?
a movement towards the midline
What is Adduction?
the movement of the limb, hand, or fingers in a circular pattern, using the sequential combination of flexion, adduction, extension, and abduction motions.
What is Circumduction?
Flexion refers to a movement that decreases the angle between two body parts.
What is Flexion
a straightening movement that increases the angle between body parts.
What is Extension?
excessive movement of a joint in one direction (straightening)
What is the muscle movement Hyperextension
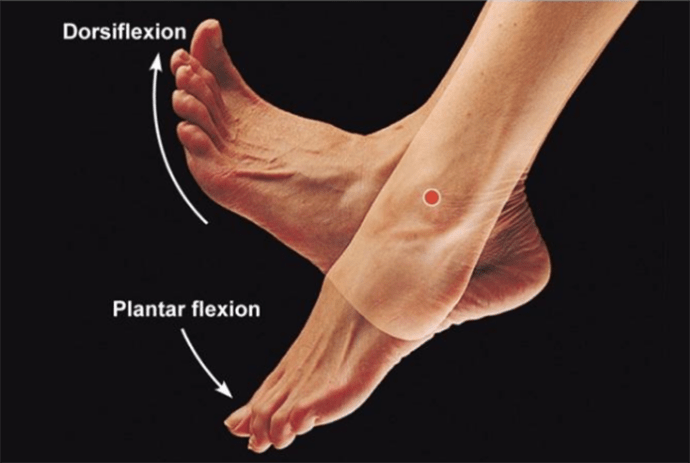
the movement that occurs when your foot and shin approximate closer together
What is the muscle movement Dorsiflexion?
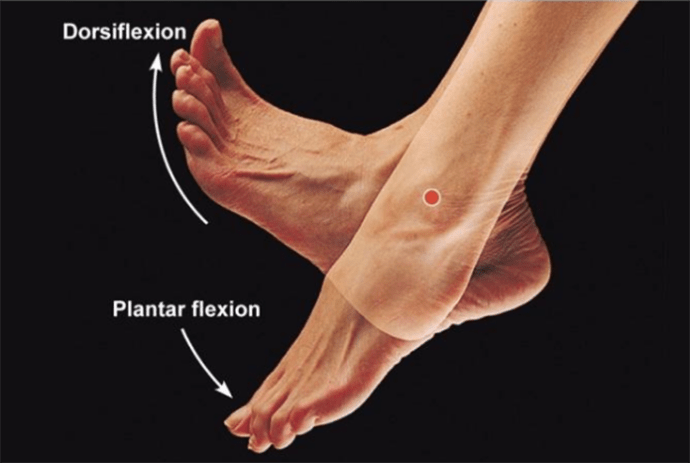
