U2
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
solutions
solute dissolved in solvent
indistinguishable (homogenous)
dissolved particles are too small to see
homogenous
uniform
well mixed
miscible
eg; NaCl in water
heterogenous
not uniform
not well mixed
immiscible
eg; choc chip cookie
aqueous
solid / liquid / gas dissolved in water
unsaturated
more solute can be dissolved in solution
saturated
no more solute can be dissolved at current temp + pressure
supersaturated
a solution containing more than the max solute that can be dissolved at given temp + pressure
this is done by increasing temp —> adding solute —> decreasing temp
suspensions
heterogenous mixture
solute not dissolved significantly in a solute
some particles settle over time + can be separated
eg; RBC’s in plasma
colloids
WEIRD LIQUIDS
mixture of particles consisting of smaller clusters of ions + molecules
evenly dispersed throughout the solvent + don’t settle over time
eg; mayo, ink, milk
dissolution
solute + solvent particles attract each other strongly enough to overcome the forces holding their own particles together
this allows the solute to disperse throughout the solvent
solubility formula
m (solute in grams)
—————————
100g water
most solids increase solubility as temp increases
most gases decrease solubility as temp increases
solubility of a substance can be graphed on a solubility curve
electrolyte
solution formed when solute dissolves to form ions
strong electrolyte
all of the solute dissolves to form ions
ionic compounds fully dissociate to form strong electrolytes
strong acids fully ionise to form strong electrolytes
weak electrolyte
some of the solute dissolves to form molecules - no ions formed
weak acids partially ionise to form weak electrolytes
like dissolves like
polar solvents dissolves polar molecules
non-polar solvents dissolves non-polar molecules
precipitation reactions
occurs between cations + anions in aqueous solutions
combine to form an insoluble ionic solid (precipitate)
eg; potassium carbonate + copper (II) nitrate
full: K2CO3(aq) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) —> 2KNO3(aq) + CuCO3(s)
ionic: CO3-2(aq) + Cu2+(aq) —> CuCO3(s)
observations: a colourless and blue solution is mixed together + a green precipitate if formed
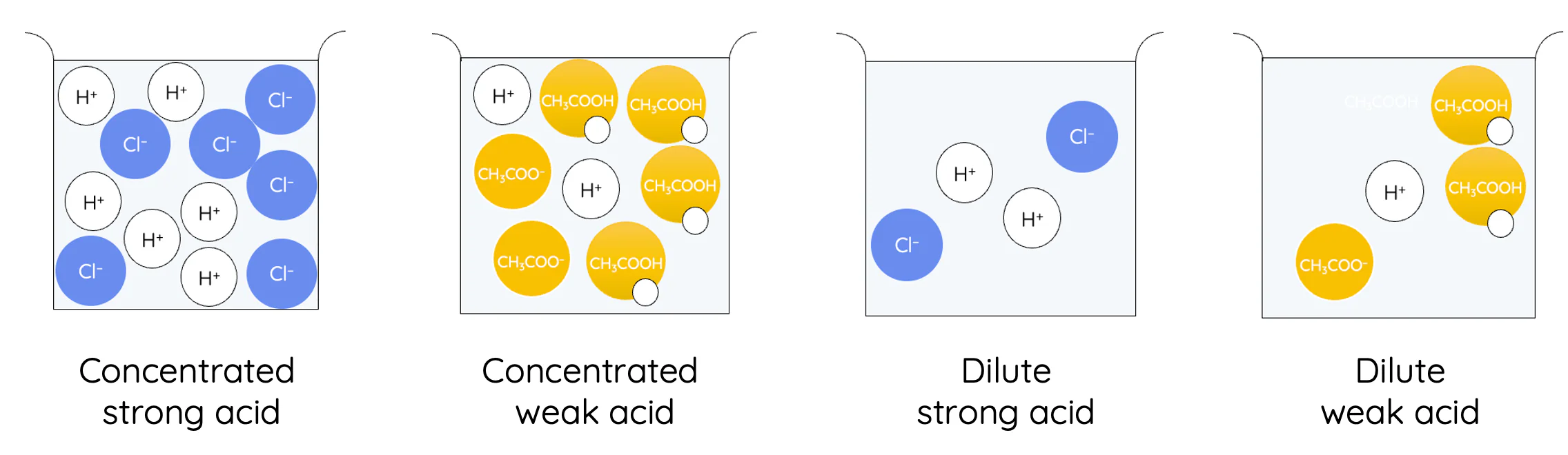
concentration
amount of solute + solvent present in solution
n = c v
moles of solute = conc.(mol / L) x volume (L)
C1V1 = C2V2
initial = dilute
properties of acids
turns litmus paper red
corrosive
sour
solutions have pH <7
solutions conduct electrical current
properties of bases
turns litmus paper blue
slippery
bitter
solutions have pH >7
solutions conduct electrical current
strong acids
completely ionises in water
HCl, HNO3, H2SO4
weak acids
only partially ionises in water
CH3COOH, H2CO3, H3PO4
bases
only partially ionises in water
NH3, metal hydroxides, metal oxides
acid reactions
Acid + Metal —> Salt + Hydrogen Gas
Acid + Metal Oxide —> Salt + Water
Acid + Metal Hydroxide —> Salt + Water
Acid + Metal Carbonate—> Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide
Acid + Metal Hydrogen Carbonate—> Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide
Acid + Metal Sulphite —> Salt + Water + Sulphur Dioxide
Base + Ammonium Salt —> Salt + Water + Ammonia
Base + Non-Metal Oxide —> Salt + Water
Arrhenius theory
acids produce H+ ions when they dissolve in water
bases produce OH- ions when they dissolve in water
doesn’t account for all acid-base behaviour
eg; why can HCO3- ions act as an acid + a base?
