The Nature of Business
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
The Role of Business
Organise resources to produce goods and services for sale for profit, to satisfy the needs and wants of society.
Organise resources
Choosing and using a variety of financial, physical, human and informational resources.
Production
Activities that combine inputs and transformation processes to create value-added outputs.
Goods
Physical objects such as clothes or shoes. They are tangible.
Products
Goods and services
Services
Things done for you by others because you lack the time, expertise or both. They are intangible.
Revenue
The money that a business receives as payment for selling its products to customers.
Sale
Customers voluntarily exchanging money to purchase goods and services produced by a business.
Expenses
The costs of operating a business
Profit
The difference between revenue and expenses. Maximising revenue and minimising expenses helps to maximise profit.
Needs
Basic requirements for human survival such as food, water, shelter, relationships.
Wants
Things that improve quality of life and make existence more comfortable.
Society
The aggregate of all people living in a community, region, nation, or across the globe.
Operations
The part of the business that turns inputs into outputs
Marketing
The part of the business that helps bring customers and the business together.
Finance
The part of the business that manages financial resources.
Human resources
The part of the business that manages the acquisition, training, development and separation of employees and other forms of labour.
Other functions of business
employment, income, innovation, entrepreneurship, wealth, quality of life and choice.
Business classification
Businesses can be classified by Industry Sector, Size, Geographical Spread, Legal Structure
Industry Sector
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
Quinary
Size
Conglomerate, large, medium, small, micro
Geographical Spread
Local, Regional, National, Global, Niche
Niche business
A business that serves a small, narrow market, but not necessarily in the one location.
Legal structure
Sole Trader
Partnership
Private company
Public company
Government Business Enterprise
Sole trader
One person owns and operates the business.
Partnership
Usually 2-20 partners own and operate a business.
Public company
A company that has floated shares in the stock market. Shareholders have ownership of the company.
Has Ltd after its name.
Private company
Can have a maximum of 50 shareholders. Shares are not floated in the market, people have to be granted permission from the owners to purchase shares.
Has Pty Ltd after its name.
Government business enterprise
A company whose only shareholder is the Government.
For example Australia Post.
Unincorporated
Where the business and the owner are one entity. All legal and financial liabilities of the business are the responsibility of the owner(s). Unlimited liability.
Incorporated
The process companies go through to become separate legal entities from their owners. This limits liabilities to invested money. Limited liability.
Primary Industry
