SciOly Anatomy + Physiology: Skeletal System 2025
1/415
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
416 Terms
What is cartilage mainly made of?
water
Is cartilage vascularized?
no
What does it mean to be vascularized?
to have veins
Is cartilage innervated?
no
What does it mean to be innervated?
to have nerves
What are the traits of cartilage?
strong, resilient, and heals poorly
Where is cartilage found?
in epiphyseal plate + as well as joints (shock absorption)
also in newborn's body
What is cartilage replaced by?
bones that form at the site and fuse together
What are chondroblasts?
mesenchymal progenitor cells that develop into chondrocytes through endochondral ossification
What are chondrocytes?
cells that secrete extracellular matrix to maintain cartilage
What is endochondral ossification?
involves the replacement of hyaline cartilage with bony tissue (endochondral bone)
What is cartilage surrounded by?
perichondrium
What is perichondrium?
layer of dense irregular connective tissue
What is the role of the perichondrium?
when cartilage is compressed, it prevents the cartilage from expanding outward
What is the extracellular matrix?
network of macromolecules that provides structural support to surrounding cells
What are lacunae?
small cavities within extracellular matrix
Where are chondrocytes found?
housed by one lacunae each
How are lacunae connected?
canaliculi (canals)
How does cartilage grow (2 ways)?
appositional growth and interstitial growth
What is appositional growth?
process that occurs when new bone matrix is secreted at bone surface, increasing diameter
What is interstitial growth?
happens when chondrocytes within extracellular matrix divide + secrete new matrix, causing the cartilage to expand from within itself
What are the three types of cartilage?
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
What is hyaline cartilage like?
most abundant, looks like glass, pearl-gray color, flexible, resilient
What are the subtypes of hyaline cartilage?
articular, costal, respiratory, nasal
Where is articular cartilage found?
ends of bones in synovial joints (knee, elbow, ankle, wrist)
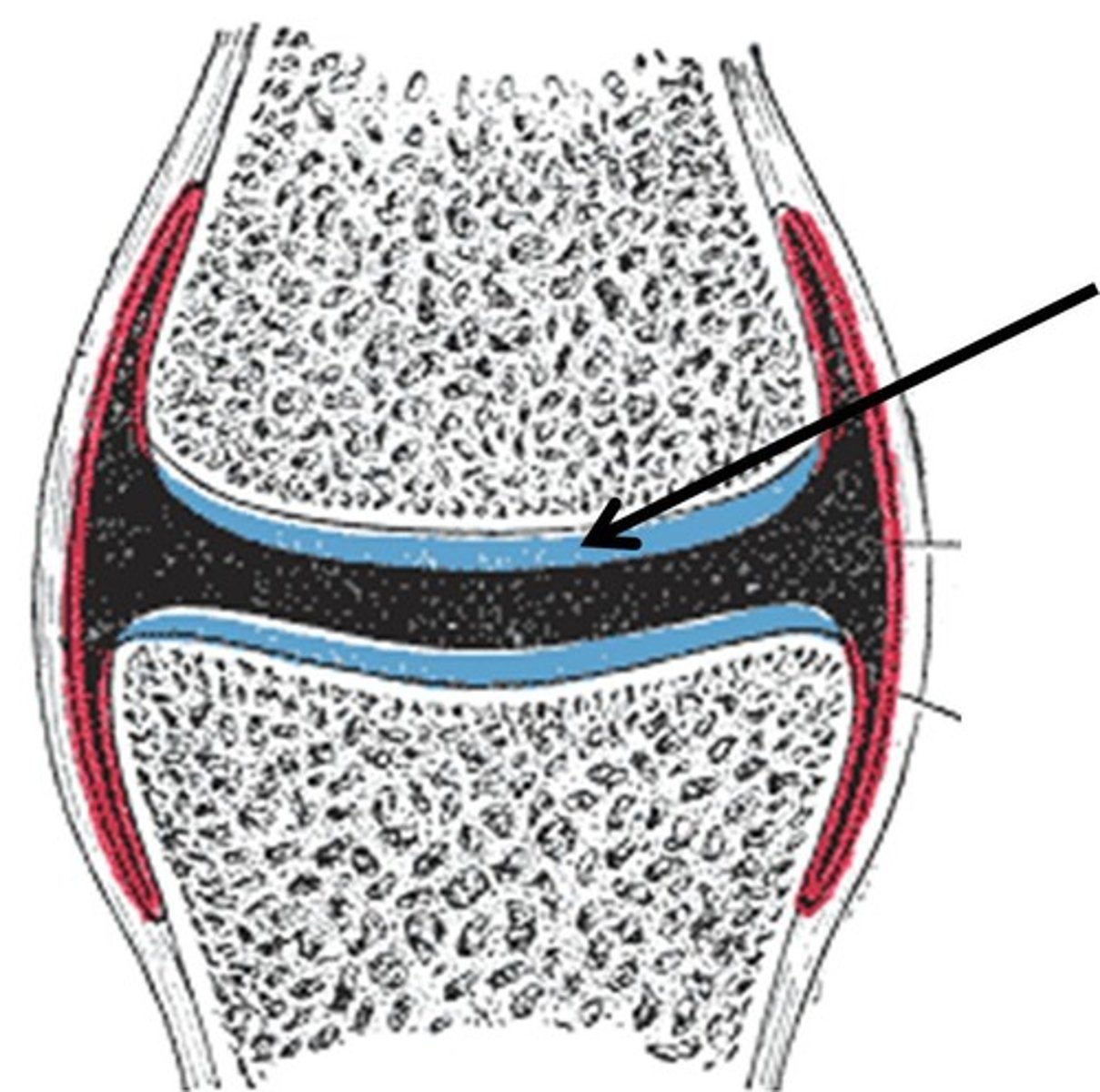
What is a synovial joint?
