Electron structure / periodicity * MOD 3 LINKS*
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
How many electrons go into each shell
1st shell: 2e-
2nd shell: 8e-
3rd shell: 18e-
4th shell: 32e-
Define orbital
a region within an atom that can hold up to two electrons with opposite spins
Where is the highest energy level?
in the outer shell
the larger number of shells, the higher the energy level of the shell and further it is from the nucleus
Describe s-orbitals
sphere
holds 2e-
found on shell 1 onwards
Describe p-orbitals & subshells
dumbbell shape
orbital holds 2e-
subshell is 3 p-orbitals
subshell holds 6e-
found on shell 2 onwards
Describe d-orbitals & subshells
rectangle holds 2e-
subshell is 5 rectangles and holds 10e-
found on shell 3 onwards
Describe f-orbitals & subshells
rectangle holds 2e-
subshell is 7 rectangles and holds 14e-
found on shell 4 onwards
What are the exceptions in electronic configuration
Cr: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s¹ 3d⁵
Cu: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s¹ 3d¹⁰
→ makes d (half) full to make it stable
Define 1st ionisation energy
amount of energy required to remove one electron from each atom in a mole of gaseous atoms
Give Mg 1-4 ionisation energies
Mg₍𝓰₎ → Mg⁺₍𝓰₎ + e-
Mg⁺₍𝓰₎ → Mg²⁺₍𝓰₎ + e-
Mg²⁺₍𝓰₎ → Mg³⁺₍𝓰₎ + e-
Mg³⁺₍𝓰₎ → Mg⁴⁺₍𝓰₎ + e-
What factors affect ionisation energy?
atomic radius
nuclear charge (no. of protons)
electron shielding
How does atomic radius affect IE?
the greater the atomic radius, the weaker the electrostatic attraction between nucleus and outermost electrons
