Comprehensive Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Chemistry, Water, Organic Molecules, pH, and Enzymes
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
Matter
anything that takes up space and has mass
Element
simplest form of matter with unique chemical properties
Atom
the smallest possible piece of an element
Atomic number
number of protons in its nucleus
Atomic mass
approximate total number of protons and neutrons
Nucleus
center of atom contains protons and neutrons
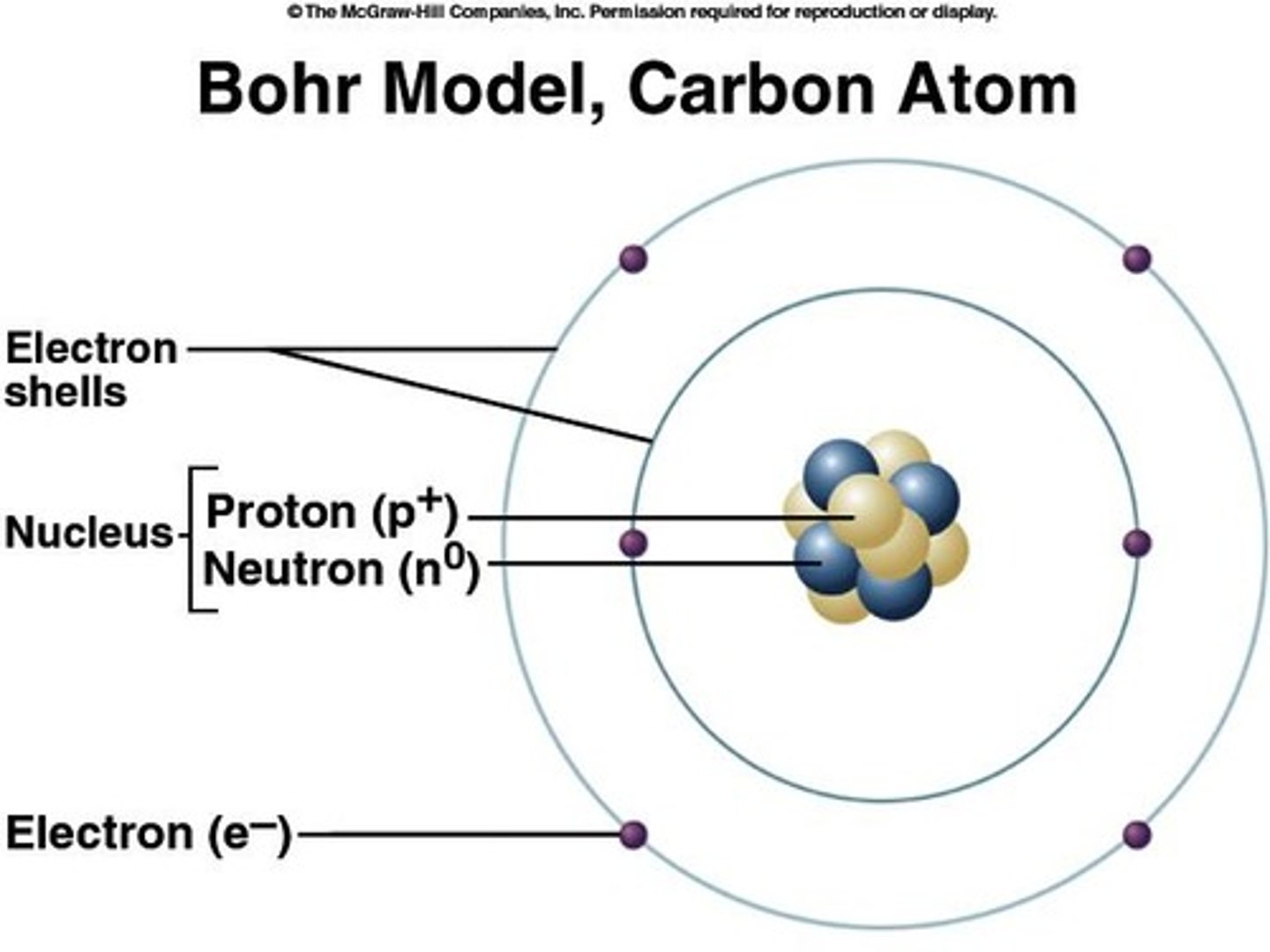
Protons
positive charge, mass of 1 amu (atomic mass unit)
Neutrons
neutral charge, mass of 1 amu
Electrons
negative charge, surround the nucleus
Valence electrons
electrons in the outermost shell that interact with other atoms
Octet rule
atoms react to obtain a stable number of 8 valence electrons
Isotopes
elements that differ in the number of neutrons
Atomic weight
Average atomic mass of the mixture of isotopes of an element found in a sample
Molecules