Extracts products from the earth and processes them into raw materials
Eg Farming, mining, fishing, forestry.
Secondary Industry
Manufactures intermediate goods or finished products using raw materials and other intermediate products.
Eg Flour mill (intermediate good)
Eg Furniture (finished product)
Tertiary Industry
Provides a service to general population and to businesses.
Retailers, wholesalers and transport/distribution businesses.
Health services, emergency services, construction.
Quaternary Industry
Services that involve the transfer and processing of information and knowledge.
Eg, finance, technology, media, education, legal services and advertising.
Quinary Industry
Domestic activities and services traditionally done at home.
Eg Hospitality/Restaurants, Travel, Child care, aged care, cleaning/gardening.
Multinational Conglomerate
Massive company, often global in scope, operating a collection of smaller companies that provide it with a range of goods and services to sell in a variety of markets.
Eg Unilever
Eg Google
Number of employees in a large business
200+ employees
Number of employees in a medium businesses
20-199 employees
Number of employees in a small business
Less than 20 employees
Number of employees in a micro business
Less than 5
Factors influencing choice of legal structure
- Size of Business
- Ownership and Control
- Finance needed
Size of business (Influences on legal structure)
As sales increase and business operations grow, the owner may need to change its business structure to minimise tax, protect owner assets, gain expertise.
Finance needed (influences on legal structure)
When a business expands it will need injections of money. Money can be obtained from debt, new owners, venture capital or floating shares in the market.
Ownership and Control (influences on legal structure)
The legal structure of the business will depend on how much control the owner wants over the business.
Business Environment
the surrounding conditions in which the business operates. It can be divided into internal and external factors.
External environment
Includes those factors over which the business has very little control.
Internal environment
Includes those factors over which the business has some degree of control.
External influences
Economic, financial, social, legal, political, institutional, technological, competitive situation and changes in the market.
Economic cycles
Are the periods of expansion (boom) and contraction (recessions/depressions) that occur as a result of fluctuations in economic activity.
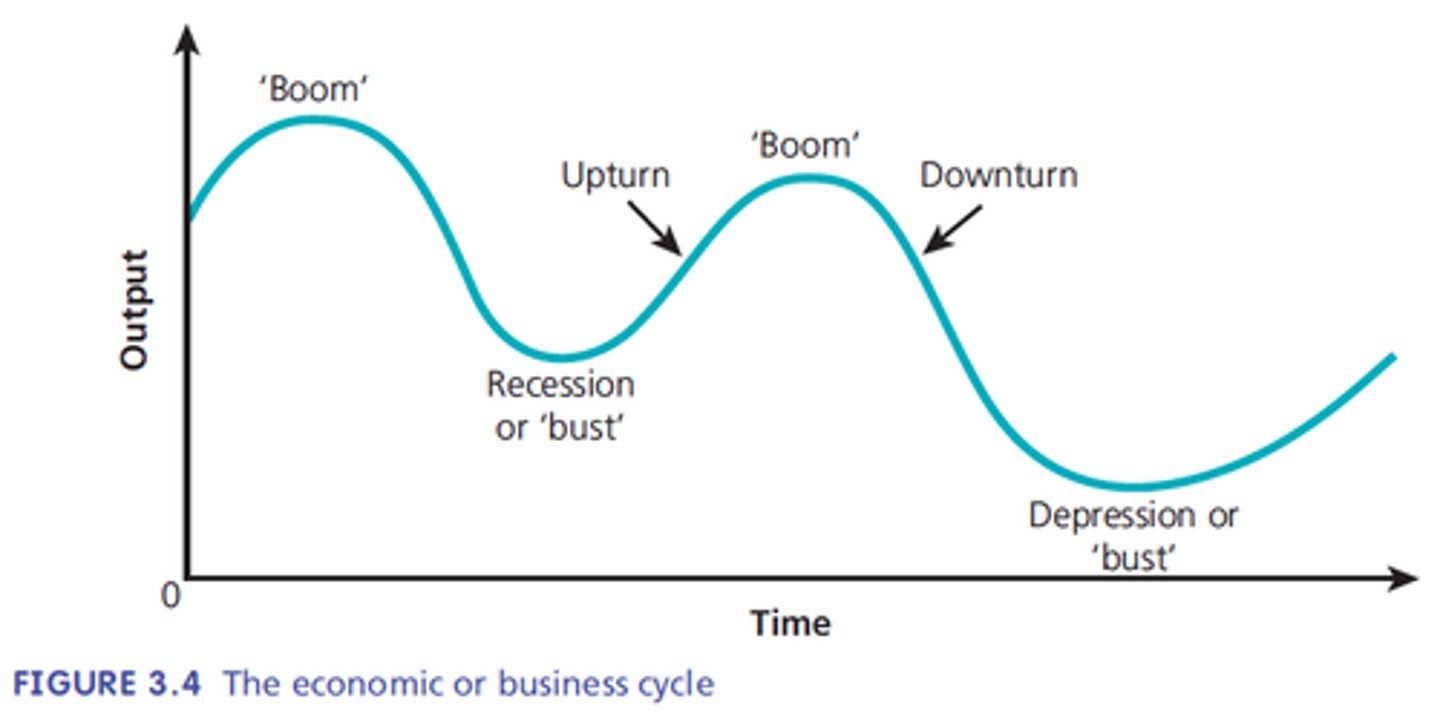
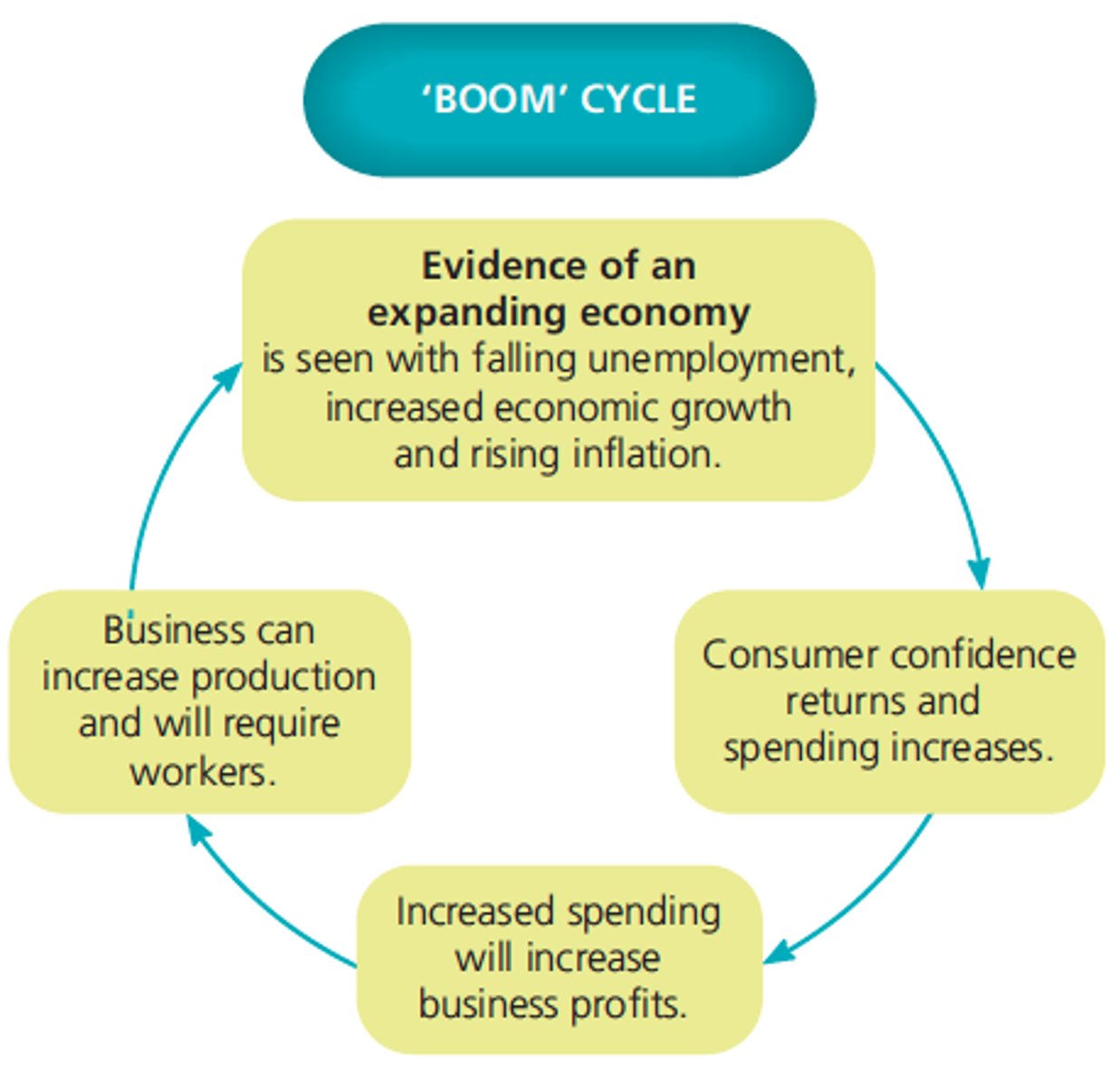
Characteristics of an expansion period
Higher levels of employment, wages increase, consumer spending increases, inflation may increase.
Eg Growth of China on Australian exports.
Characteristics of a contraction period
Unemployment levels rise, wages stagnant, level of spending decreases, inflation may remain stable or fall.
Eg Global financial crisis and the Covid19
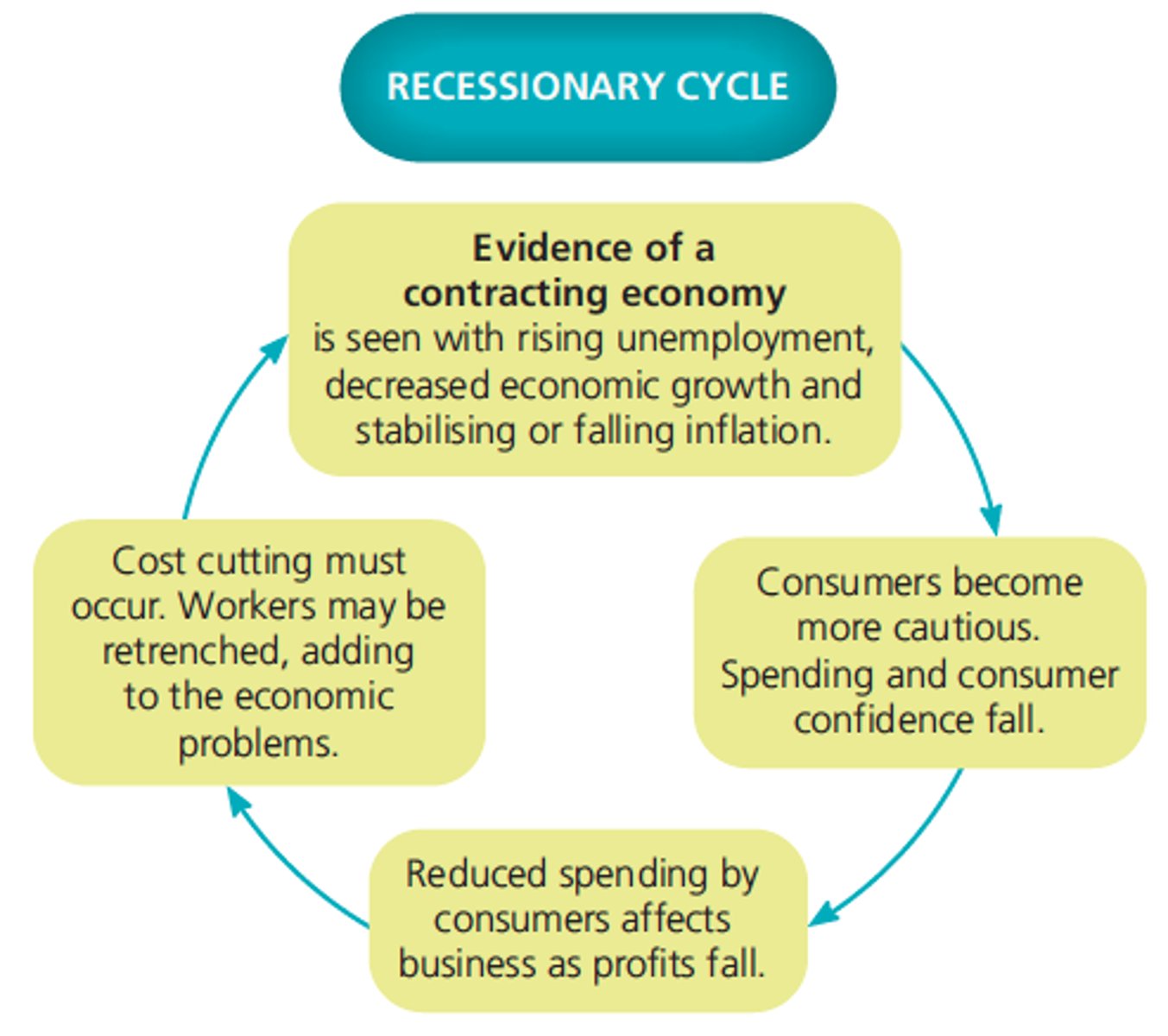
Discretionary income
Household spending after all necessities have been paid for. This type of spending falls during contractions and grows during expansions.
