Klein - Cyanotic CHD AI
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AI and personal cards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease
Group of heart defects that produce systemic desaturation and clinical cyanosis due to right-to-left or bidirectional shunting.
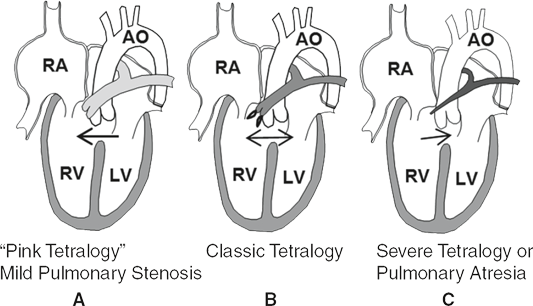
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
Most common cyanotic defect; tetrad of large malalignment VSD, overriding aorta, RVOT obstruction, and right-ventricular hypertrophy.
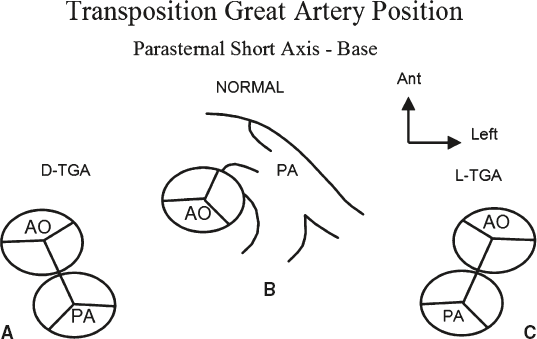
Transposition of the Great Arteries (D-TGA)
Ventriculo-arterial discordance in which the aorta arises from the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery from the left ventricle, creating parallel circulations.
Truncus Arteriosus
Single common arterial trunk giving rise to systemic, pulmonary, and coronary arteries; always associated with a large VSD.
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR)
All pulmonary veins connect to systemic venous circulation instead of the left atrium; obligatory right-to-left atrial shunt ensures survival.
Supracardiac TAPVR
Pulmonary venous confluence drains via vertical vein to innominate vein or SVC before entering right atrium; most common TAPVR type.
Infracardiac TAPVR
Pulmonary veins drain below diaphragm to portal/hepatic venous system or IVC; almost always obstructed.
Cardiac TAPVR
Pulmonary veins drain directly to right atrium or coronary sinus; obstruction is uncommon.
Mixed TAPVR
Combination of two or more TAPVR drainage patterns in the same patient.
Tricuspid Atresia
Absence of a right atrioventricular connection; obligatory ASD/PFO and usually a VSD supply pulmonary flow.
Ebstein Anomaly
Apical displacement of septal and posterior tricuspid leaflets producing an atrialized portion of the right ventricle and severe tricuspid regurgitation.
Atrialized Right Ventricle
Portion of the ventricular cavity proximal to displaced tricuspid leaflets in Ebstein anomaly that functions physiologically as atrium.
Displacement Index
Measurement from mitral annulus to septal tricuspid leaflet insertion; >8 mm/m² indicates Ebstein anomaly.
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS)
Spectrum with under-developed left ventricle, aortic/mitral atresia or stenosis, and hypoplastic ascending aorta; ductus-dependent systemic flow.
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
Intracardiac communication between right and left ventricles; size and location influence shunt direction and pressure.
Malalignment VSD
Septal defect created by anterior or posterior deviation of outlet septum; typical in TOF and truncus arteriosus.
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
Persistent opening in atrial septum; allows shunting, often right-to-left in cyanotic lesions.
Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO)
Flap-like potential communication at the fossa ovalis that can permit atrial level shunting post-natally.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
Persistent fetal connection between aorta and pulmonary artery; may supply systemic or pulmonary flow in ductal-dependent lesions.
Right-to-Left Shunt
Blood flow from systemic venous to systemic arterial side bypassing lungs, causing desaturation.
