EXPERIMENT 4: Properties of Carbohydrates (Part 1)
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Cn(H2O)n
General molecular formula for carbohydrates:
Carbohydrates
Were once considered hydrates of carbon
Carbohydrates
Cn(H2O)n
hydrates of carbon
Carbohydrates were once considered what?
inaccurate
Examination of the structures of carbohydrates readily reveals that this view is (accurate/inaccurate), but use of the term persists.
monosaccharides
Simplest carbohydrates
polyhydroxy aldehydes
polyhydroxy ketones
The simplest carbohydrates are monosaccharides, which can either be?
polyhydroxy aldehydes
Have the general structure A
polyhydroxy aldehydes
Are referred to as aldoses
polyhydroxy ketones
Have the general structure B
polyhydroxy ketones
Referred to as ketoses
A; aldoses
Polyhydroxy aldehydes, which have the general structure ___ and are referred to as ____
B; ketoses
Polyhydroxy ketones, which have the general structure ___ and referred to as ____.
3-6 carbons
A monosaccharide usually consists of how many carbons?
monosaccharide
Usually consists of 3-6 carbons
number of carbons
The _______ in a monosaccharide can also be used as a way classifying them, specifically trioses (3C), tetroses (4C), pentoses (5C), and hexoses (6C).
trioses
3C
tetroses
4C
pentoses
5C
hexoses
6C
ribose, glucose, and fructose
Examples of monosaccharides:
monosaccharides
Ribose, glucose, and fructose are?
cyclic form
In solution, most monosaccharides exist in what form?
aldehyde or ketone group
In solution, most monosaccharides exist in a cyclic form - the _______ reacts with one of the -OH groups on the other end of the same molecule to form a cyclic hemiacetal.
-OH groups
In solution, most monosaccharides exist in a cyclic form - the aldehyde or ketone group reacts with one of the ____ on the other end of the same molecule to form a cyclic hemiacetal.
cyclic hemiacetal
In solution, most monosaccharides exist in a cyclic form - the aldehyde or ketone group reacts with one of the -OH groups on the other end of the same molecule to form a _____.
a-D-glucose and B-D-glucose
Two possibilities of D-glucose (Different anomers of glucose):
a-D-glucose
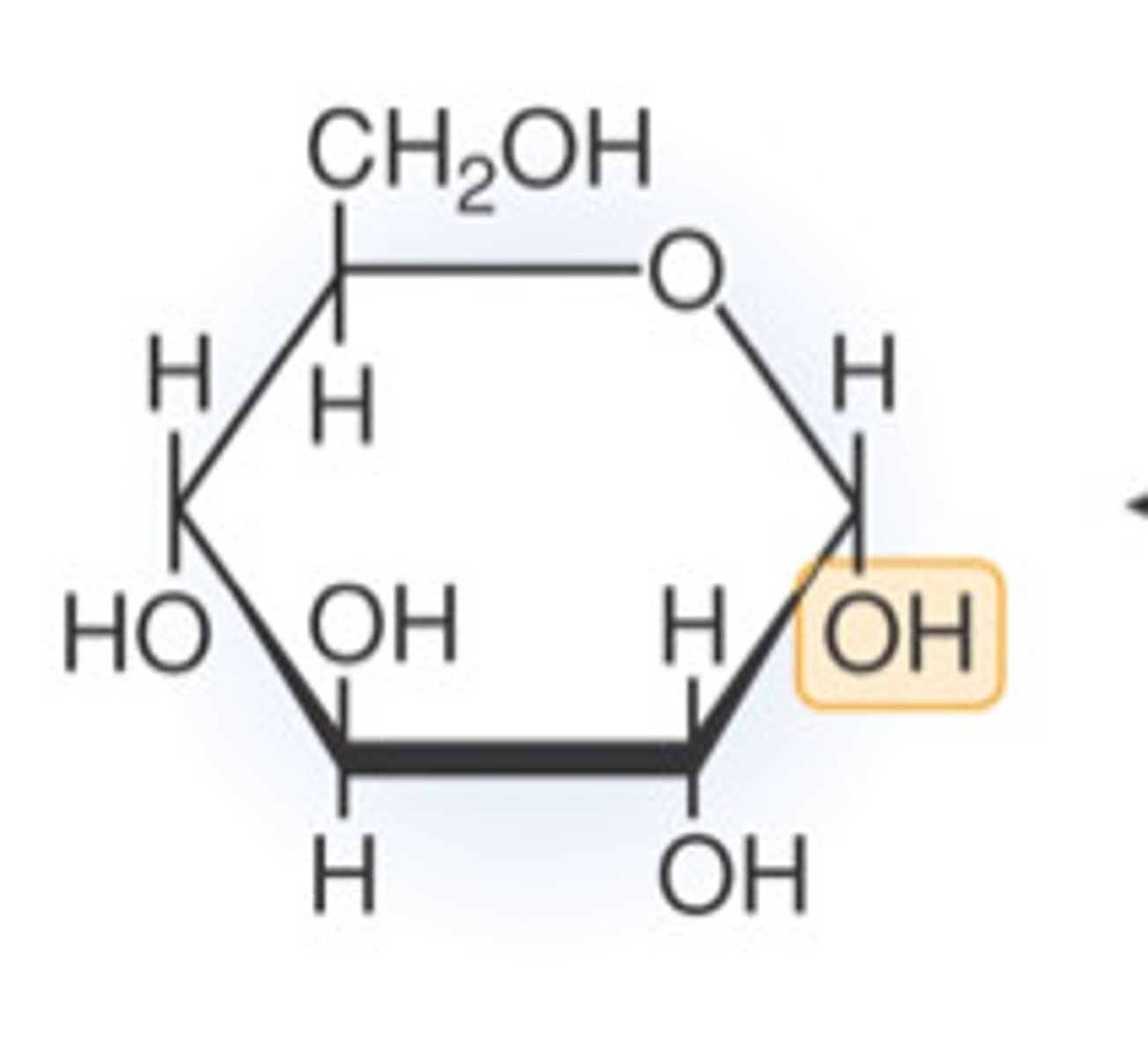
B-D-glucose
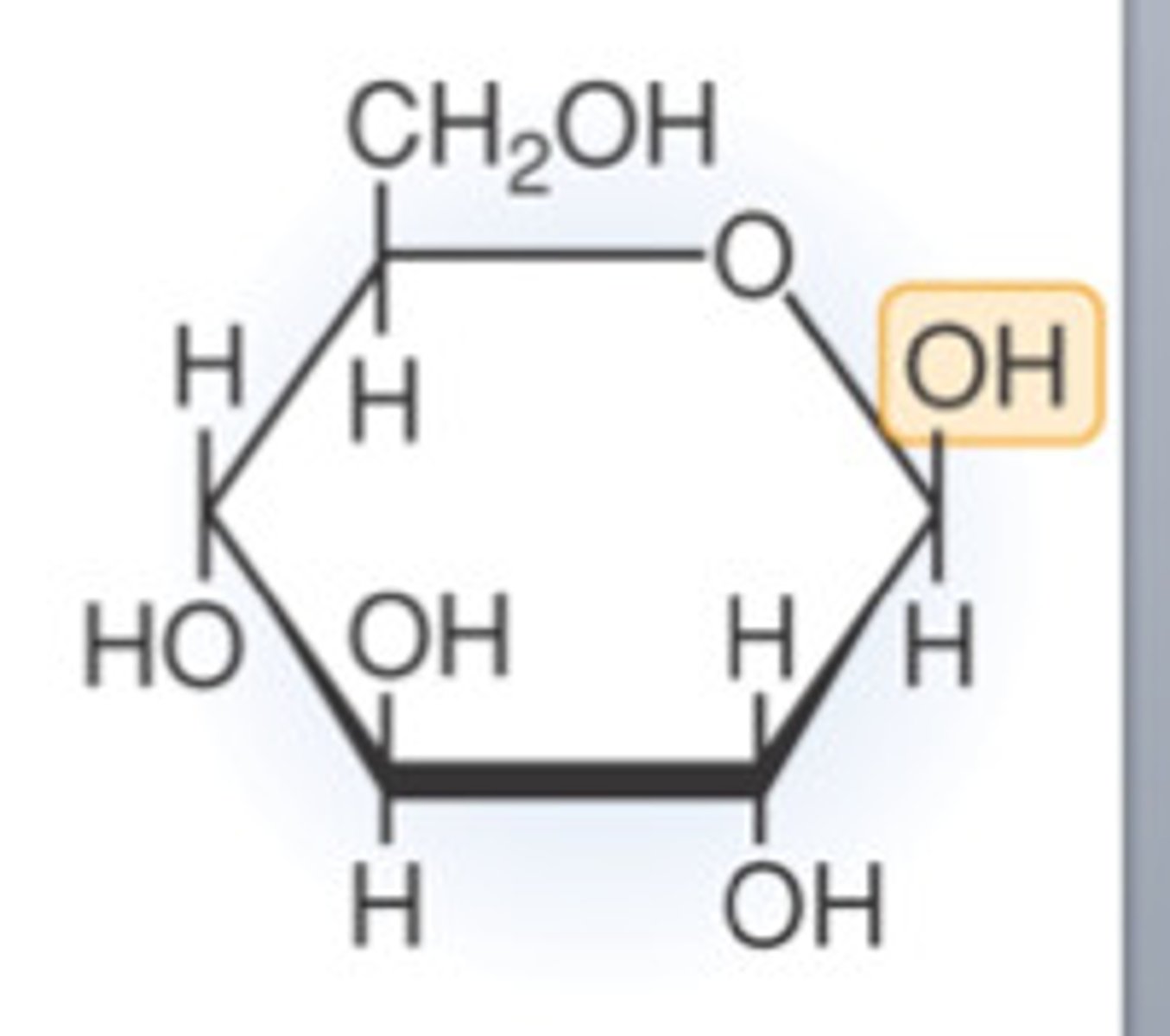
different anomers of glucose
a-D-glucose and B-D-glucose are called the?