Eg. Travel, luxuries, restraurants.

Substitute discretionary spending
During contractions, households may forgo some goods and services and seek cheaper alternatives.
Eg renovations instead of full house builds, fast food instead of restaurants, new makeup instead of beauty therapists.
Financial Deregulation
Is the removal of government regulation from industry, with the aim of increasing efficiency and improving competition.
Eg Lowering tariffs, allowing non-bank lenders
Geographical influences
relate to Australia's location in Asia-Pacific region, Globalisation and Demographics.
Globalisation
The process where people, goods, money and ideas move around the world faster, in greater volume and more cheaply than before.

Demographics
Features of a population such as age, sex, income, cultural background and family.
Social Influences
Changes in society's organisation and preferences.
Eg environmental awareness, time-poor consumers, work-life balance.
Legal Influences
laws on taxation, industrial relations, occupational health and safety, equal employment opportunity, anti-discrimination and protection of the environment.
ACCC
Australian Competition and Consumer Commission - a government body that monitors prices set by sellers and promotes competition.
Political influences
Government policies have a considerable impact on the business environment.
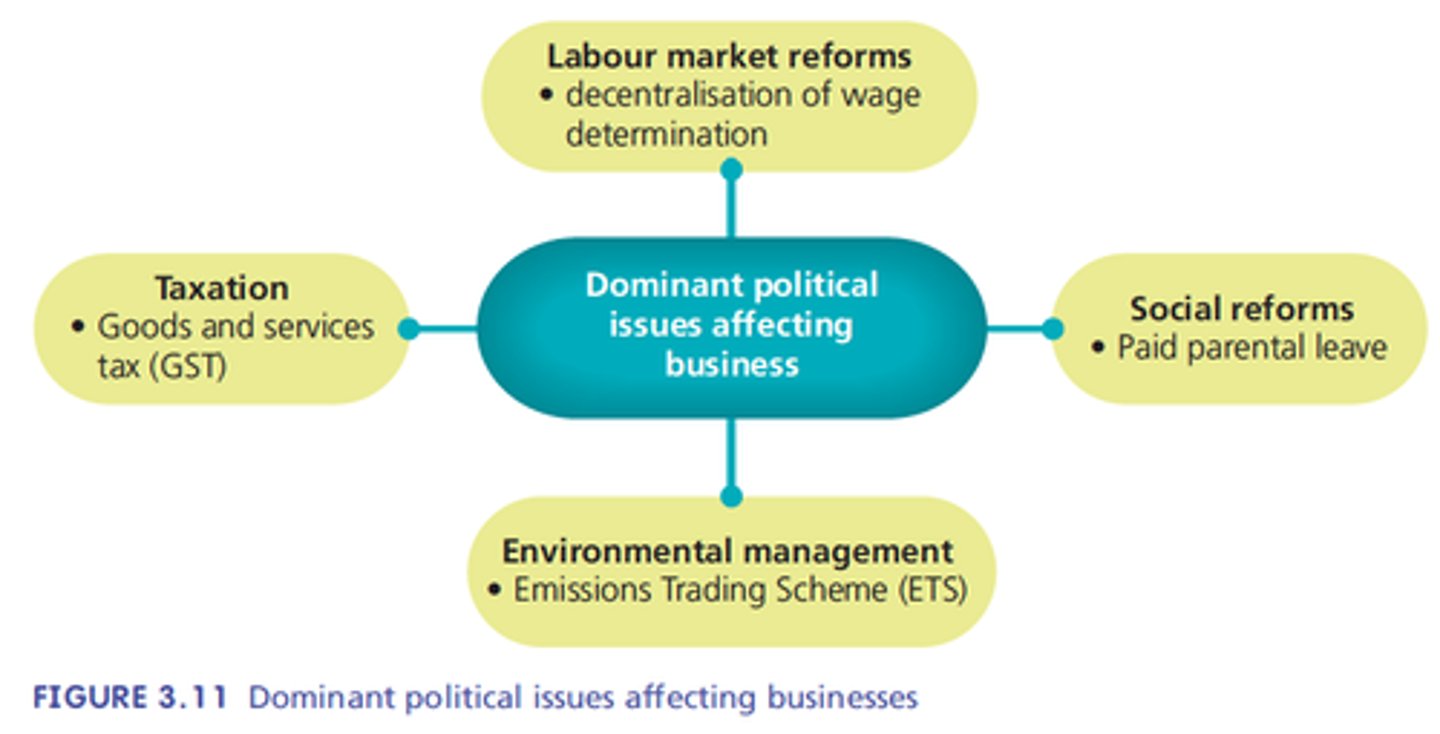
Institutional influences
Government, regulatory bodies and
other groups.
