Agriculture
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
A farming practice involving 'slash and burn' techniques and moving fields to find better land.
common
A form of agriculture focused on raising livestock that can be sedentary, nomadic, or semi-nomadic.
domesticated animals are released onto the vegetated land where they graze and feed
nomadic people who move with herds
in places where climates make crop growing near impossible
A method of rice cultivation that is water-intensive and practiced in paddy fields.
rice planted on dry land in a nursery and then moved to a deliberately flooded field to promote growth
grown to be seedling and then moved into flooded paddy fields
Asia
Farming with high labor and investment relative to land size, often involving complex systems.
farming practice that maximizes yields from a area through high levels of labor, fertilizers and tech
increase labor → increase yields
found in developing countries — subsistence farming
Farming that utilizes less labor and investment relative to the size of the land used.
low inputs of labor per unit of land
large area of land that is used to make more food, but less labor
high land and low labor per unit of land
increase land size → increase yield
The transition from nomadic hunting and gathering to settled agriculture about 12,000 years ago.
human first began domesticating plants and animals → no more reliance on hunting and gathering
A period of significant agricultural development in the 20th century resulting in higher crop yields through genetic improvements.
large increase in crop production in developing countries
fertilizers, pesticides, and high-yield crop varieties
Large commercial farms in less developed countries focusing on producing cash crops for export.
human led cultivation of plants and animals in which a single type of crop is grown on a large area of land
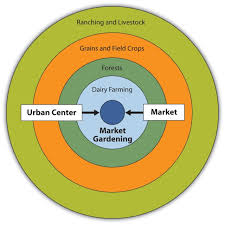
A model developed to explain the location of agricultural activities based on proximity to a city center.
patterns in the distance between central markets and growing crops
the farthest crops being the least perishable and the closest being the most perishable
agriculture exists in concentric patterns around a city → cost of farming per ring depends on the cost of goods and transportation
genetically modified organisims
A living organism that possesses a novel combination of genetic material obtained through the use of modern biotech
passed through a genetic change to create a more sustainable product
desertification
Degragation of land, especially in semiaric areas. Due to human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing and tree cutting.
when vegetation disappeared in semi-arid and aird areas
CAFOs
Confined animal feeding operation
agricultural meat, dairy, or egg facilities
animals are raised in confinement
raising animals for slaughter efficiently in small living conditions
Environmental racism
disproportionate impact of environmental hazards, pollution and degradation on marginalized communities.
Dry lot dairy
fenced in dairy farms free of vegetation and free range
used for large commercial farms
factory farms
food deserts
an area limited to affordable and nutritious foods
lack of access
deforestation
large scale destruction of forests
milksheds
milksheds are regions surroudnings a milk source that milk is supplied to without spoiling
metes and bounds
A system of describing land boundaries by using natural features like rivers, streams, large trees, and man-made markers. Define and precise perimeters of properties and usually end in an irregularly shaped land.
township and range
cadastral cuervey method that divides the land into squares to be further divided into squares
division of rural areas west of the Appalachians into squares
long lots
French long lot system is a method of dividing land into narrow strips that ran parallel to a sources of mater
crop rotation
The practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year to avoid exhausting the soil
norman borlaug
Norman Borlaug was an agricultural scientist who is credited with starting the Green Revolution that sought to end world hunger through cross-breeding and the introduction of pesticides.
mediterranean agriculture
crops grown in the mediterranean region of Europe
bordering te sea, breezes, moderate temperatures, hilly land
crops grown on trees primarily
mixed crop/livestock
agricultural system where farmers grow crops and raise animals on the same farm
transhumance
the seasonal migration of livestock and the people who tends them.
between the lowlands and the adjacent mountains
seasonal movement of livestock between different grazing areas
ranching
commercial grazing of livestock over an extensive area
livestock for the purpose of producing food commercially
cattle ranching and horse ranching
market/truck farming
commericial gardening and fruit farming
called truck bc truck means bartering
commercial dairy farming
A farm that specializes in the production of milk and other dairy products
commercial grain farming
grain farming on a large scale
terrace farming
method of growing crops on the side of a hill by planting terraces that are built onto a slope