9 Kinetics I
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What needs to happen for a reaction to happen between particles according to collision theory?
They need to collide at the correct orientation and with enough energy.
Draw a Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution, marking the energy that most molecules have, the average (mean) energy, the activation energy and labelling the axes.
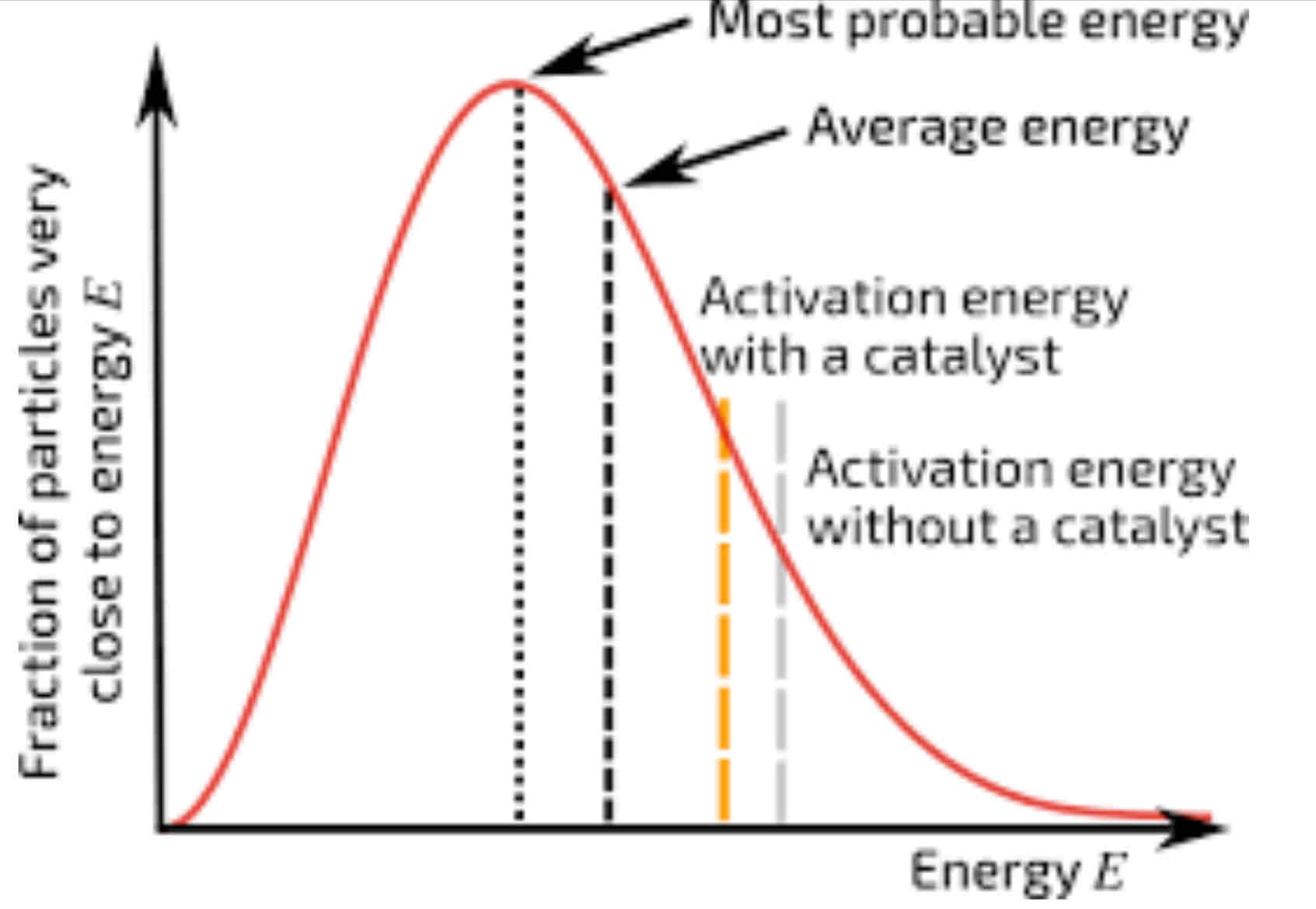
What impact does increasing the temperature have on a reaction?
