Lecture 27-28: Rabbits vs. Rodents
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
what is important about the skin and hair of rabbits?
very delicate
easily tear or rip when clipping fur
lack footpads
female rabbits possess a
dewlap
where are pododermatitis risks located on rabbits?
points of the hock and tips of third phalanges
what are the only glandrous areas of the rabbit?
nose tip, scrotal sacs, and inguinal folds

what is this pointing to?
dewlap
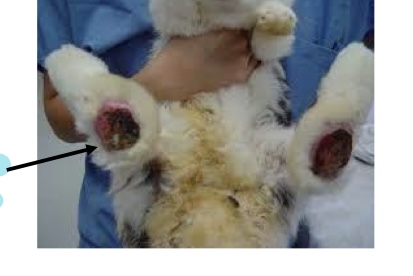
what is this picture showing?
pododermatitis lesion at hock
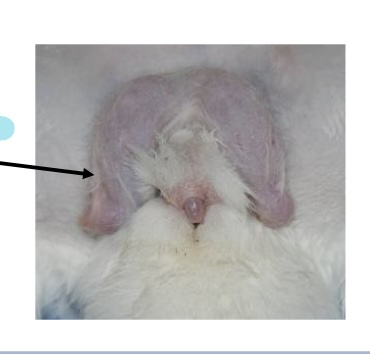
what is this picture?
rabbit scrotal skin
what are the rabbit scent glands?
chin gland
perineal glands
inguinal glands

what is this rabbit doing?
scent marking with chin gland
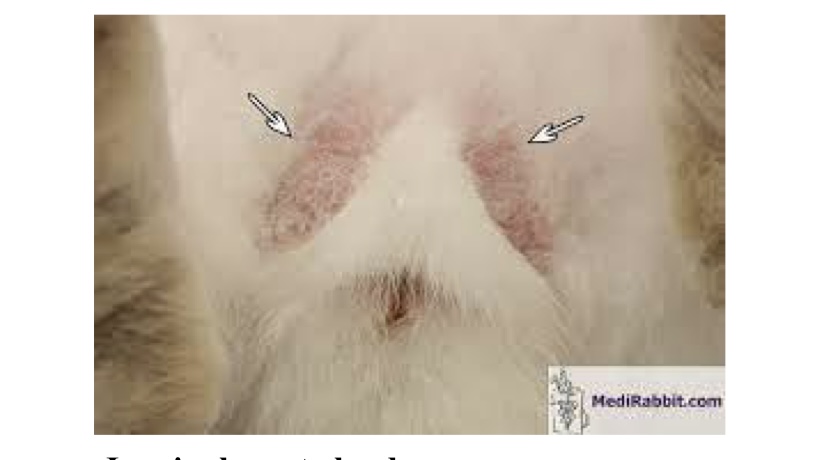
what are these arrows pointing to?
inguinal scent glands
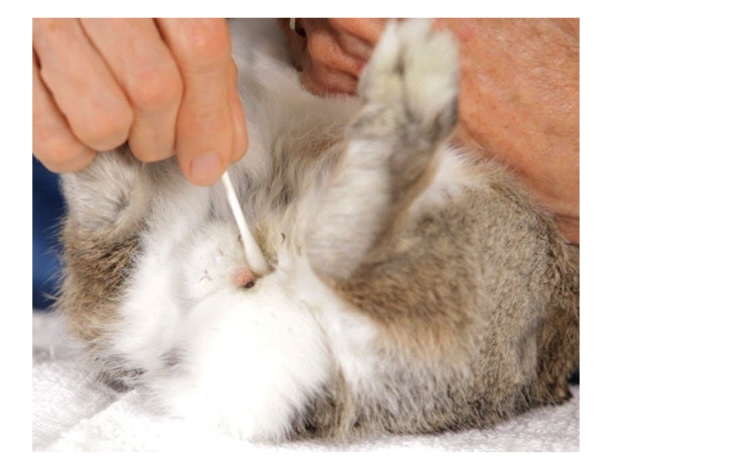
what is this picture showing?
perineal scent glands
cornea of rabbit eye =
30% of eyeglobe
rabbit eye position
lateral position of eye globe in skull
wide field of view by OU
OU =
ocular universal
OD =
ocular dexter
OS =
ocular sinister
what kind of vision do rabbits have?
binocular vision
what do rabbits have right behind their incisors?
