Clinical Implications of the Critical Period
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
True or false: In both cats and humans, plasticity peaks rapidly.
true
At what point does plasticity reach zero?
never - just a slow gradual decline
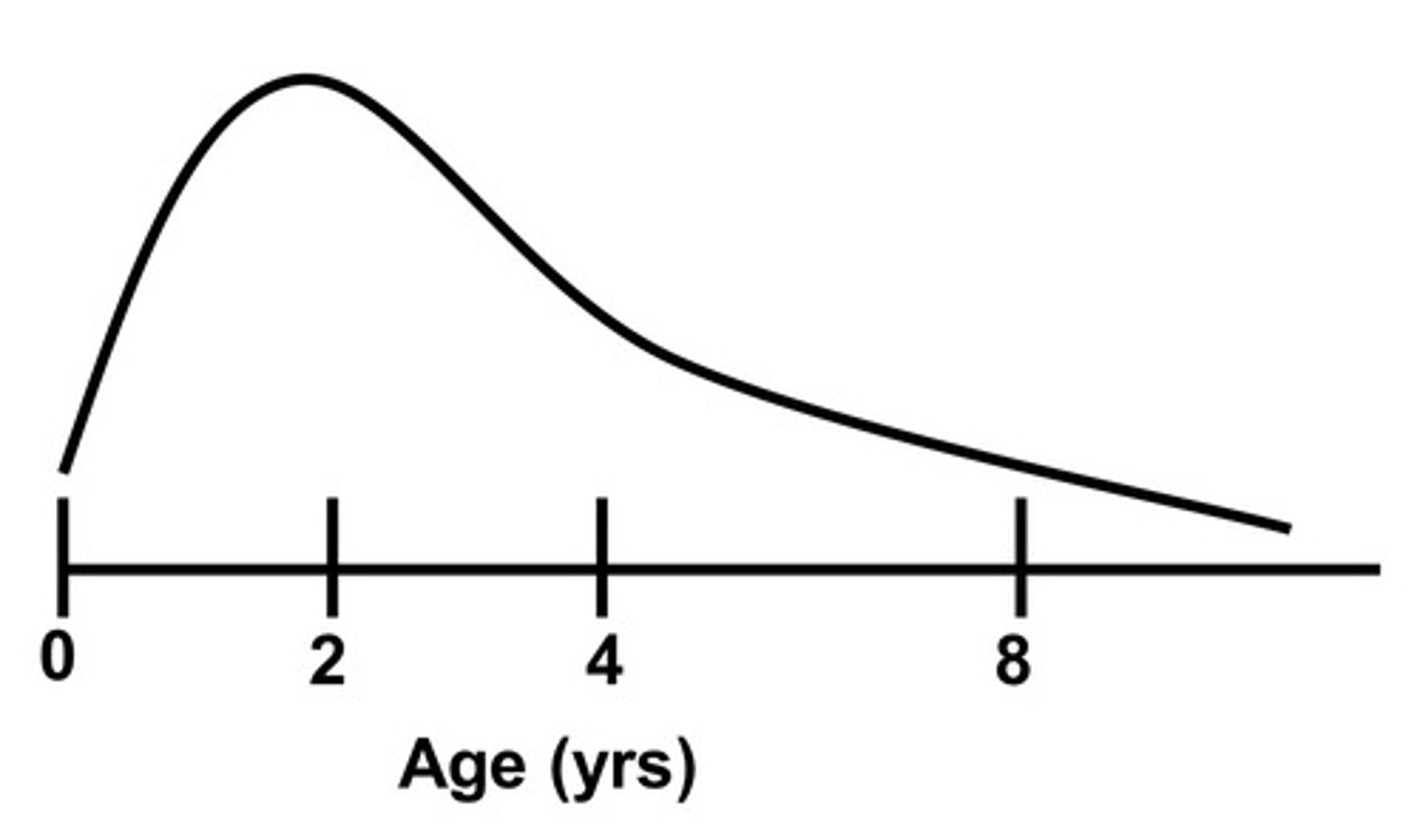
Plasticity is NOT ____ with respect to the peak.
symmetrical
When is the peak of plasticity for humans?
