Mendelian Inheritance Terms & Definitions | Biology Study Set
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Theory of Pangenesis
- proposed by Hippocrates
- "seeds" are produced by all parts of the body
- collected in reproductive organs
- then transmitted to offspring at the moment of conception
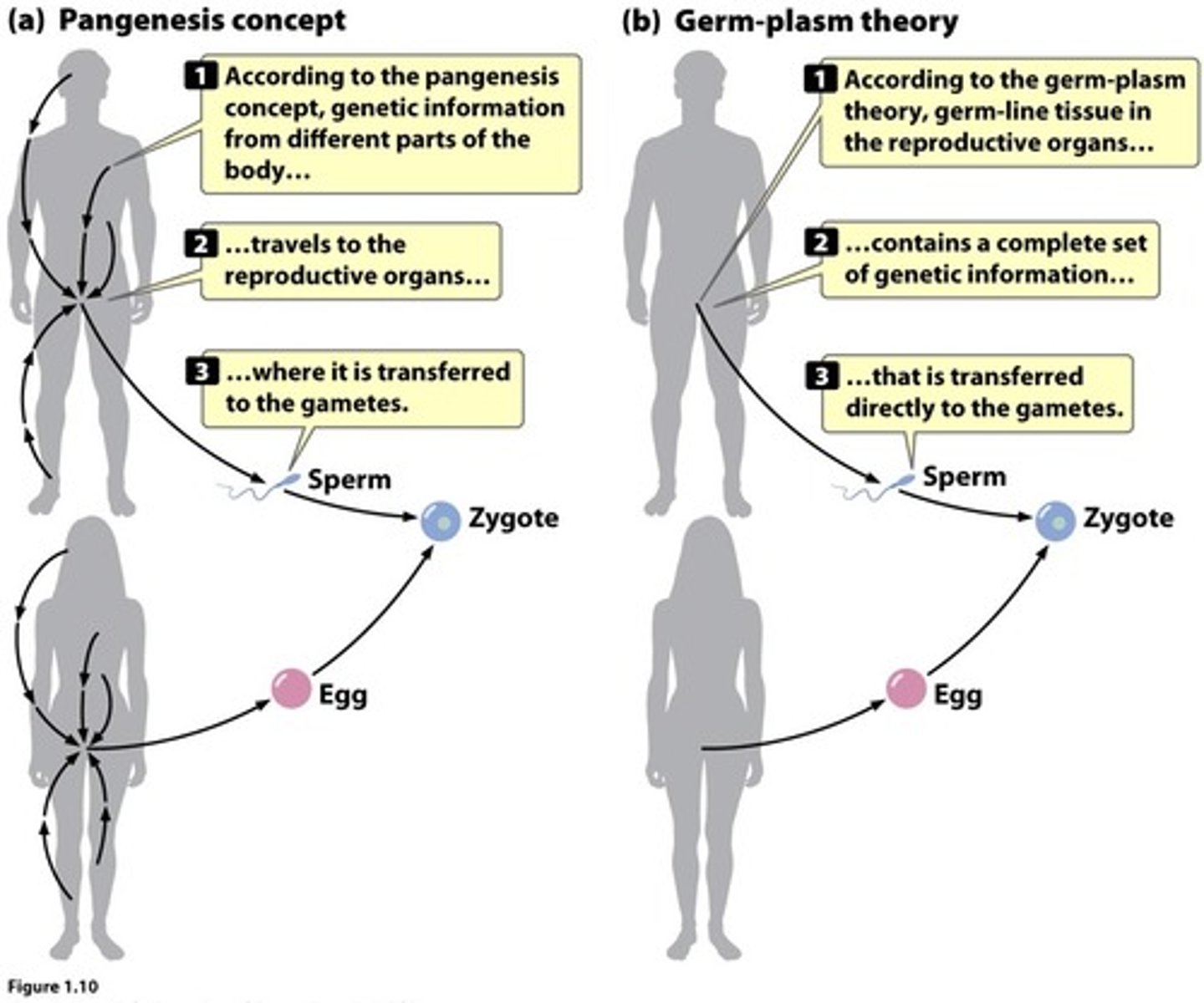
Theory of preformation
Stated that the fertilized egg contains a complete miniature adult, called a homunculus
- is incorrect
Blending Theory of Inheritance
-Factors that control hereditary traits are malleable
-They can blend together from generation to generation
Gregor Johann Mendel
Father of genetics
- chose garden pea to study the natural laws governing plants hybrids
Laws of Inheritance
law of dominance,
law of segregation,
law of independent assortment
gardening pea (Pisum Sativum)
- existed in several varieties with distinct characteristics
- structure allowed for easy crosses where the choice of parental plants could be controlled
Hybridization
taking chromosomes from 2 different individuals and fusing them together
- purple plant x white plant
Hybrids
Offspring of crosses between parents with different traits
Two types of crosses
- self-fertilization
- cross fertilization
self-fertilization
When pollen fertilizes eggs from the same flower
- occurs in peas due to a modified petal isolates the reproductive structures
cross-fertilization
Pollen and egg are derived from different plants
- required removing and manipulating anthers
cell fertilization
characters
morphological characteristics of an organism
- Ex: eye color
what characters that mendel study
- height
- flower color
- flower position
- seed color
- seed shape
- pod color
- pod shape
trait/variant
the specific properties of a character
- Ex: blue eyes
what variants did Mendel study
Tall/dwarf = height
purple/white = flower color
axial/terminal = flower position
yellow/green = seed color
round/wrinkled = seed shape
green/yellow = pod color
smooth/constricted = pod shape
emperical approach
evidence based method that draws on observation and experimentation
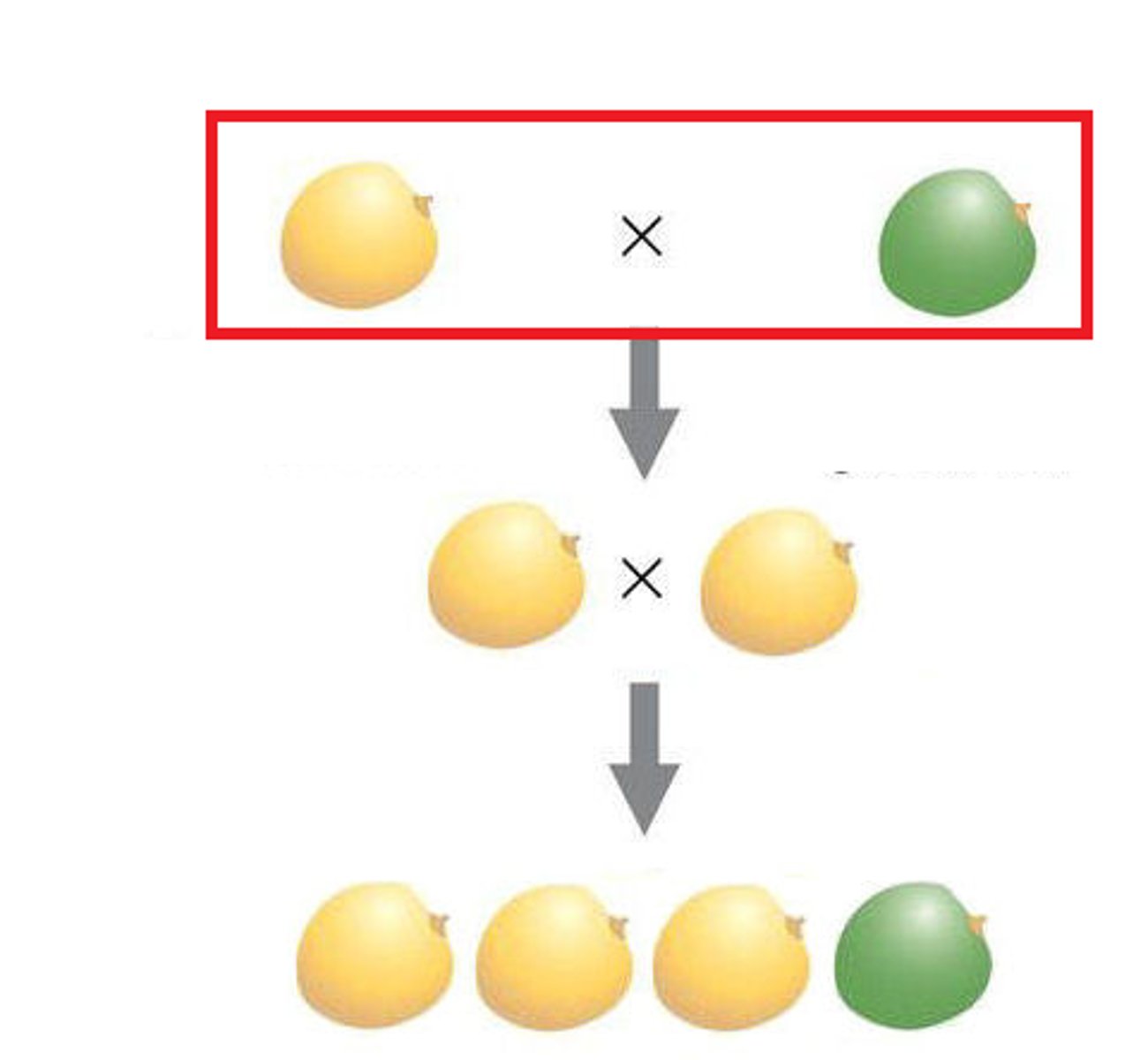
true-breeding
Organisms that, when reproducing, create offspring of all the same variety.
(usually involves homozygous genes)
P generation
Parental generation, the first two individuals that mate in a genetic cross
Homozgous Dominant
Both alleles (factors) for a trait are the same and dominate (AA)
homozygous recessive
Both alleles (factors) for a trait are the same and are recessive (aa)
- are not functional

heterozygous dominant
two different genes; Aa
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.

Phenotype
the set of observable characteristics of an individual resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment.