two or more atoms of same element covalently bonded
Compounds
two or more atoms of different elements covalently bonded
Molecular weight
the sum of the atomic weights of its atoms
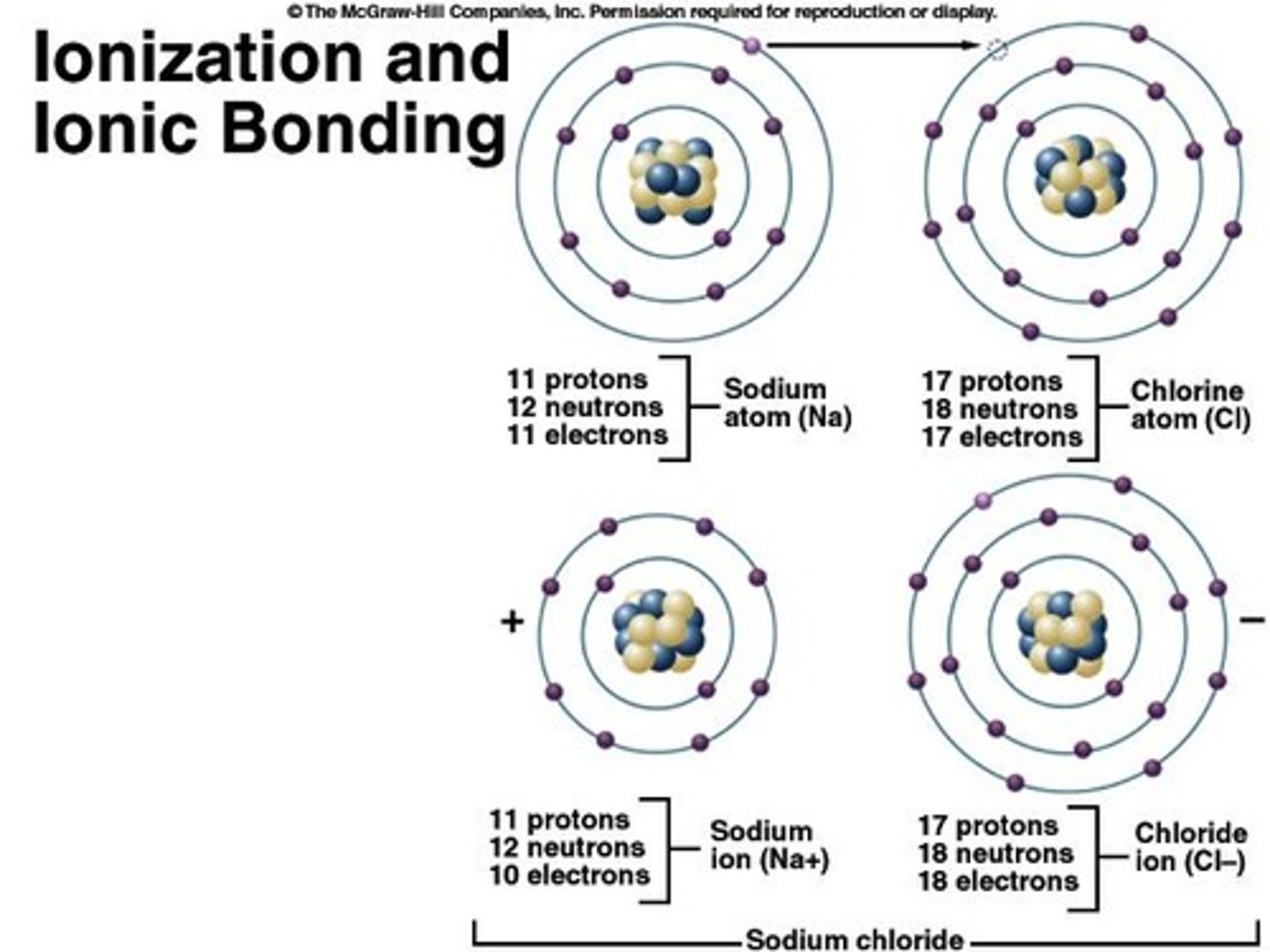
Ions
charged particles with unequal numbers of protons and electrons
Ionization
transfer of electrons from one atom to another ( stability of valence shell)
Electrolytes
Salts, acids, or bases that ionize (gain or lose e⁻) in water and form solutions capable of conducting electricity
Acid
molecule or compound that donates a H+ ion, a proton donor
Base
molecule or compound that accepts a H+ ion, a proton acceptor
Anion
atom gained electron, net negative charge
Cation
atom lost an electron, net positive charge
Free Radicals
An unstable and very reactive particle with an odd number of electrons
Antioxidants
neutralize free radicals
Ionic Bonds
Attraction of oppositely charged ions (cation & anion) to each other forms an ionic bond - no sharing of electrons.
