topic 2. 1-7
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Metabolic rate
Rate at which metabolism (biochemical reactions) occur in an organism
Lumen
Inner open space or cavity of a tubular organ, such as a blood vessel or an intestine
Gas exchange air flow
Air - nose - nasal cavity - trachea - bronchi - bronchioles - alveoli - capillaries
Trachea structure
Lined by ciliated epithelium
Supported by c-shaped rings of cartilage to prevent collapse and allow food to pass down the oesophagus behind trachea
Bronchi structure
lined with ciliated epithelium
Supported by C shaped rings of cartilage to prevent collapse
Bronchioles structure
lined by ciliated epithelium
Compromised of smooth muscle and elastic fibres
Alveoli structure
Alveoli surfaces moist as oxygen has to be dissolved in water to move across membrane
Alveoli walls made up of squamous cells that are one cell thick
Alevoli walls contain elastic fibres that stretch and recoil during respiration
Large difference in concentration
Primary structure of a protein
sequence of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds
Secondary structure of a protein
weak hydrogen bonds form between the negative oxygen of the c=o group and the positive hydrogen of the nh group
the hydrogen bonds cause a regular 3D shape (like an alpha helix or b pleated sheet)
Tertiary structure
the conformational change of secondary structure leads to additional bonds between different parts of the polypeptide chain
the bonds are: hydrogen, disulphide and ionic bonds
the new bonds cause it to fold into a more complex 3D structure
Quaternary structure
3D arrangement of more than one polyptode
Fibrous proteins
long parallel polypeptides
Insoluble due to hydrophobic R groups
Used for structure and support
Hydrogen bonds between the chains
Example: collagen
Globular proteins
fold into a 3D spherical structure
Soluble due to hydrophilic R groups
Example: insulin
Globular protein (conjugated)
Conjugated proteins contain a non protein component called a prosthetic group
Soluble
Example: haemoglobin
Glycoprotein
A group of proteins which have carbohydrate groups attached to a polypeptide chain
Functions of the plasma membrane
form a barrier between cell and external environment
Controls movement in and out the cell
Isolates organelles from the rest of the cytoplasm allowing cellular processes to occur separately
Cell signalling
Allows cell to change shape
Why are some molecules hydrophobic and some hydrophilic
In phospholipids the phosphate group is polar, therefore one end is slightly positive and the rest is negative.
Therefore it attracts other polar molecules - it is hydrophilic
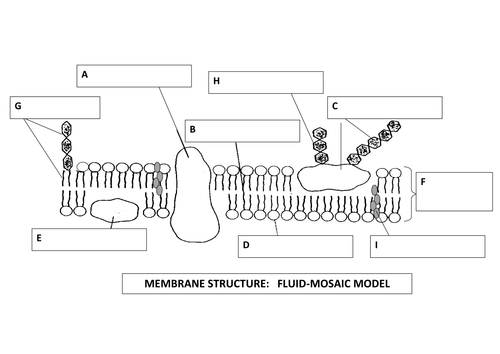
Label diagram
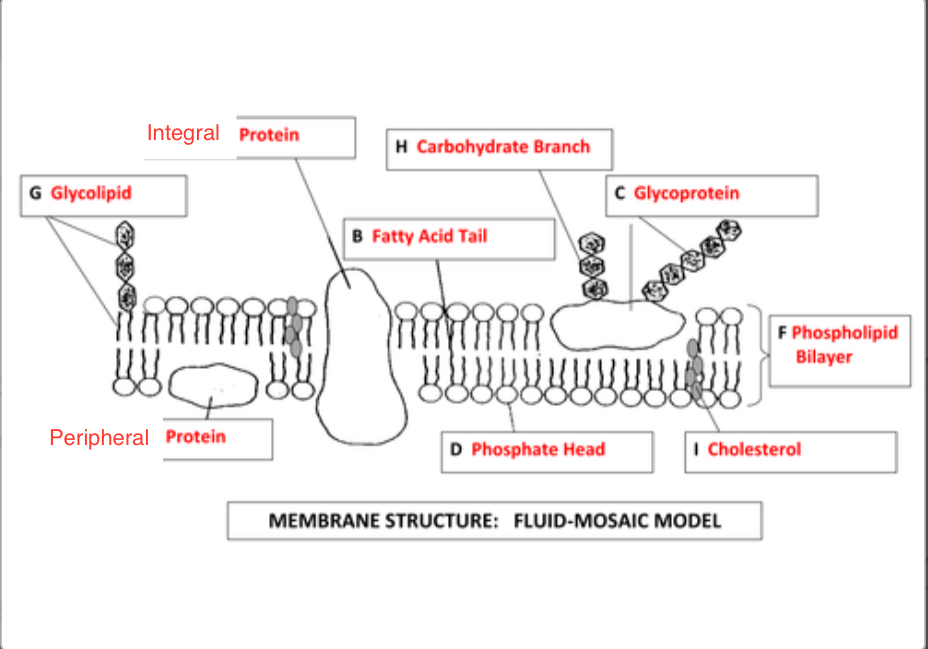
Properties of phospholipid bilayer
Membrane is fluid meaning Proteins are not fused and parts of the membrane can easily break away to form vesicles, or new cell surface membranes
Simple diffusion
Net movement of molecules of ions from a region of high concentration to low concentration