can only be used when talking about aqueous solutions
Bronsted-lowry theory
acids will donate protons (H+ ions)
bases will accept protons (H+ ions)
beaker
conjugate acids + bases
once a base has accepted a proton, it has the potential to donate the proton (act as a base)
once an acid has donated a proton it has the ability to gain it back (act like a base)
indicators
acid and base react with indicators
changes their colours
allows the pH of the solution to be determined
litmus paper: red = acidic blue = basic
universal indicator: changes colour over the whole pH scale
pH
describes the conc of H+ ions in solutions
pH = -log [H+]
[H+] = 10-pH
0 = acidic
7 = neutral
14 = basic
monoprotic acids
can make 1H+ per molecule
polyprotic acids
can make 2 or more H+ per molecule
electronegativity (EN)
ability to attract a bonding pair of electrons to form a covalent bond
increases left—> right
higher nuclear charge
increases down —> up
less electron shells
polar
uneven distribution of charge
all ionic compounds are polar
for covalent molecules, the polarity is determined by the shape + direction of polar bonds (if present)
polar bonds
2 different elements are sharing electrons with different EN (ability to attract / bond with electrons)
2 of the same elements are non-polar since they have the same EN
big dipole movement
very different EN
small dipole movement
very similar EN
VSEPR theory
the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory
valence electrons repel each other
they will spread apart as much as possible to minimise the repulsion between them.
linear
1 or 2 bonds
no lone pairs
180 degrees
non - polar: both of the atoms coming off the central atom are the same element (equal charges in opposite directions cancel each other out
eg; CO2
polar: not all the same element
bent
2 bonds
1 or 2 lone pairs
v shaped
polar: not all the same element
trigonal planar
3 bonds
no lone pairs
120 degrees
non-polar: all atoms coming off the central atom are the same
eg; BF3
polar: not all the same element
pyramidal
3 bonds
1 lone pair
polar: not all the same element
tetrahedral
4 bonds
no lone pairs
105.5 degrees
non-polar: all atoms coming off central atom are the same
eg; CH4
polar: not all the same element
shape of molecules can determine physical properties of covalent molecular substances, such as:
vapour pressure
melting point
boiling point
solubility
shape of molecules determines…
…how it will interact with other molecules
lone pairs
electrons around central atom that are not involved in bonding
head to tail
draw dipoles with head touching tail
if its a closed shape it is non-polar since charges cancel out
if it is an open shape is is polar since charges do not cancel out
IMF’s
electrostatic force
between the (+) and (-) charges in the molecules as a result of uneven distribution of electrons
increase EN = more likely an atom in a molecule will attract electrons towards it and away from atom with lower EN
polar diatomic molecules
2 different elements with different EN in a covalent bond are polar
electrons will stay closer to the most EN atom as it has the stronger pull on electrons.
non-polar diatomic molecules
2 of the same atoms with same EN in a covalent bond are non-polar
electrons are shared equally
no charge on either end of the molecule.
polar polyatomic molecules
Molecules made up of more than two atoms
Asymmetrical molecules are polar
non-polar polyatomic molecules
Molecules made up of more than two atoms
Symmetrical molecules are non-polar
3 types of IMF forces
dispersion forces
dipole-dipole
hydrogen bonding
dispersion forces
all molecules
electrons are constantly moving
at any given time there will be more on one side of the molecule than the other
causes a temporary dipole
increase dispersion forces —> increase size of molecule
more electrons = more temporary dipoles
dispersion forces is the weakest IMF
dipole-dipole
polar molecules
dipole on one molecule is attracted to the oppositely charged dipole on neighbouring molecule
stronger than dispersion forces as dipole is not temporary
hydrogen bonding
a H bonded to a N,O or F (most EN elements)
lone pairs on the N,O or F
attraction between the (+)H and lone pair of electrons
strongest IMF