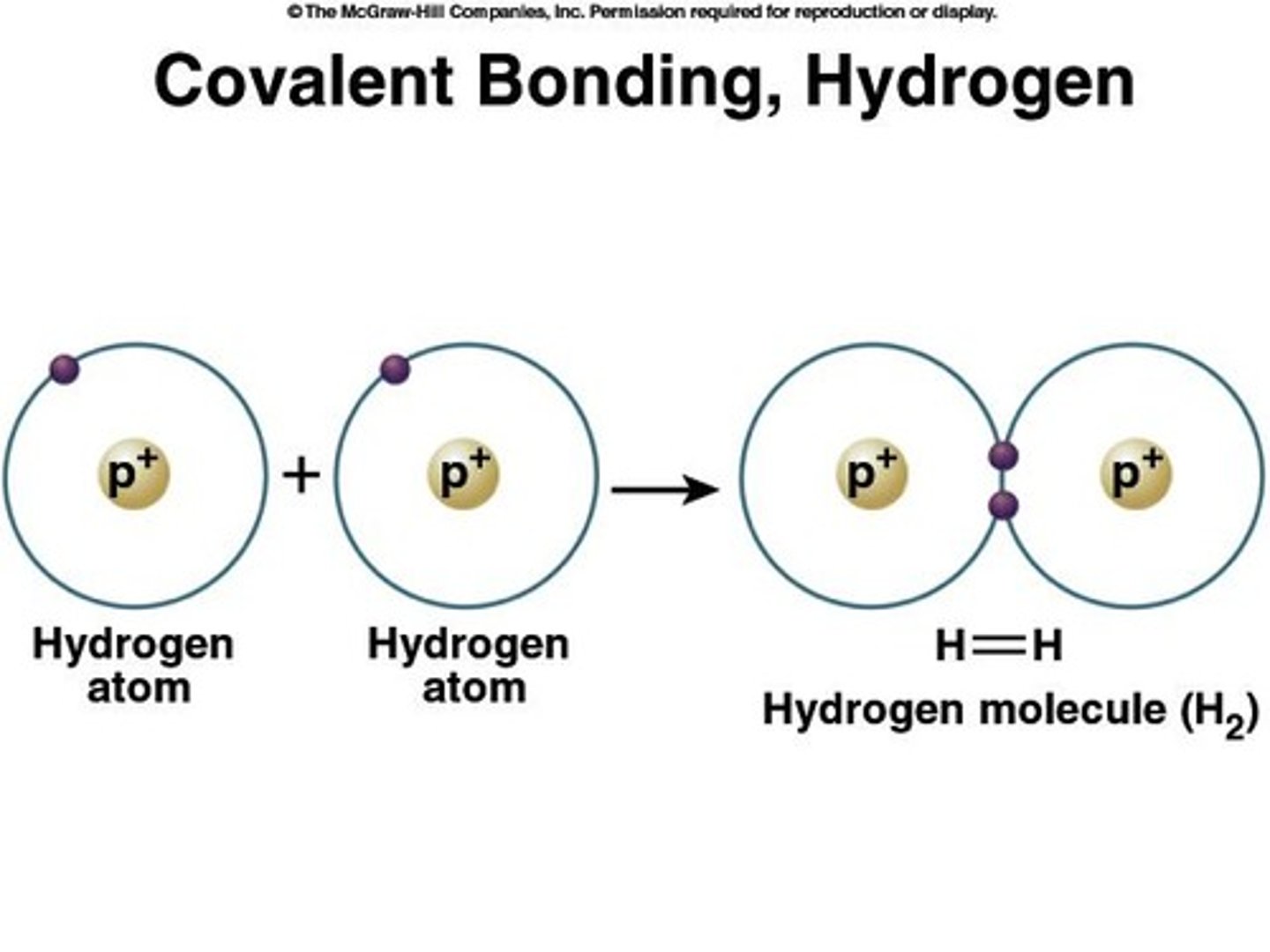
Covalent Bonds
Formed by sharing valence electrons.
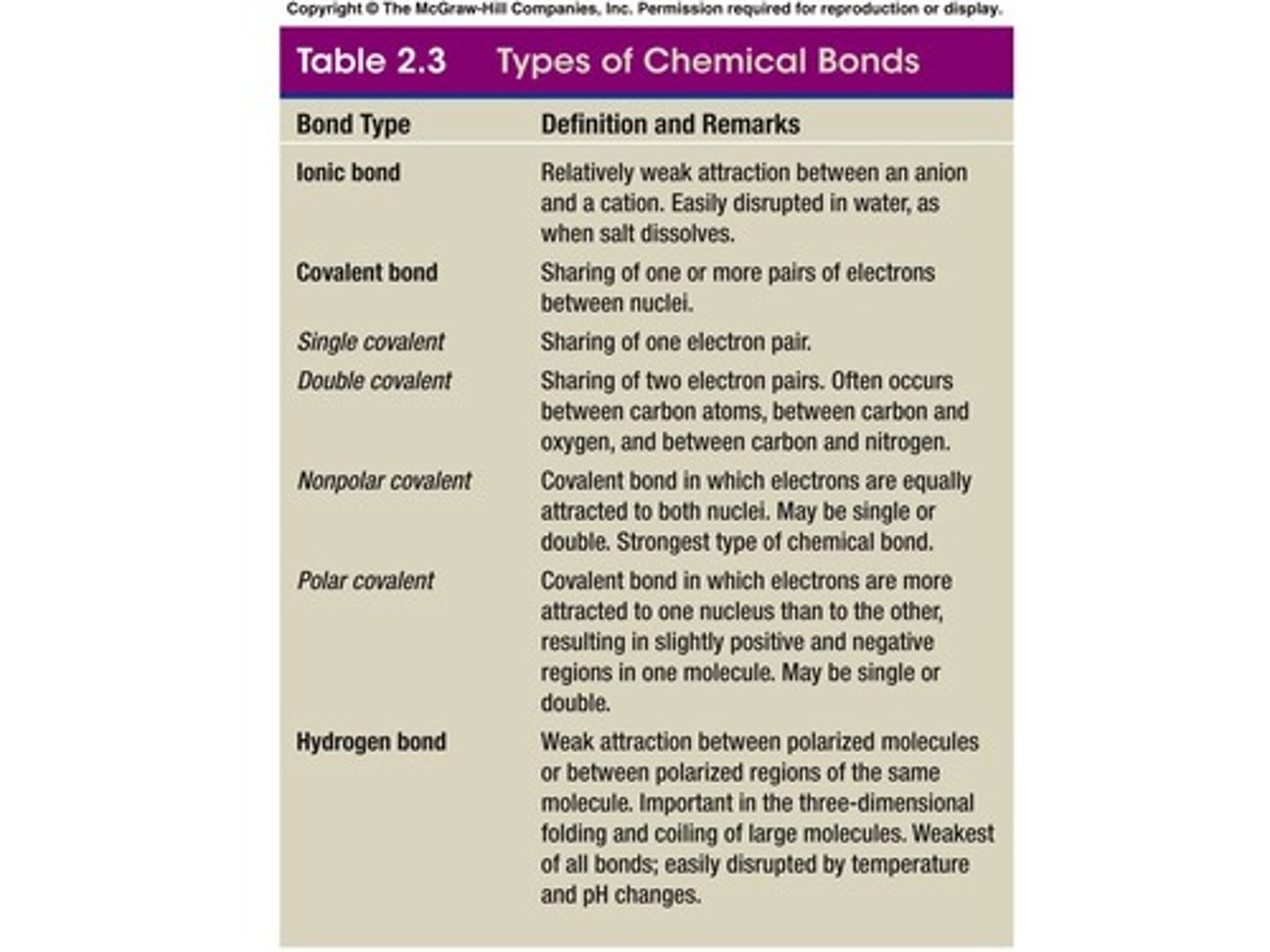
Single Covalent Bond
Share one electron pair.