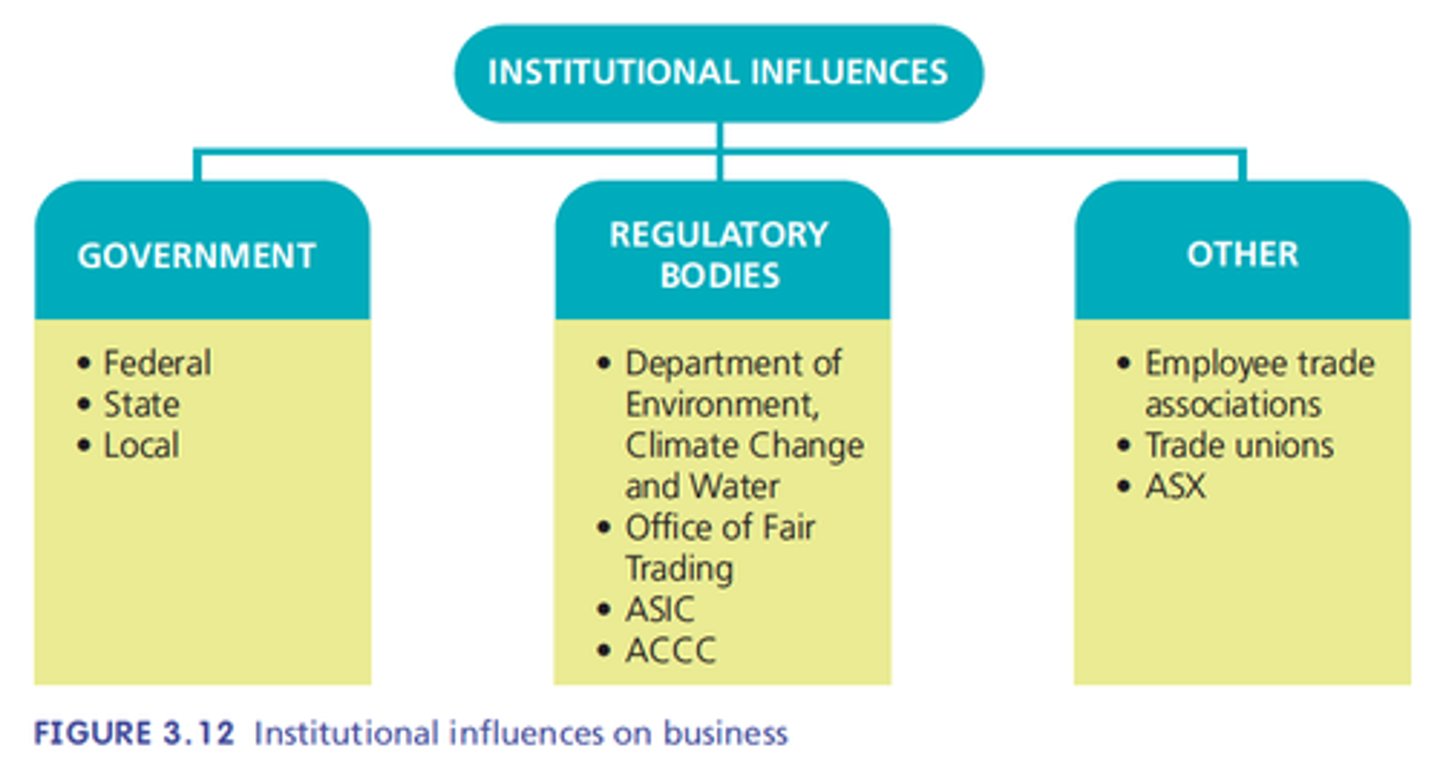
Regulations
Rules, laws or orders that businesses must follow.
Regulatory bodies
Fairwork Australia (Industrial relations)
The Australian Tax Office
Australian Securities and Investments Commission.
Australian Competition and Consumer Commission.
Levels of Government in Australia
Federal, state and local impose regulations.
Eg Taxes, employee entitlements, approve new developments.
ASIC
Australian Securities and Investments Commission. Regulates companies (public and private) and the Australian Stock Exchange.

Technological Influences
Increase in efficiency, productivity, innovation through new goods/services.
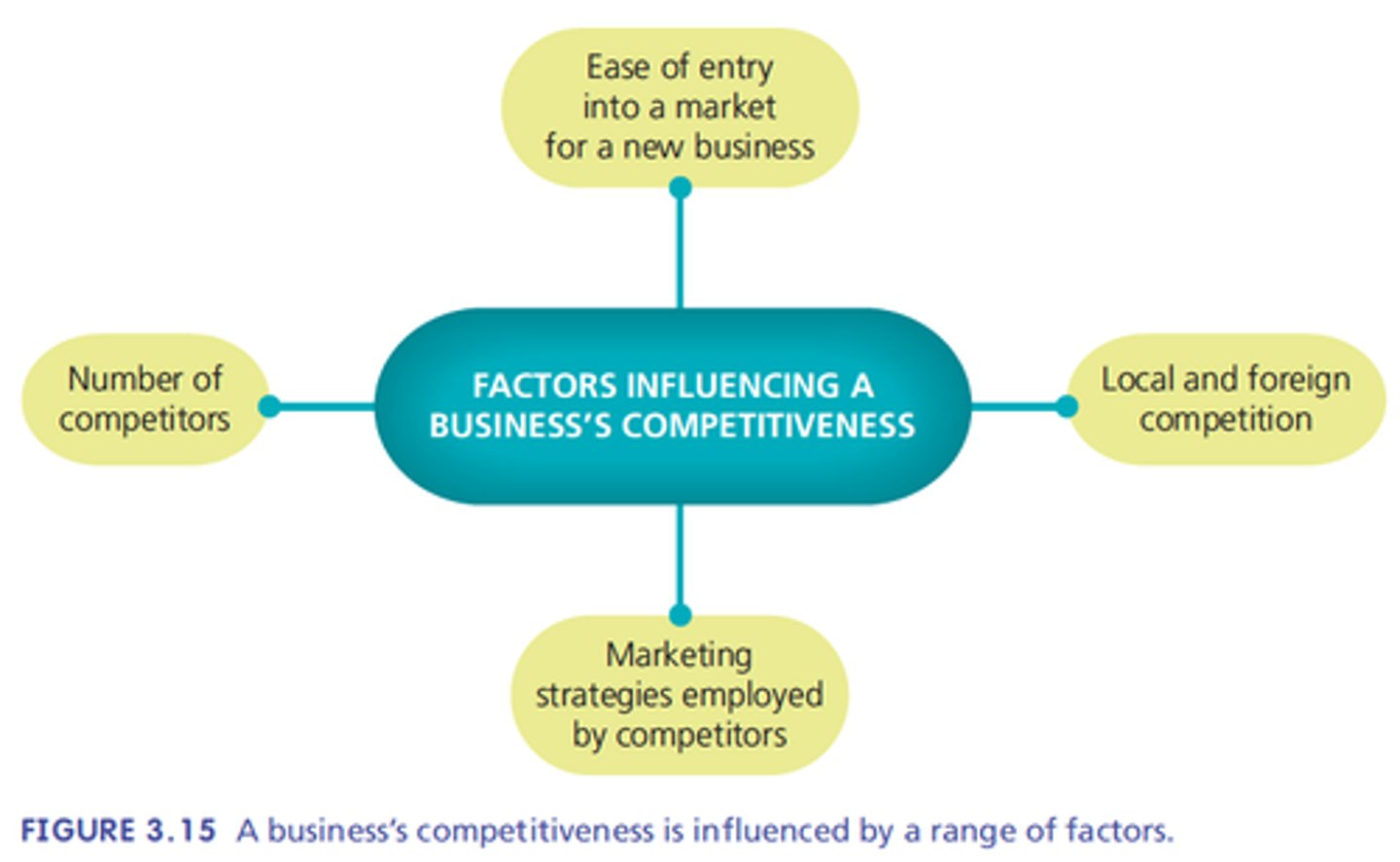
Competition
Number of competitors, Local and foreign Marketing, Ease of entry.