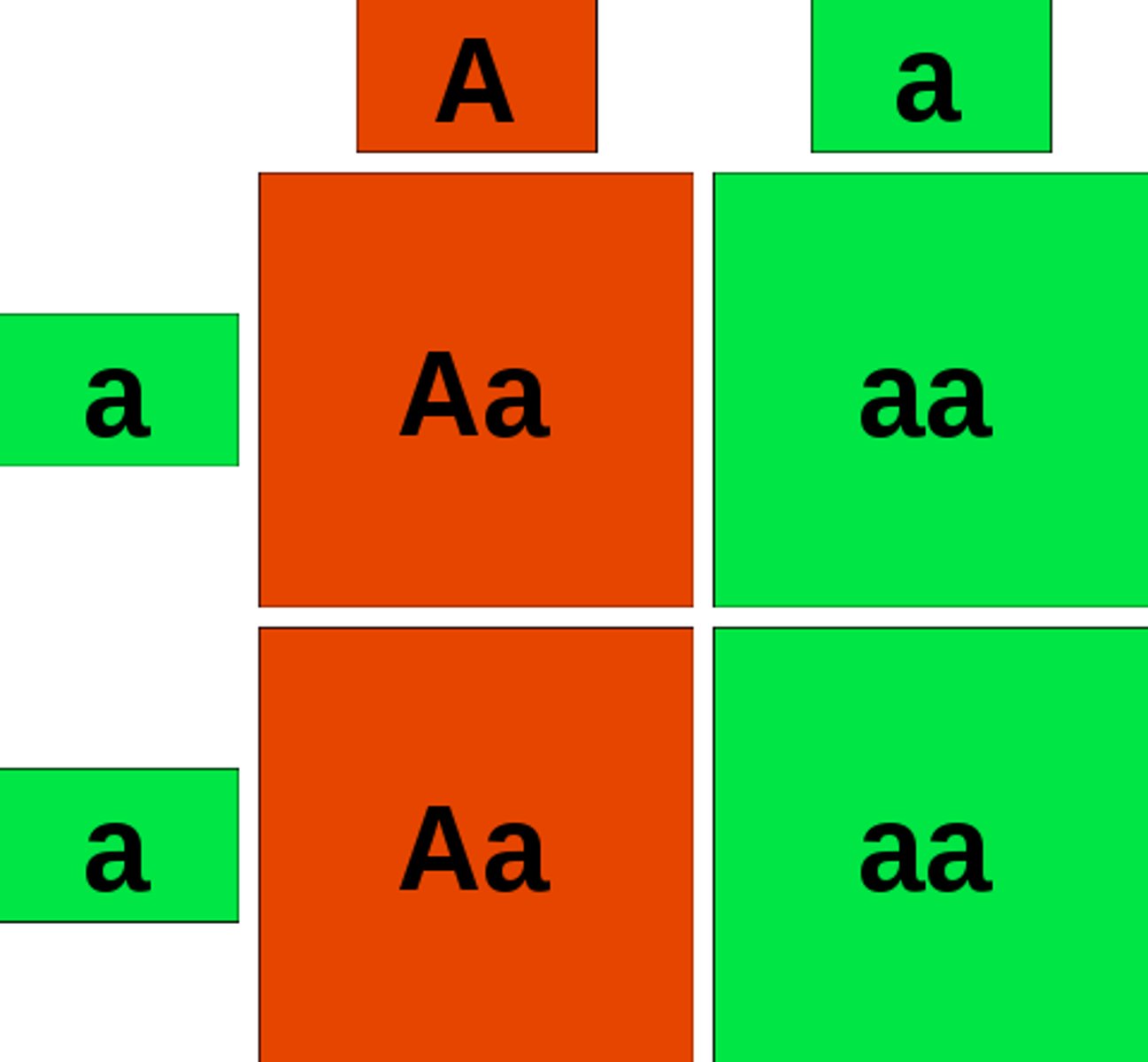
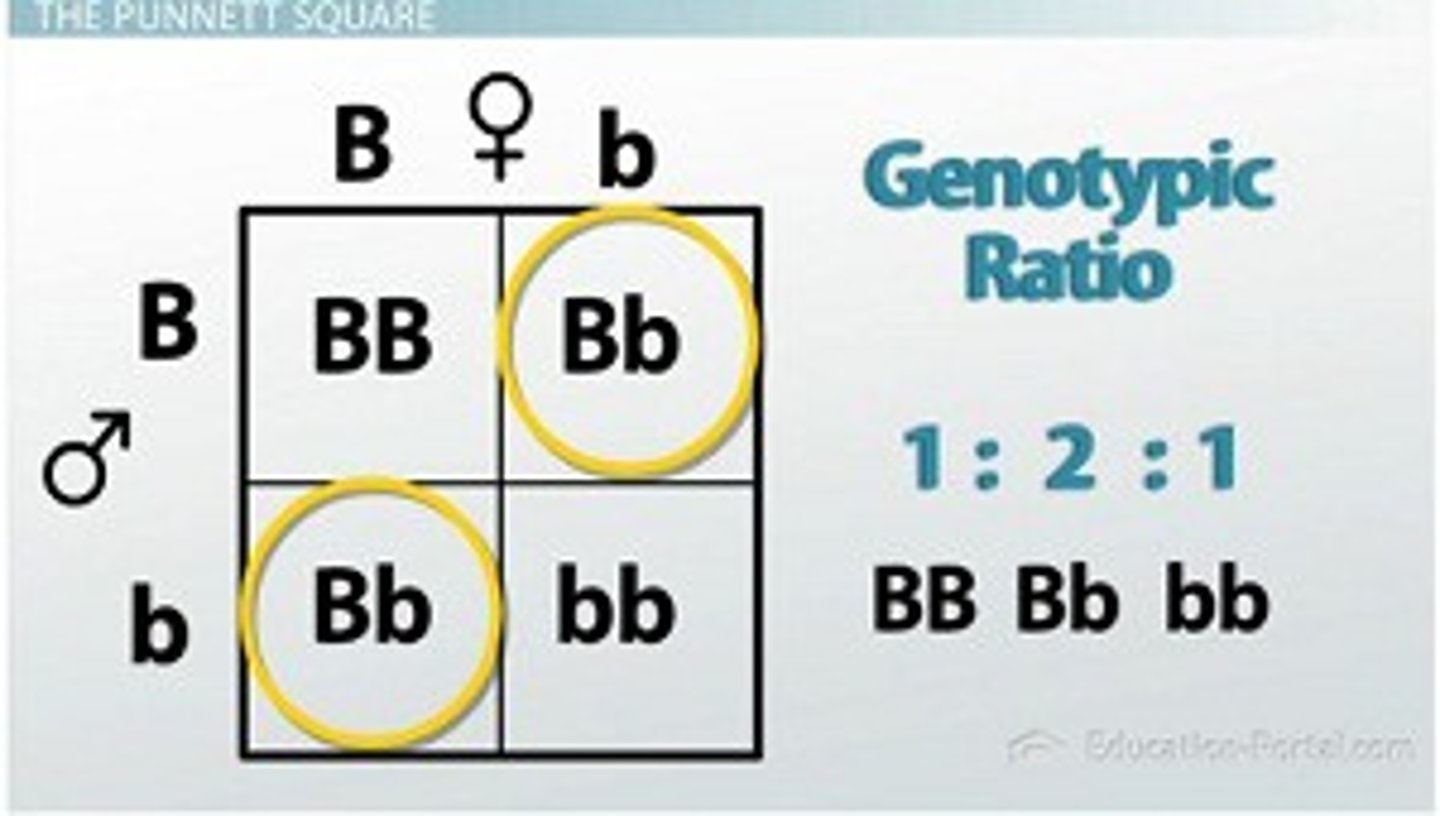
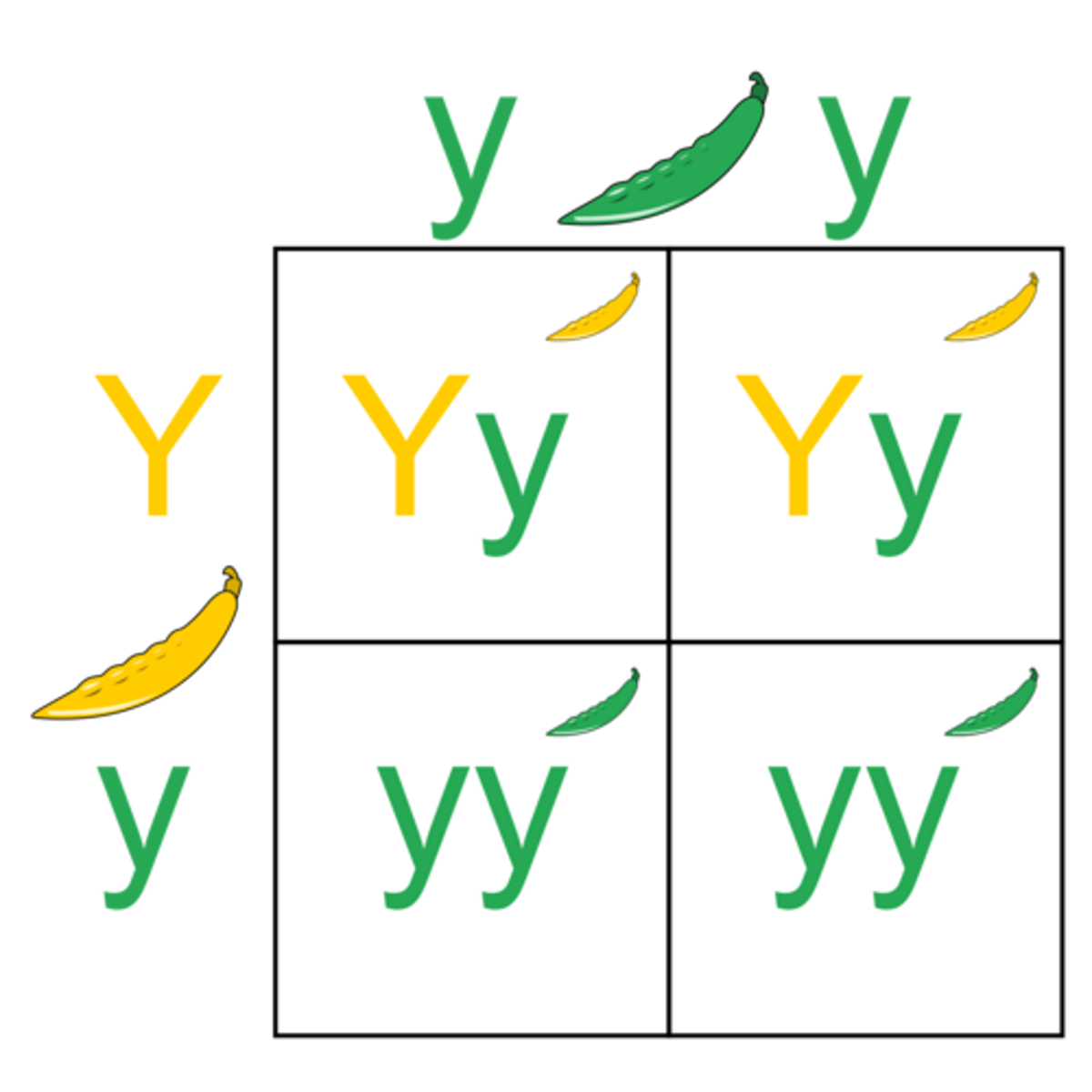
monohybrid cross (single factor cross)
A cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits (one gene, one character)
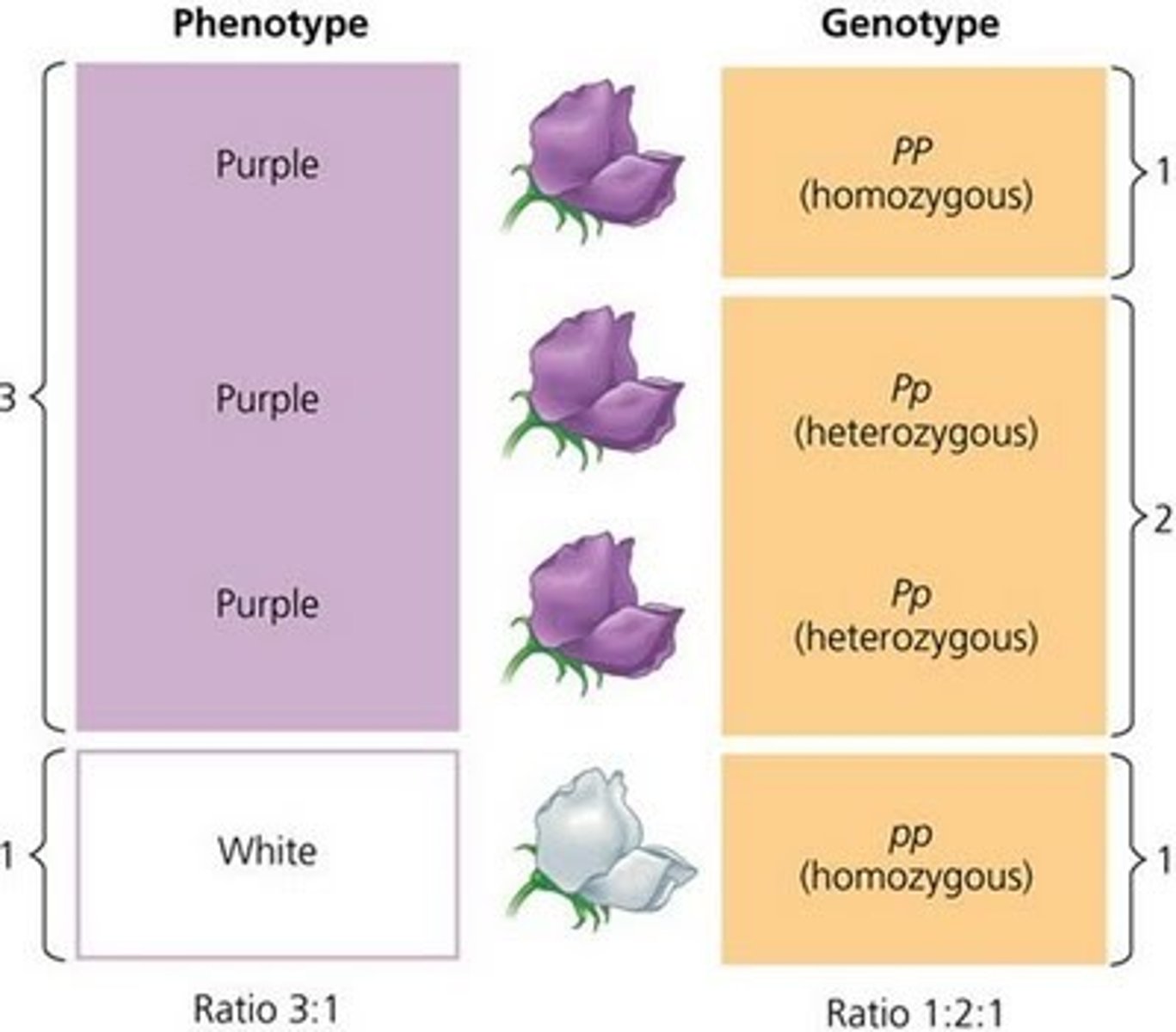
phenotypic ratio
the ratio of phenotypes that could appear in offspring
3:1 (P_ dominant)
genotype ratio for monohybrid cross
1:2:1 (HD, HD, HR)
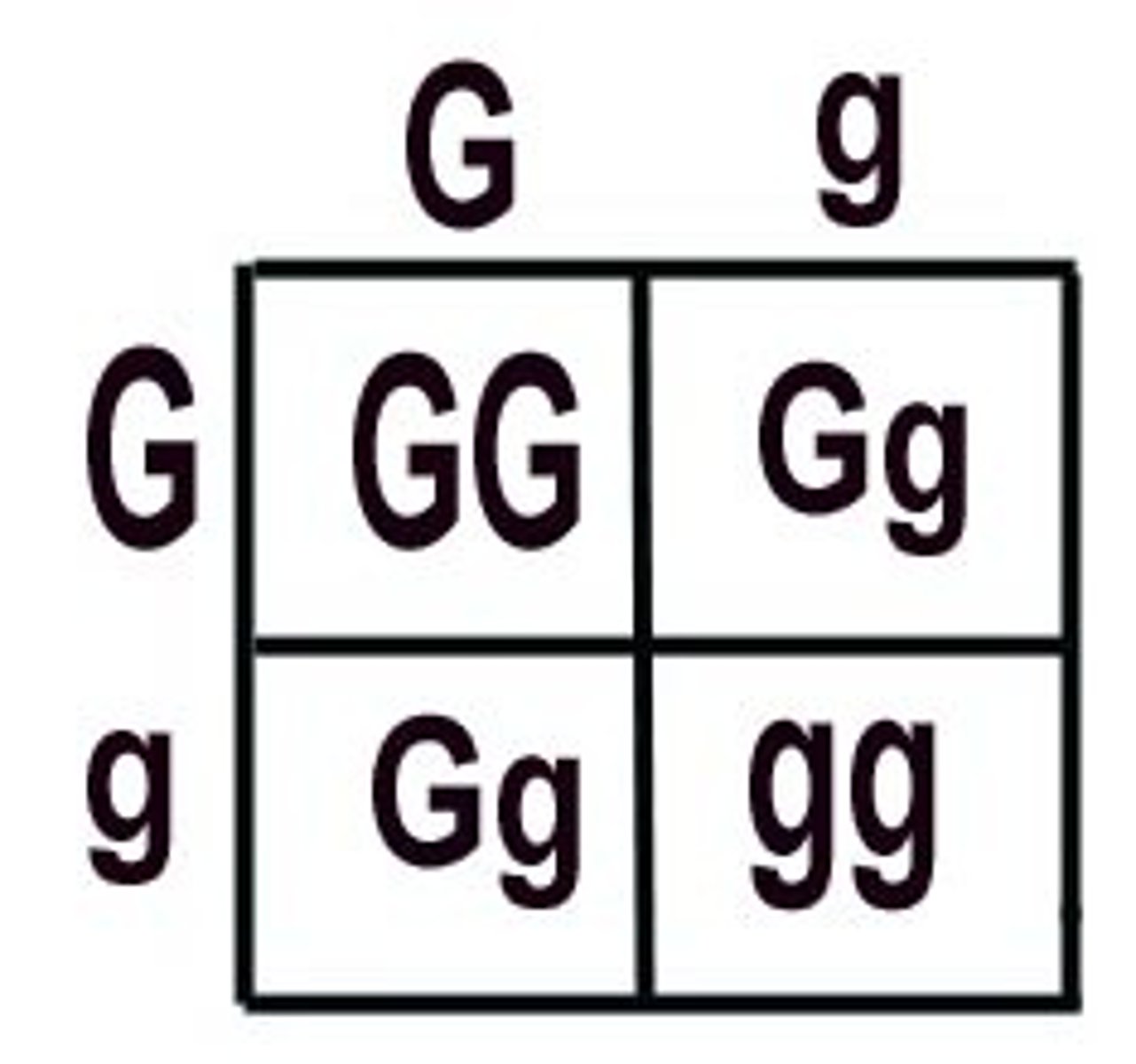