1-2 years
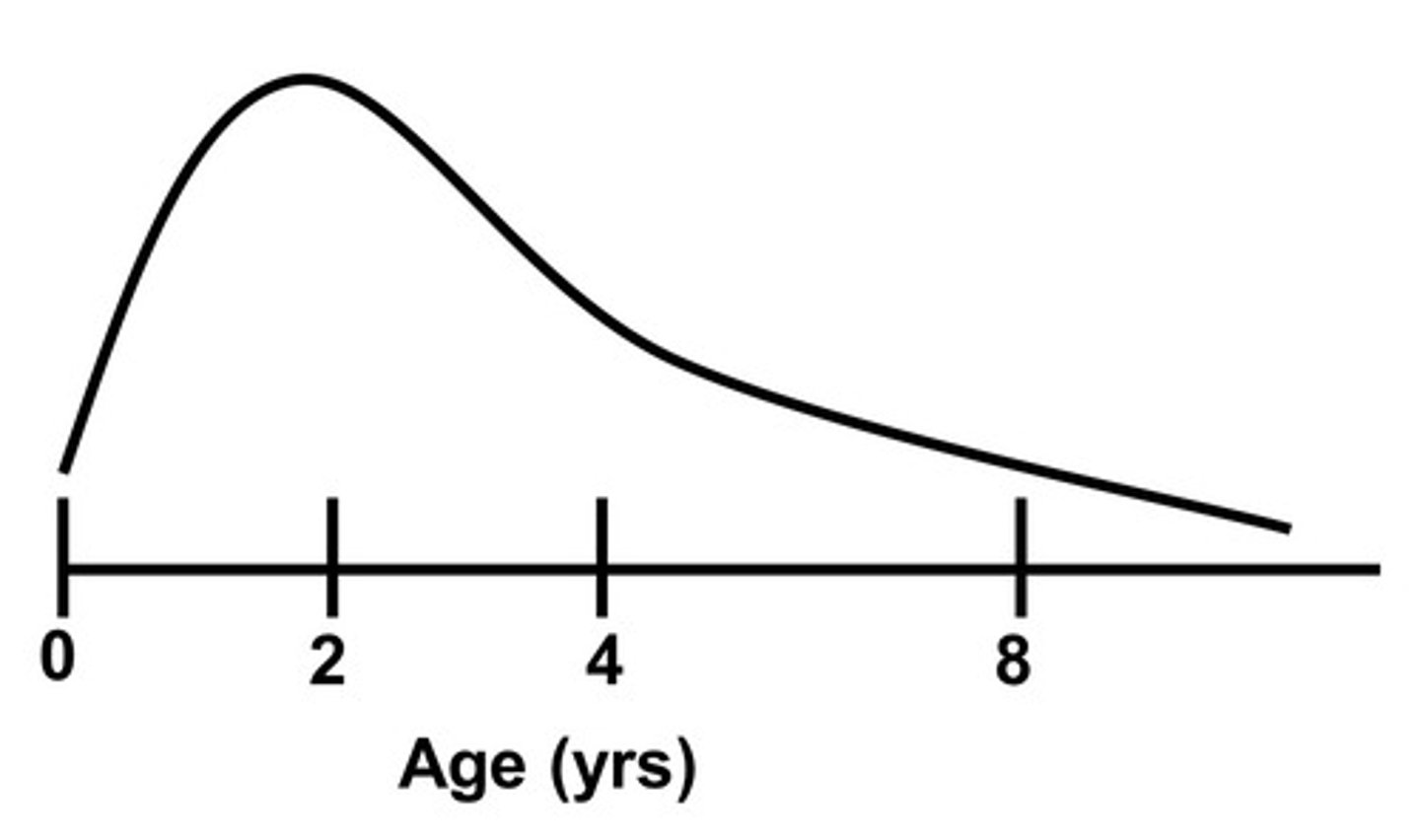
The critical period is the time frame in which you can CHANGE the visual pathway. What can be changed about the retina?
not much
(plasticity is minimal after birth)
The critical period is the time frame in which you can CHANGE the visual pathway. What can be changed about the LGN?
cell size
The critical period is the time frame in which you can CHANGE the visual pathway. What can be changed about the visual cortex?