allows for wide range of movement, most common, prescence of fluid-filled joint cavity wtihin fibrous capsule
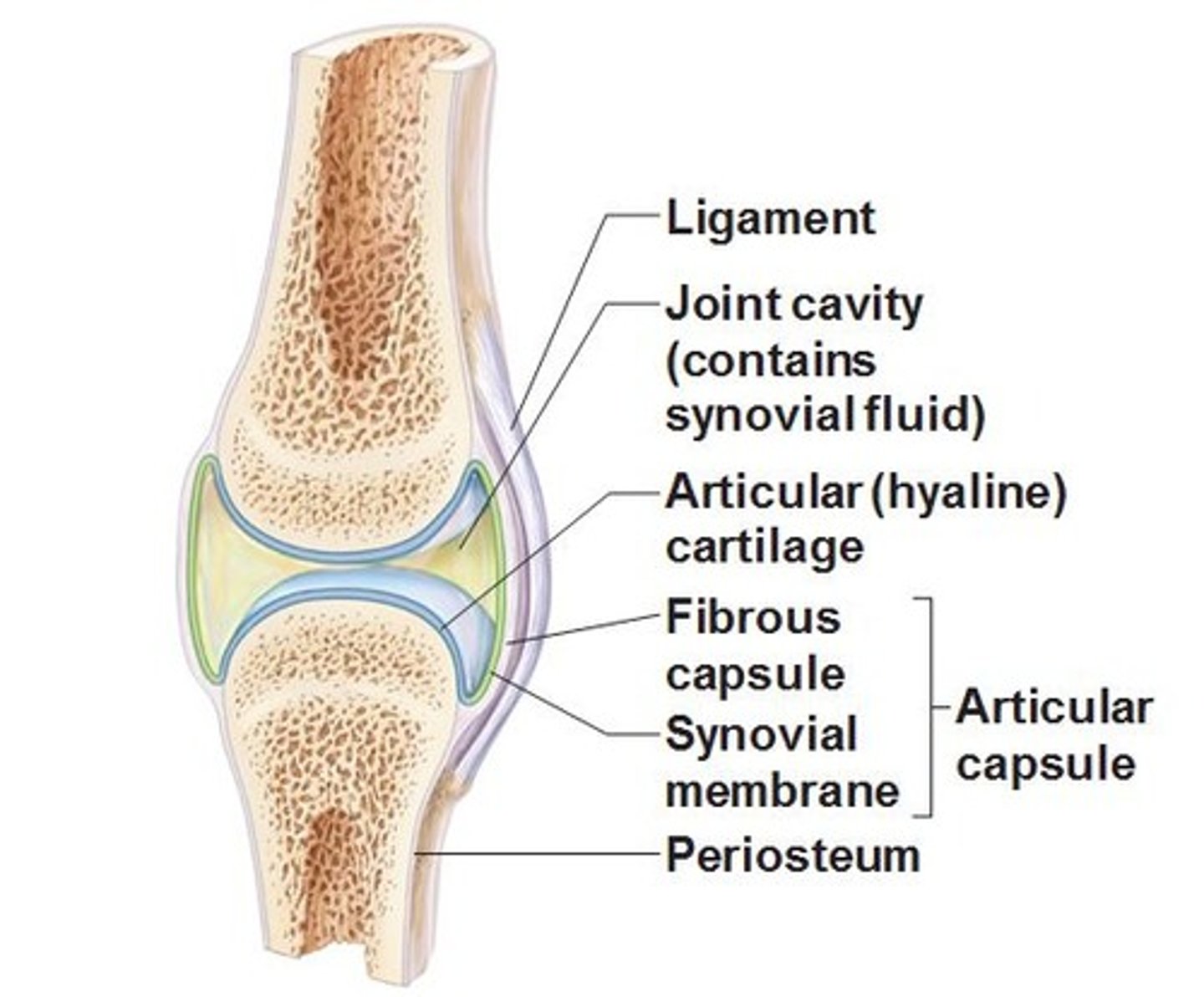
What is a fibrous capsule?