Left-to-Right Shunt
Blood flow from systemic arterial to venous side, increasing pulmonary circulation without causing cyanosis.
Right Ventricular Outflow Tract (RVOT) Obstruction
Restriction of flow from right ventricle to pulmonary artery; may be subvalvar, valvar, or supravalvar.
Infundibular Stenosis
Dynamic or fixed narrowing of the muscular RVOT just below the pulmonary valve, common in TOF.
Pulmonary Atresia with Intact Ventricular Septum (PA/IVS)
Absent pulmonary valve opening and no VSD; right ventricle often hypoplastic.
Pulmonary Atresia with VSD (PA/VSD)
Severe form of TOF where pulmonary valve is atretic and pulmonary blood flow depends on collaterals or ductus.
Eisenmenger Syndrome
Irreversible pulmonary vascular disease causing reversal of a long-standing left-to-right shunt to right-to-left.
Blalock-Taussig (BT) Shunt
Surgical systemic-to-pulmonary artery shunt (classically subclavian to pulmonary) to augment pulmonary blood flow.
Modified BT Shunt
Use of interposed Gore-Tex tube graft between subclavian and pulmonary artery; current standard.
Transannular Patch
Surgical enlargement of RVOT across pulmonary annulus in TOF repair, usually producing free pulmonary regurgitation.
TET Spell
Acute hypercyanotic episode in TOF characterized by sudden increase in RVOT obstruction and right-to-left shunt.
Prostaglandin E1 (PGE1)
Medication used to maintain ductus arteriosus patency in ductal-dependent heart defects.
FYI if great transposition baby is still cyanotic despite PDA kept widely patent… check to see if the ASD that is also helping their blood mix is really small. You need both to maintain minimal cyanosis
Mustard Operation
Atrial switch procedure diverting systemic venous blood to mitral valve and pulmonary venous blood to tricuspid valve in D-TGA.
Senning Operation
Atrial switch similar to Mustard but constructed from native atrial tissue instead of synthetic baffle.
Jatene Procedure (Arterial Switch)
Anatomic correction for D-TGA moving great arteries and coronary buttons to appropriate ventricles.
LeCompte Maneuver
Anterior translocation of pulmonary arteries during arterial switch to relieve tension and avoid compression.
Glenn Operation
Bidirectional cavopulmonary anastomosis connecting SVC to right pulmonary artery as stage toward Fontan.
Fontan Procedure
Completion of total cavopulmonary connection routing systemic venous return directly to pulmonary arteries in single-ventricle physiology.
Norwood Procedure
Stage-1 palliation for HLHS: reconstructs aorta using main pulmonary artery and provides controlled pulmonary flow via shunt.
Right Ventricular-to-Pulmonary Artery (RV-PA) Conduit
Surgically placed valved tube connecting right ventricle to pulmonary artery, often after truncus repair or TOF variant.
Pulmonary Venous Baffle
Channel in atrial switch directing pulmonary venous blood to systemic ventricle (right ventricle in Mustard/Senning).
Systemic Venous Baffle
Channel in atrial switch directing caval blood to left ventricle and pulmonary artery.
Unroofed Coronary Sinus
Defect where roof between coronary sinus and left atrium is absent, allowing right-to-left shunt especially with persistent left SVC.
Persistent Left Superior Vena Cava (LSVC)
Embryologic remnant draining left upper body venous blood, often into coronary sinus; may cause cyanosis if draining to left atrium.
22q11 Deletion (DiGeorge Syndrome)
Chromosomal microdeletion frequently associated with conotruncal defects such as truncus arteriosus and interrupted aortic arch.
Anterior Deviation of Outlet Septum
Embryologic malalignment causing RVOT obstruction and VSD in TOF.
Conotruncal Anomaly
Malformation arising from abnormal development of outflow tract (conotruncus) e.g., TOF, truncus arteriosus, D-TGA.
Right Aortic Arch
Aortic arch that courses to the right of trachea; present in ~25 % of TOF and PA/VSD cases.