The particles will, on average, have more kinetic energy and move faster. This means that a greater proportion of molecules will have at least the activation energy and be able to react, making the reaction occur faster.
What does the area under the Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution show?
The number of molecules
Why does the Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution always start at 0,0?
No molecules have zero energy.
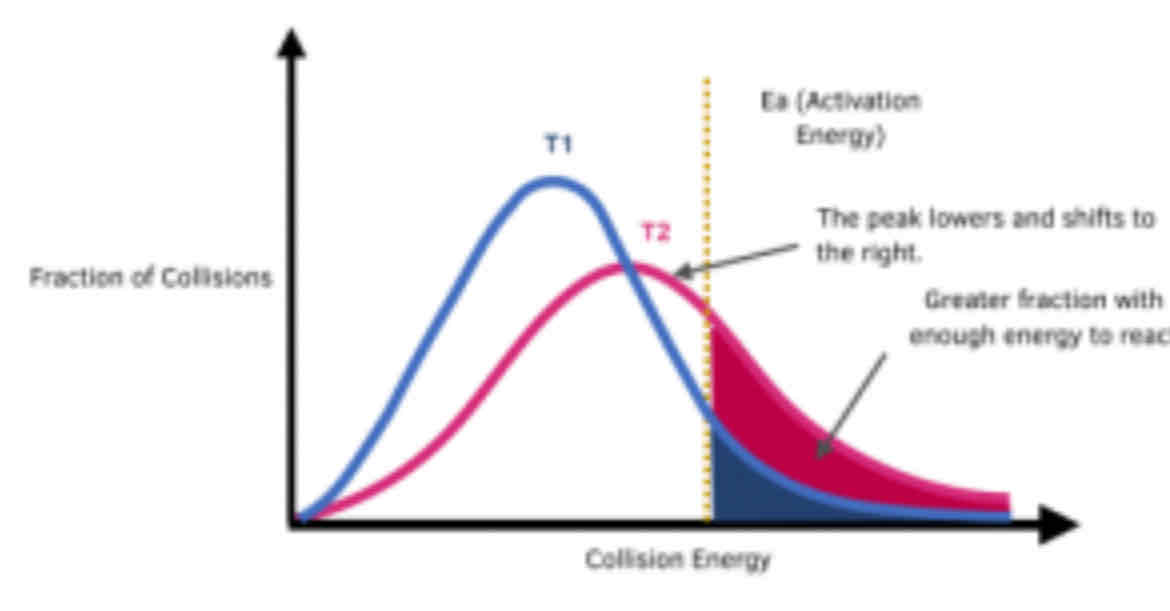
Draw a Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution, and then on the same graph draw a Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution of a reaction that occurred at a higher temperature than the first. Describe the change.
The peak is lower and to the right as the average energy and most common energy have increased. The area under the graph is still the same as no molecules have been lost, and the activation energy has not changed but more particles have at least the activation energy.
How does increasing the concentration of a reaction change rate of reaction?
There will be more particles in a given volume, causing the particles to collide more frequently. This means there are more chances for them to react and so the rate of reaction increases.
How does increasing pressure speed up reactions?
At higher pressures, there are more particles in a given volume of gas, increasing the frequency of successful collisions and therefore increasing the rate of reaction.