outer layer of joint structure, made of dense connective fibrous tissues
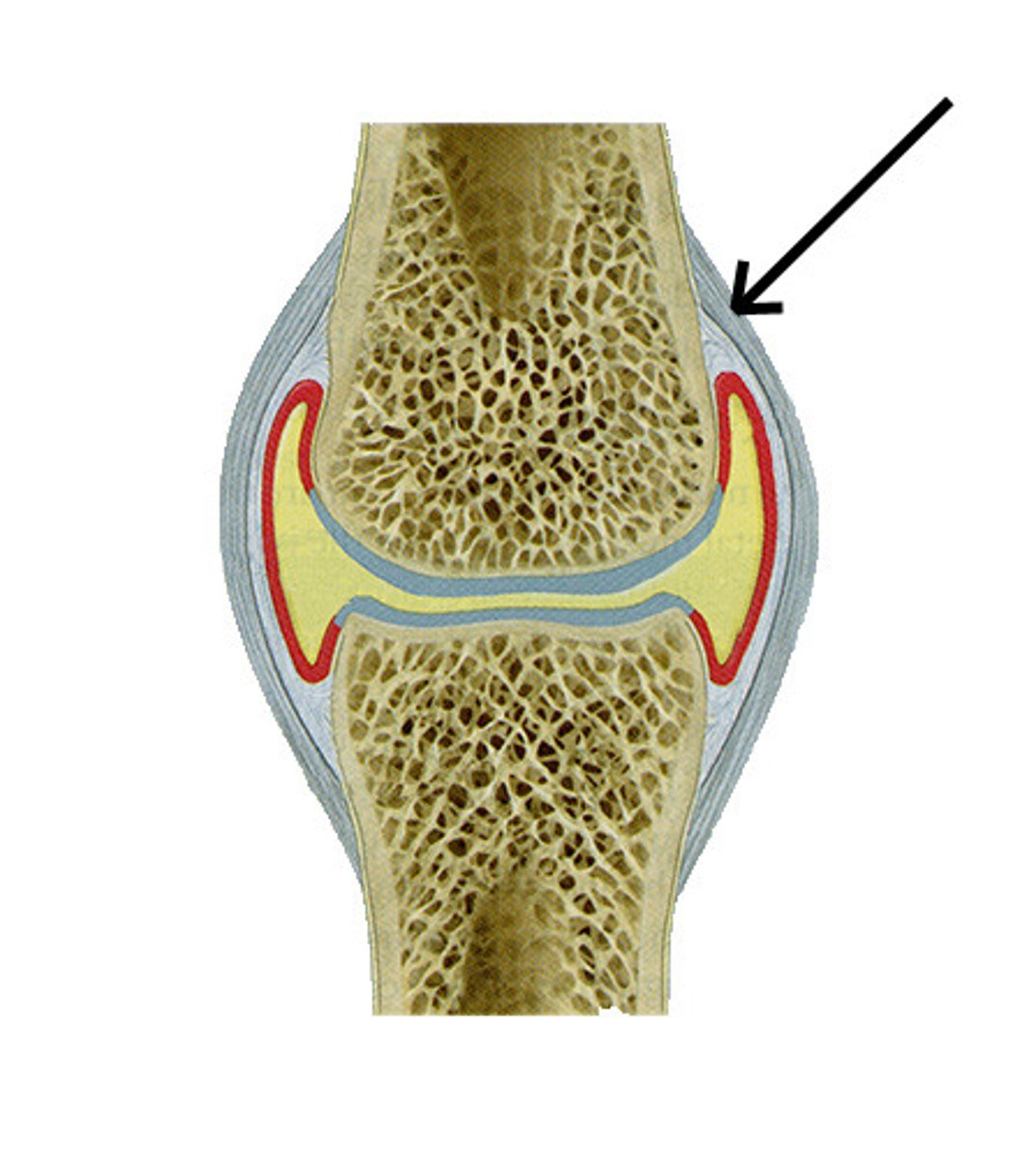
Where is costal cartilage found?
