3. Population Ecology (Unregulated & Regulated Populations Growth)
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
N1 = N0R0
geometric growth
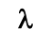
(pic)
finite growth rate
zero population growth occurs when
the birth rate equals the death rate
N is:
population size
t is:
time
r is:
per capita rate of increase
= birth - death
Nt = N0ert
lnNt = lnN0 + rt
(lnNt - lnN0) / (t) = r
R0=erT; r=ln(R0)/T per generation growth rate
r < 0, population is decreasing
r = 0, population is stable
r > 0, population is increasing
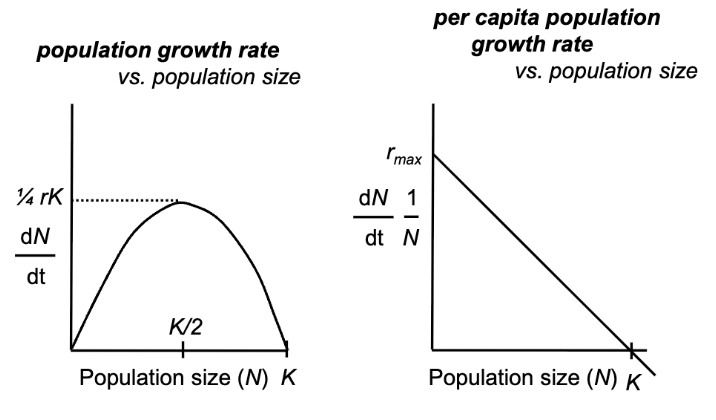
exponential population growth
is population increase under idealized conditions
equation of exponential growth is:
(dN) / (dt) = rmaxNp
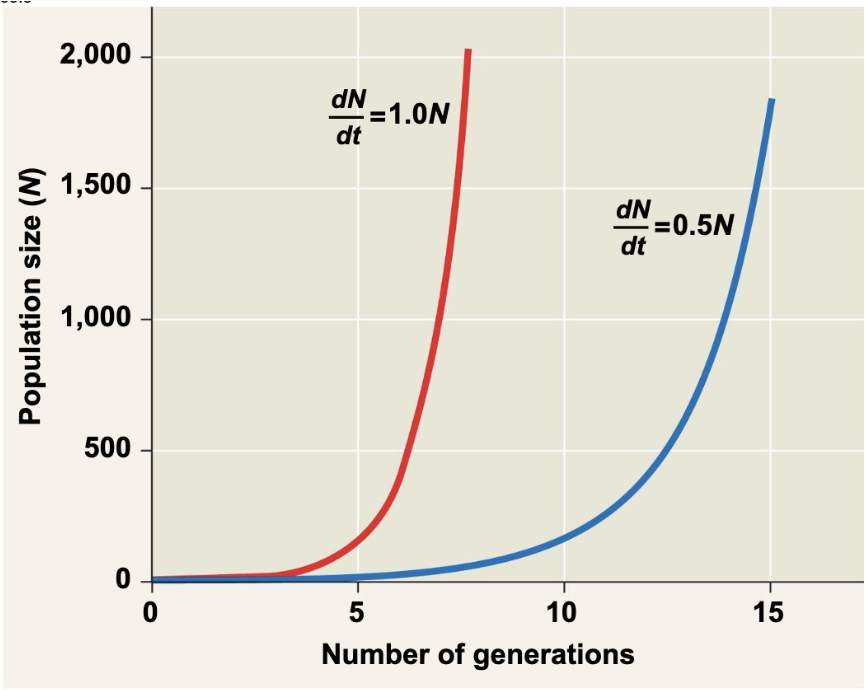
population growing exponentially exhibit characteristics:
positive feedback of population size on population hrowth; larger populations grow faster than do smaller populations
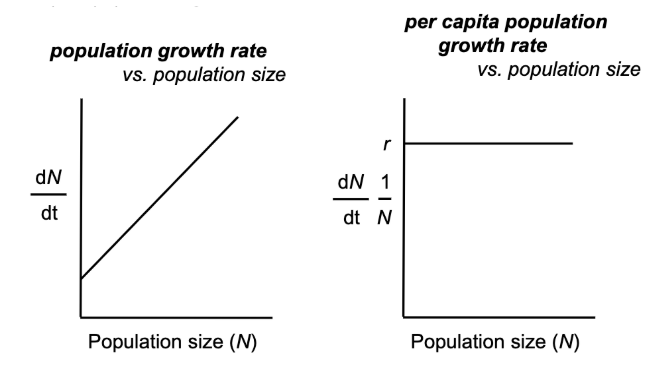
per capita population growth is constant
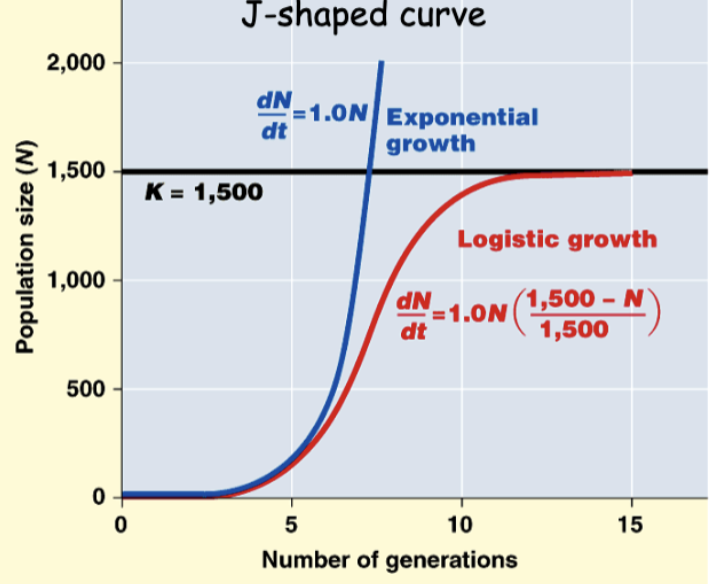