peg teeth
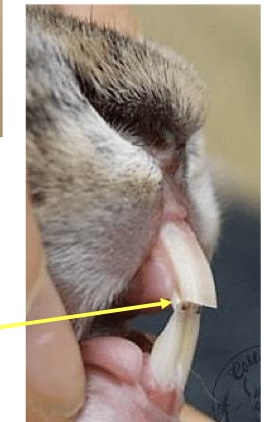
what is this?
peg teeth
the rabbit GI tract is designed for
hindgut fermentation
what does hindgut fermentation mean for rabbits?
they rely specifically on their cecum to digest fibrous plant material
where is the cecum located in the rabbit?
superficially in the caudal peritoneal cavity
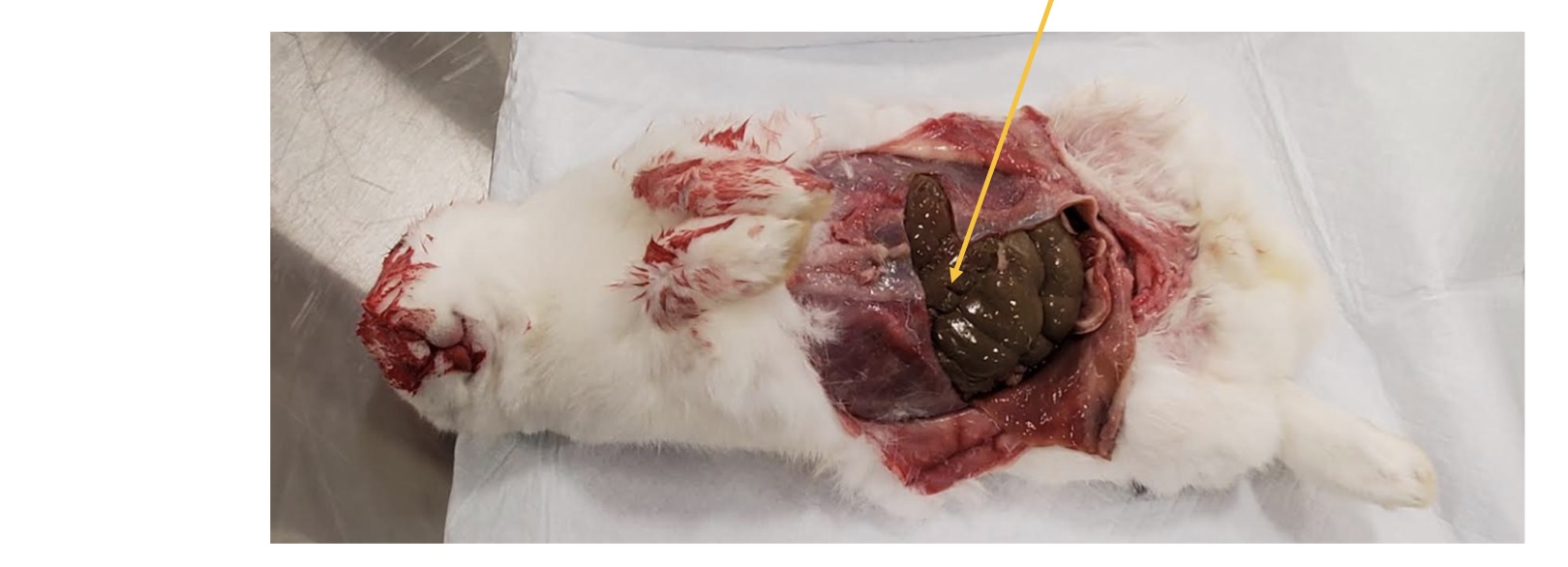
what is the arrow pointing to?
cecum
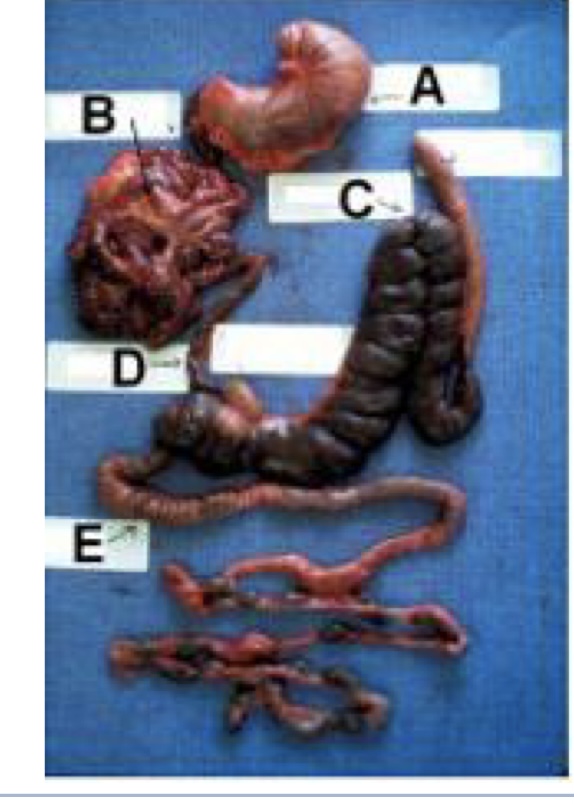
what are these GI structures?