Internal influences
Things that can be controlled including the product, location, management, resources, business culture.
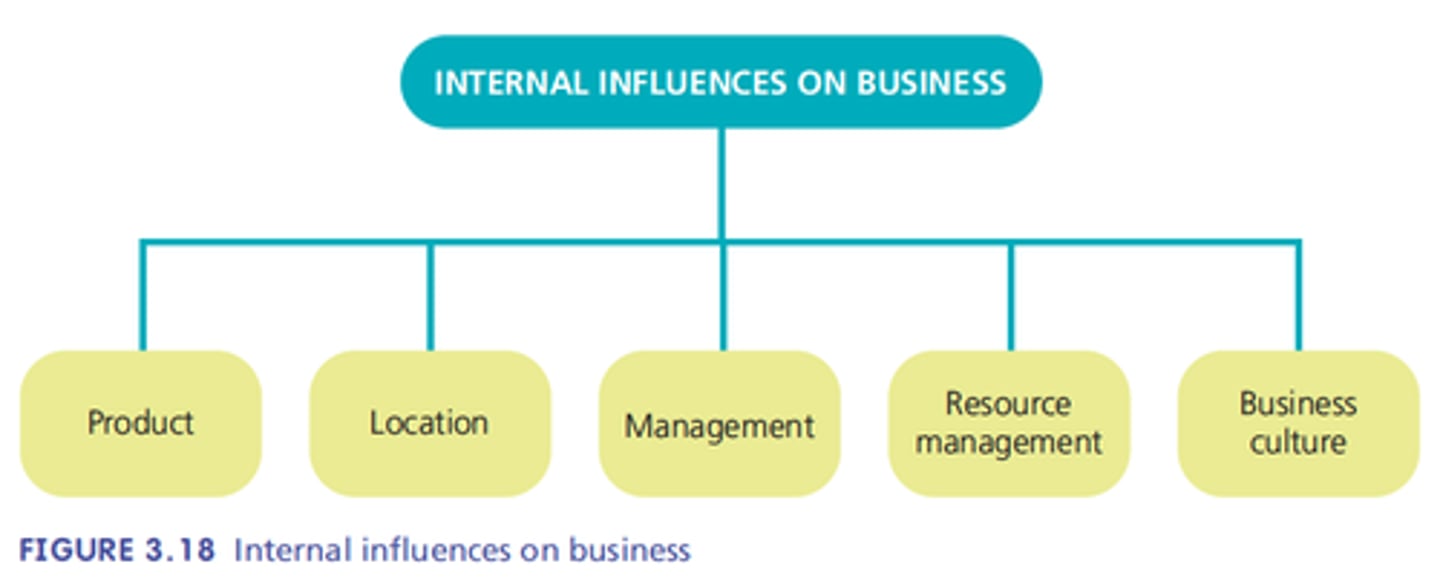
Product
Type and range of goods, services offered, packaging, branding. (Total product concept).

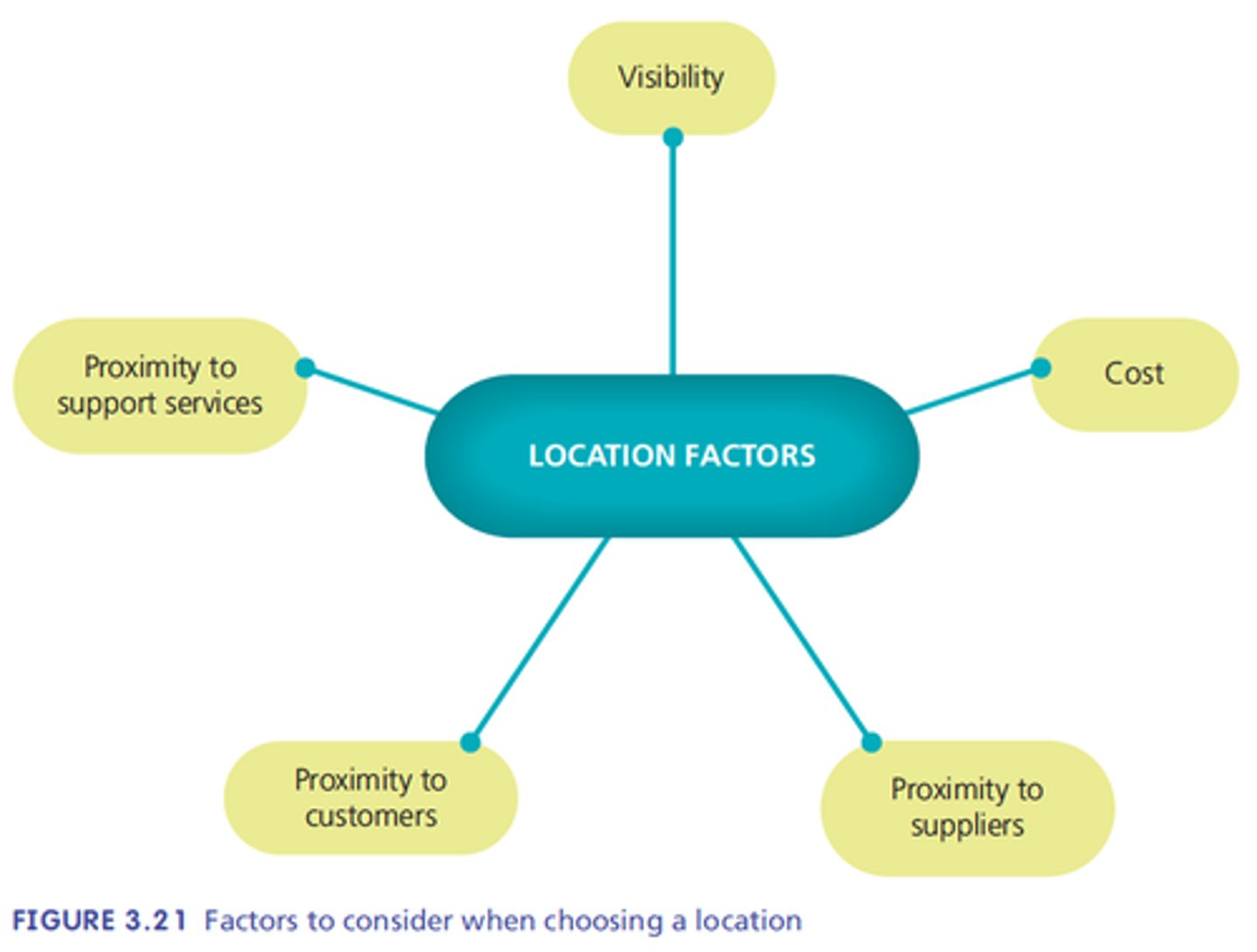
Location influence
Customer convenience, visibility, proximity to other businesses (suppliers, competitors), costs.
Resources
The things a business needs to produce goods and services - human resources, information resources, physical resources, financial resources.