Double Covalent Bond
Share two electron pairs.
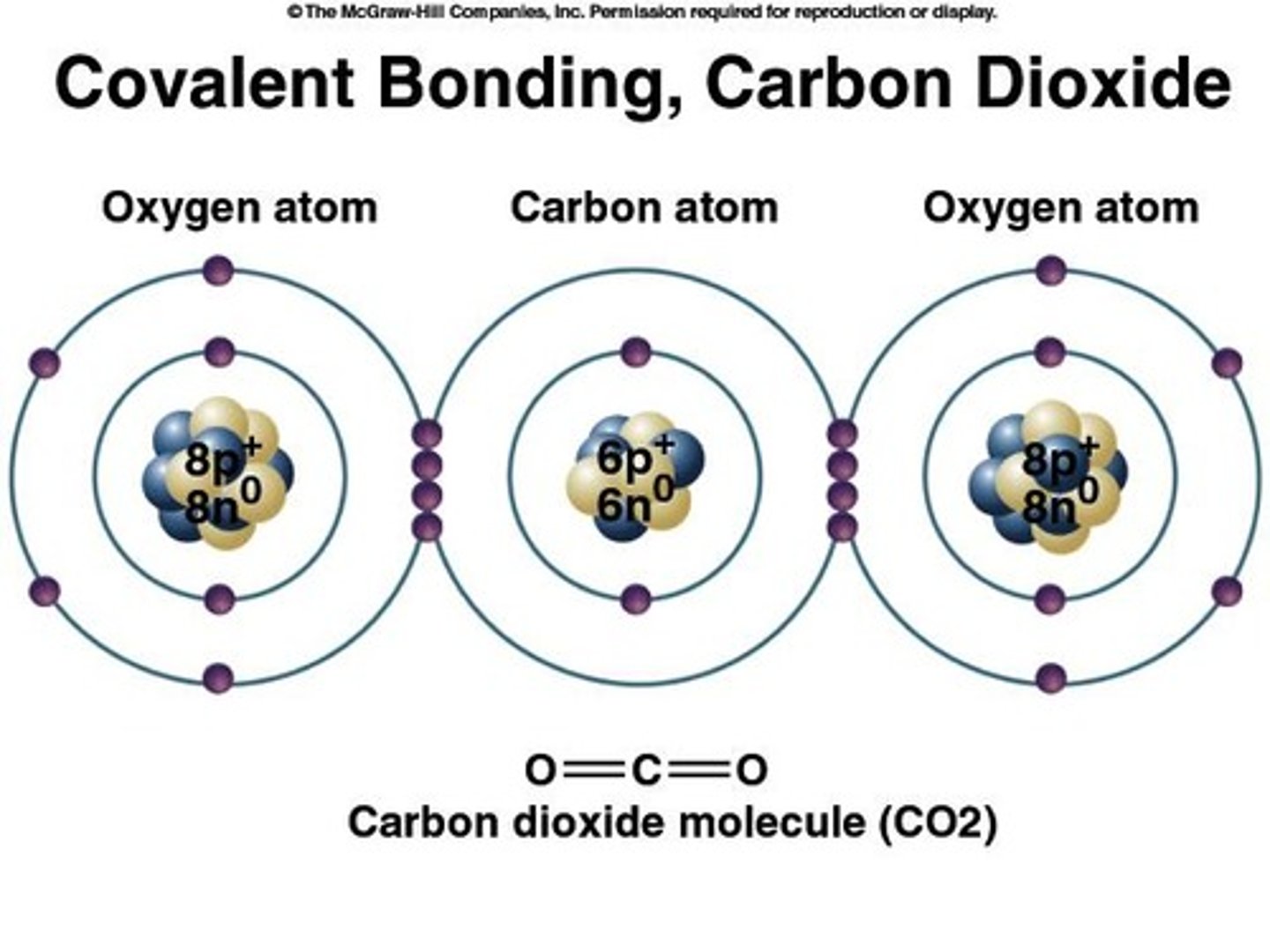
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
Electrons are equally attracted to both nuclei.