A - stomach
B - small intestine (jejunum)
C - cecum
D - ileum
E - colon
what side of the body is the descending duodenum on?
the right
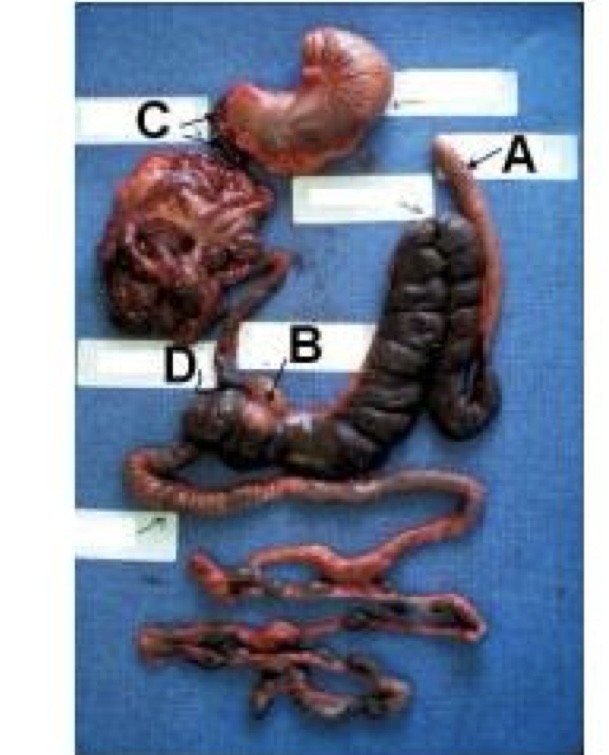
label these structures.
A - lymphoid appendix
B - sacculus rotundus
C - duodenum
D - ileocecal junction
A and B are both GALT
what is a cecotroph?
soft, nutrient-rich feces produced by rabbits and other hindgut fermenters
what is another name for cecotrophs?
night feces
what is coprophagy?
when rabbits re-ingest cecotrophs to absorb nutrients that were not fully digested the first time
in female rabbits, the uterine artery branches from the
vaginal artery
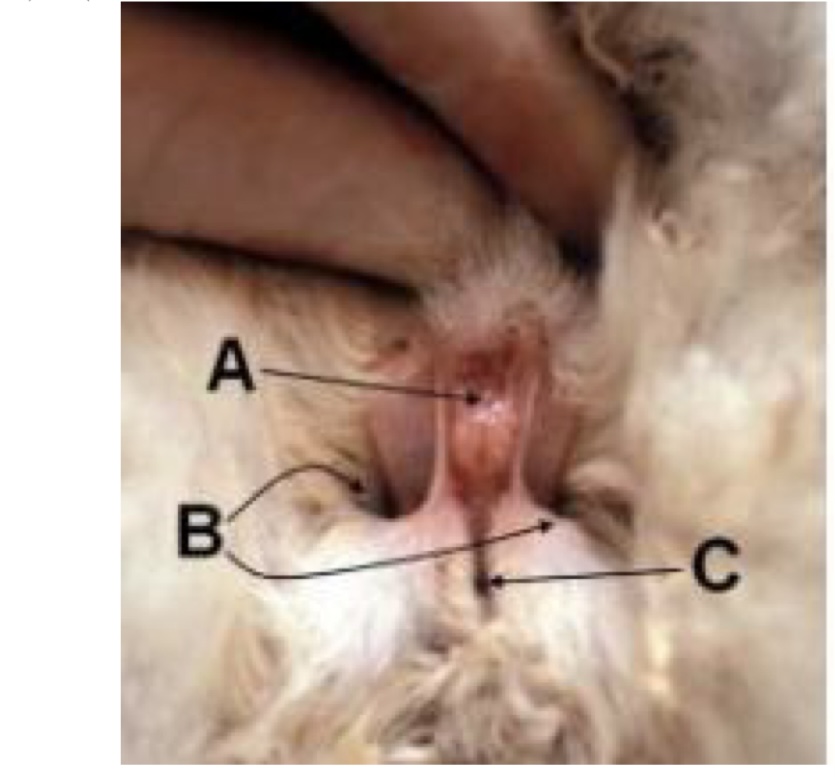
label these regions of the female rabbit external genitalia.