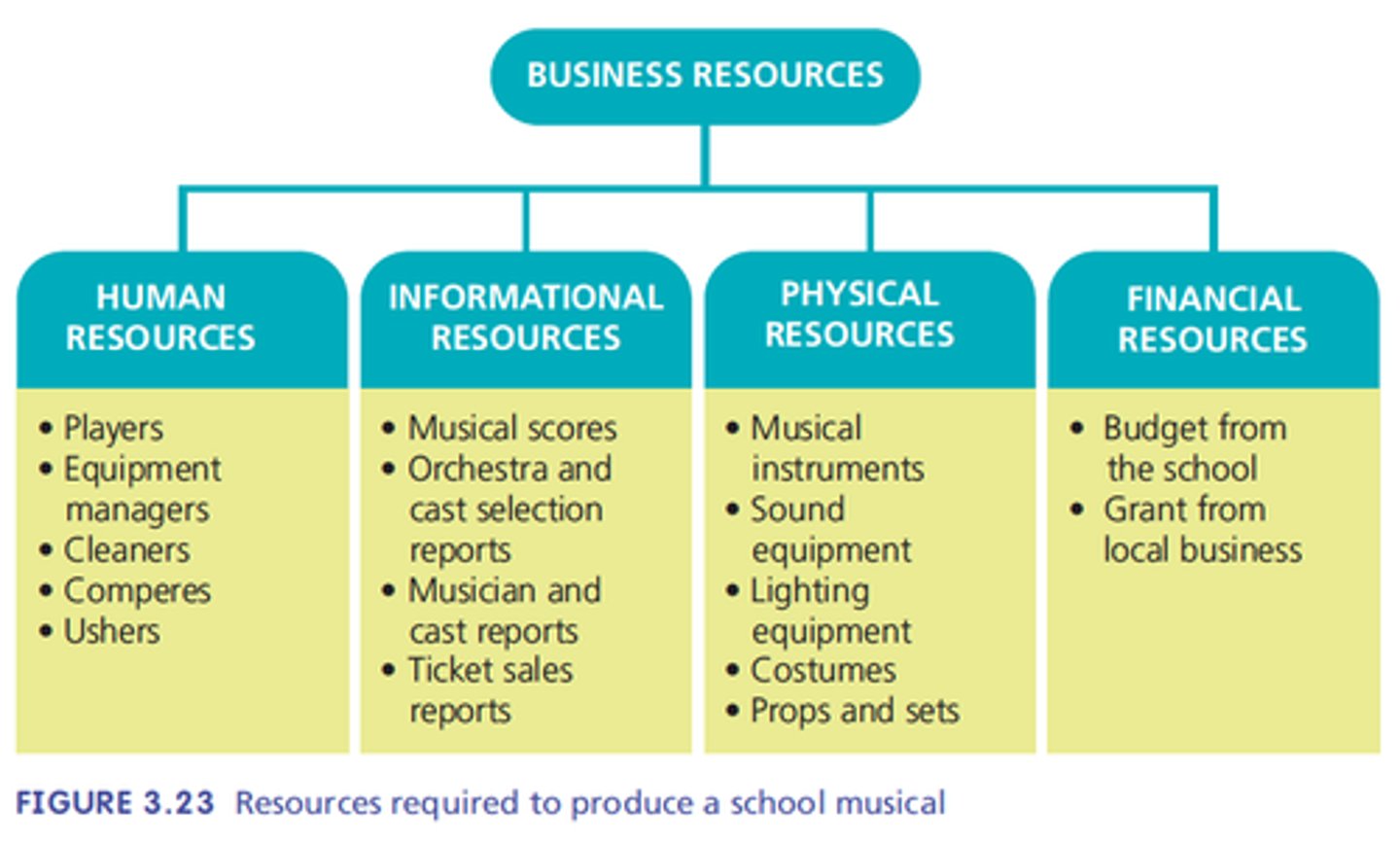
Human resources
the employees of the business and people who regularly supply services. Employed full time, part-time, casual or as contractors.
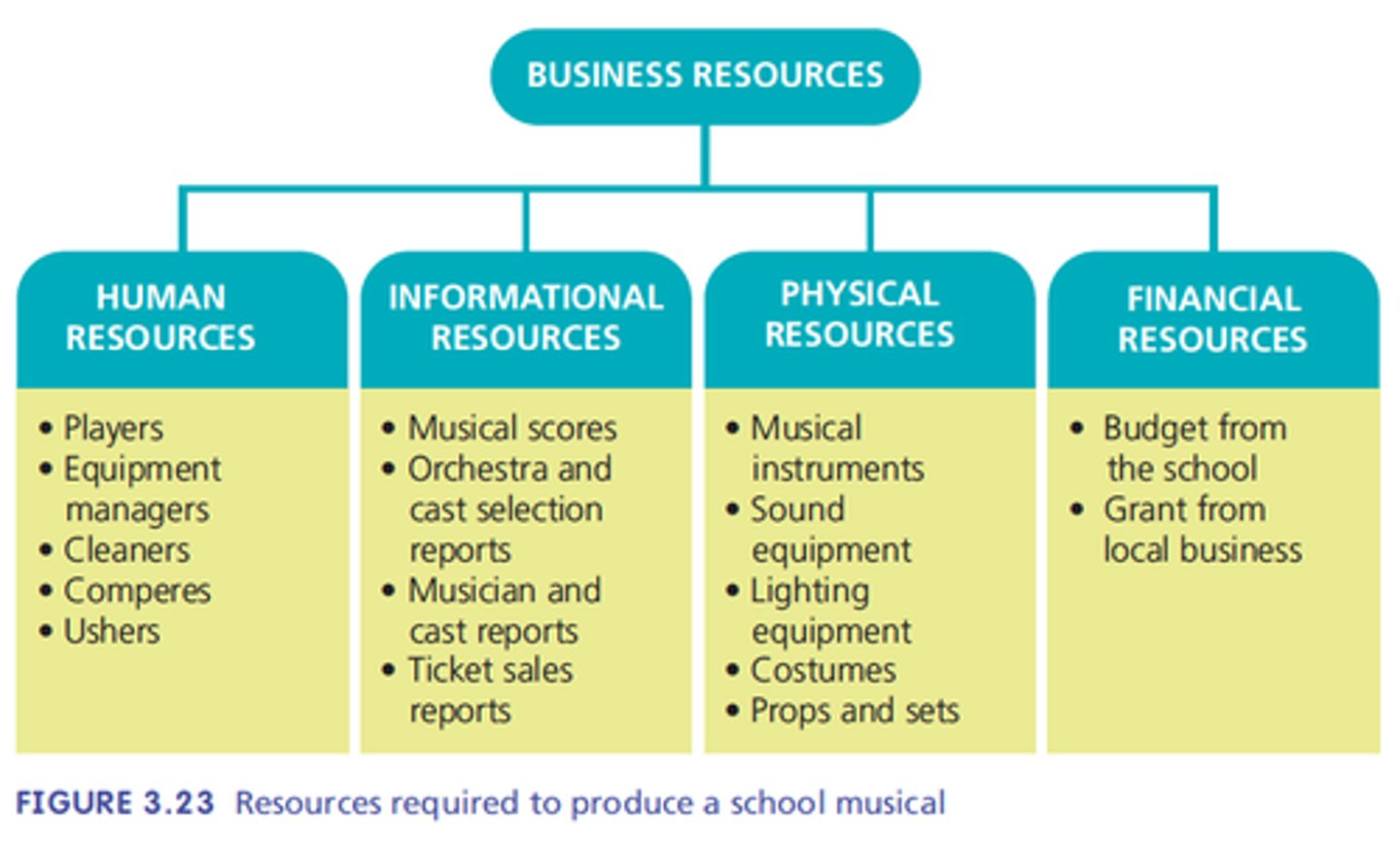
Information resources
The knowledge, expertise, ideas and data required by the business.