what is (K)
Carrying Capacity = the maximum population size the environment can support
populations growing logistically also exhibit the following characteristics:
negative feedback of population size on population growth; unimodal response for population growth rate vs. population size
per capita population growth declines with increasing population size
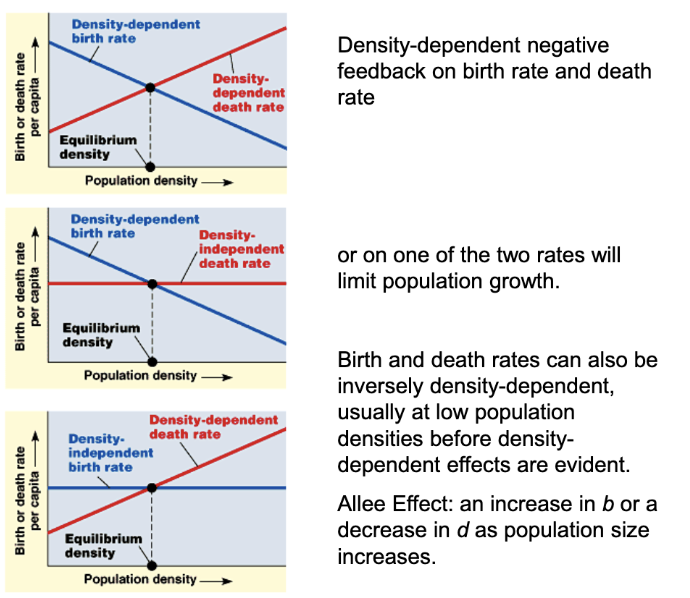
density-independent populations
birth rate and death rate do not change with population density
density-dependent populations
birth rates fall and death rates rise with population density
negative feedback
territoriality
defense of a defined geographical area,
ex. cheetahs are highly territorial, using chemical communication, to warn other cheetahs of their boundaries
predation
as a prey population build up, predators may feed preferentially on that species
toxic waste
accumulation of toxic waste can contribute to density-dependent regulation of population size
intrinsic factors
for some populations, (physiological) appear to regulate population size