Facilitated diffusion
Movement of molecules often lower down their conc. gradient through membrane proteins w/o using energy
Osmosis
movement of water from a high concentration to a low concentration
Movement of water from a low solute concentration to a high solute concentration
Active transport
Movement of molecules/ions against a conc gradient
Exocytosis
involves vesicles (small membrane bound sacs) fusing with the cell surface membrane to release their contents outside the cell
Endocytosis
cell engulfs substances by folding its membrane to form a vesicle
Beetroot practical (Temp)
beetroot cubes already cut
Left overnight to wash away excess dye
Place 8 labelled boiling tubes each containing 5cm distilled water into water bath at temperature (0-70 degrees), leave for 5 minutes
Add a beetroot cubes to each tube and leave for 15 minutes
Decant liquid into second boiling tubes and shake the boiling tube
Set up the colorimeter using a cuvette containing distilled water, to put the absorbance to 0
Using the Pipette take out 2cm of dye solution from the boiling tubes
Take a reading for each dyes absorbance
beetroot practical alcohol
beetroot cubes already cut
Left overnight to wash away excess dye
Place one beetroot section into each of 8 labelled boiling tubes. The tubes contain 0-70% alcohol concentration
leave for 15 minutes
Decant liquid into second boiling tubes and shake the boiling tube
Set up the colorimeter using a cuvette containing distilled water, to put the absorbance to 0
Using the Pipette take out 2cm of dye solution from the boiling tubes
Take a reading for each dyes absorbance
Osmosis definition
movement of free water molecules through a partially permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration
Passive transport
Not requiring energy
Types:simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion
Simple diffusion
Movement of molecules down the conc gradient. Small non-polar molecules diffuse across the membrane easily, larger molecules diffuse slower.
Facilitated diffusion
Diffusion of molecules across membrane via channel proteins or carrier proteins embedded in the membrane, molecules move down the concentration gradient
Active transport
Movement of molecules against the concentration gradient using carrier proteins and ATP as a source of energy
Exocytosis
involves vesicles (small membrane-bound sacs) fusing with the cell surface membrane to release their contents outside the cell
Endocytosis
cell engulfs substances by folding its membrane to form a vesicle
Explain why mutations in the CFTR channel protein result in thicker mucus.
CFTR is absent or non-functional.
Na+ channel is permanently open
Cl- diffuse down electrical gradient into the tissue fluid
Water is continuously removed from mucus by osmosis - MUCUS BECOMES DRY + STICKY.
Mono-nucleotide structure
a pentose sugar - deoxyribose (DNA) or ribose (RNA)
A phosphate group
An organic base: T,C,G,A (DNA) OR U,C,G,A (RNA)
Pyrimidines
C AND T (U - RNA)
PURINES
A AND G