A - vulva
B - inguinal scent glands
C - anus
what are the reproductive tract differences in rabbits compared to small carnivores?
2 cervices
abundant adipose in broad ligament
numerous vessels in broad ligament
lacking thick suspensory ligament
what do female rabbits lack in their repro tract?
thick suspensory ligament
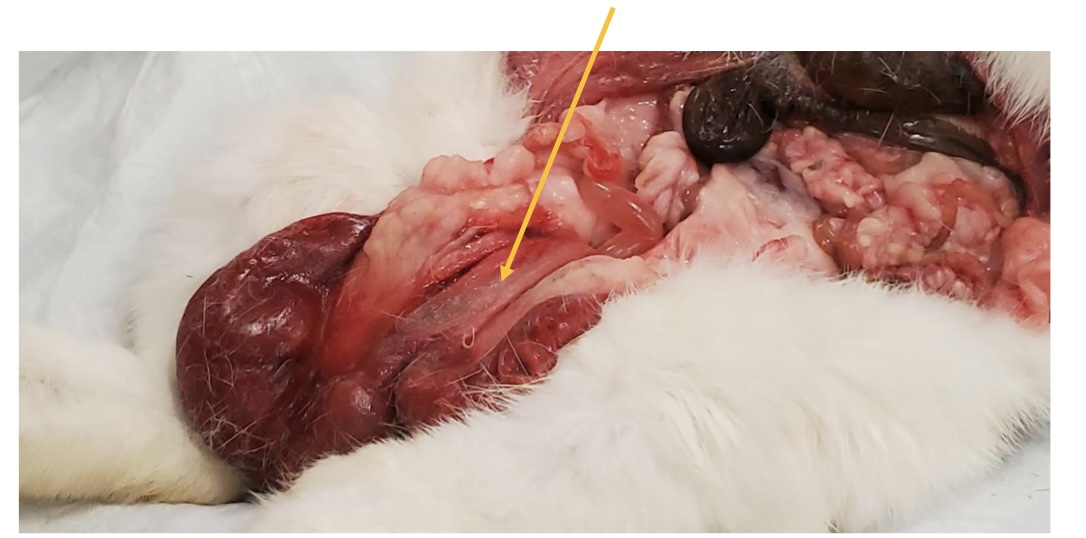
what is this picture showing?
uterine left horn of rabbit
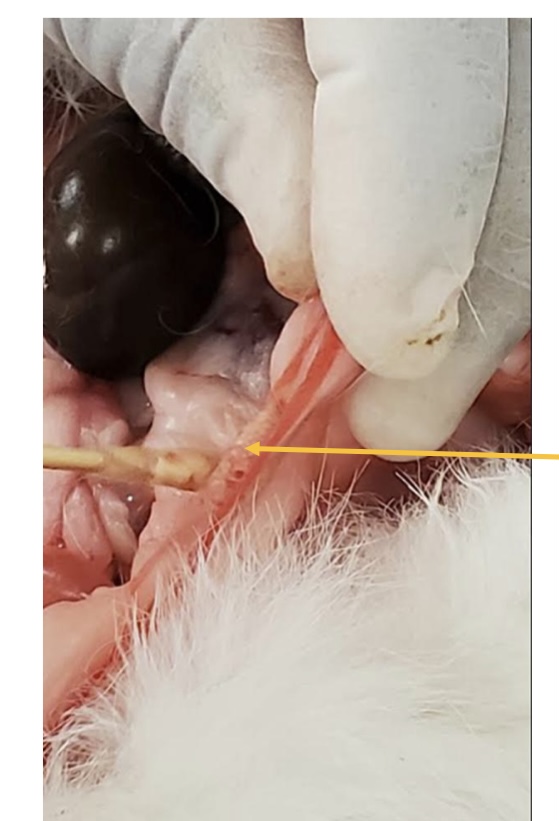
what is the arrow pointing to?