genes vs alleles
Genes: the factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next.
Alleles: Different forms of a gene.
model organisms
species that are easy to raise in the lab and use in experiments
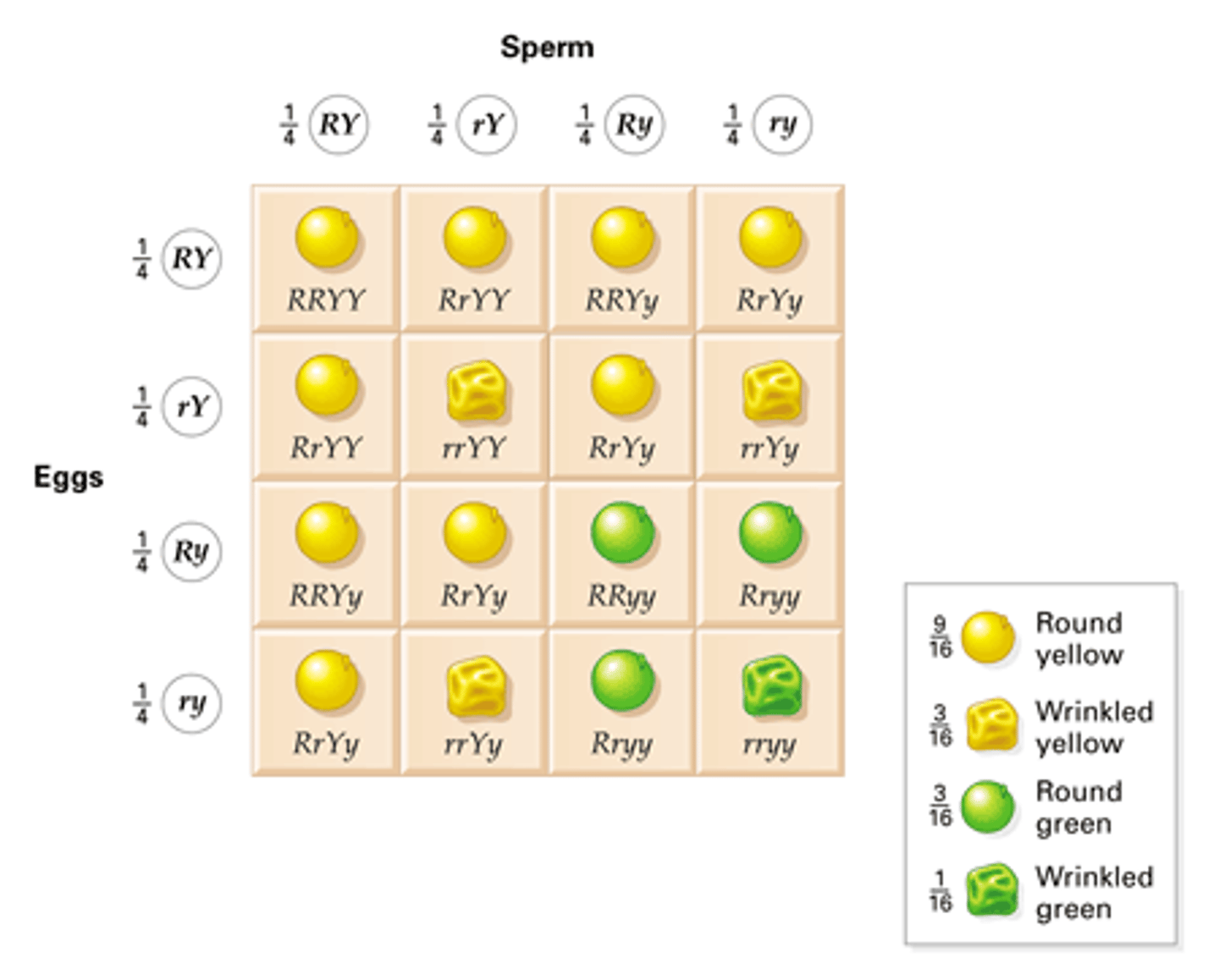
dyhybrid cross
a cross between 2 genes that have different alleles for the same gene
-----------------
Phenotypic ratio
9:3:3:1 ratio
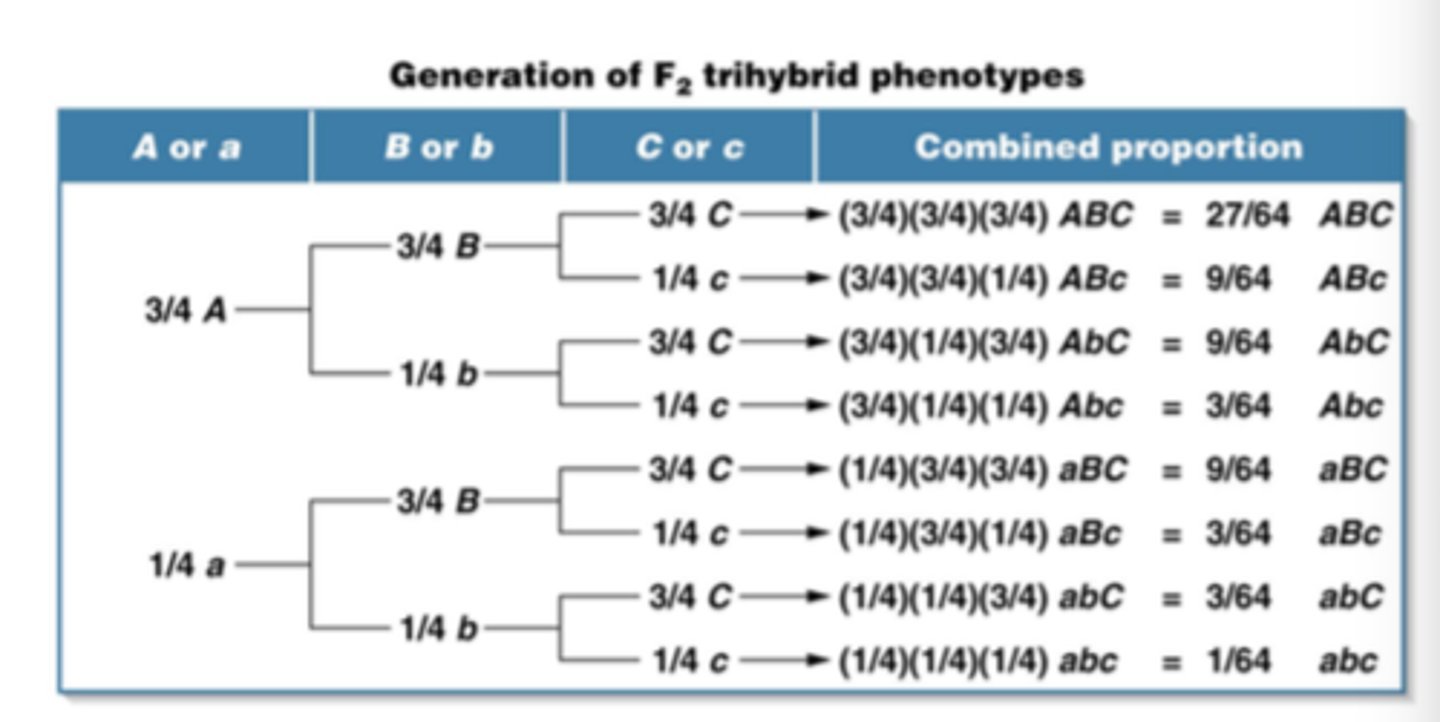
Branch Diagram