Polar Covalent Bond
Electrons are more attracted to one nucleus more than the other.
Diatomic Molecule
When two of the same atoms are participating.
Hydrogen Bonds
Weakest of the bonds; attraction between polar molecules - no sharing of electrons.
pH
Measures the concentration of H+ ions in solution.
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
Stomach acid; the reason why it burns when you vomit.
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
Strong Base.
Normal pH Range
Humans' normal pH range is 7.35-7.45.
pH Scale
Ranges from 0-14; levels below 7 are considered acidic, and above 7 are considered basic (alkaline).
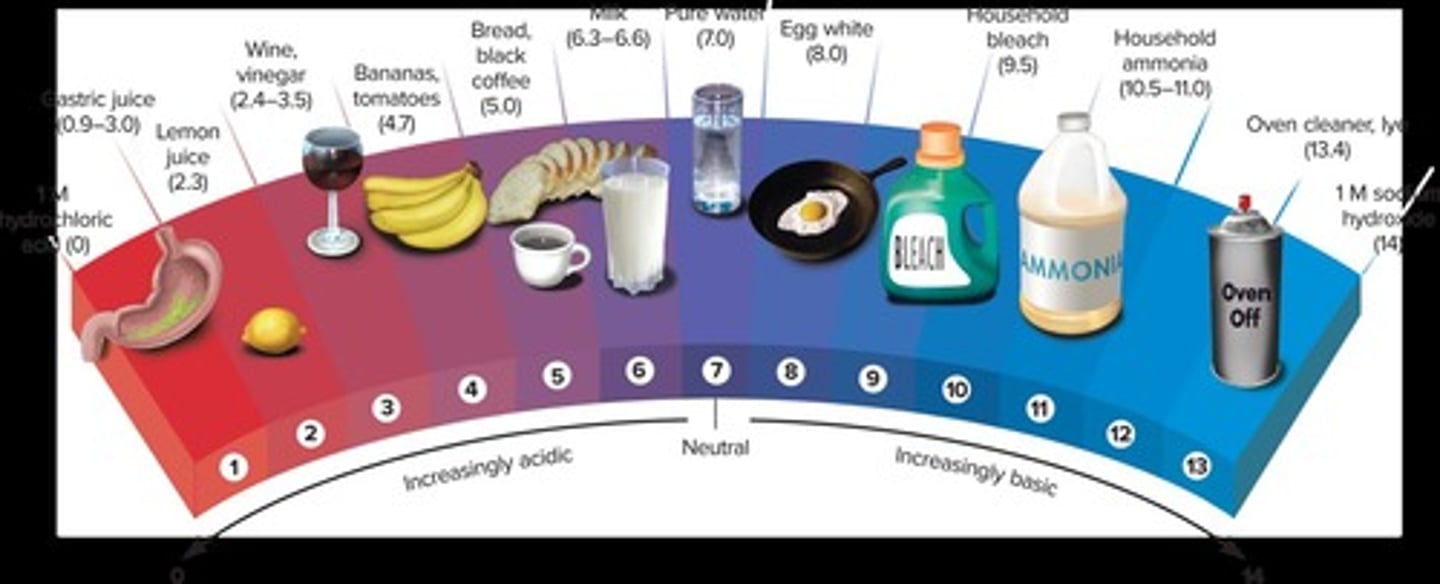
Acidosis
Arterial pH drops below 7.35 (physiological acidosis).
Alkalosis
Arterial blood pH rises above 7.45.
Sources of Hydrogen Ions
Most hydrogen ions originate from cellular metabolism.
Strong Acids
All their H+ is dissociated completely in water.
Weak Acids
Dissociate partially in water and are efficient at preventing pH changes.
Buffer System
Any mechanism that resists pH changes by converting a strong acid or base into a weaker acid or base.
Chemical Buffering System
A substance that binds to H⁺ and removes it from solution as its concentration begins to rise, or releases H⁺ into a solution if the concentration drops.
Physiological Buffering System
A system that stabilizes pH by controlling the body's output of acids, bases, or CO₂.
Respiratory system
Acts within a few minutes.
Urinary system
Acts within several hours or days.