ovary in female rabbit
female rabbit is called a
doe
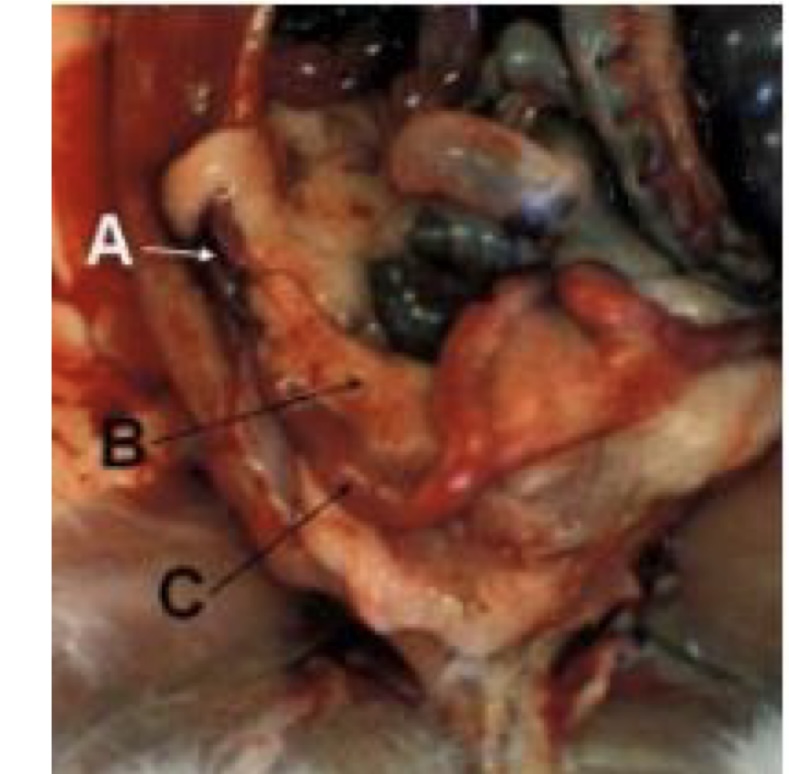
label these regions of the rabbit repro tract.
A - ovary
B - broad ligament (fat filled)
C - uterus (duplex)
male rabbits are called
bucks
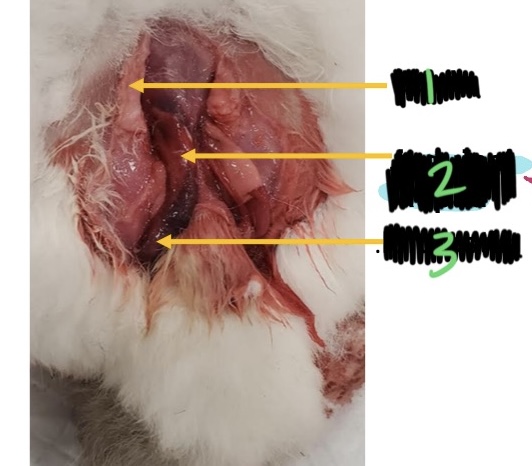
label the parts of the male rabbit genitalia.
penis
inguinal fat pad
left testis
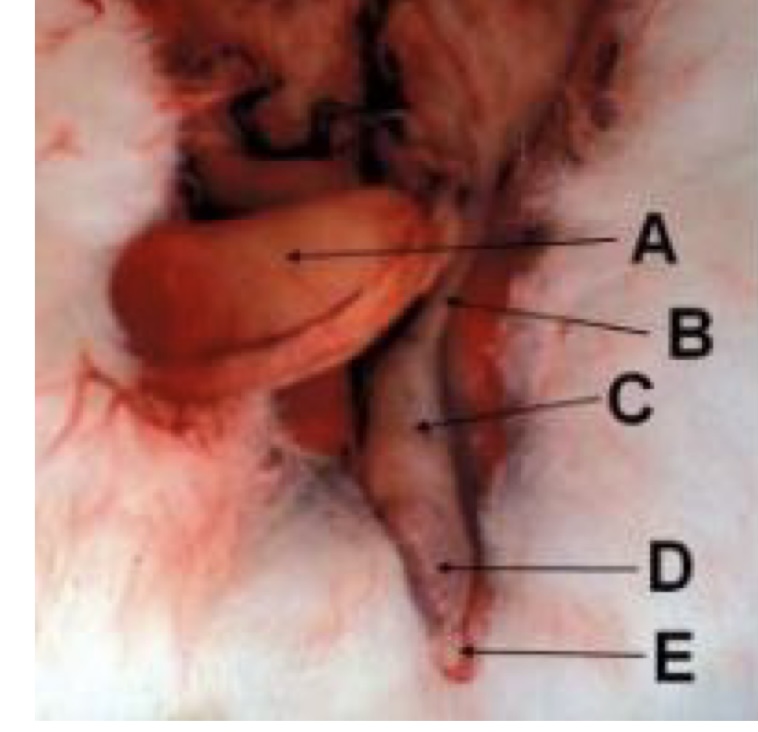
label the male rabbit internal genitalia.
