AP BIO Unit 1: College Board Videos
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Covalent Bond
The bond type in which atoms share electrons
Polarity
-When there are differences in atomic electronegativities
-Since oxygen is more electronegative compared to hydrogen, there is an unequal sharing of electrons between oxygen and hydrogen
Hydrogen bond
A weak bond interaction between the negative and positive regions of two separate molecules.
Cohesion
When two of the same molecules for hydrogen bonds with each other.
Adhesion
When two different molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other
Surface tension
Results from increased hydrogen bonding forces between water molecules at the surface
-Example: water droplet on a penny
Properties of water
-Adhesive property gives water a high solvency ability in it’s liquid state
-Cohesive property causes water to be less dense as a solid(ice) compared to as a liquid (explains why ice is able to float).
-High heat capacity
Caplillary action
The movement of water within the spaces of a porous material as a result of both the adhesive and cohesive properties of water
The law of the conservation of energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed only transformed
What molecules require carbon?
-Carbohydrates
-Proteins
-Nucleic acids
-Lipids
What molecules require nitrogen?
-Proteins
-Nucleic acids
What molecules require phosphorus?
Nucleic acids and certain lipids
Monomers
Chemical subunits used to create polymers
Polymer
A Macromolecule made of many monomers
Dehydration Synthesis reaction
-The subcomponents of a water molecule (H and OH) are removed from interacting monomers and a covalent bond forms between them.
-Used to create macromolecules
-The H and OH join together to for a molecule of water, water is a byproduct of this reaction
Hydrolysis reaction
-Polymers are hydrolyzed (broken down) into monomers
-Covalent bonds between the monomers are cleaved (broken)
-A water molecule s hydrolyzed into subcomponents (H and OH) and each subcomponent is added to a different monomer.
Nucleic acids
Polymers comprised of monomers called nucleotides
Nucleotides basic structure
-5-carbon sugar
-Phosphate group
-Nitrogen base
Amino Acids
Monomers that make up proteins
Directionality with an amino (NH2) terminus and a carboxyl (COOH) terminus
Polypeptide
-The primary structure of a protein
-Consists of a specific order of amino acids and determines the overall shape the protein can achieve
R group
-The atoms attached to the central carbon
-Can be hydrophobic, hydrophilic, or ionic
Lipids
Nonpolar macromolecules that do not have true monomers but are comprised of subunits such as fatty acids and glycerol
Phospholipid
-Contain hydrophilic(polar head)and hydrophobic(non polar tail) regions that determine their interactions with other molecules
Directionality of nucleic acids
3’ hydroxyl and 5’ phosphate of the sugar in the nucleotide
Direction of DNA strands
Antiparalleel 5’-3’ direction
Where can nucleotides be added during the synthesis of nucleic acid polymers
The 3’ end
Primary Structure of a Protein
Determined by the sequence of amino acids held together by covalent bonds, called peptide bonds
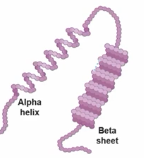
Secondary Structure of a Protein
Arises through local folding of the amino acid chain into elements such as alpha-helices and beta-sheets.
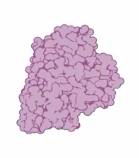
Tertiary Structure of a Protein
-The overall 3D shape of the protein and often minimizes free energy; -Various types of bonds and interactions stabilize the protein at this level.
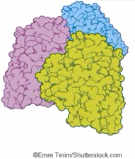
Quaternary structure of a Protein
Arises from the interactions between multiple polypeptide units.