Eg market research, sales reports, economic forecasts, technical material, legal advice, processes.
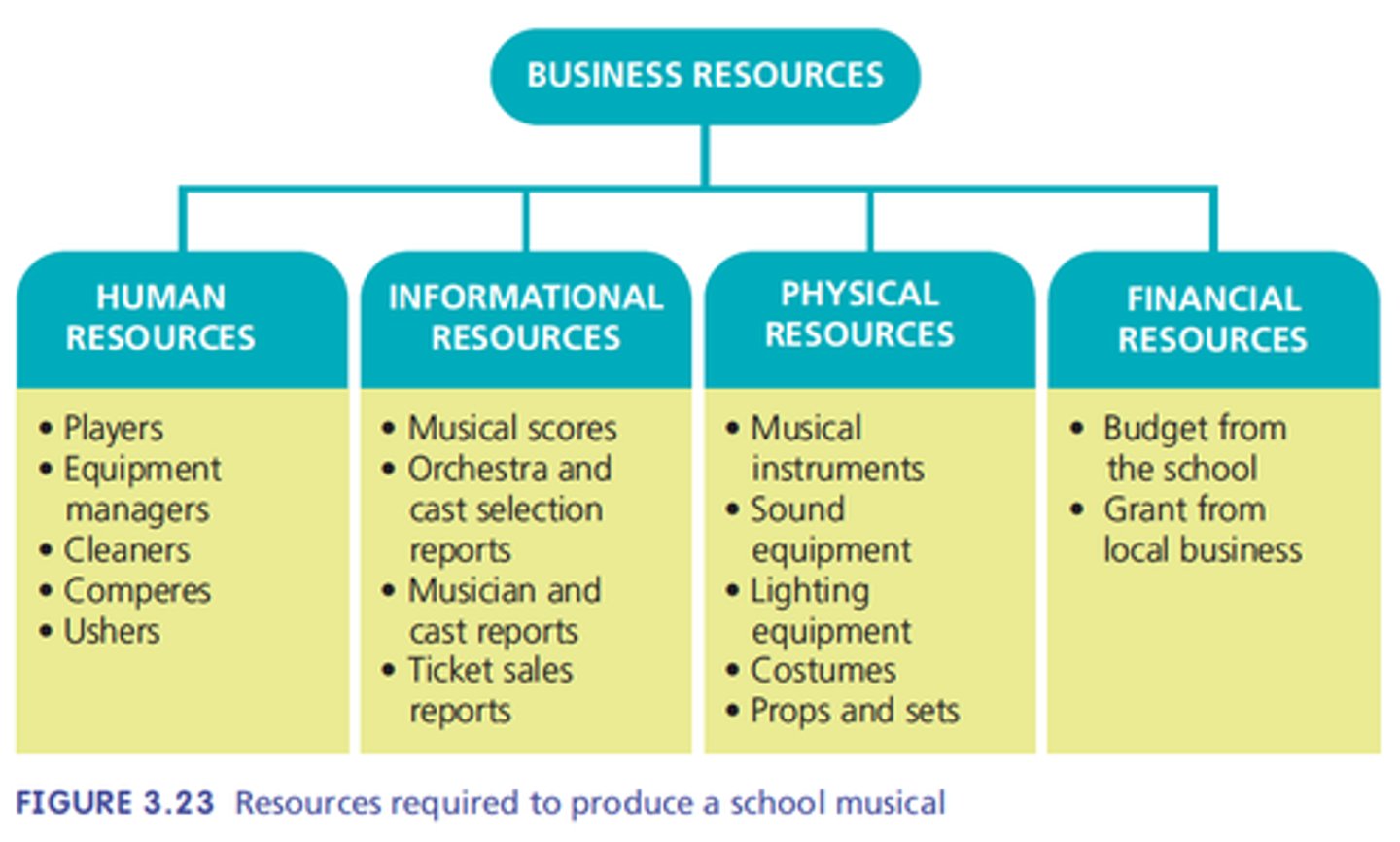
Physical resources
Include equipment, machinery, buildings and raw materials.
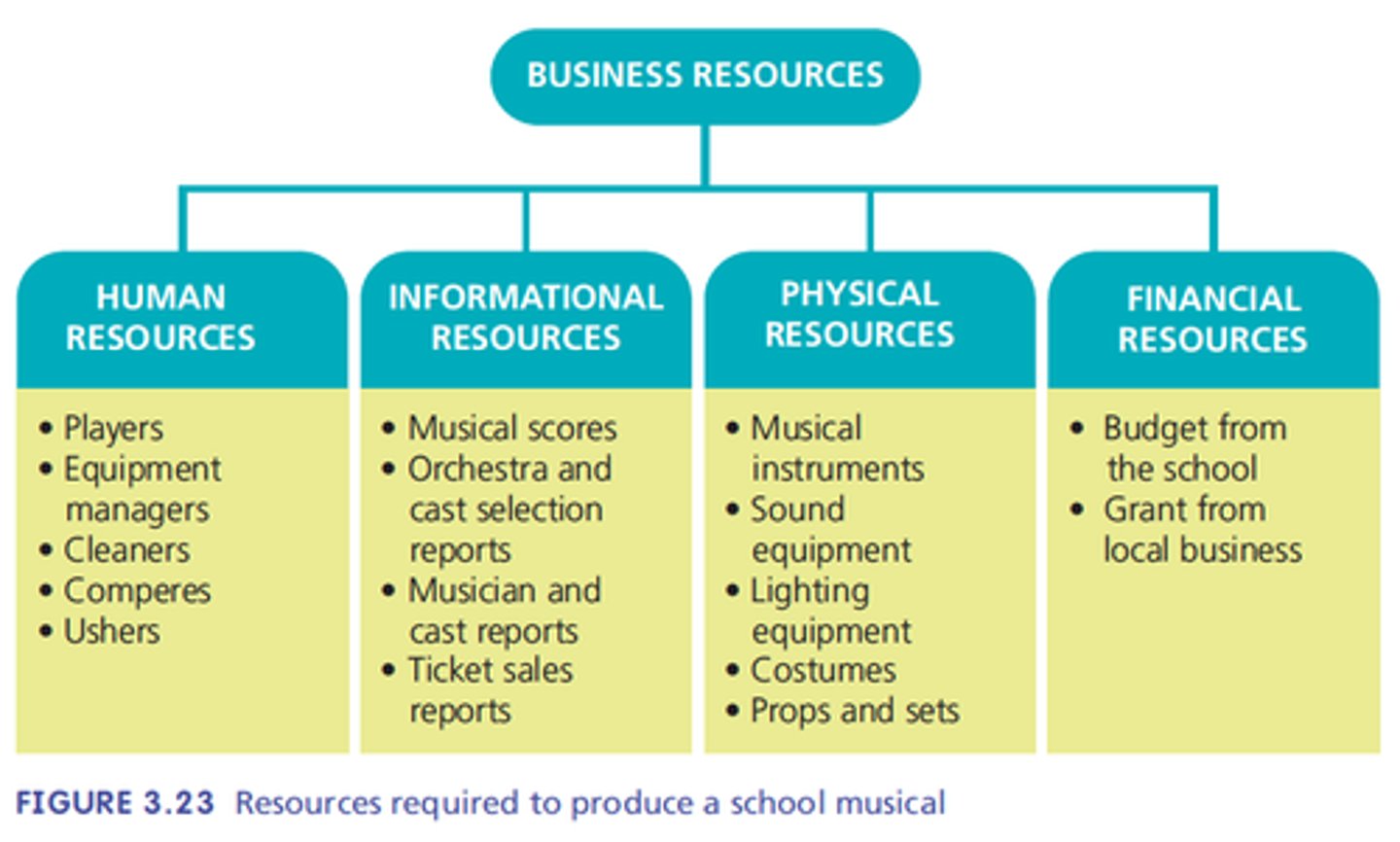
Financial resources
Funds the business uses to meet its obligations, including loans, lines of credit, owner's equity and retained profits.