Left Anterior Descending (LAD) from Right Coronary Artery
Coronary anomaly important in TOF surgery because LAD may cross RVOT incision site.
Gooseneck Deformity
Elongated, narrowed LVOT seen in AVSD, caused by abnormal inlet-outlet alignment.
Right-to-Left Atrial Septal Flow on Bubble Study
Early appearance of agitated saline in left atrium indicating intracardiac or pulmonary venous right-to-left shunt.
Sail-Like Anterior Tricuspid Leaflet
Redundant mobile anterior leaflet characteristic of Ebstein anomaly.
Systemic Desaturation
Reduced arterial oxygen saturation measurable by oximetry, hallmark of cyanotic defects.
Parallel Circulation
Physiology in which systemic and pulmonary circulations run side-by-side without mixing; classic of untreated D-TGA.
Atrioventricular Concordance
Normal connection between atria and ventricles (RA-RV, LA-LV) despite abnormal ventriculo-arterial relations.
Ventriculo-Arterial Discordance
Mismatch where ventricles connect to opposite great arteries, as in D-TGA.
Pulmonary Atresia
A congenital heart defect where the pulmonary valve is completely absent, obstructing blood flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery.
Aortic Valvar Stenosis
Narrowing of the aortic valve opening, restricting blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta.
Coarctation of the Aorta (CoA)
A congenital narrowing of the aorta, typically at the site of the ductus arteriosus insertion, which obstructs systemic blood flow.
Postductal Coarctation
A form of aortic coarctation where the narrowing occurs distal to the re-entry point of the ductus arteriosus into the aorta.
Bicuspid Aortic Valve (BAV)
A congenital heart defect in which the aortic valve has two leaflets (cusps) instead of the normal three, often predisposing to stenosis or regurgitation.
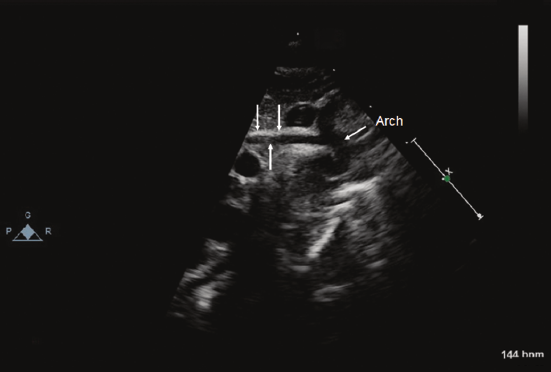
A severe congenital heart defect marked by underdevelopment of the left side of the heart, including the left ventricle, aortic/mitral valves, and ascending aorta. It is a ductal-dependent lesion, requiring a patent ductus arteriosus for systemic blood flow. Pulmonary venous return shunts primarily through the atrial septum to the right heart, which then supplies both pulmonary and systemic circulation.
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS)
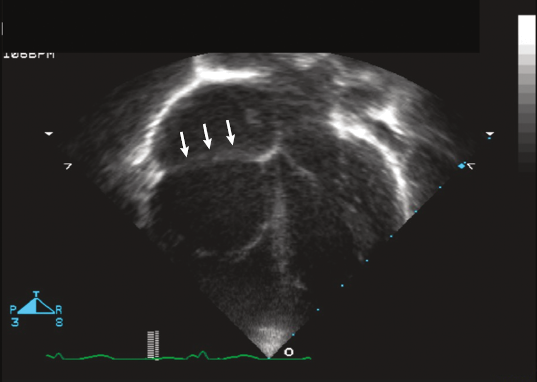
Atrialized portion of RV that is continuous with true RA
Apical displacement of the septal and posterior leaflets of the TV into the RV.