cell number
refers to the stage in development that encompasses birth to the peak of the critical period
stage A
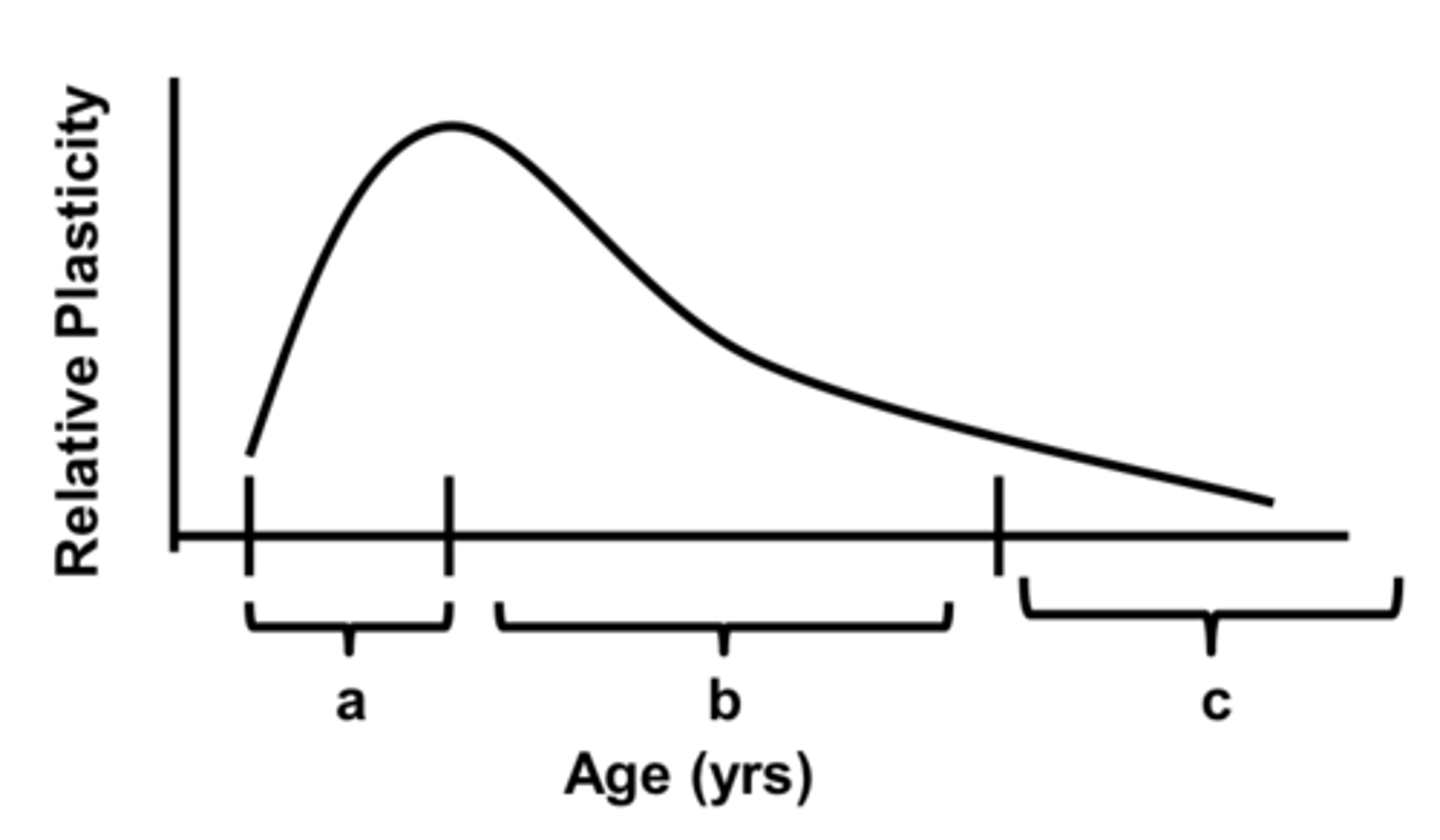
What does the peak of the critical period correspond with?
development of adult-like visual capacity
What results from an abnormality that occurs during stage A?