anterior (front) ends of ribs, prolonging them forward
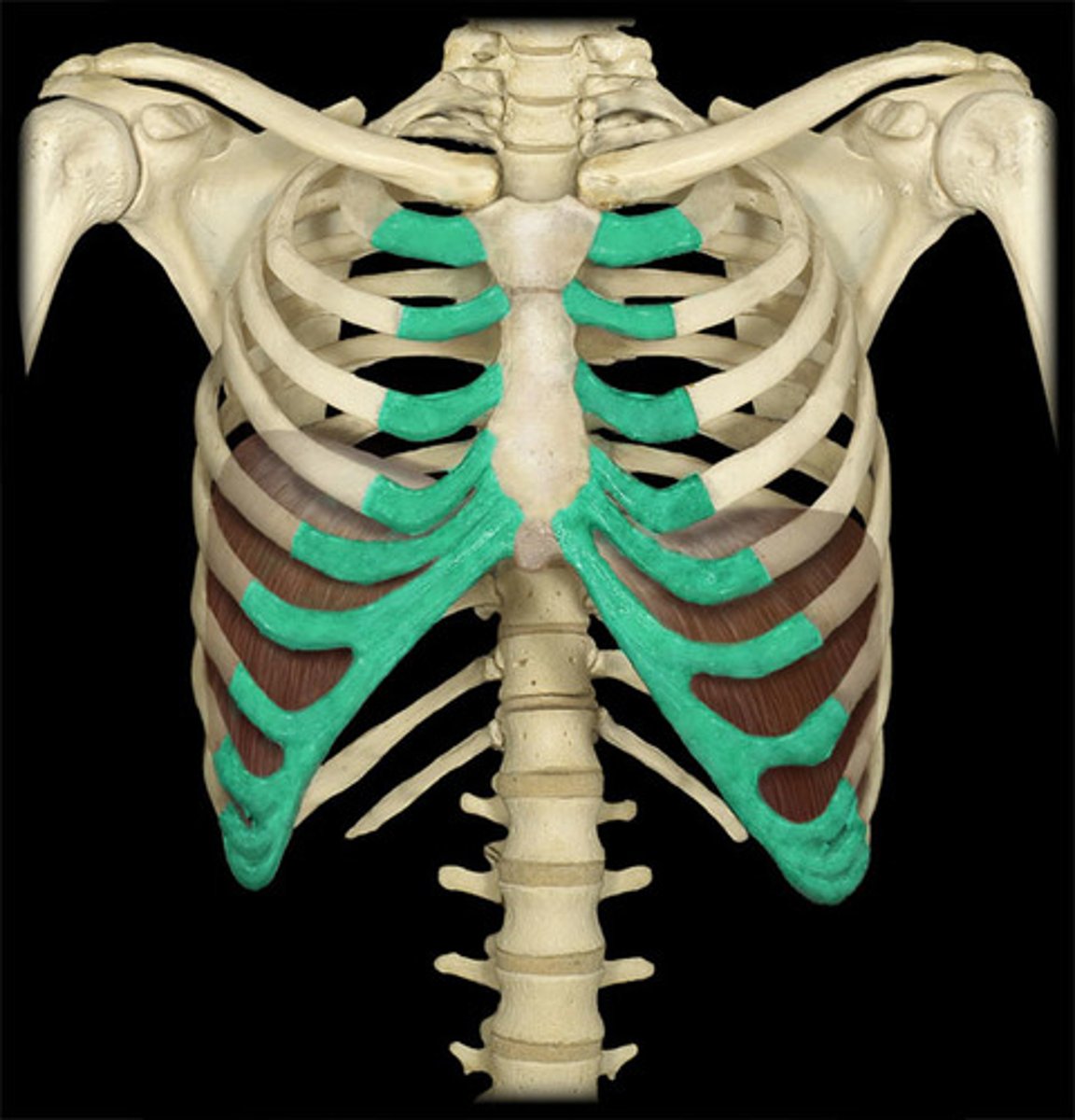
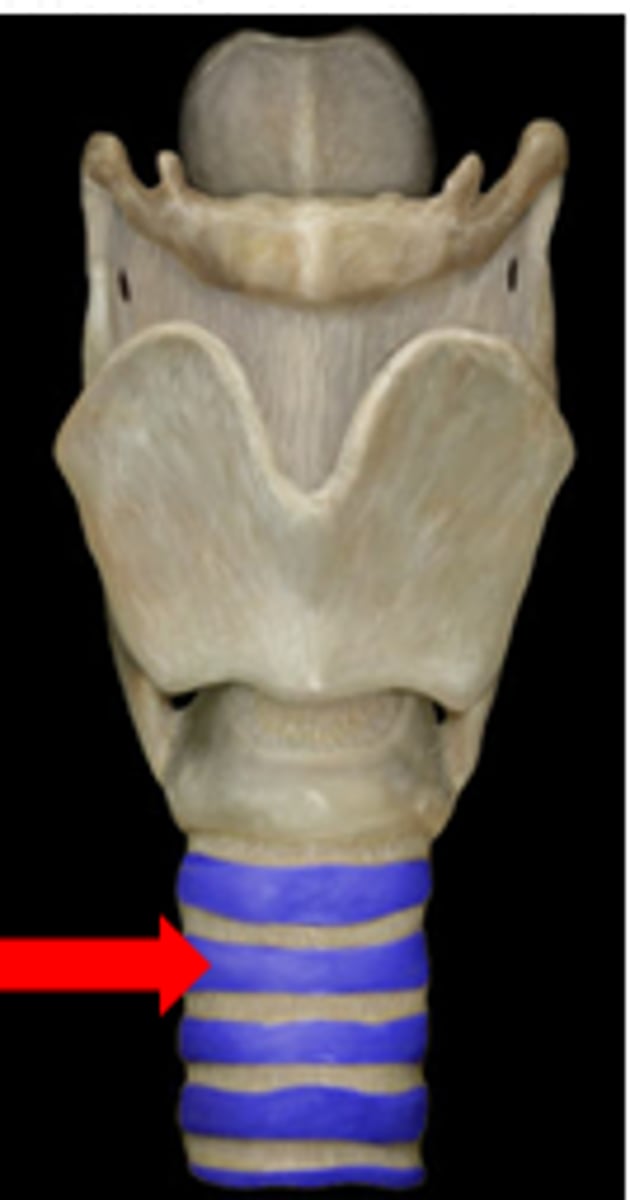