A - urinary bladder
B - ductus deferens
C - cranial fat pad
D - testis
E - tail of epididymis
what is the natural habitat for chinchillas?
Andes Mountain and high elevation terrain
what is large on the chinchilla skull?
tympanic bulla
what do chinchillas have for hearing?
large pinna
yellow enamel color means
the enamel is thicker
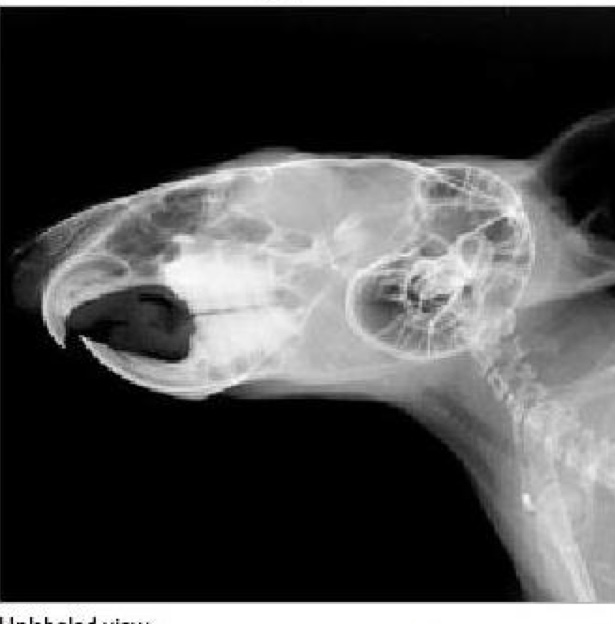
what is this a radiograph of?
chinchilla skull
what type of teeth do chinchillas and guinea pigs have?
elodont and hypsodont
what does elodont mean?
incisor teeth, continuously growing throughout life of mammal
what does hypsodont mean?
high crowns to teeth; irregular occlusal surfaces, enamel crests and dentinal grooves, cheek teeth, both premolars and molars
chinchilla/guinea pig incisors are
elodont type
chinchilla and guinea pig premolars and molars are
elodont and hypsodont type
what types of teeth do gerbils, hamsters, mice, and rats have?
anelodont, elodont, and brachydont
what does anelodont mean?
premolars and molars, rooted, but not growing throughout life
what does brachydont mean?
low crowns to teeth; premolars and molars, enamel over entire occlusal surfaces
gerbil, hamster, mouse, rat incisors are
elodont and hypsodont type
gerbil, hamster, mouse, rat premolars and molars are
anelodont and brachydont type
what is important during castration of rat?
the fat pad → do not move it
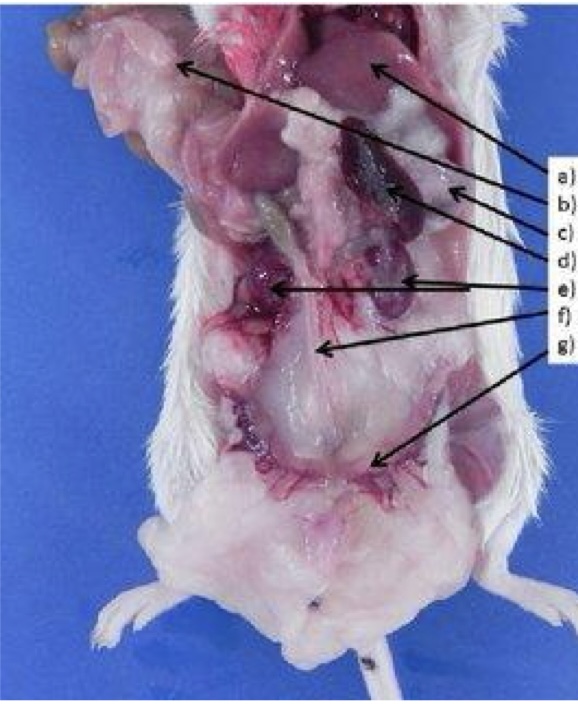
label the abdominal viscera of the rat.