amblyopia of arrest
(this will STOP the further development of visual function if no treatment is done, and full maturity is never reached)
refers to the stage in development that encompasses the peak to the end of the critical period
stage B
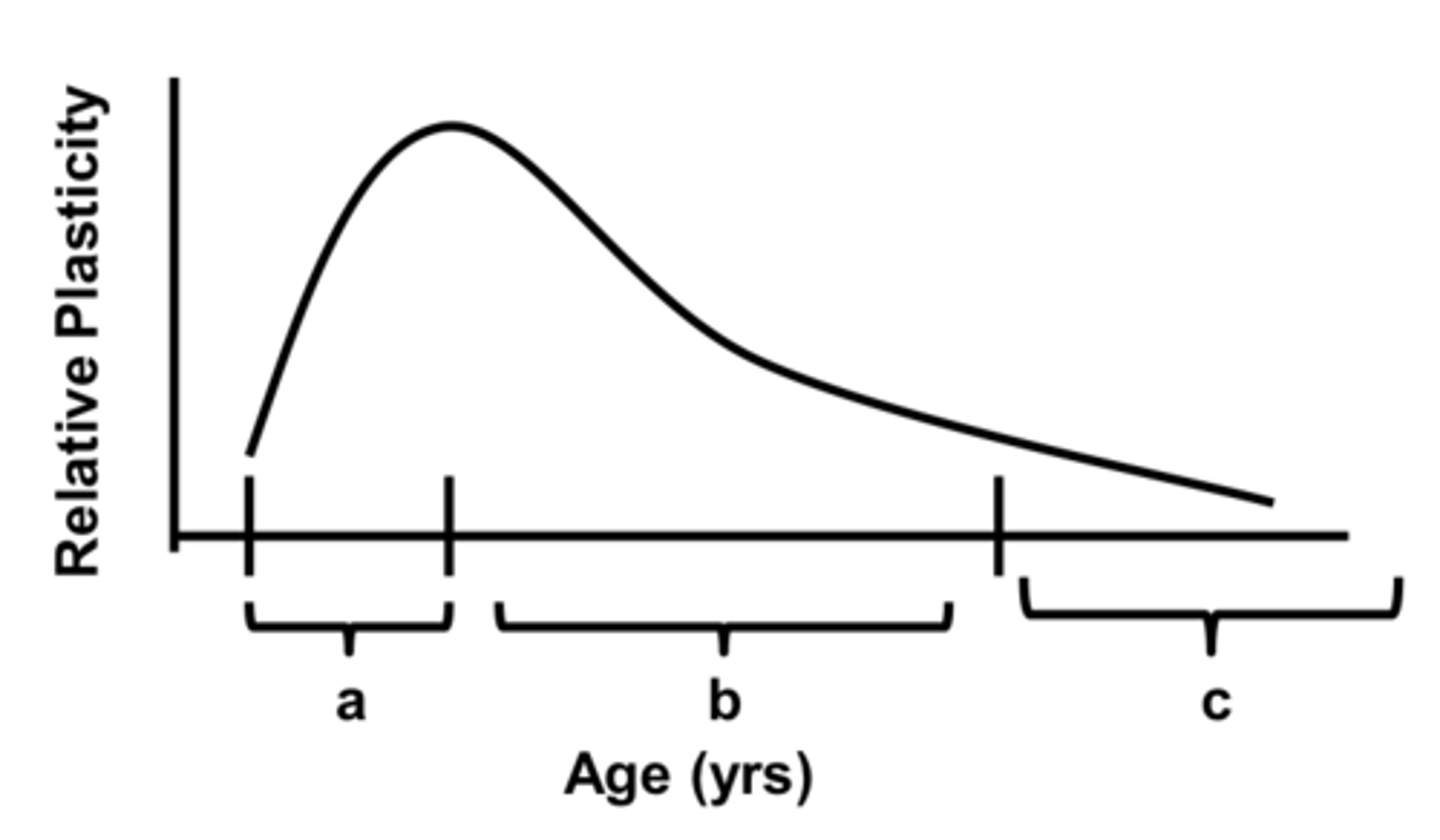
What results from an abnormality that occurs during stage B?
amblyopia of extinction
visual condition that results when normal neuron connectivity had been obtained and the patient had reached normal adult VA, but then some kind of abnormality changed and modified visual function
some but not all connectivity is altered because plasticity is no longer at its peak!
amblyopia of extinction
In what stage does amblyopia of arrest occur?
stage A
In what stage does amblyopia of extinction occur?
stage B
What is the difference between amblyopia of arrest (AA) and amblyopia of extinction (AE)?