Where is respiratory cartilage found?
trachea + primary bronchi
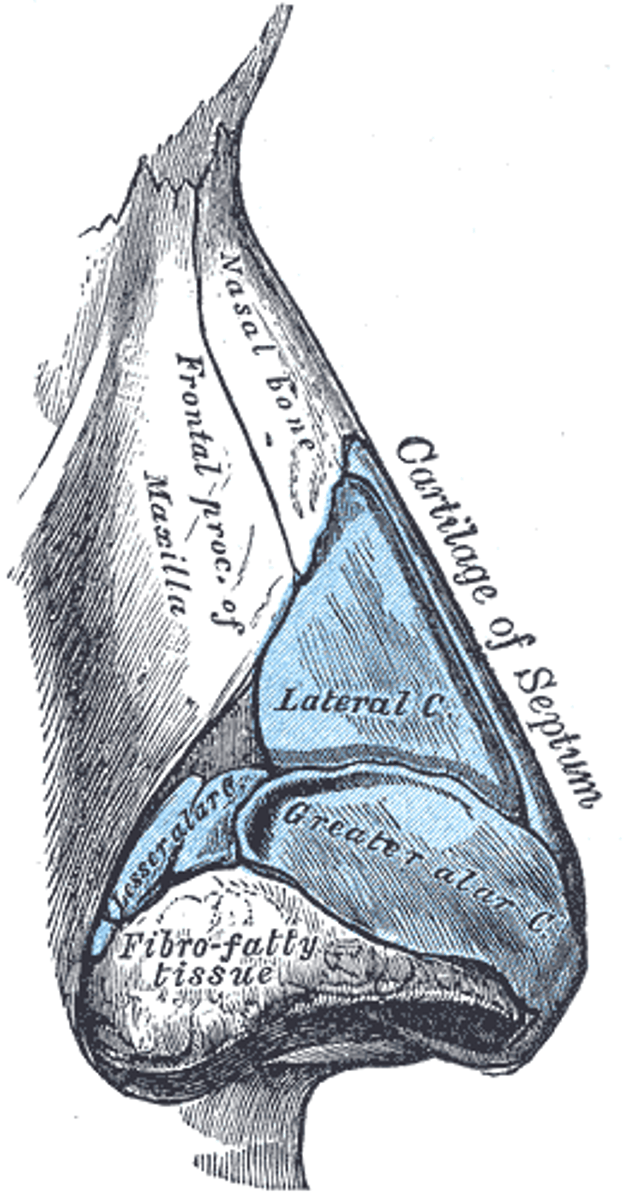
Where is nasal cartilage found?