cyclic form; open chain or free aldehyde form
In solution, there is equilibrium between the ____ and the _____.
inter-converted
The rings are constantly opening and closing again. In this way, the a and ẞ forms can be ____.
Two monosaccharides; loss of one molecule of water
______ may be combined with the ______ to form a disaccharide.
disaccharide
Two monosaccharides combined with the loss of one molecule of water
glycosidic bond
The bond that connects 2 monosaccharide units in a disaccharide is known as?
2 monosaccharide units
The glycosidic bond connects how many monosaccharide units in a disaccharide?
sucrose and lactose
Examples of disaccharides:
Sucrose
table dugar
Lactose
milk sugar
disaccharides
Sucrose and lactose are examples of?
polysaccharide
Consists of many monosaccharides linked together.
Starch, pectin, glycogen, and cellulose
Examples of polysaccharides:
polysaccharides
Starch, pectin, glycogen, and cellulose are examples of what?
Molisch's Test
Qualitative detection of carbohydrates in solution is usually done in the laboratory using the _______.
Molisch's Test
Is a qualitative detection of carbohhydrates
Molisch's Test
Is named after Czech-Austrian botanist Hans Molisch.
Hans Molisch
Molisch's Test is named after Czech-Austrian botanist _____.
Molisch's reagent; concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
Molisch's test involves the addition of _____ to the analyte and the subsequent addition of a few drops of ____ to the mixture.
analyte; mixture
Molisch's test involves the addition of Molisch's reagent to the _____ and the subsequent addition of a few drops of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) to the ____.
formation of purple or purplish-red ring
This confirms the presence of carbohydrates in the analyte
tetroses and trioses
A positive reaction for Molisch's test is given by almost all carbohydrates; exceptions include?.
Molisch's Test
General test for the presence of carbohydrates:
Benedict's Test
Picric Test
Moore's Test
Tests for Reducing Sugar:
Benedict's Test
Picric Test
Moore's Test
Barfoed's Test for Monosaccharides
Seliwanoff's Test for Ketoses
Bial's Test for Pentoses
Iodine Test for Polysaccharides
Classification Tests for Carbohydrates:
reducing sugar
Is a carbohydrate that is oxidized by a weak oxidizing agent in basic aqueous solutions.
non-reducing sugar
A sugar which cannot serve as a reducing agent and is not oxidized.
True
Ali aldoses are the true reducing sugars. (True or False)
aldehyde functional group
All aldoses are the true reducing sugars because they contain the _____.
Ketoses
_____ do not contain aldehyde (they contain ketone); however, as you will later find out, they also show reducing properties
ketone
Ketoses do not contain aldehyde (they contain _____); however, as you will later find out, they also show reducing properties
False
Ketoses contains aldehydes (True or False)
Yes
Do ketoses show reducing properties, yes or no?
keto-enol tautomerization
Ketoses also show reducing properties because ketoses, when in basic aqueous solutions, undergo _____ converting them to mixture of aldoses.
basic
Ketoses also show reducing properties because ketoses, when in (acidic/neutral/basic) aqueous solutions, undergo keto-enol tautomerization converting them to mixture of aldoses.
mixture of aldoses
Ketoses also show reducing properties because ketoses, when in basic aqueous solutions, undergo keto-enol tautomerization converting them to _____.
True
All monosaccharides are reducing sugars. (True or False)
free anomeric carbon
The only disaccharides that are reducing are those that contain ______ because a ______ has the capacity to open and expose the aldehyde group.
free anomeric carbon
Has the capacity to open and expose the aldehyde group.
True
All polysaccharides are non-reducing. (True or False)
Benedict's reagent
Fehling's reagent
Tollen's reagent
Nylander's reagent
picric acid with sodium carbonate solution
There are several weak oxidizing agents that can be used to determine whether a carbohydrate is reducing or not, such as:
They are all in basic conditions (pH > 7).
Benedict's reagent Fehling's reagent Tollen's reagent, Nylander's reagent, and picric acid with sodium carbonate solution.
What is common to all these reagents?
a-naphthol in Ethanol 99% and concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
Molisch’s reagent:
Copper sulfate pentahydrate, sodium citrate and sodium carbonate
Benedict’s Reagent