AA = visual pathway never developed, can't fix it if critical period is passed already
AE = visual pathway already developed, disruption can be reversed
refers to the stage in development that encompasses the time after the critical period
stage C
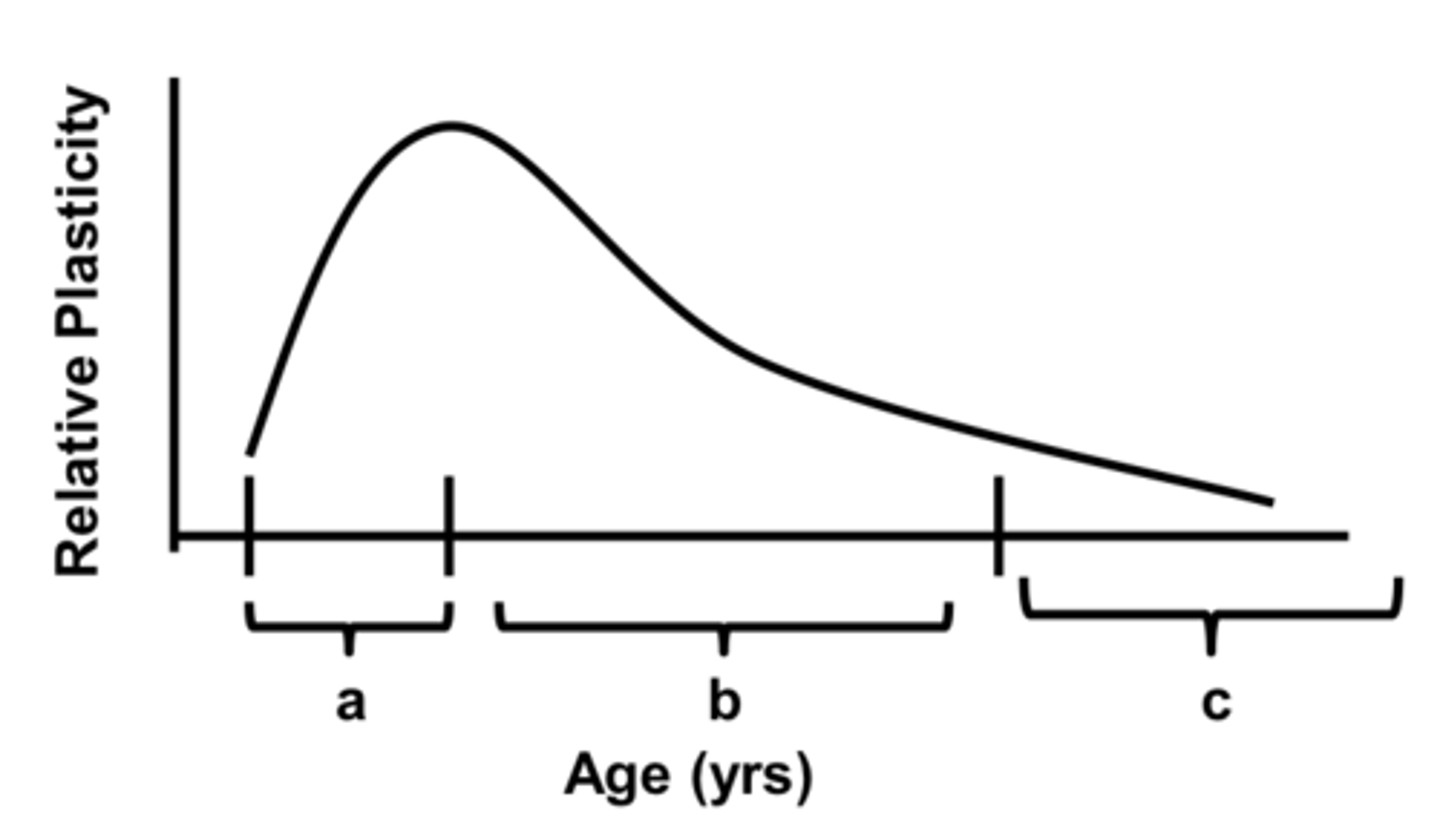
What results from an abnormality that occurs during stage C?
not much - no significant change on the visual pathway
Even though a stage C abnormality won't have a significant change on the visual pathway, what can still change? (4)
1. retraction of the synaptic site
2. neurotransmitter release
3. degeneration of cell bodies/receptors
4. neural suppression
What stages make up the critical period?