inferior portion of external nose
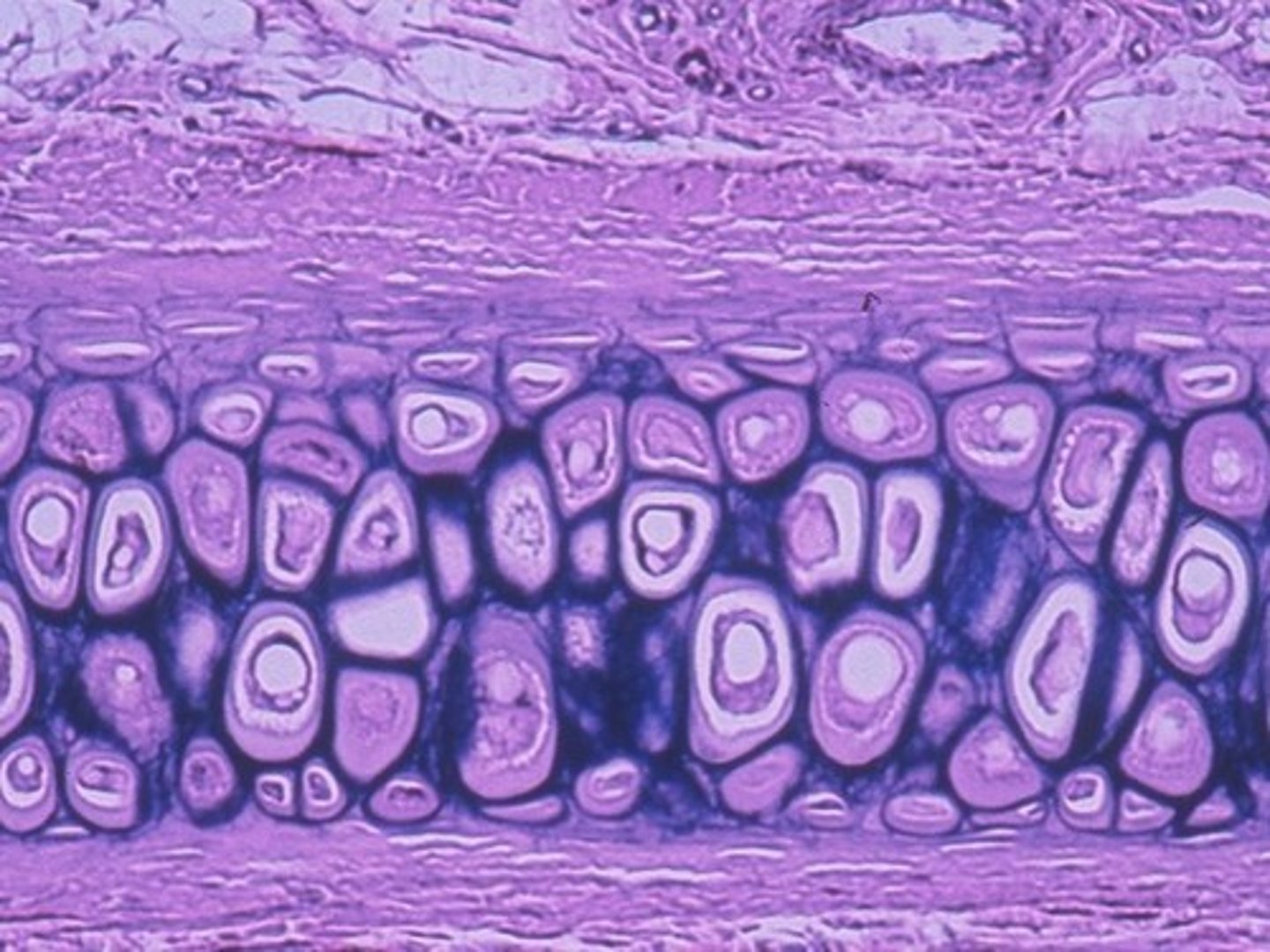
What is elastic cartilage?