How does nuclear charge affect IE?
the greater the nuclear charge, the greater the forces of attraction between the nucleus and electrons
How does shielding affect IE?
inner shells electrons repel outer shell electrons → repulsion = shielding
as the number of inner shells increase, shielding effect increases
there is a weaker nuclear attraction between nucleus and outer electrons
What is the trend of 1st IE down groups?
IE decreases down the group
atomic radius increases
shielding increases
so there is less/weaker nuclear attraction between nucleus and outershell electrons
What is the trend of 1st IE across periods?
IE increases across period
increased nuclear charge so atomic radius decreases
so greater nuclear attraction between nucleus and OUTER electrons
shielding remains the same / outer electrons are in the same shell
Why does it require more energy to remove each successive electron?
atomic radius decreases as same amount of protons attract fewer electrons
nuclear attraction between remaining electrons and nucleus increases
Successive ionisation energy (potassium example)
large increase indicates change of shell
amount of e- lost in last shell indicate group number
every element left with 2e- in inner shell
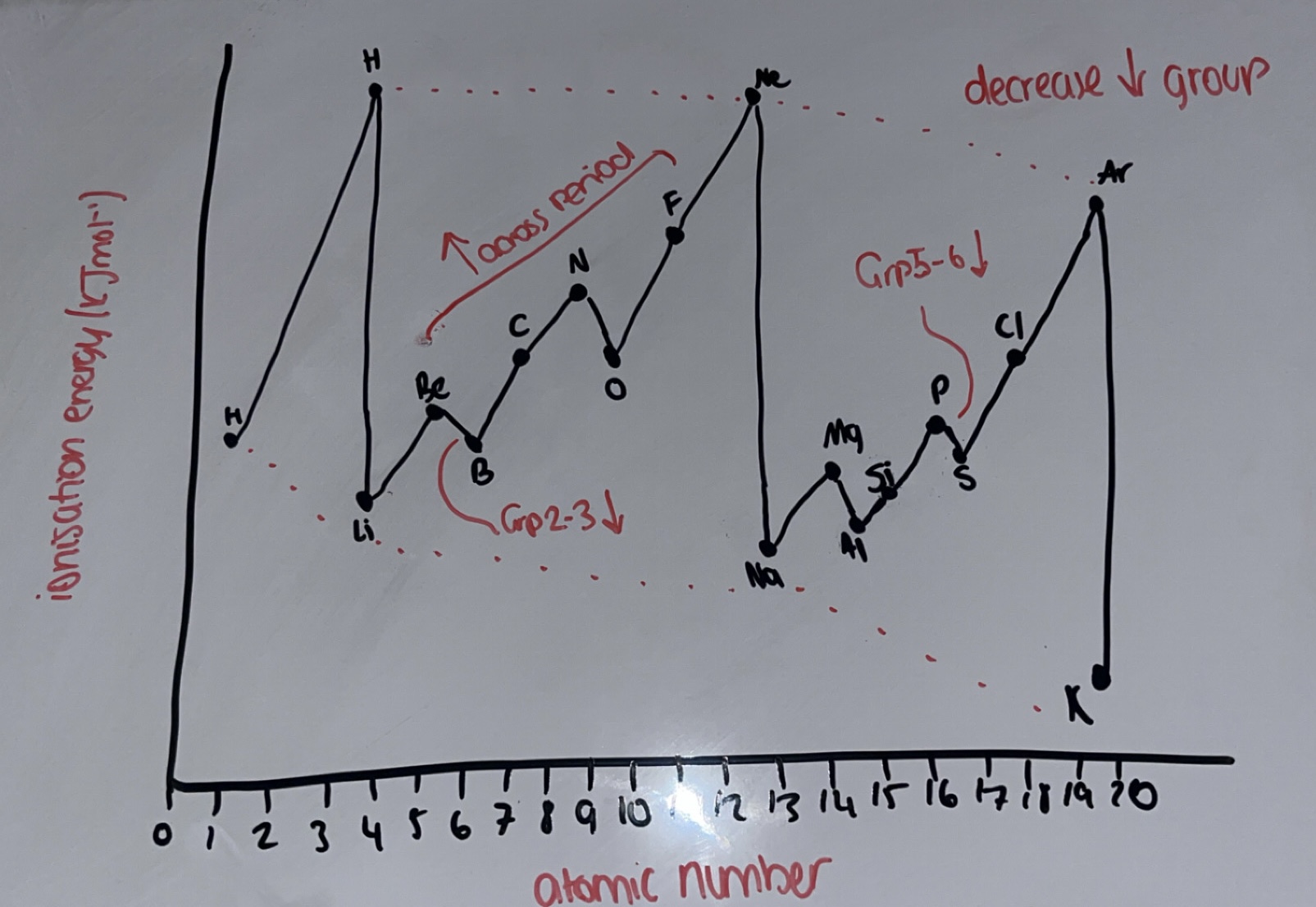
Why is there a decrease in energy from group 2-3?
Be outer electron is in s subshell whereas B outer electron is in a p subshell
p subshell is in a higher energy level than s subshell so less energy is required to remove the e-
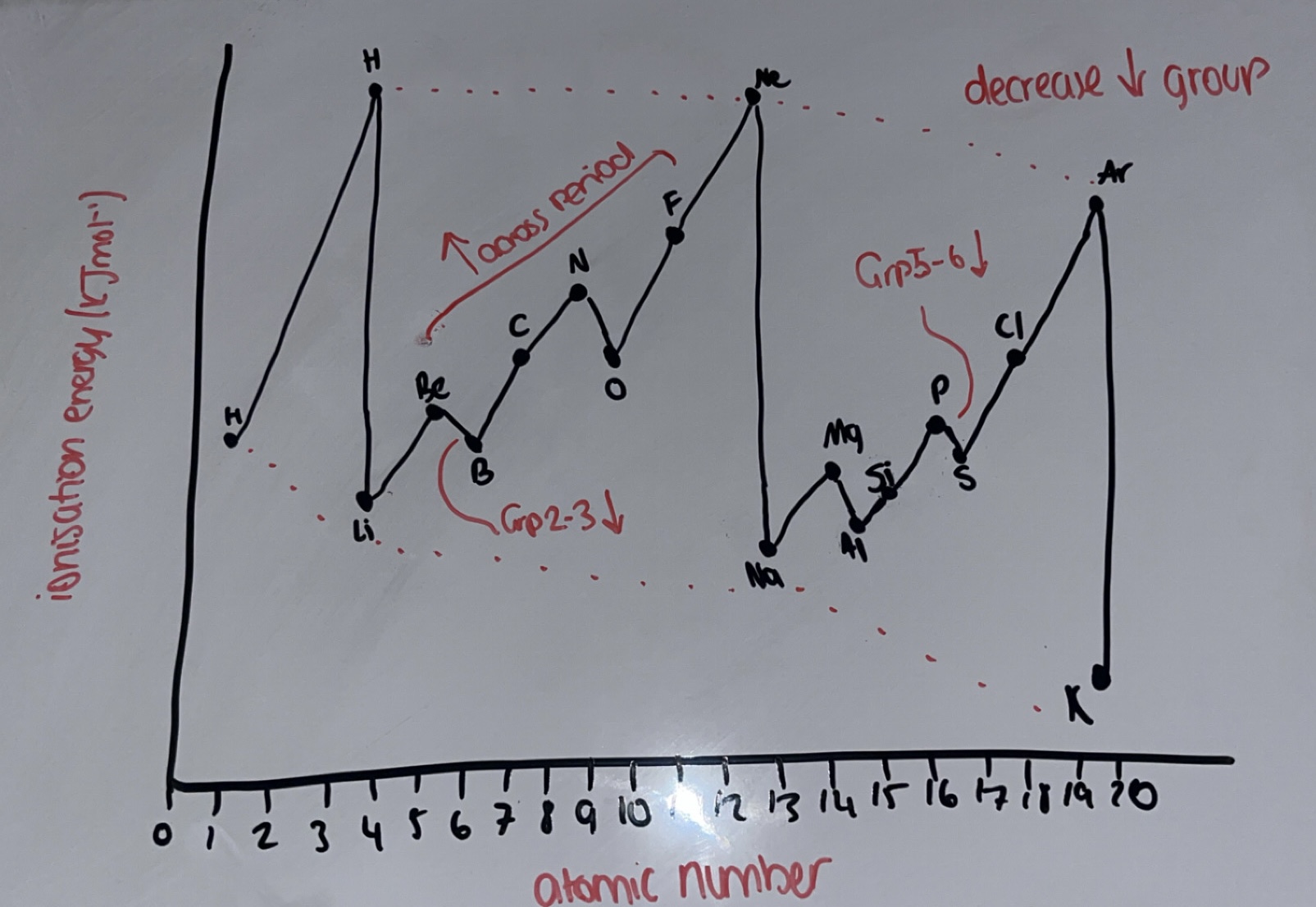