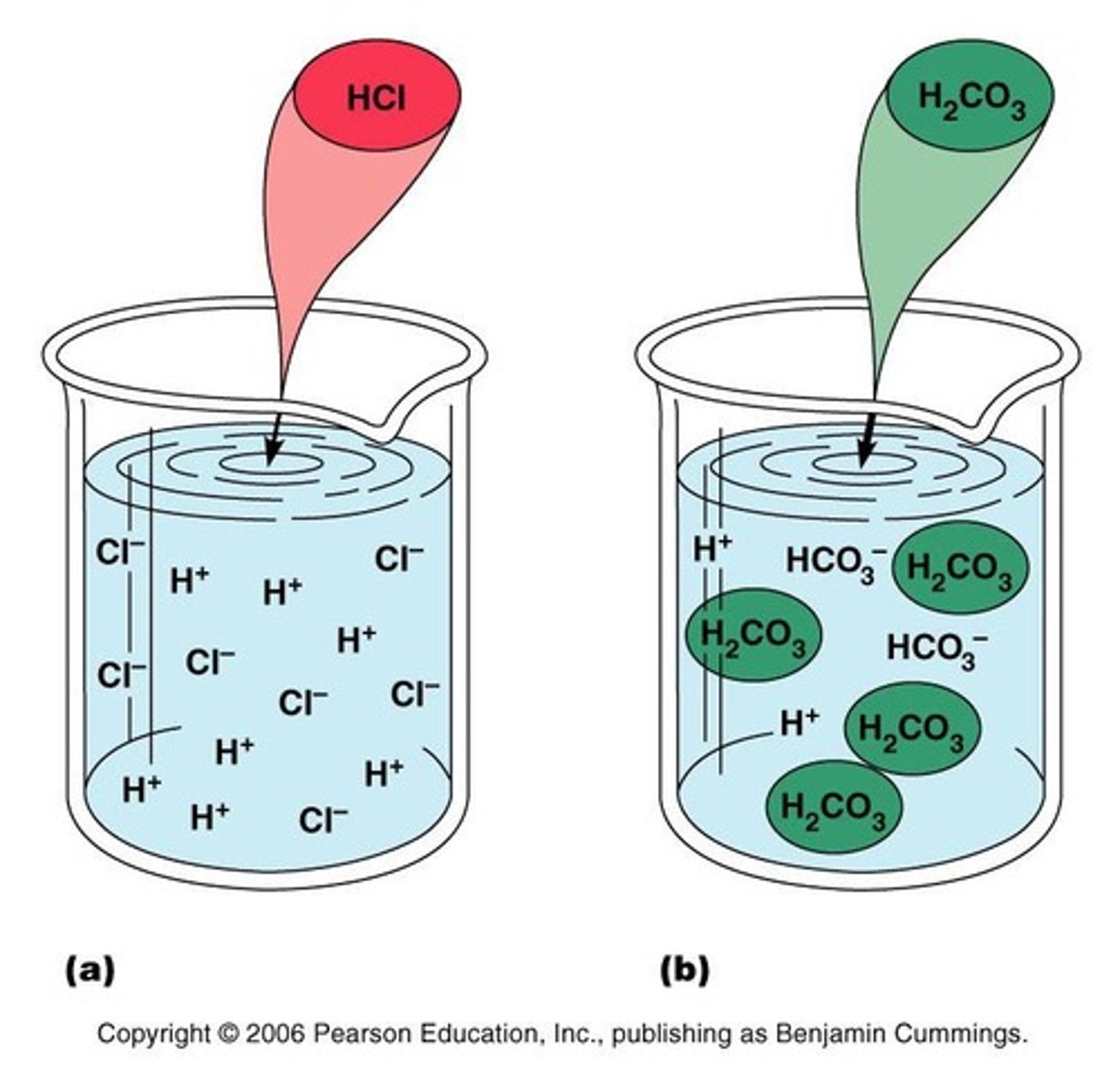
Bicarbonate Buffer System
A solution of carbonic acid (H2CO3) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3).
Bicarbonate Buffer System (strong acid)
If strong acid is added, hydrogen ions released combine with the bicarbonate ions and form carbonic acid (a weak acid). The pH of the solution decreases only slightly.
Bicarbonate Buffer System (strong base)
If strong base is added, it reacts with the carbonic acid to form sodium bicarbonate (a weak base). The pH of the solution rises only slightly.
Bicarbonate Buffer System (importance)
This system is the only important ECF buffer.
Phosphate Buffer System
Nearly identical to the bicarbonate system; its components are sodium salts of dihydrogen phosphate (H2PO4¯), a weak acid, and monohydrogen phosphate (HPO42¯), a weak base.
Phosphate Buffer System (effectiveness)
This system is an effective buffer in urine and intracellular fluid.
Protein Buffer System
Proteins are more concentrated than either bicarbonate or phosphate buffers, especially in the intracellular fluid (ICF).
Protein Buffer System (function)
It is able to buffer a solution because of the protein's side groups of their amino acids.
Carboxyl side groups
Will release H⁊ when pH rises.
Amino side groups
Will bind H⁊ when pH falls.
Physiological Buffer Systems: Respiratory
Respiratory buffer system adjusts pH by raising or lowering the rate and depth of breathing.
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) effect
Too much carbon dioxide (CO₂) will raise H⁺ concentrations, and the removal of CO₂ will lower H⁺ concentrations.
H+ and pH relationship
A drop in H+ raises pH, the body will decrease breathing rate to accumulate more CO₂, thus lowering the pH to normal.
Renal (Urinary) Mechanisms of Acid-Base Balance
Chemical buffers can tie up excess acids or bases, but they cannot eliminate them from the body.
Lungs and carbonic acid
The lungs can eliminate carbonic acid by eliminating carbon dioxide.
Kidneys and metabolic acids
Only the kidneys can rid the body of metabolic acids (phosphoric, uric, lactic acids, and ketones) and prevent metabolic acidosis.
Renal Mechanisms of Acid-Base Balance
The most important renal mechanisms for regulating acid-base balance are conserving (reabsorbing) or generating new bicarbonate ions and excreting bicarbonate ions.
Kidneys Regulate pH (low pH)
If pH too low, excrete excess hydrogen ions, retain bicarbonate.
Kidneys Regulate pH (high pH)
If pH too high, retain hydrogen ions, excrete bicarbonate.