Ebstein’s anomaly
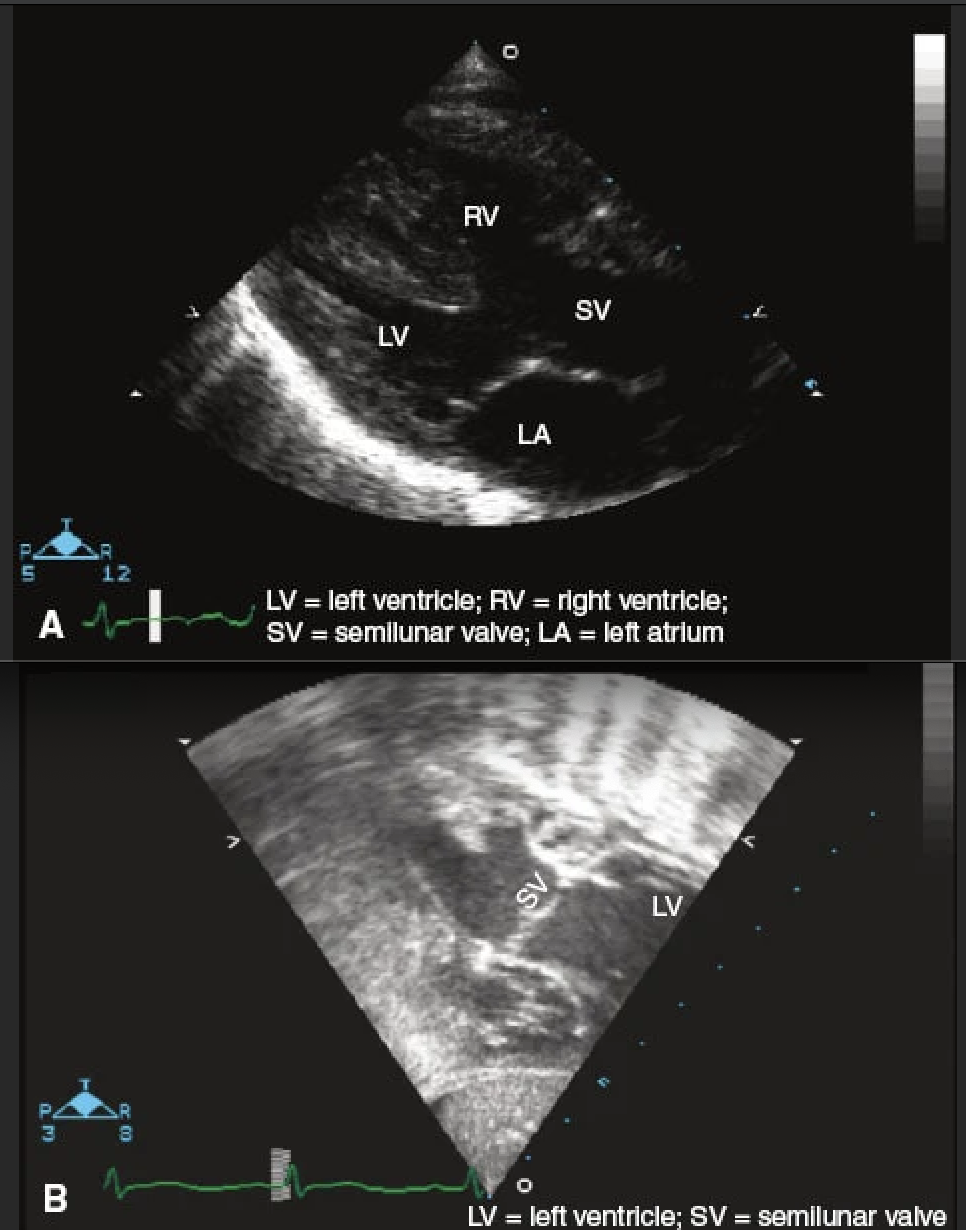
What is the disease?