Why is there a decrease in energy from group 5-6?
N outer electron has 3e- in 3 p orbitals whereas O outer electron has 4e- in 3 p orbitals
O has paired electrons in a p orbital which repel each other
O has increased shielding
Whys there a sharp decrease in IE from the end of the period to the start of the next period
there is a new subshell so outer electron is removed from a higher energy level
increased shielding → increased atomic radius → less nuclear attraction
Whats periodicity
trend in physical and chemical properties that is repeated across each period
Why does the B/MP increase from Na-Al
the charges of each ion increases and the number of delocalised electrons increase
the ionic radius decreases
so stronger ef attraction between +ve ions and -ve delocalised electrons
more energy required to overcome
Why does Si have a higher MP than Al
Si is a giant covalent structure and atoms held tightly by strong covalent bonds which require more energy to break
Why does Si have a higher MP than P
Si is a giant covalent structure with atoms held tightly by strong covalent bonds
whereas P is a simple molecular molecular structure which has weak VDW forces between molecules which requires less energy to break than Si
Why is there a general decrease in M/BP from P-Ar
all simple molecular structures
molecules held together by weak London forces
requires a small amount of energy to break
Why is there a slight increase in M/BP from P-S
S is bigger than P
S has more e- so has stronger London forces
required more energy to break