Water properties
Evaluate the properties of water & their importance to the body, including these terms: polarity, capillary action, high heat of vaporization, adhesion, surface tension, solvency, cohesion, high specific heat, chemical reactivity.
Water
Most mixtures in the body consist of chemicals dissolved or suspended in water.
Universal Solvent
Water is called the universal solvent because it dissolves a broader range of substances than any other liquid.
Hydrophilic
Charged substances that dissolve easily in water.
Hydrophobic
Neutral substances that do not easily dissolve in water.
Polarity (solubility)
To be soluble in water, a molecule usually must be polarized or charged.
Adhesion
Attraction between one substance and another substance.
Cohesion
Molecules of the same substance cling to each other.
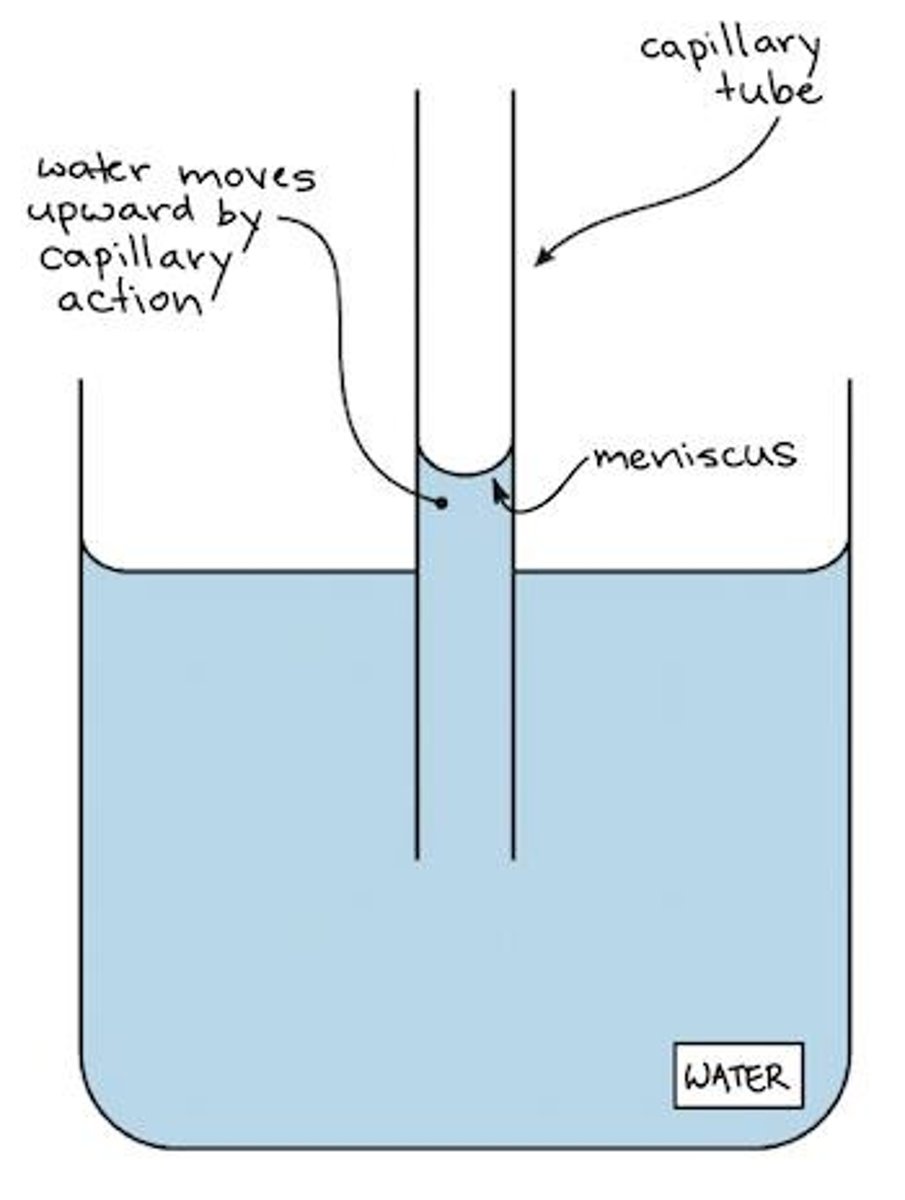
Capillary Action
Capillary action is the movement of a liquid through a narrow space, such as a tube, against gravity or without external forces. It occurs when the adhesive forces between the liquid and the surrounding solid surfaces are stronger than the cohesive forces between the liquid particles.
Surface Tension
Because of the cohesion between water molecules, the surface of water forms an elastic film.
Chemical Reactivity of Water
Facilitates and participates in chemical reactions, very chemically reactive, ionization of acids, salts and itself, important in the transport of molecules for reactions (universal solvent), involved in hydrolysis and dehydration synthesis.
Thermal Stability of Water
Water stabilizes internal temperature of the body.
High Specific Heat
Amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1°C.
Hydrogen Bonds in Water
Water's hydrogen bonds inhibit increased temperature (molecular motion) caused by increased heat.
Heat Absorption of Water
Water can absorb a given amount of heat without changing temperature as much.
High Heat of Vaporization
1 ml of perspiration evaporating from the skin removes 500 cal of heat from the body.
