Revolutions_Trianon
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Aster revolution
democratic revolution in 1918 October aiming multiparty elections, increased rights of franchise and land reform (Károlyi Mihály)
Hungarian Party of Communists (KMP)
left wing party stringthened by Bolshevik ideology and the disastrous outcome of the WW1 - lead by Kun Béla
Council Republic (Hungarian Soviet Republic)
communist revolution and takeover in 1919 March, introducing Soviet type self-government system
counter-revolution
a revolution whose aim is to reverse the changes introduced by a previous revolution - right wing, moderate change directed by Bethlen and his conservative-Christian political forces
Red Terror
The campaign of mass arrests and executions conducted by the (Bolshevik) Kun Béla government
White Terror
The hunting down and assassinating of former representatives of the Council Republic
revision
the act of rewriting the false Versailles/Trianon treaty, claiming the territories back

Károlyi, Mihály
Leader of the Party of 48 and Independence, aimed to change the old royal Hungary to a modern, democratic one
Garami, Ernő
the first Social Democratic Poltician
Kun, Béla
Communist Party, Council Revolution, dictatorship of the Proletariat,1919
Apponyi, Albert
Dualist politician, member of the Hungarian delegation travelling to Paris signing the Trianon Treaty, famous speech against it

Teleki, Pál
Christian Conservative poltician, Geographer, Cartographer. Made the Red Map claiming territorries with pure Hungarian nationality at the peace conference. Prime minsiter for two times, 1920-21 and 1939-41.
1918 Oct 31.
Aster revolution is victorious
Nov 3.
Padova armistice
1919 March 21.- 1919 August
Dictatorship of the Proletariat in Hungary
June 04
Trianon peace treaty
Independence Party (Independence and 48 Party)
Party of Károlyi, Mihály 1918, part of the Hungarian National Council founded in 1918. Oct.24.
Hungarian Social Democratic Party
Lead by Peyer Károly, part of the Hungarian National Council founded in 1918. Oct.24.
Lenin's Boys
During the Hungarian Soviet Republic in 1919, the Revolutionary Governing Council was a political task force during the months of the Red Terror.
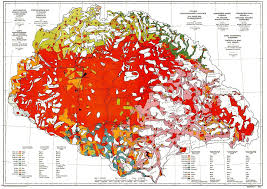
red map
Created by Teleki, Pál it shows the distribution of ethnic groups in the Carpathian Basin (Hungarians marked by red)
reparations
As part of the Treaty of Versailles, Germany and Hungary were ordered to pay fines to the Allies to repay the costs of the war.
Rongyos gárda (Ragged Militia)
The aim of the self-organising (irregular) armed group was to resist the communists during the Soviet Republic in Hungary, and after its fall they actively participated in the White Terror.
St. Stephen's State ideology
Basic theory of Interwar Hungary developed by Teleki Pál. Main ideas: the Hungarian state has never been, and after the First World War must never be, limited to the territories inhabited by the Hungarian ethnic group, but must include all the peoples of the Carpathian Basin. It serves a basis for revision.
irredentism
the doctrine that irredenta should be controlled by the country to which they are ethnically or historically related, extreme form of revision of territorial claims in order to reclaim lost lands.

Charles IV.
Last king of Hungary. The Padova armistice, then the Trianon treaty forbid his return as a king, however he tried to return 2 times in 1921. The Bethlen government refused to support his restoration, leading to his eventual exile.
minority protection (kisebbségvédelem)
guaranteed rights can be divided into three categories: (1) equality of citizenship: there should be no discrimination between minorities and members of the majority nation of the state; (2) religious and cultural autonomy; (3) territorial autonomy (self-determination).
In the formulation of minority rights, there has always been a minimum requirement that members of a minority group should have the same civil rights as any other citizen of the state. Involves measures to ensure equal rights, cultural autonomy, and self-determination for minority groups. It aims to prevent discrimination and promote coexistence within the state. Most cases it remained a theory.
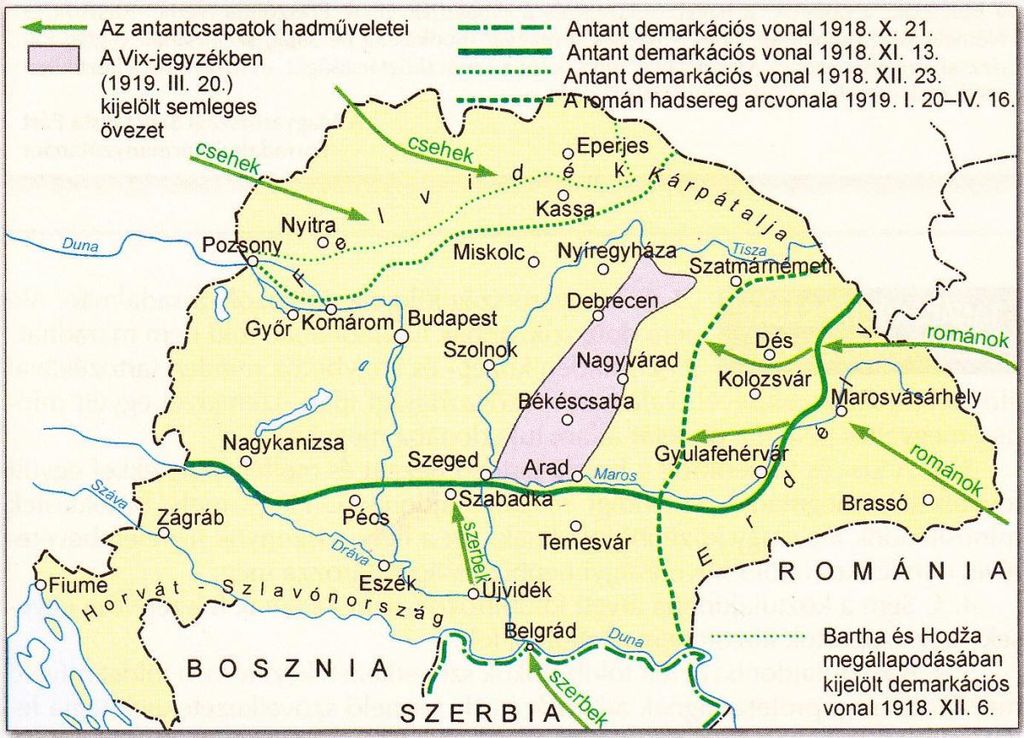
demarcation lines
Boundaries established to delineate territorial divisions between states or regions, often influenced by strategic or political factors.