the movement of the foot in a downward motion away from the body
What is the muscle movement Plantarflexion?
rotation towards the center of the body.
What is Internal Rotation?
Rotation away from the body
What is External Rotation
When your palm or forearm faces up
What is Supination Position?
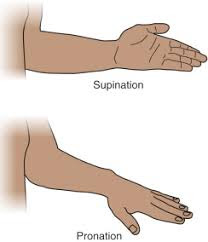
When your palm or forearm faces down
What is Pronation position?
When your toes point inwards
What is Inversion?
When your toes point outwards from the center of your body
What is Exersion?
Left/Right
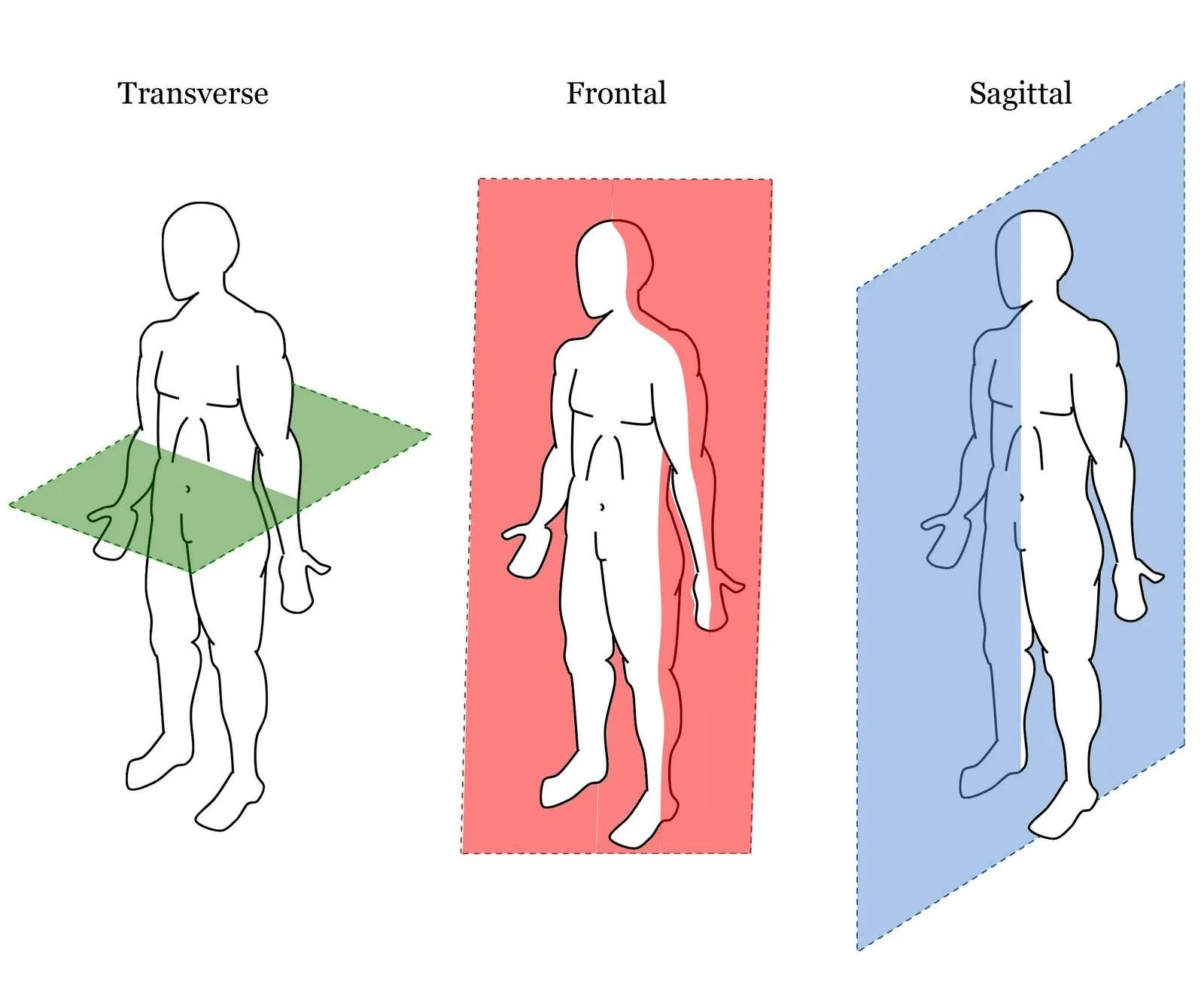
What 2 halves are divided in the sagittal plane?
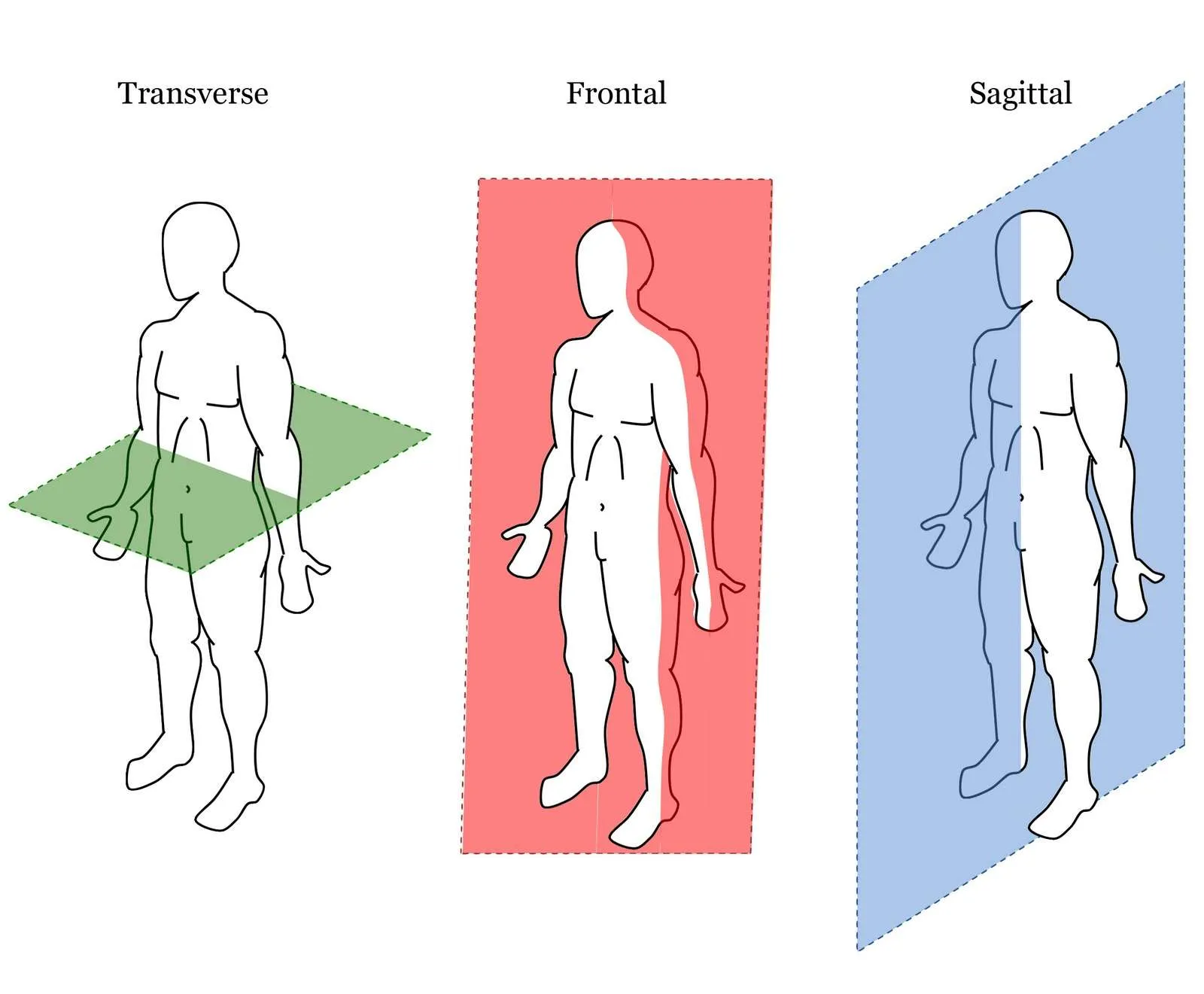
Up/down
What 2 halves are divided into the transverse plane?
