GABA and Glycine
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
GABA
- major inhibitory aa NT in mature CNS
- locations = brain and spinal cord (major), peripheral tissues (lungs, intestines, etc.)
GABA synthesis
derived by decarboxylation of Glu by glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD)
glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD)
key enzyme and rate limiting step
Glycine
- smallest aa and achiral
- precursor and building block for proteins (i.e. collagen)
- forms key step in biosynthesis of porphyrins (heme) and purines
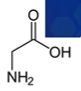
Glycine synthesis
biosynthesized from serine via hydroxy methyltransferase
GABA transporters
- sodium- and chloride-dependent reuptake transporters found in neurons and glia
- Terminates GABA signaling by co-transporting GABA with Na⁺ and Cl⁻ into the cell.
- Utilizes the movement of Na⁺ and Cl⁻ down their electrochemical gradients for transport
- hydrophobic, 12 transmembrane proteins w/ high sequence homology
Type 1 (GAT1)
- found in brain cell membranes
- high affinity for GABA
Type 2 (GAT2)
- mostly in liver, kidneys
- low concentration in meninges
Type 3 (GAT3)
- found in glial cells
- terminates GABA signaling in neighboring synapse by uptake
Betaine transporter (BGT1)
- ancient protein found in bacteria, similar to GAT2
- low affinity for GABA
- primarily transports betaine class chemicals (ex: glycine betaine)
Glycine transporters (GlyT1 and GlyT2)
- Plasma membrane proteins in neurons that terminate glycine signaling through electrogenic ion co-transport.
- Require three Na⁺ and one Cl⁻ to move one glycine molecule into the presynaptic neuron for repackaging.
vesicular GABA transporter (VGAT)
- similar structure to VGKUT, but highest affinity for GABA and Gly
- creates pH gradient → 2H+ for 1 GABA/Gly
- works fast
Gly fate
repackaged or degraded (via Gly cleavage enzyme)
GABA fate
- presynaptic = recycled into vesicle or metabolized
- glial = metabolized via transamination of alpha-ketoglutarate (catalyzed by GABA transaminase)
GABA-A receptor
- pentameric ion channel
- fast inhibition (↑ Cl- conductance influx = inhibitory)
- allosteric modulation: benzodiazepines, barbiturates, ethanol, steroids
- muscimol
GABA-B receptor
heterodimer metabotropic receptor that’s inhibitory (ex: Balcofen = agonist)
GABA-C receptor
- narrow distribution; all p-subunits
- inhibitory ion channel, insensitive to allosteric modulation
Glycine receptors
- composed of subunits (4alpha, Beta) = pentameric channel
- fast inhibitory (↑ Cl- conductance influx)
- ethanol = + allosteric modulator and strychnine antagonist
hyperekplexia
- caused by mutation of alpha 1 subunit in Gly receptor
- rare genetic condition defect that results in exaggerated startle reflex + ↑ rigidity at birth
major effects of Gly
analgesia, motor coordination, schizophrenia, sleep
analgesia
GlyR activation in substantia gelatinosa of spinal cord inhibits nociceptive input in lamina 1 and 2
motor coordination (ref. GlyR)
GlyR activation in brainstem and spinal cord smooths locomotor output
Schizophrenia (ref. GlyR)
↑ NMDA, GlyT1 inhibitors in clinical trials for negative symptoms
sleep (ref. GlyR)
Glycine (3g nightly) found to improve sleep quality
GABAergic pathways
- striatum → substantia nigra (inhibits dopamine signaling, ↓ locomotion, reward)
- substantia nigra → colliculus (prevents locomotor activity)
GABA effects
- analgesia → inhibit nociception in brain
- inhibits descending pathway in midbrain PAG which regulates nociceptive relay neurons
- opioids → ↑ descending control + analgesia
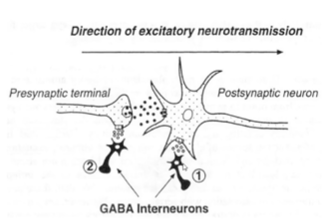
GABA interneurons
control neuronal excitability:
- Postsynaptic inhibition = ↑ Cl- hyperpolarizes neuron, ↓ EPSP
- presynaptic inhibition = GABA-A ↑ Ca2+, causing ↓ NT release
GABA agonists
produce sedation
GABA antagonists
produce convulsions → induce seizures and feelings of anxiety/dread
epilepsy (ref. GABA)
- increase in GABAergic signaling inhibits neuronal activity correlated w/ seizures
- GABA agonists, PAM (BDZ) = antiepileptic + anticonvulsants
anxiety (ref. GABA)
- GABA + allosteric modulation (benzodiazepines, barbiturates, ethanol) are all anxiolytics
- ↑ GABA activity = ↓ locus ceruleus output and inhibition of amygdala/hippocampus
Sedation (ref. GABA)
- PAM or GABA agonists suppress neuronal firing → calming w/o sleep (hypnotic effects = produced drowsiness, promote sleep)
Motor function (ref. GABA)
- inhibit locomotor activity, especially at substantia nigra (ex: Huntington’s disease)
- cerebellum = highly organized brain structure, works to coordinate and refine locomotor output (5/6 are GABAnergic)
Muscimol
GABA-A agonist, sedative found in mushrooms