Label the chambers
D-TGA
Both TGA will have parallel AV and PV in short axis, but D-TGA the
a = LV
b = RV
c = PV
d = AV
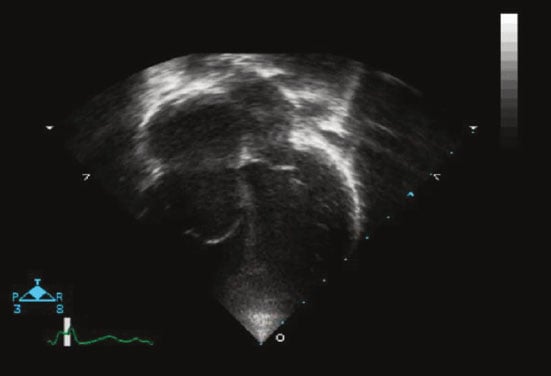
19 yo M with easy fatiguability with exercise. O2 saturation is 86% with this echo.
What condition?
Ebstein anomaly - failure of normal dev of the septal and posterior leaflet of TV. And anterior leaflet becomes “sail like”.
FYI this image also suggests large ASD given dilated RA and RV with L to right shunt.
Total absence of the RV myocardium, extremely rare. Only 20 cases reported so far. TV is normal.
Uhl’s anomaly
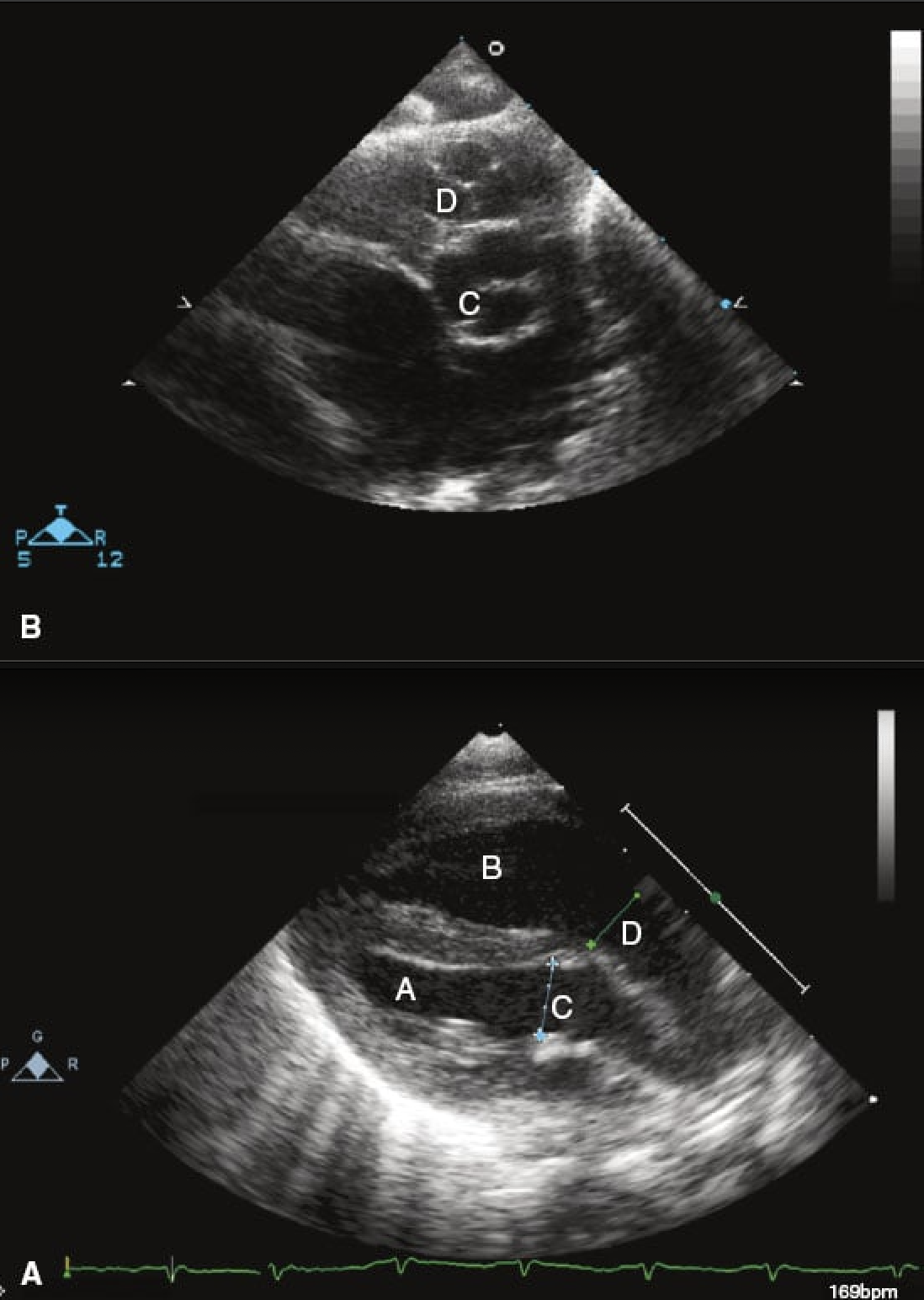
6 week old infant with poor feeding, respiratory distress and mild cyanosis. CXR with pulm vasc congestion. Diagnosis?