diagram that considers contrasting pairs of traits separately then combines results based on a set of assumptions
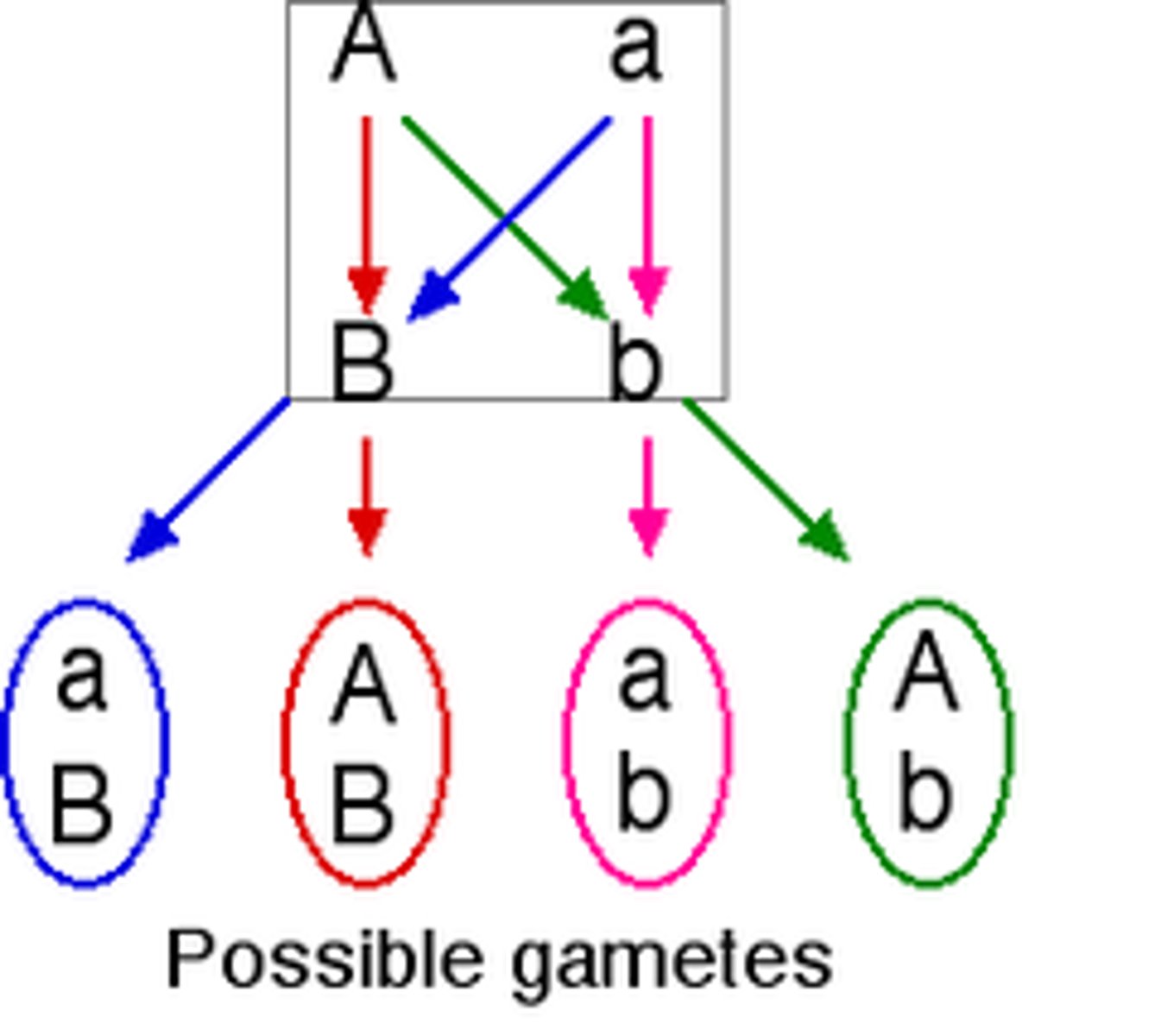
law of independent assortment
genes separate independently of one another in meiosis
-----------------
- during gamete formation, the segregation of any pair of hereditary determinants is independent of the segregation of other pairs
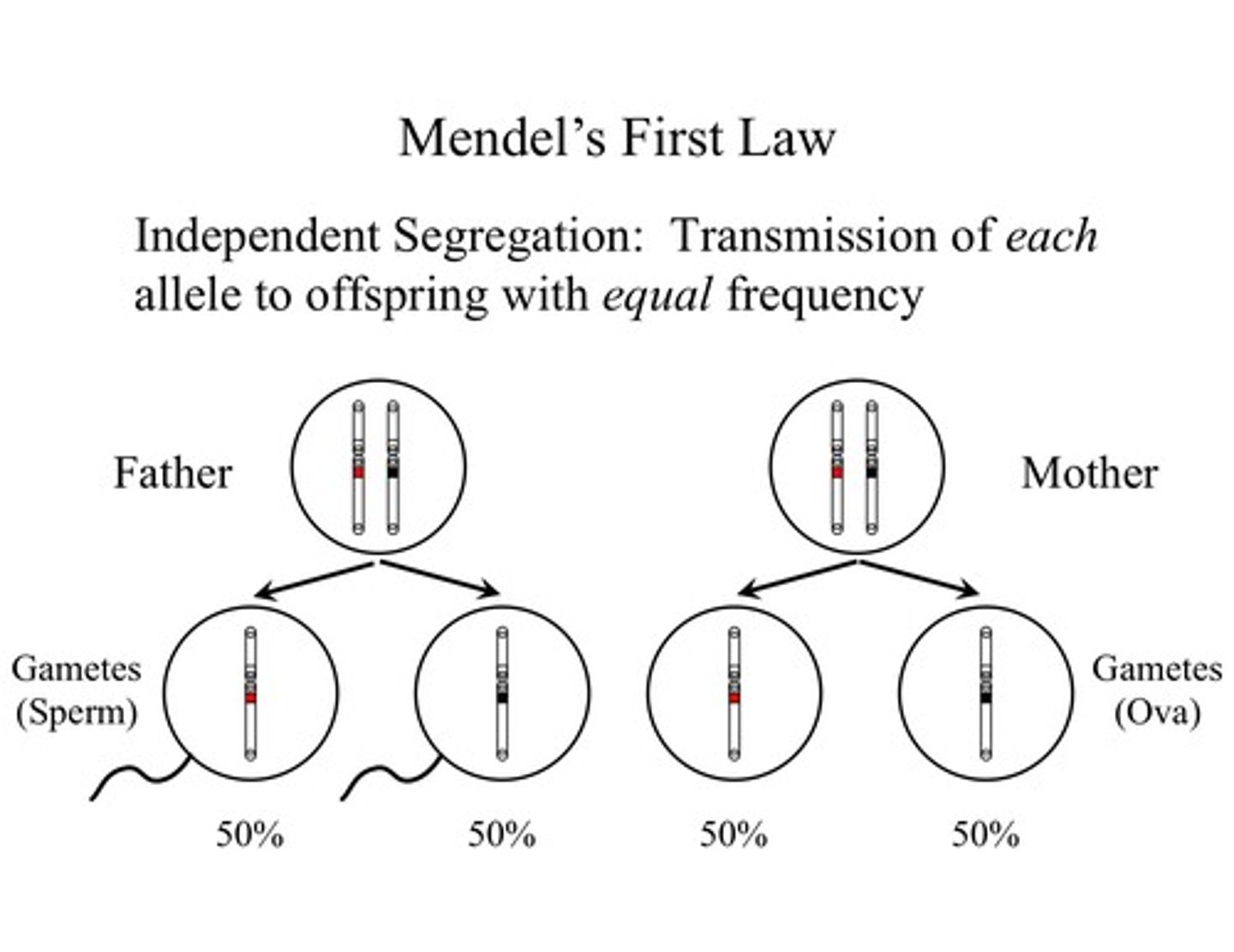
Law of Segregation
pairs of genes separate in meiosis and each gamete receives one gene of a pair