A - liver
B - intestines
C - stomach
D - spleen
E - kidneys
F - descending colon
G - uterus
the norway rat does not possess a
gallbladder
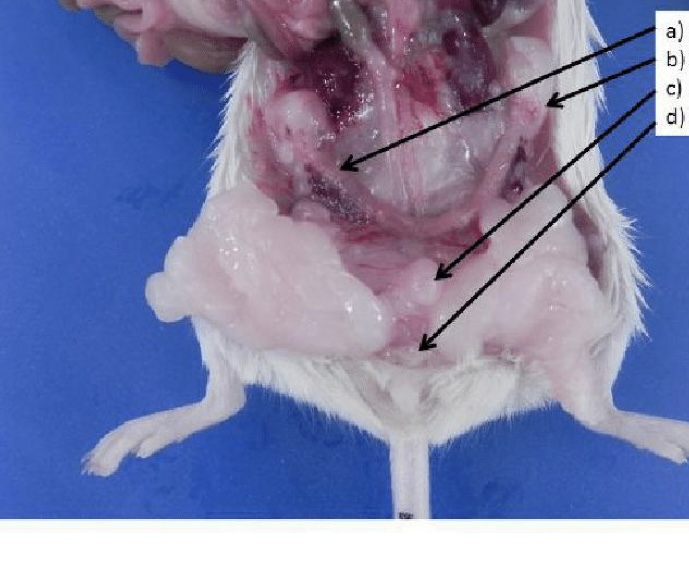
label the female rat pelvic cavity viscera.
A - uterus
B - ovary
C - urinary bladder
D - clitoral gland
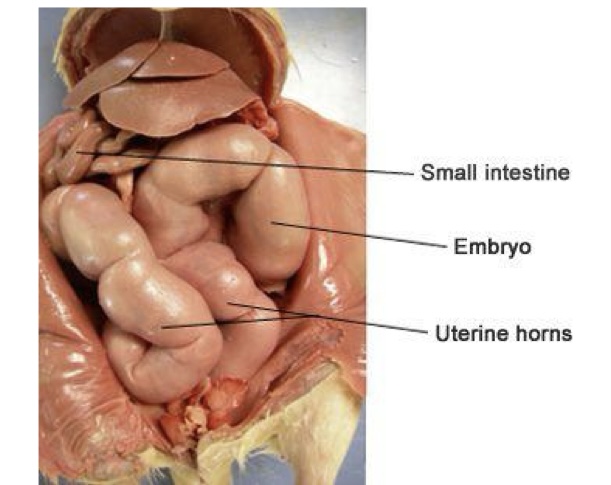
what is this picture showing?
rat gravid uterus with multiple feti
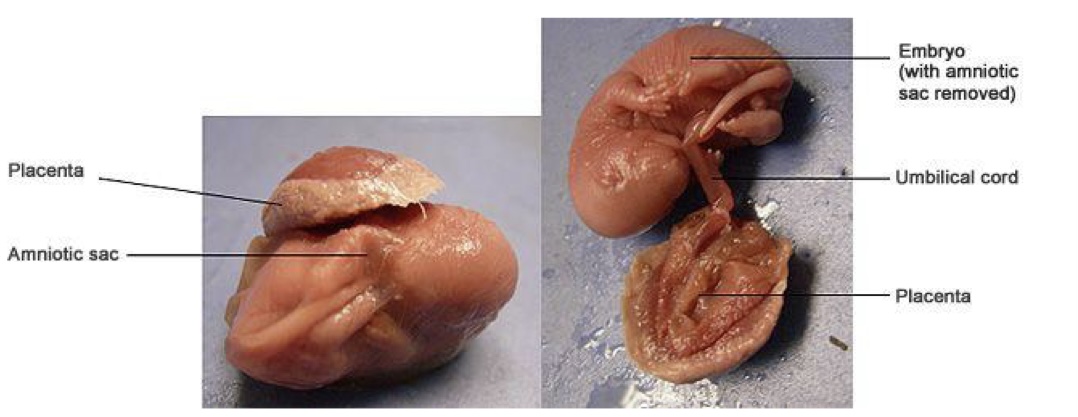
what is this picture showing?
rat fetus with attached placenta
how many mammary glands does the norway rat possess?