Truncus arteriosus
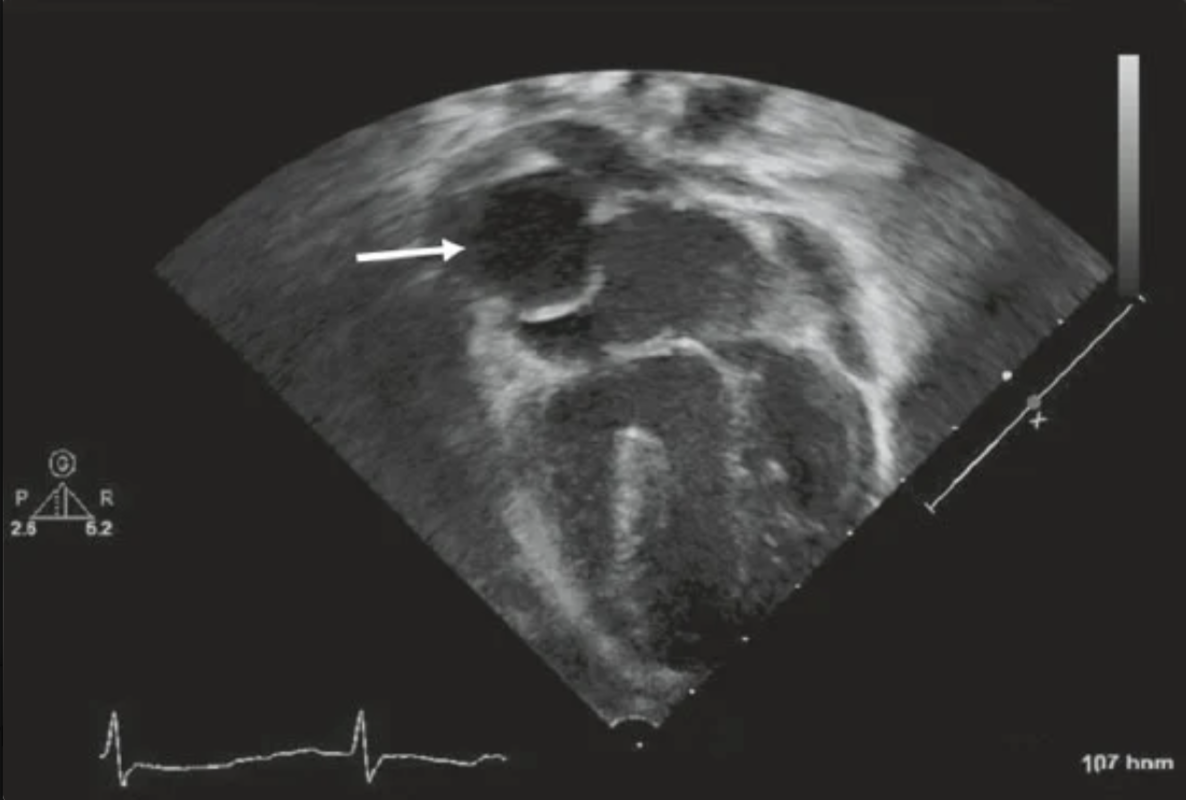
A4C view in a patient with tricuspid atresia is obtained following surgical palliation. The structure adjacent to the arrow is…
Lateral tunnel Fontan operation from single ventricle palliation. This is an atrial lateral tunnel that carries systemic venous blood flow to the pulmonary arteries.