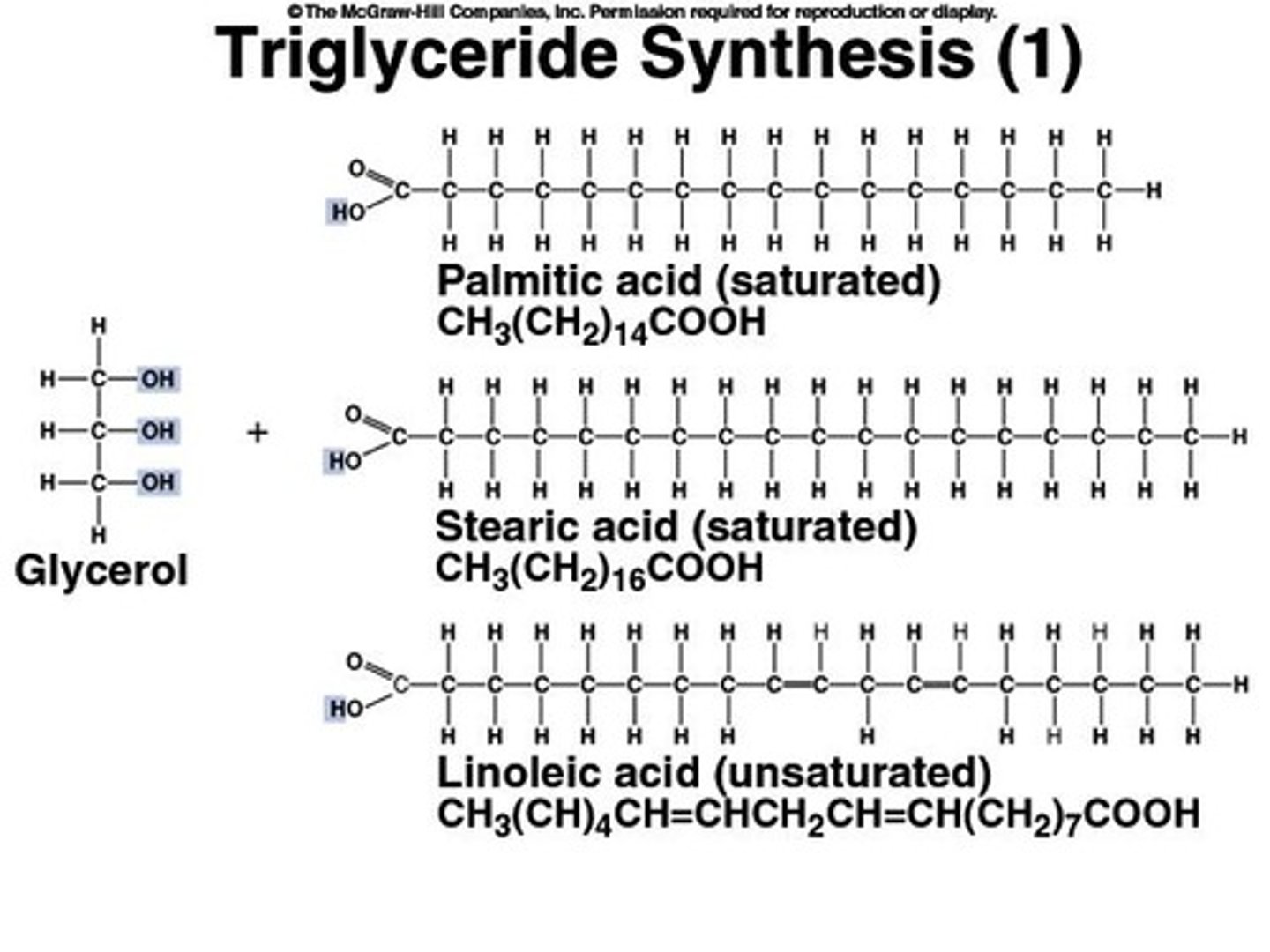
Dehydration Synthesis
A process by which two molecules are joined together with the removal of water.
Hydrolysis
A chemical process that splits a molecule by adding water.
Organic Compounds
Includes carbohydrates, monosaccharides, nucleotides, lipids, fatty acids, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), proteins, glycerol, nucleic acids, and amino acids.
Monosaccharides
The simplest form of carbohydrates, consisting of single sugar molecules.
Nucleotides
The basic building blocks of nucleic acids, consisting of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
Lipids
A group of organic compounds that are insoluble in water, including fats and oils.
Fatty Acids
Carboxylic acids with long aliphatic chains, which can be saturated or unsaturated.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
A high-energy molecule that stores and provides energy for cellular processes.
Proteins
Large biomolecules made up of amino acids that perform a variety of functions in the body.
Glycerol
A simple polyol compound that forms the backbone of triglycerides and phospholipids.
Nucleic Acids
Biomolecules essential for all known forms of life, including DNA and RNA.
Amino Acids
Organic compounds that combine to form proteins, consisting of an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain.
Organic Molecules
Carbon compounds that include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleotides, and nucleic acids.
Carbon
Bonds readily with other carbon atoms because it has 4 valence electrons and wants 4 more.
Monomers
Subunits of macromolecules (gigantic organic molecules).
Polymers
Series of identical or similar monomers bonded together.
Polymerization
The bonding of monomers together to form a polymer, caused by a reaction called dehydration synthesis.