similar to hyaline cartilage, but more elastic fibers in matrix, so stands up better due to repeated bending
found in external ear + epiglottis
What is fibrocartilage?
resembles fibrous tissue (but it has chondrocytes)
very strong + compressible
found in menisci of knee, intervertebral disks, pubic symphysis
What are the three types of bones?
long, short, flat
What are long bones like?
most familiar, length > width
What are long bones composed of?
shaft (diaphysis) + 2 ends (epiphyses)
outer layer - compact bone
inner layer - spongy bone
What bones are long bones?
all limb bones (except patella, wrist, + ankle bones)
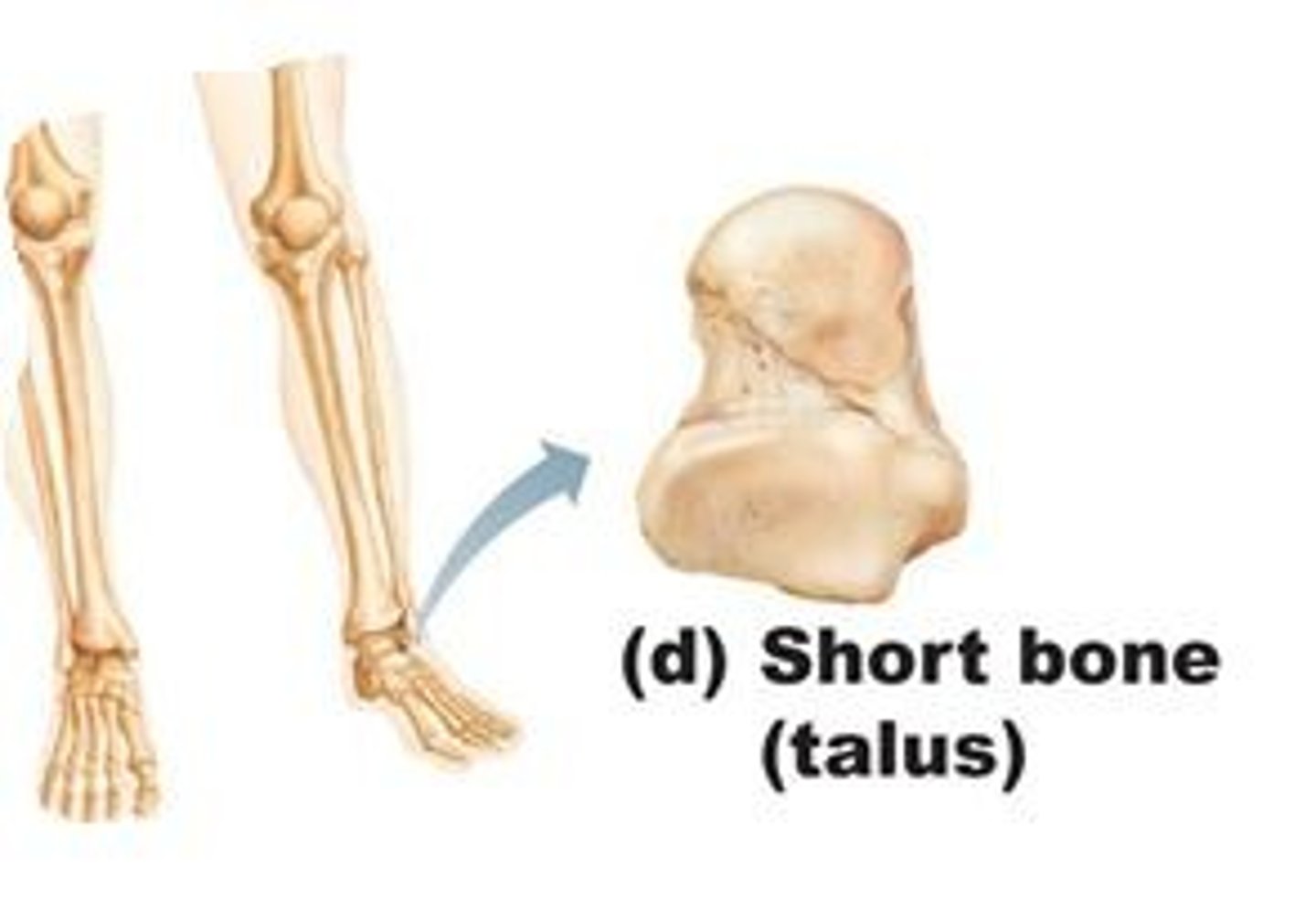
What are short bones like?