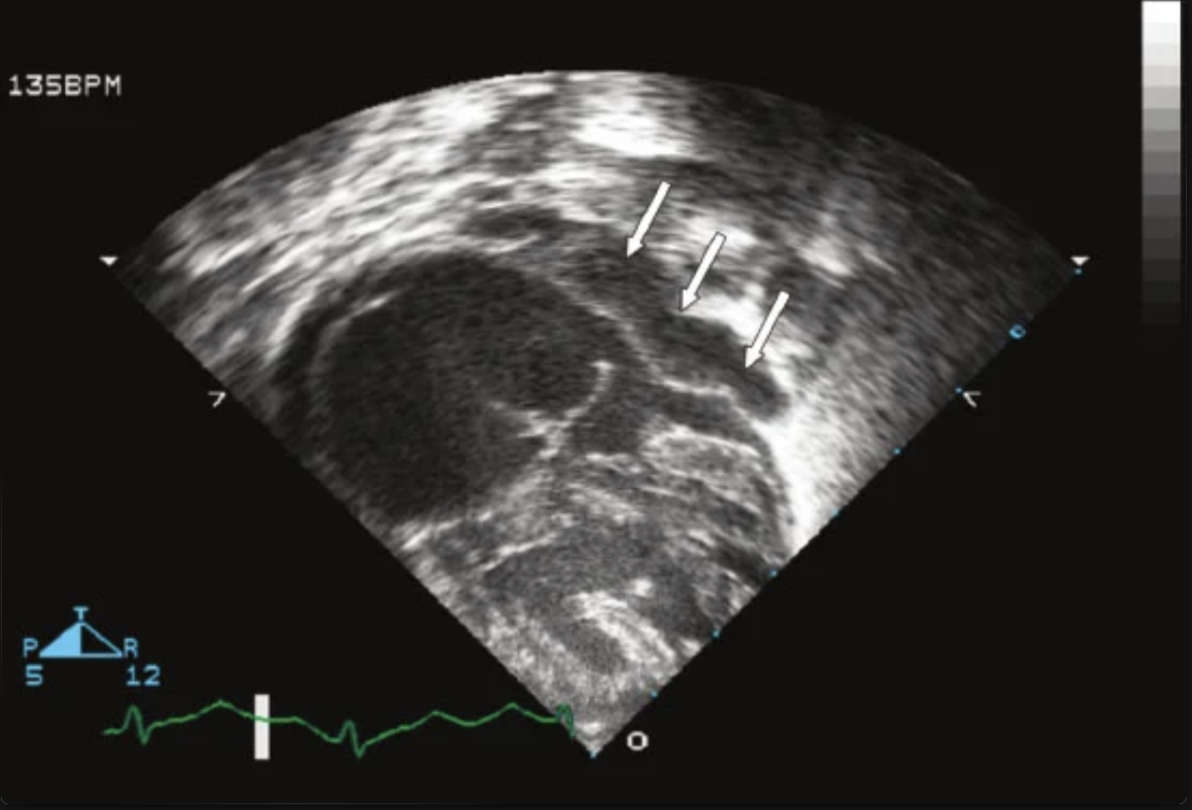
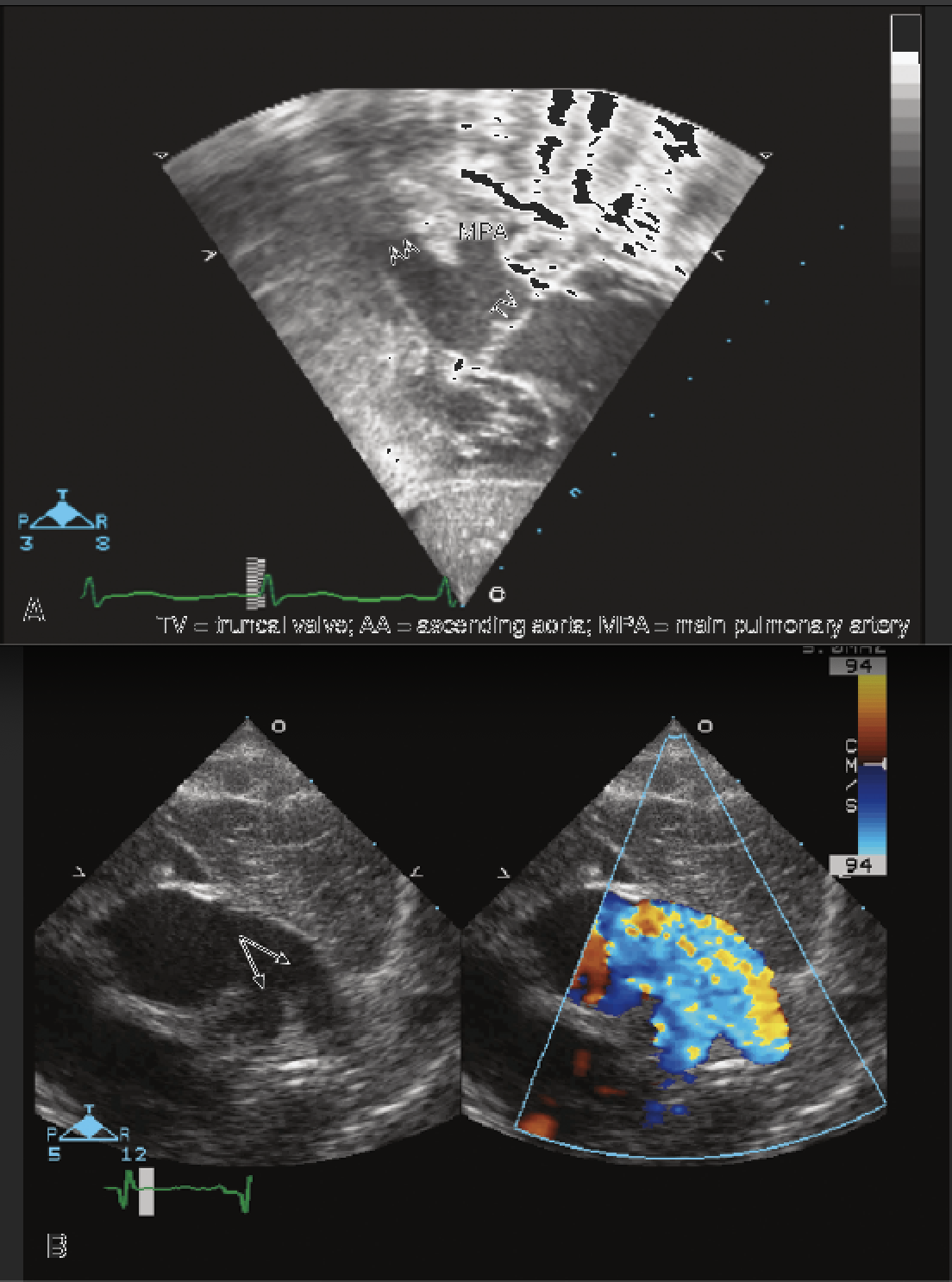
3 week old F presents to doc with respiratory distress and oxygen saturation in the 80s. Subcostal picture shows…
Pulmonary venous confluence highly suspicious of total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)