A+B
For older children (aged 7 to 18 years) with strabismic and anisometropic amblyopia, does age affect treatment outcomes?
yes
True or false: For children 7-18 years old, optical correction may be enough to improve amblyopia.
true
(but only in about 25% of patients - most will require additional treatment)
What has been shown to be an effective treatment for 7-13 year olds with amblyopia? (even if they were previously treated!)
patching 2-6 hours/day with near activities OR atropine
For 13-18 year olds, can the same patching/atropine treatment be just as effective as it is for the 7-13 year olds?
possibly if it hasn't previously been treated, but not really if it has already
For children aged 7-18 years old, complete resolution of amblyopia is unusual even when there is a response to treatment. So should we even still bother treating them?
yes!
What is the critical period of onset amblyopia?
birth to 8 years old
What is the critical period of amblyopia treatment?
birth to 18 years old (possibly later)
What is an example of how an adult could experience vision recovery if they have amblyopia?
the good eye has some sort of new abnormality that restricts vision, like a cataract or hemorrhage
but so far, there has been no big clinical trial in adults focusing on amblyopia treatment outcomes - only these few cases where the amblyopic eye's vision can be partially recovered if the good eye's vision becomes poor
True or false: Vision can possibly be improved even with adult onset amblyopia.
true
Why can vision still possibly be improved in amblyopic adults?
visual system always has some degree of plasticity
The [earlier/later] the onset of the abnormality, the more profound the effect on the visual pathway.
earlier
(can result in amblyopia of arrest)
The [shorter/longer] the abnormality, the more profound the effect on the visual pathway.
longer
(especially true in stages A and B)
What are 2 other factors in assessing clinical prognosis of amblyopia?
age of treatment start, severity/etiology of abnormality
An 8 year old patient was diagnosed with left anisometropic amblyopia and VA cc was 20/100 initially. Refraction was OD plano, OS +3.00 DS. He had refractive correction and patching treatment for 2 years. His compliance with treatment was excellent, and his final VA OS was 20/25+. Why?
A. etiology
B. severity of anisometropia
C. age of treatment start
D. compliance
E. onset age
E
If an ocular media opacity is the reason for the amblyopia, then what might be required to regain the visual function?
early surgical treatment
If the abnormality occurs in stage A, how soon do we need surgical treatment?
immediately
(since visual pathway is still very plastic - otherwise, you will get amblyopia of arrest)
What are 5 treatment options for strabismus?
1. refractive correction
2. prism
3. vision therapy
4. surgery
5. patching for amblyopia
Congenital esotropia has considerable ____ in angle and constancy.
variation
Amblyopia is common with congenital esotropia, so you should always examine infants with this condition closely. If the esotropia is stable, what should you recommend?
early surgery
What kind of strabismus manifests after cyclorefraction?
accommodative esotropia
Patients with accommodative esotropia typically have what general refractive error?
high hyperopia
In a patient with accommodative esotropia, treat what first before considering prism, VT, or surgery?
refractive error
How do we typically treat accommodative esotropia?
optical correction
(since it is caused by high hyperopia)
Depending on the residual angle in partial accommodative esotropia, you should treat with prism, VT, or surgery only after treating with what first?
glasses
Do patients with intermittent exotropia typically get amblyopia?
no
Patients with intermittent exotropia may have relatively good ____ depending on the frequency and angle of exotropia.
binocularity
What are 3 issues to consider in strabismus?
amblyopia, cosmetics, effects of longstanding strabismus (e.g., suppression, diplopia)
Ultimately, we need to fully correct anisometropia to avoid potential amblyopia. If the anisometropia is <3.00 D, what form of optical correction should we use?
glasses
Ultimately, we need to fully correct anisometropia to avoid potential amblyopia. If the anisometropia is >3.00 D, what form of optical correction should we use?
contacts
refers to equal refractive error, similar to binocular atropinization
isometropia
True or false: Bilateral amblyopia can result from isometropia.
true
If the Rx is greater than what for hyperopia, this can cause isometropic amblyopia?
+5.00 D
If the Rx is greater than what for myopia, this can cause isometropic amblyopia?
-8.00 D
If the Rx is greater than what for astigmatism, this can cause isometropic amblyopia?
-2.50 D
How should we treat isometropic amblyopia?
optical correction
(not alternating patching)