- allelic pair that separates during meiosis
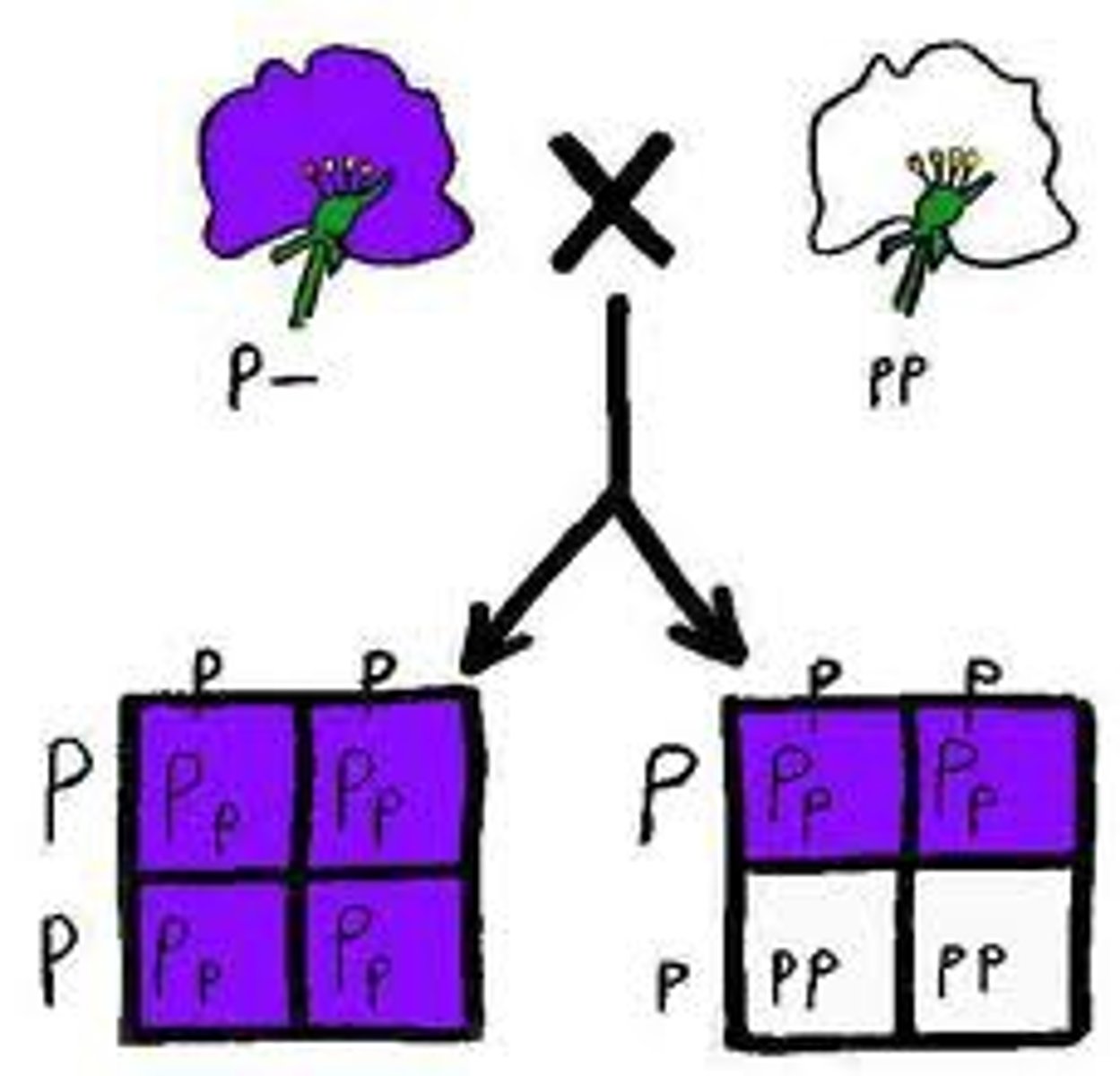
test cross
the crossing of an individual of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the unknown genotype
loss-of-function allele
a mutant allele that does not produce a functional product
- usually occurs on recessive alleles
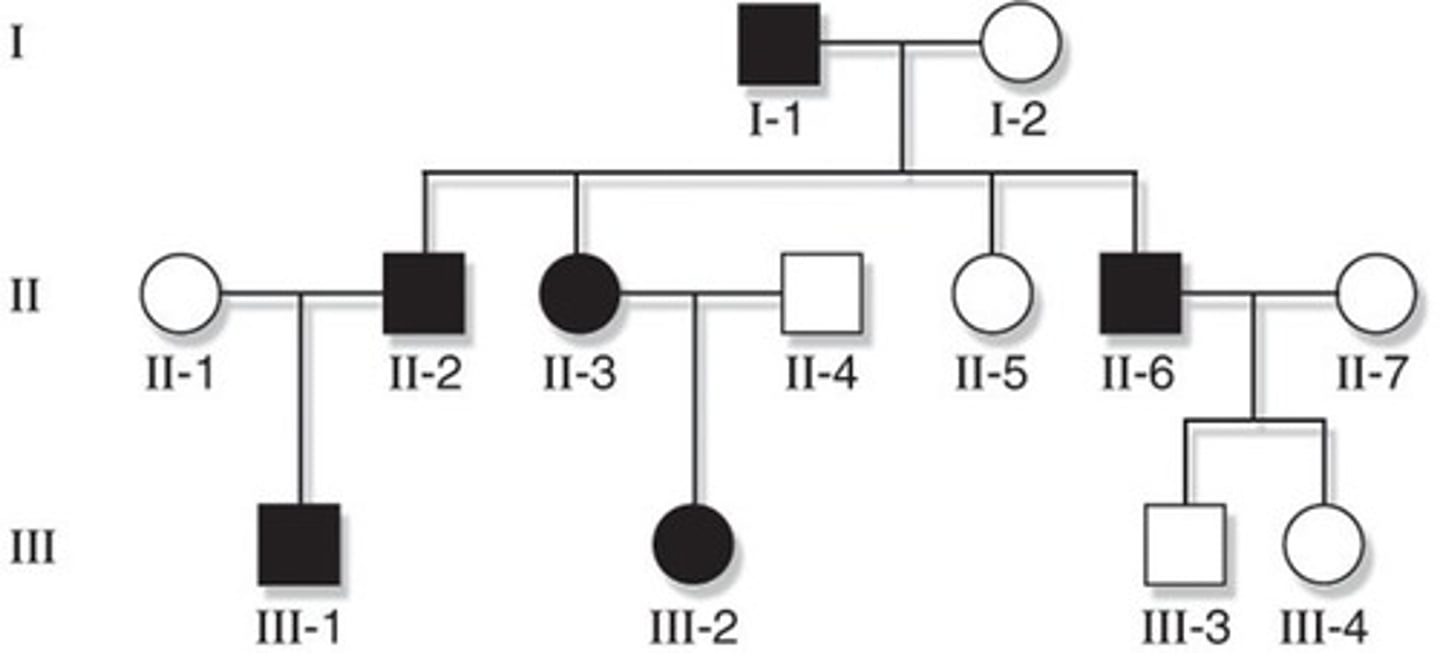
Pedigree
A diagram that shows the occurrence of a genetic trait in several generations of a family.