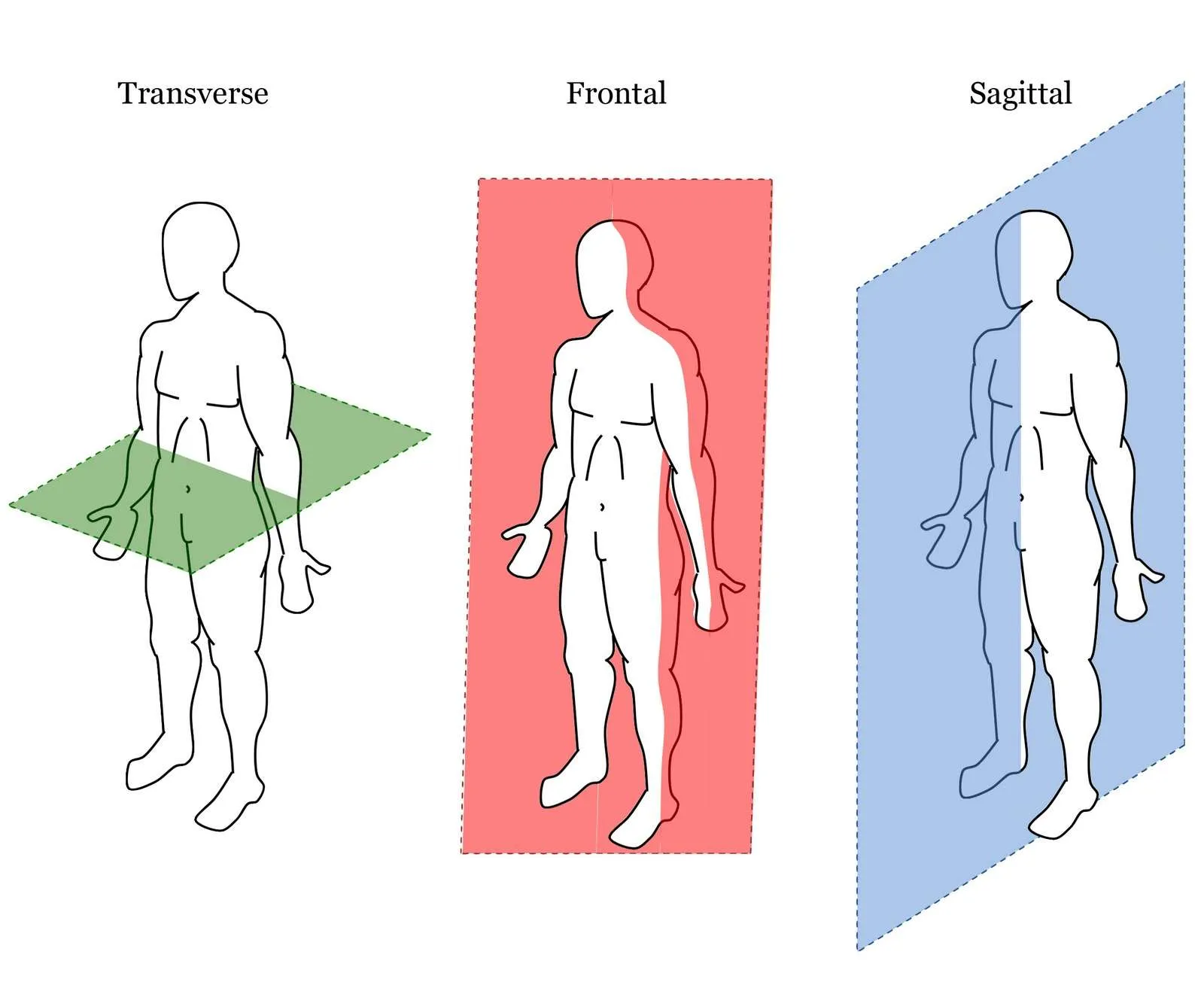
Anterior/Posterior
What 2 halves are divided into the frontal/coronal
45 - 60 degrees
What is Semi-Fowler’s position?
Bed position
Bed is angled 45-60 degrees
What is Fowler’s Position?
Supine Position
During male perineal care the patient should be in what position?
Red Wristband
What does a Red Wristband on a Patient indicate?