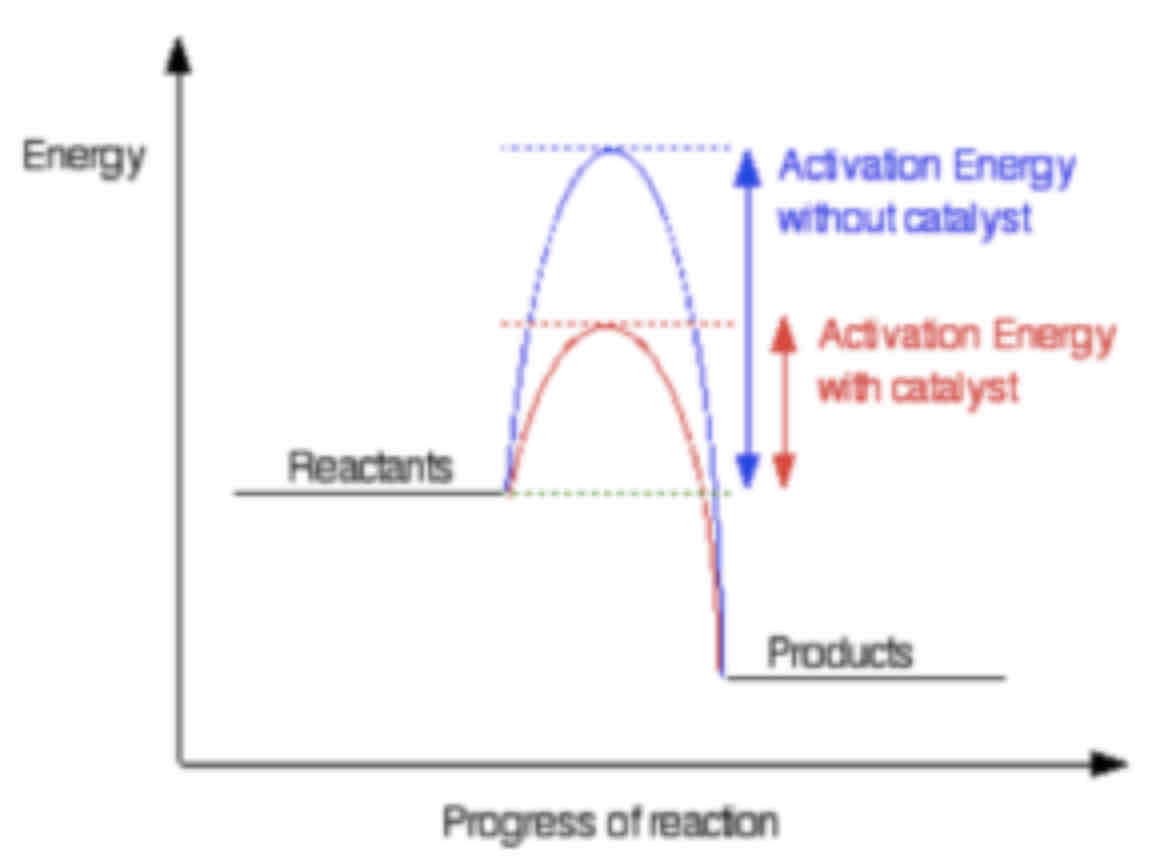
How do catalysts speed up reactions?
Catalysts lower the activation energy by providing an alternate reaction pathway. This is done by providing a different way for the bonds to be broken and made. If the activation energy is lower, more particles will have sufficient energy to react and a greater proportion of collisions are successful, increasing the rate of reaction.