pedigree analysis
Chart showing one trait being carried over many generations
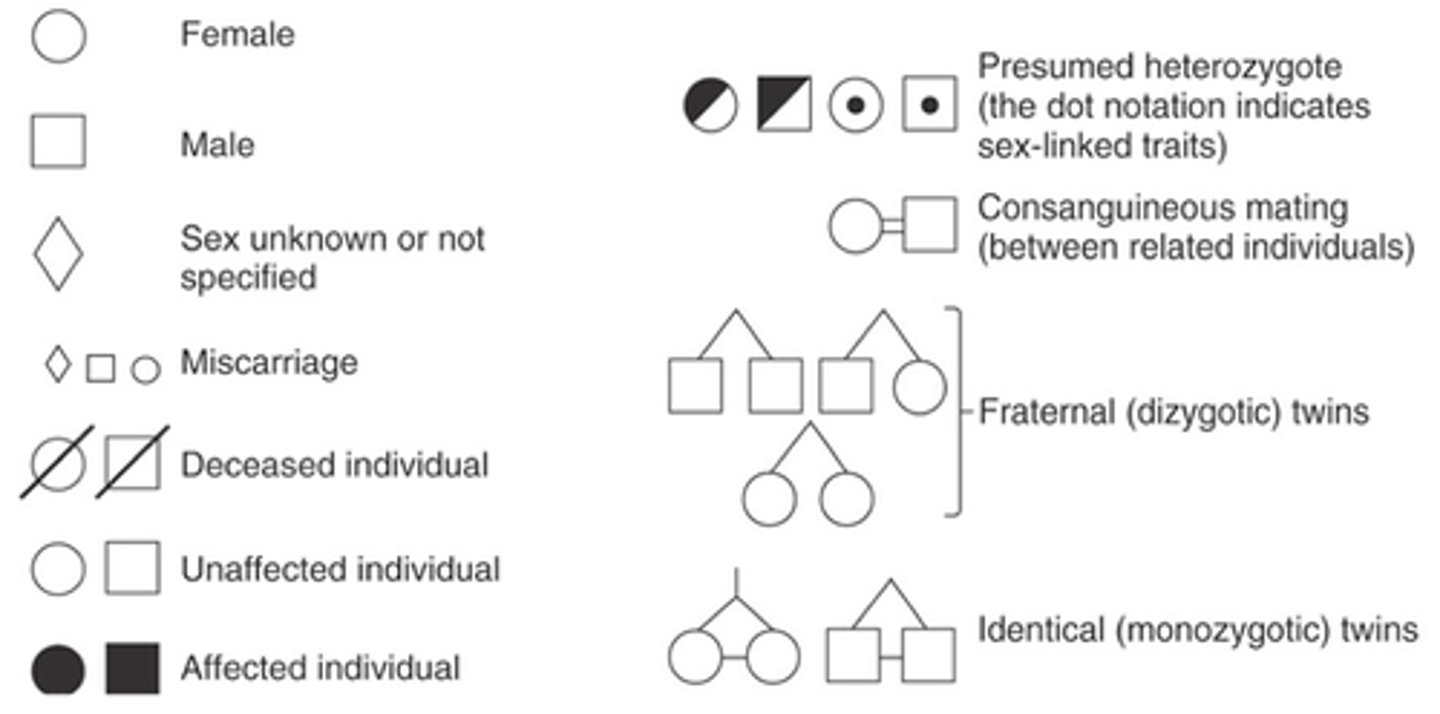
Pedigree symbols
Squares are male. Circles are females. Shaded means you have disease. Half shaded means you are a carrier
modes of inheritance
Autosomal dominant
Autosomal recessive
X-linked dominant
X-linked recessive
Y-linked
autosomal dominant
anyone affected must have al least 1 affected allele
------------------
- R = affected (RR or Rr)
- r = unaffected (rr)
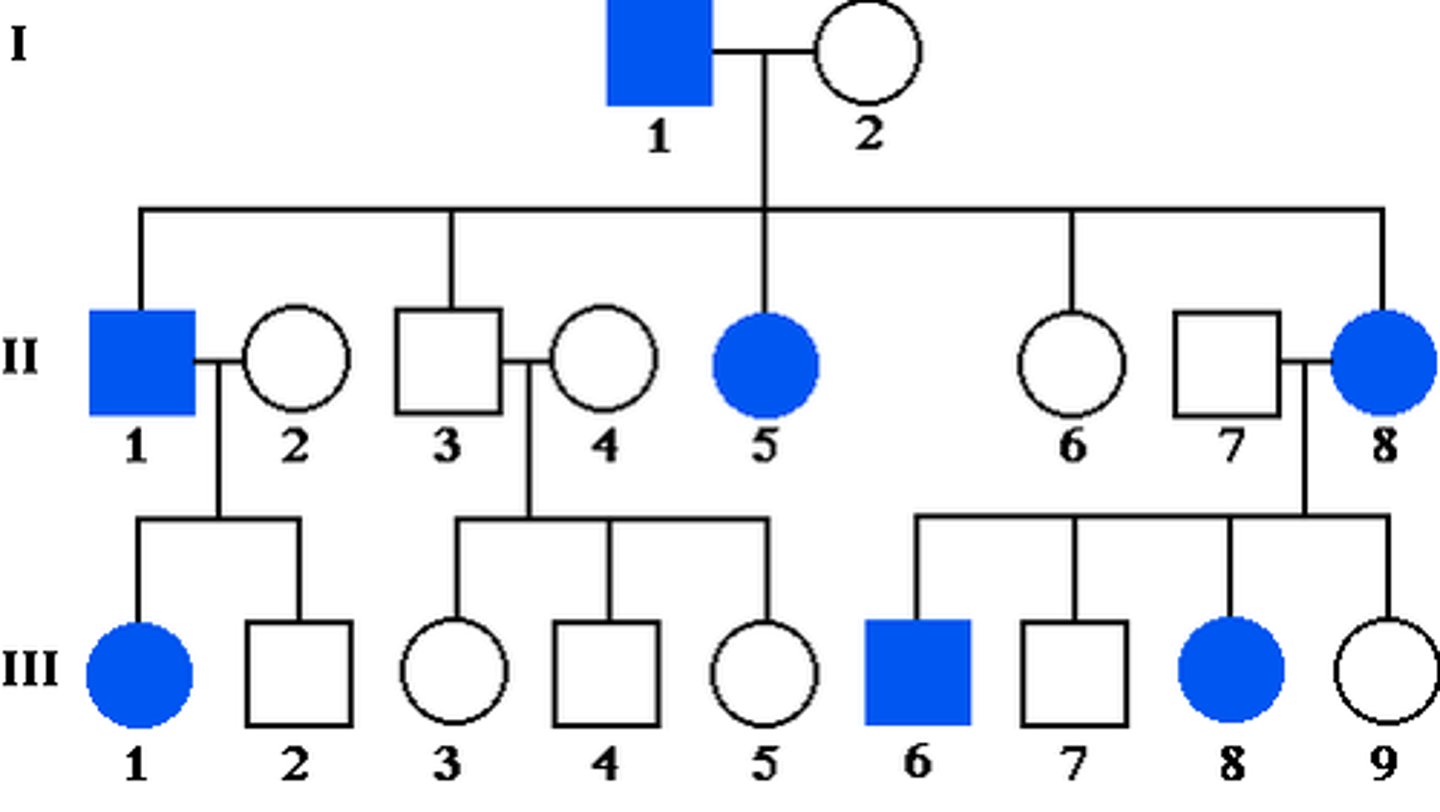
autosomal recessive
anyone affected must have the homozygous recessive genotype
------------------
- R = Unaffected (RR pr Rr)
- r = affected (rr)
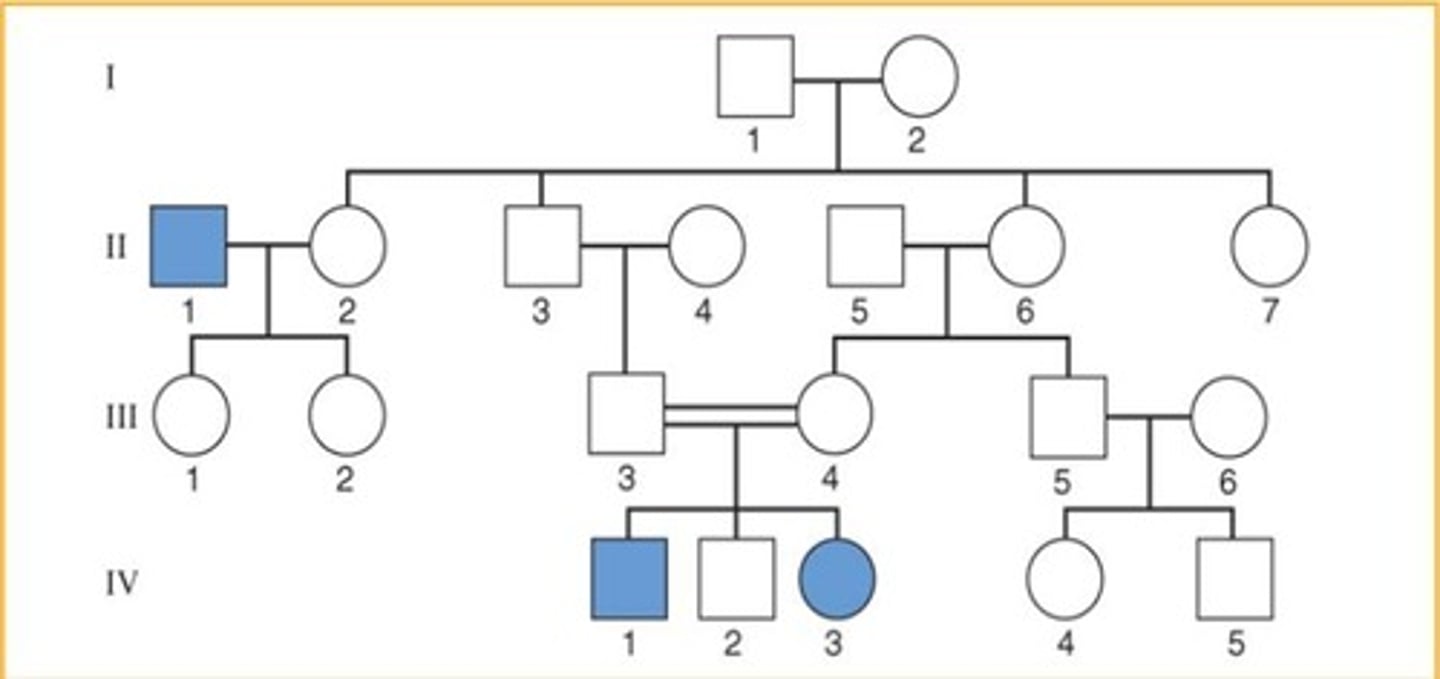
X-linked dominant
Father passes its XD to all his daughters
- does not skip generations
------------------
- father= XDY
- daughters= XDX
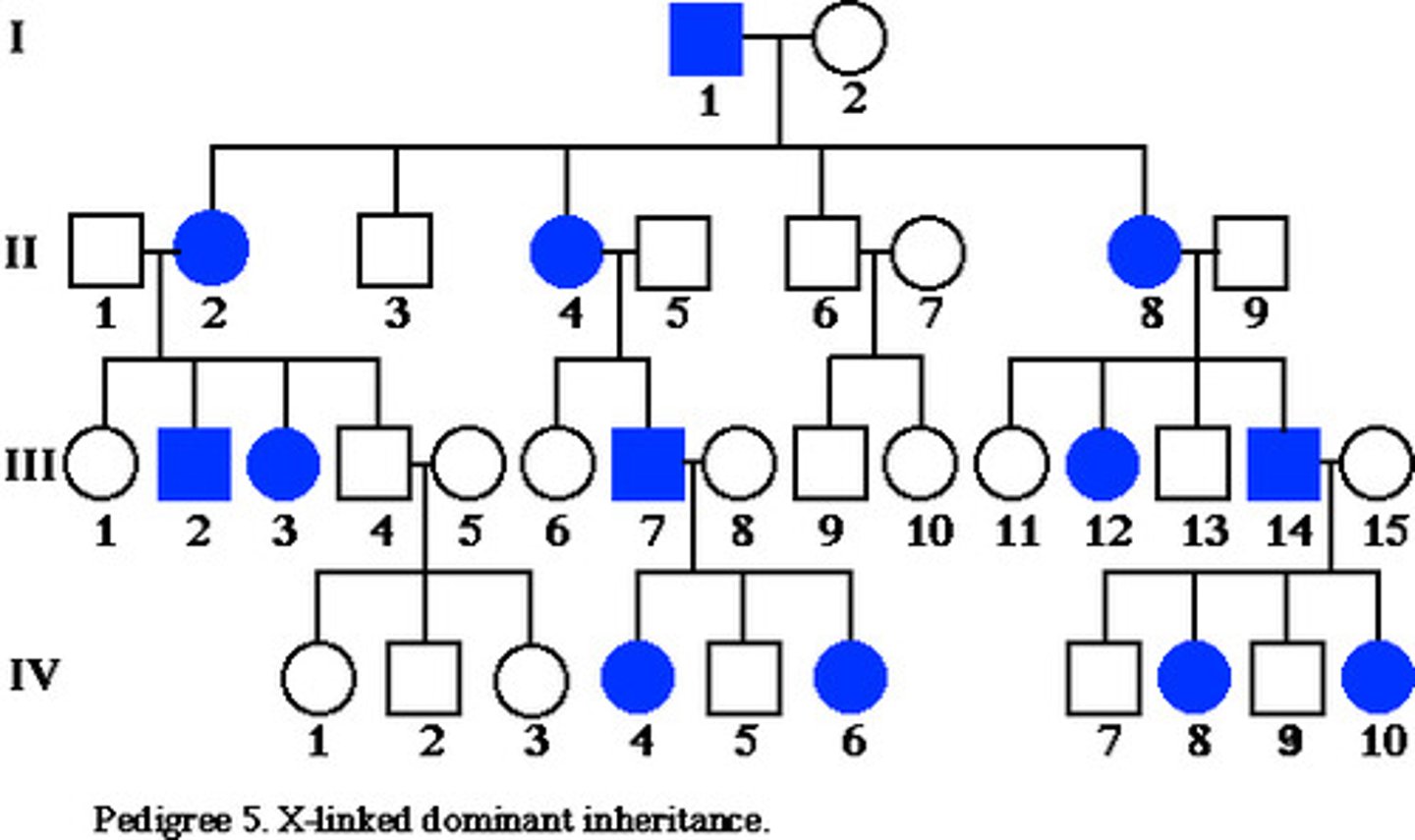
X-linked recessive
carried by females and affects males (all sons)
- can skip a generation (but doesn't have to
------------------
affected
- son has to have XRY
------------------
unaffected
- men has to have XY