6 pairs, 12 in total
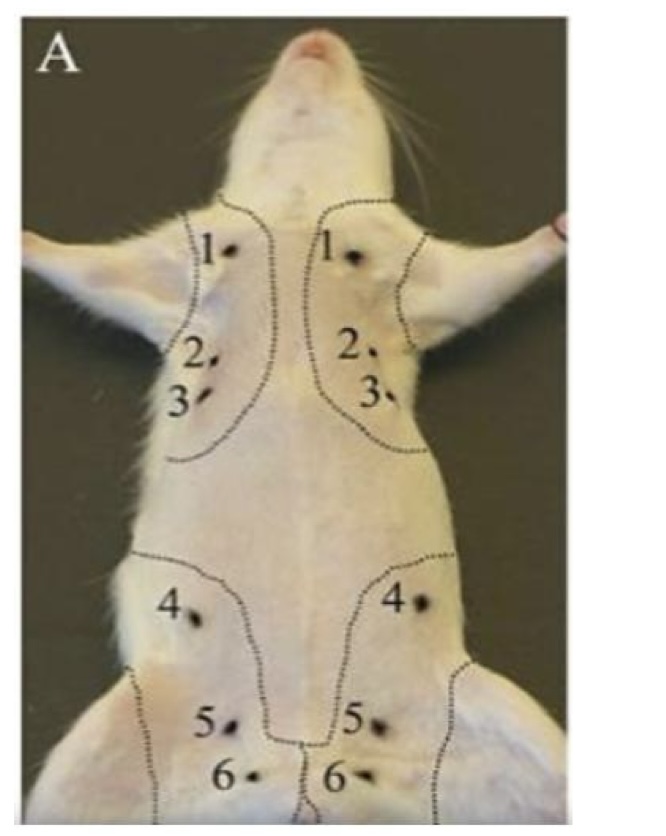
label the mammary glands of the norway rat.
cervical
cranial thoracic
caudal thoracic
abdominal
cranial inguinal
caudal inguinal
lab rats have a high prevalence of
mammary gland neoplasia
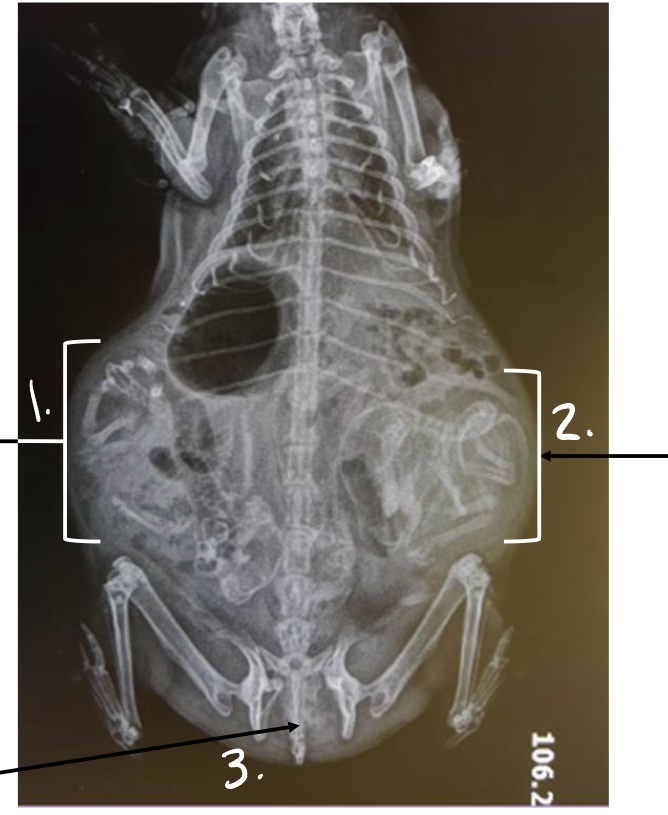
what is this radiograph showing?
guinea pig fetus
guinea pig fetus
open pubic symphysis
when a guinea pig sow is close to parturition, what opens up?
pubic symphysis ligaments
what is relatively common in both guinea pigs and chinchillas?
dystocias (difficult or obstructed pregnancy)
when should a guinea pig sow have a litter?
prior to fusion of pubic symphysis by 6-9 months
what happens if a sow has a litter before the fusion of the pubic symphysis?
cartilage union forms and persists for life
what expands prior to parturition to allow passage of large feti?
cartilage union
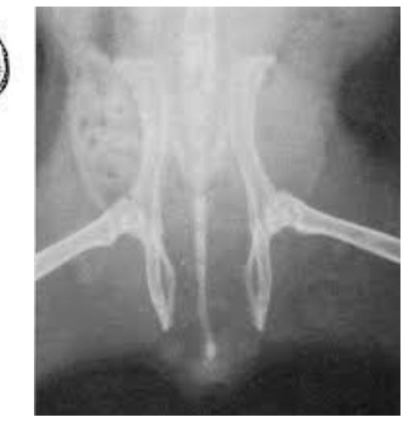
what is this radiograph showing?
open/relaxed pubic symphysis of Guinea pig sow