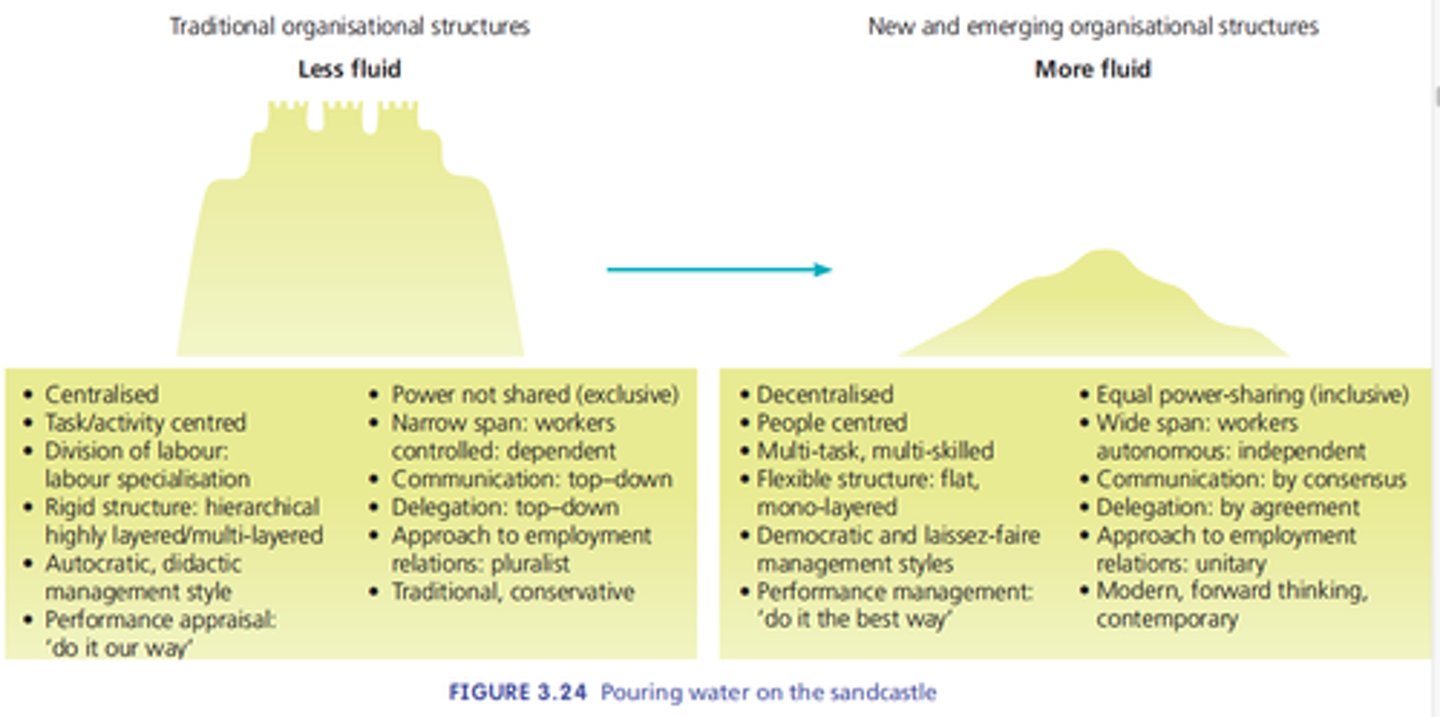
Management influences
Levels of business structure, employee autonomy and managerial styles.
Business Culture
Refers to the values, ideas, expectations, beliefs and modelled behaviour shared by members of the organisation.
Explicit business culture
The official policies, goals, slogans and stated expectations of how people in the business behave.
Implicit business culture
The way values, attitudes and behaviours are acted out in the day to day running of the organisation.
Monopoly market conditions
Complete concentration by one firm in the industry.
Eg Australia post
Eg Bunnings (to an extent)
Oligopoly market conditions
Consists of a small number of large firms.
Eg Banks
Oil companies
Car manufacturers
Phone manufacturers
Duopoly
An oligopoly with two businesses dominating the market.
Eg Supermarkets - Coles/Woolworths
Eg Casinos - Crown Melbourne/Star Sydney
Monopolistic Competition
A large number of buyers with similar but slightly different needs/wants being served by a large number of sellers with similar but not identical products.
Shoes and clothing manufacturers
Local retailing
Ease of entry
Ability of a person to establish a business within an industry. This depends on the market concentration.
SWOT analysis
Strengths, Weakness, opportunities, threats in the business environment.
Business life cycle
The stages of growth and development a business can experience
Establishment
This stage generally has the highest level of risk, low sales revenue, poor cash flow and lowest market share.
Growth
This stage is characterised by dramatic growth in sales and market share, positive cash flow and an increase in marketing.
Vertical integration
When a business expands at different but related levels of production and marketing of a product.
Backward vertical integration
A business integrates with one of its suppliers e.g. a bakery acquiring a wheat farm
Forward vertical integration
A business integrates with a firm it sells to e.g. a bakery merging with a supermarket chain
Horizontal integration
Occurs when a business acquires or merges with another firm that makes and sells similar products e.g. a bakery merging with another bakery
Diversification
When a business acquires or merges with a business in a completely unrelated industry e.g. a bakery merges with a shoe store.
Maturity
In this stage, sales and revenue slow, expenses need to be controlled, competition increases and the business tries to maintain customers through brand loyalty.
Post maturity
A stage that has 3 options - renewal, steady state or decline (possible cessation/ closure)
Cessation
Closure of a business - can be voluntary or involuntary
Voluntary cessation
Occurs when the owner closes the business of their own accord
Involuntary cessation
Occurs when the owner is forced to close the business by its creditors