- women have to have XXR
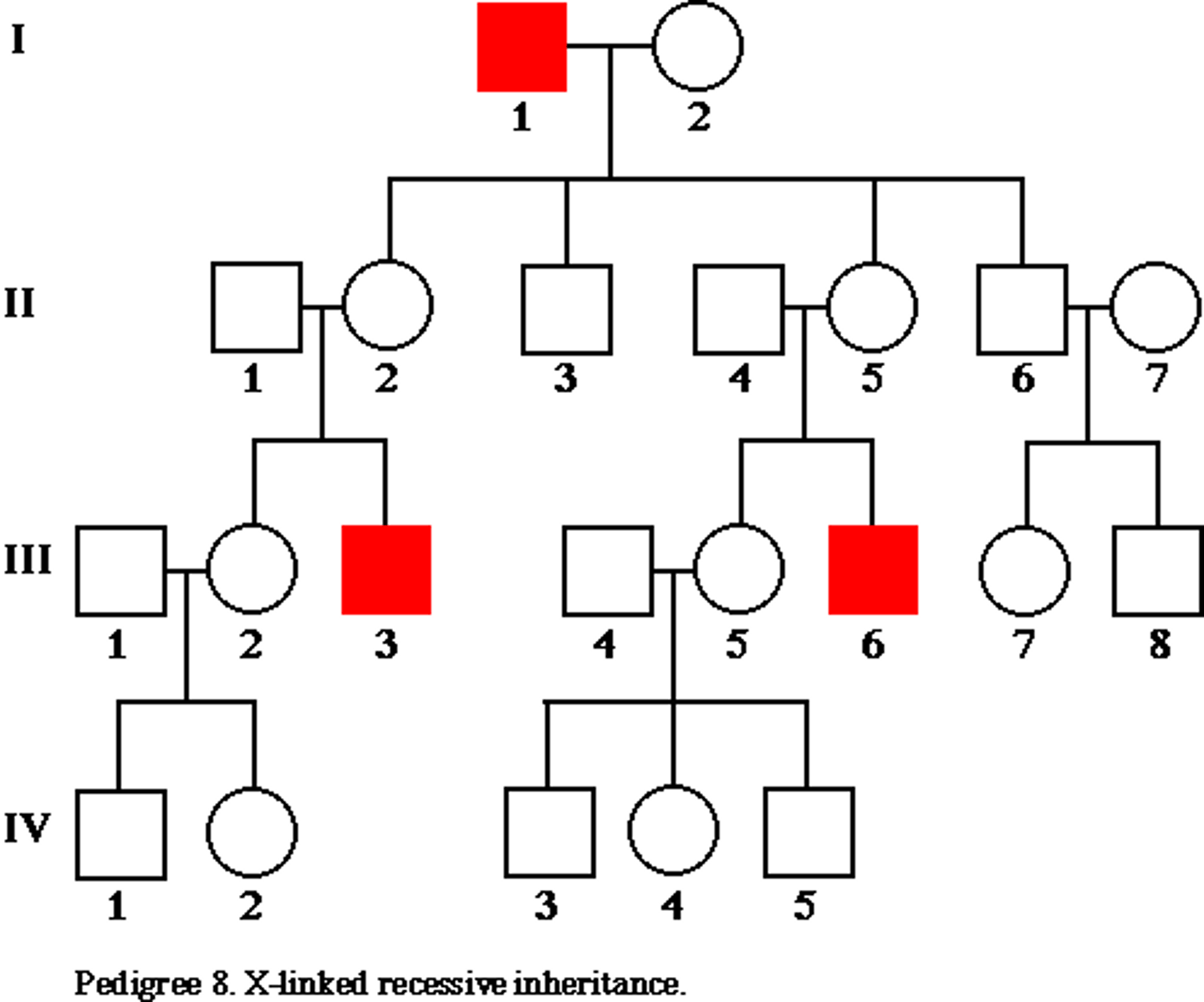
Y-linked
only males affected
- passed on from generation to generation
------------------
- A = affected
- a = unaffected
Recessive models of inheritance
if you see any skipping then its a recessive
- remove any dominant models
cystic fibrosis (CF)
autosomal recessive mutation
- the gene encodes a protein called the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)
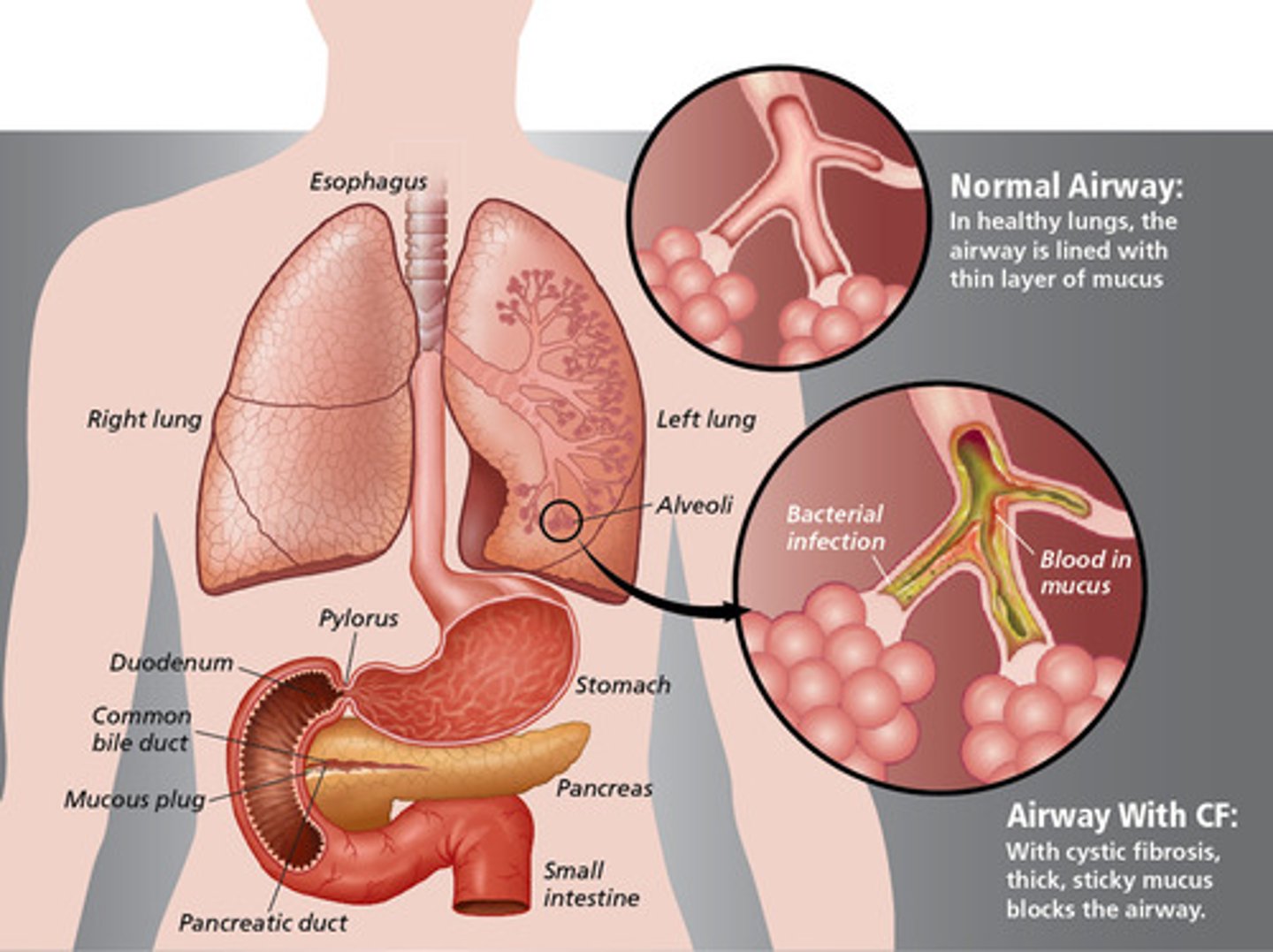
CFTR
- protein regulates chloride ion transport across the cell membrane
- mutant alles create an altered CFTR protein that causes ion imbalance
probability prediction (requirements)
the accuracy depends on the size of the sample
Probability Equation
(Number of desired outcomes) / (Total number of outcomes)

expected outcome vs observed outcome
observed: the results you see and record
--------------------
expected: the results you expect to see (forecasted results)
Product Rule
the probability that two or more independent events will occur is equal to the product of their individual probabilities
- when reading a question the word and signifies product rule