roughly cube shaped
What are sesamoid bones?
special type of short bones located inside tendons
Where are sesamoid bones found?
patella + pisiform, but #s vary by person
What are flat bones like?
thin, flat, slightly curved
What do flat bones do?
protect internal organs
What are some flat bones?
ribs + cranial bones
What are irregular bones?
don't fit in short, flat, or long
What are some irregular bones?
hip bones, vertebrae
What is the purpose of the skeleton?
a framework that supports the body, protects vital structures (brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs)
What is the skeletomuscular system?
bones, muscles, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, joints, connective tissue work together to make movement possible
What are some functions of bones?
storage of triglycerides inside yellow bone marrow, serve as reservoir for minerals, produce hormones like osteocalcin + growth factors
What are triglycerides?
a type of fat (lipid) that circulated in your blood, most common
How is the outside of a bone structured?
outer layer - compact bones, looks smooth + solid
How is the inside of a bone structured?
spongy bones (diploe in flat bones)
What is spongy bone composed of?
trabecular, pores of bone marrow
What is trabeculae?
bands or columns of connective tissue, help the bone resist stress
What is the diaphysis?
long axis of the bone, shaft
What is the diaphysis composed of?
compact bone that surrounds the medullary cavity
What is the medullary cavity?
hollow part of the bone that contains bone marrow
What are the 2 types of bone marrow?
red, yellow
What is red blood marrow like?
produces blood cells, replaced by yellow as you age
What is yellow bone marrow like?
stores fat, replaces red as you age
What happens with extreme blood loss?
revert yellow bone marrow to red to increase blood cell production
What are the epiphyses?
ends of the bone
What is the exterior of epiphyses composed of?
compact bone
What is the interior of epiphyses composed of?
spongy bone
What is articular cartilage?
complex living tissue, thin layer covers joint surface of each epiphysis
What is the metaphysis?
neck portion of a long bone (contains growth plate)
What is the growth plate?
part of the bone that grows during childhood
Where is the metaphysis found?
where diaphysis and epiphysis meet
What is the diaphysis?
main portion of long bone
What is the epiphyseal line?
disc of hyaline cartilage
Where is the epiphyseal line found?
metaphysis of adult long bones
What is the periosteum?
white membrane that covers external surface of bones
What is the fibrous layer?
outer layer of periosteum, made up of dense irregular connective tissue
What is irregular connective tissue?
tissue is which the extracellular fibers are not arranged in parallel bundles
What is the osteogenic layer?
inner layer, made up of osteogenic cells
What are Sharpey's fibers?
collagen fibers that secure the periosteum to the bone
What is the endosteum?
membrane made up of delicate connective tissue that covers internal surface of bones, along medullary cavity
What is the endosteum made of?
osteogenic cells
What are osteogenic cells?
stem cells in the bone that help bone repair and growth
What are osteons?
structural units of long bones, long cylinders parallel to long axis of bones
What are the function of osteons?
small, weight-bearing pillars
What are Harversian canals?
microscopic tubes in cortical bone
What is the purpose of a Haversian canal?
allows bone to get oxygen + nutrition + communication w/ bone cells
Where are Haversian canals found?
runs through center of each osteon
What are Volkmann's canals?
perforating canals; channels that allowed blood vessels to enter bones from periosteum, perpendicular to Haversian canal
What is the function of Volkmann's canals?
enable vessels + nerves to enter the bone to supply nutrients
What are bone markings?
surface features on bones
What is the function of bone markings?
enable joint motion, lock bones in place, provide structural support, provide stabilization, protect
What bone markings are sites of muscle + ligament attachment?
tuberosity, crest, trochanter, line, tubercle, epicondyle, spine, process
What is a tuberosity?
large rounded projection (often roughened)
What is a crest?
narrow, prominent ridge of bone
What is a trochanter?
very large, blunt, irregularly shaped process
What is a line?
narrow ridge of bone (less prominent than crest)
What is a tubercle?
small rounded projection or process
What is a spine?
sharp, slender, often pointed projection
What is a process?
bony prominence w/ abundant markings
What is a type of tuberosity?
ischial tuberosity, found in lower part of pelvis
What is an example of a crest?
iliac crest, found on ilium (often the sites where connective tissue attaches muscle to bone)
What is an example of a trochanter?
only ones are the greater and lesser one of the femur
What is an example of a line?
intertrochanteric line of femur
What is an example of a tubercle?
adductor tubercle of femur
What is an example of the epicondyle?
medial epicondyle of femur (above medial condyle)