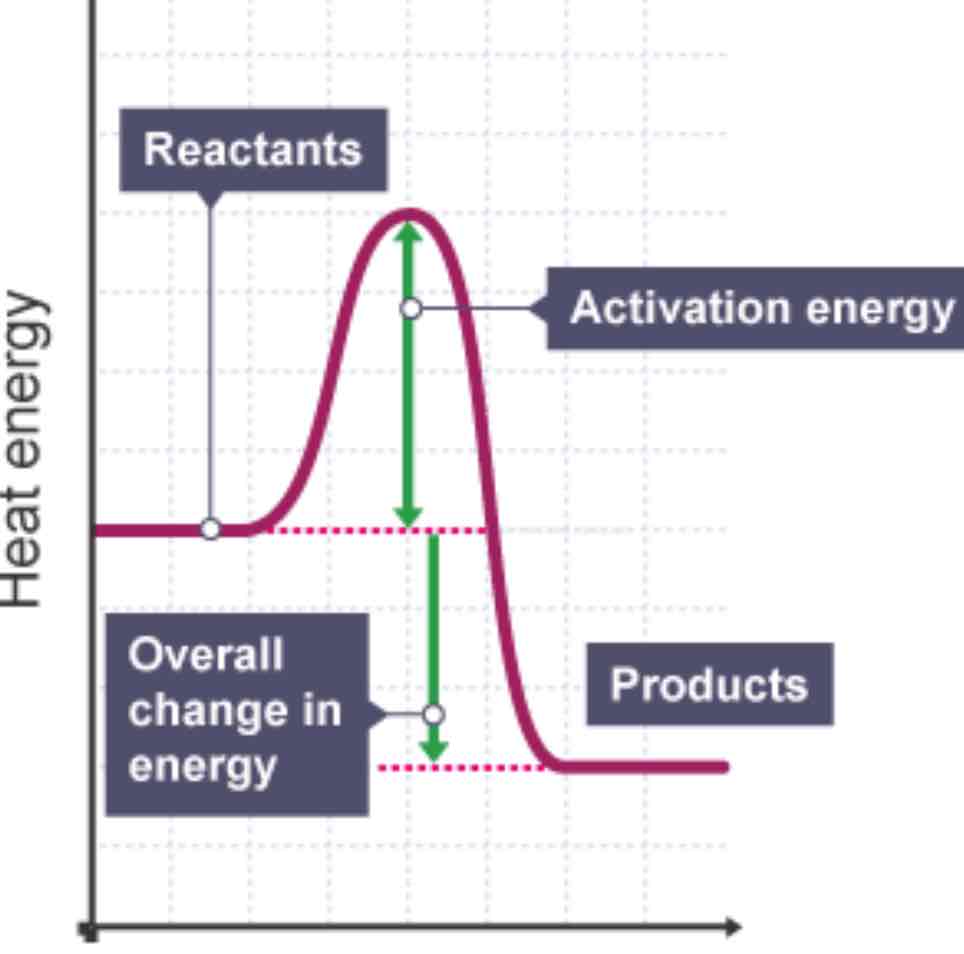
Draw a reaction profile diagram for an exothermic reaction, marking reactants, products, activation energy, overall energy change and axes.
Draw a reaction profile for an exothermic reaction, and then on the same graph draw a profile for the same reaction occurring in the presence of a catalyst.
What is a heterogenous catalyst?
A catalyst in a different phase from the reactants, eg reacting gases with a solid catalyst.
With a heterogenous solid catalyst, how can you increase the rate of reaction further?
Increase the surface area of the catalyst: this will increase the number of molecules that are able to react at the same time, increasing rate of reaction.
How do solid heterogenous catalysts work?
Adsorption- reactant molecules arrive at the surface and bond with the catalyst.
The bonds between the reactant’s atoms are weakened and broken up, forming radicals which then react and form new molecules.
Desorption- the new molecules detach from the catalyst.
What is a homogenous catalyst?
A catalyst in the same phase as the reactants.
How do homogeneous catalysts work?
The reactants combine with the catalyst to make an intermediate species, which then react and form the products and reform the catalyst.
What are the potential economic benefits of catalysts?
lower production costs as temperatures and pressures do not have to be as high
More product in a shorter time
Can change the properties of a product to make it more useful, eg. with a catalyst poly(ethene) is more dense, rigid and has a higher melting point.
How does decreasing the surface area of a solid slow down a chemical reaction?
A smaller surface area decreases the rate of reaction because the same number of particles have less opportunity to collide and react.