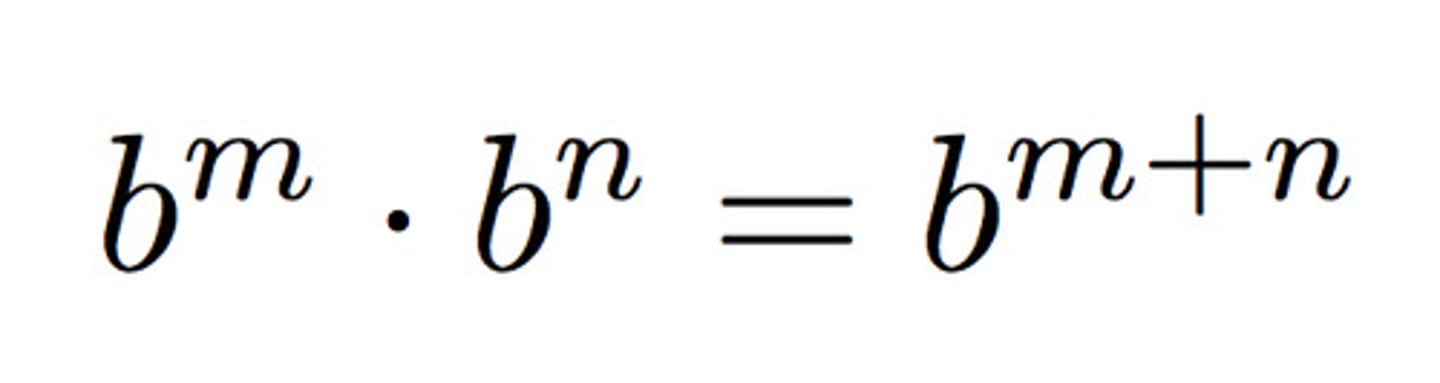
sum rule
probability of either of two mutually exclusive events occurring is the sum of their individual probabilities
- will always equals 1
binomal expansion equation
represents all of the possibilities for a given set of unordered events
-------------------
P= probability that the unordered outcome will occur
n = total number of events
X = number of events in one category
p = individual probability of x
q = individual probability of other category
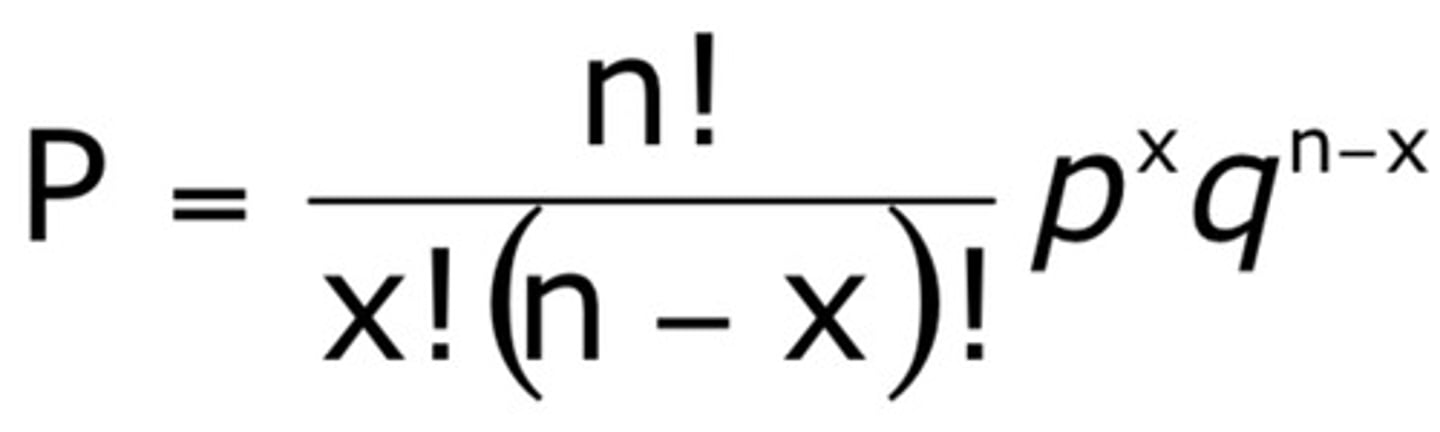
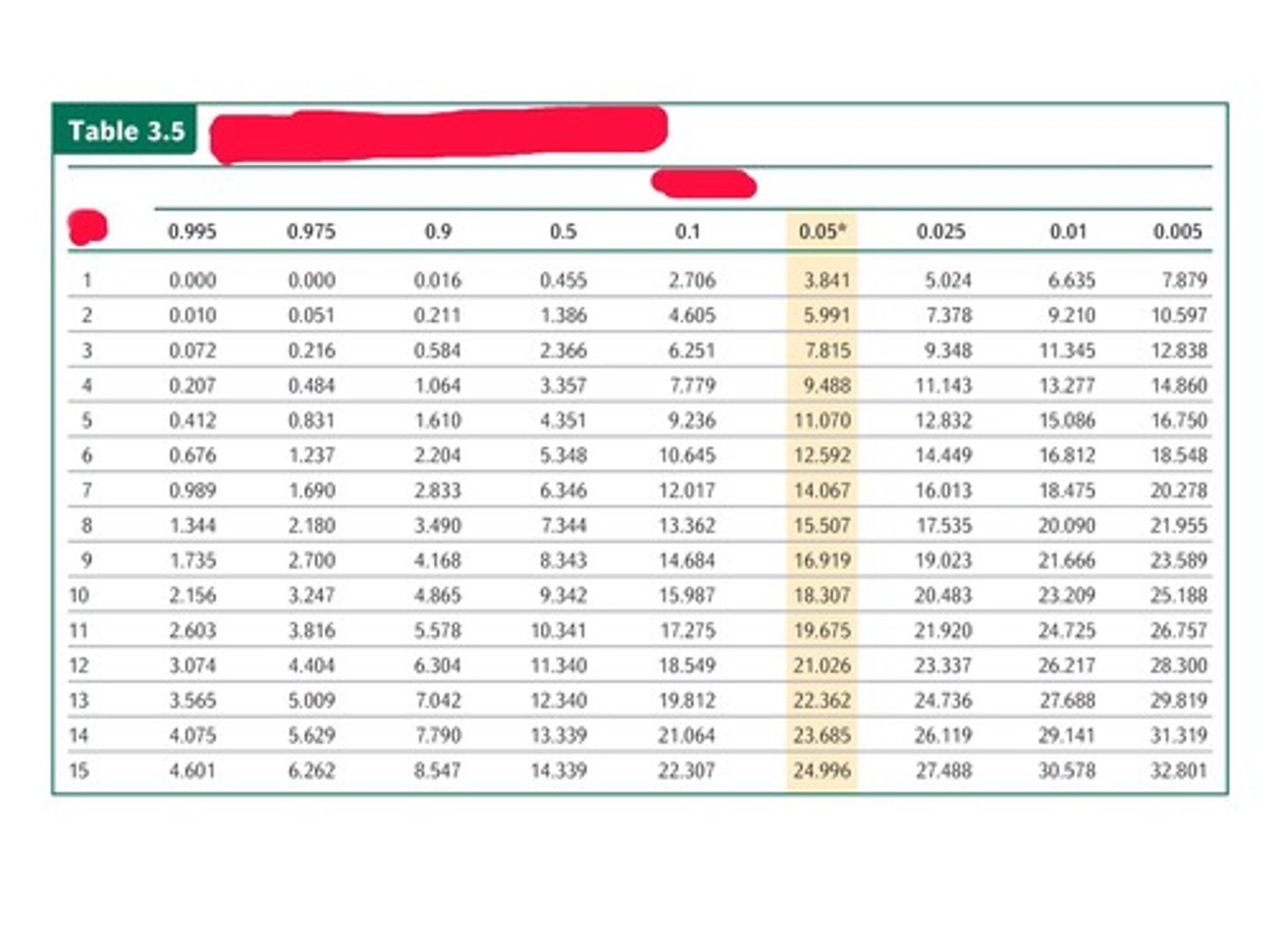
Chi-square test
method used to determine goodness of fit
- how close the observed data are to those predicted from a hypothesis
- dose not prove if a hypothesis is correct
chi square equation
(observed-expected)^2/expected
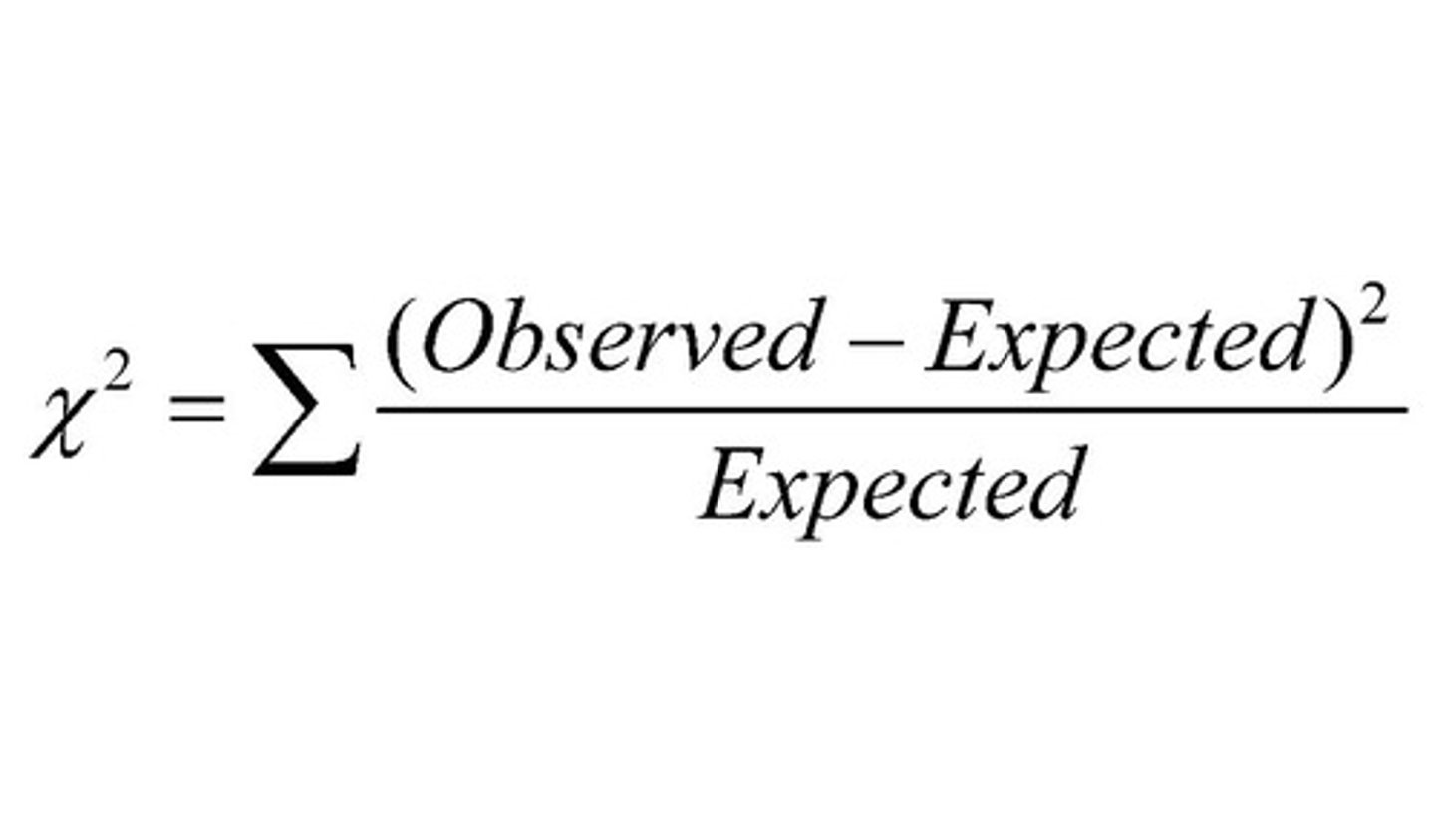
Low chi square values
high probability that the observed deviations could be due to random sampling errors
High chi square values
low probability that the observed deviations are due to random chance alone
- less than 5%
- usually rejects null hypothesis