IB DT: Topic 5.7: innovation, design and marketing specifications
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits https://dl.ibdocs.re/IB%20BOOKS/Group%204%20-%20Sciences/Design%20Technology/VARIOUS/Design%20Technology%20-%20Study%20Guide%20-%20Core%20Topics%201-6%20SL.pdf
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
why do successful designs usually start out with detailed design and marketing specifications?
designers must establish clear parameters for a marketing specification to create unique and creative solutions to a problem - they also need to collect valid and useful data from the target market and audience throughout the design cycle
what is a target market?
a broad group of potential customers defined by shared characteristics who might benefit from a product
what is a target audience?
a subset of the target market - the intended audience of individual campaigns or messages (the one actually buying the product)
what is market analysis?
an appraisal of economic viability if the proposed design from a market perspective - taking into account fixed and variable costs and pricing. typically a summary about potential users and the market.
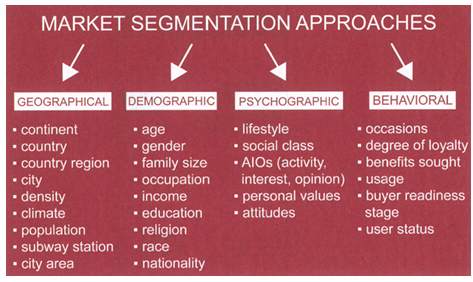
what is user need?
the essential requirements that the product must satisfy, in the marketing specification
why should you consider competing products in your marketing specification?
helps you clarify how you can edge out and respond to competition based on the pitfalls in their satisfaction of consumer need
what research methods are used to establish market need?
literature search (authoritative sources)
user trial: members of the target market are observed using the product in a lab
user research: the questioning of users about their experience using a product (questionnaire or focus group)
expert appraisal: where an expert is asked to give their opinion
performance test: where the product is tested and data is collected (instrumental models)
what must all of the requirements, constraints and considerations in a design specification be?
specific, feasible and measurable
what would a design specification include?
aesthetic requirements
cost constraints
customer requirements
environmental requirements
size constraints
safety constraints
performance requirements
materials requirements
manufacturing requirements