Blood bank exam 3
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
PRBC stored in AS-3 storage requirements
1-6C temp
42 days
85% RBC retention
<5.0×10^6 WBC
FFP storage requirements
-18C or colder
1 year
min volume 180mL
Apheresis platelets storage requirements
20-24 C
5 days
3.0×10^11 plts min ph of 6.2
Whole blood derived plts derived storage requirements
20-24C
5days
5.5×10^10 plts
min ph of 6.2
PRBC open container- spiked
1-6C
24hrs
85% RBC retention
Cryoprecipitate storage requirements
-18C or colder
1 year
80 IU FVIII
What is the storage temp and transport temp requirements for All RBC products?
storage: 1-6C
transport: 1-10C
What is the storage temp and transport temp requirements for Frozen RBC products?
storage: -65C
transport: maintain frozen state
What is the storage temp and transport temp requirements for platelets?
storage: 20-24C with agitation
transport: 20-24C; can be without agitation for up to 30 hours
What is the storage temp and transport temp requirements for cold stored platelets?
storage:1-6C agitation optional
transport: 1-10C
What is the storage temp and transport temp requirements for Frozen plasma and cryo?
storage: atleast -18C
transport: must maintain frozen state
What is the storage temp and transport temp requirements for thawed plasma?
stored: 1-6C
transport: 1-10C
What is the storage temp and transport temp requirements for thawed cryo?
storage: 20-24 C
transport: 20-24 C
What is the storage temp and transport temp requirements for granulocytes?
storage: 20-24 C
transport: 20-24 C
Why do platelets need to be stored with agitation?
so they get proper oxygenation
How are platelets prepared from whole blood?
•A soft spin and then a hard spin
What are benefits of leukocyte reduction of blood product?
•Reduce the probability of CMV transmission
•Reduce the risk of HLA alloimmunization
•Reduce the likelihood of febrile, non-hemolytic transfusion reaction
What individuals would likely need an irradiated product?
•Immunocompromised patients, directed donations (all must be irradiated)
A unit of RBCs has an expiration date of 5/15/24. The unit is irradiated on 5/2/24. What is the correct expiration date post irradiation?
•5/15/24
What are donor requirements? (BP, Temp, weight, pulse, hgb)
a.Blood pressure
a.90-180mm Hg systolic; 50-100mm Hg diastolic
b.Temperature
a.37.5C (99.5F) or lower
c.Weight
a.50kg (110lbs)
d.Pulse
a.50-100 bpm without irregularities
e.Hemoglobin
a.Women – 12.5g/dL or higher Men – 13.0g/dL or higher
. What are the requirements for autologous donation?
•Must have physician's order
•No risk of bacteremia in donor
•Hemoglobin 11 g/dL or higher
•Blood must be collected 72 hours or more before procedure.
Which diseases have tests in post donation process?
HIV, HCV, HBV, syphilis, HTLV, WNV, ZIKA
Which diseases are screened for by question only?
•Chagas (tested only on 1st donation), CJD, Malaria
Which diseases are transmitted by mosquito?
•ZIKA, WNV, Malaria, Dengue
What is the vector and organism that are responsible for the transmission of Chagas disease?
•Kissing bug, Trypanosoma cruzi
What is a window period?
The time between when a person gets a disease and when a test can accurately detect it.
. What type of donors are given colony stimulating growth factor (CSGF)?
•Granulocyte
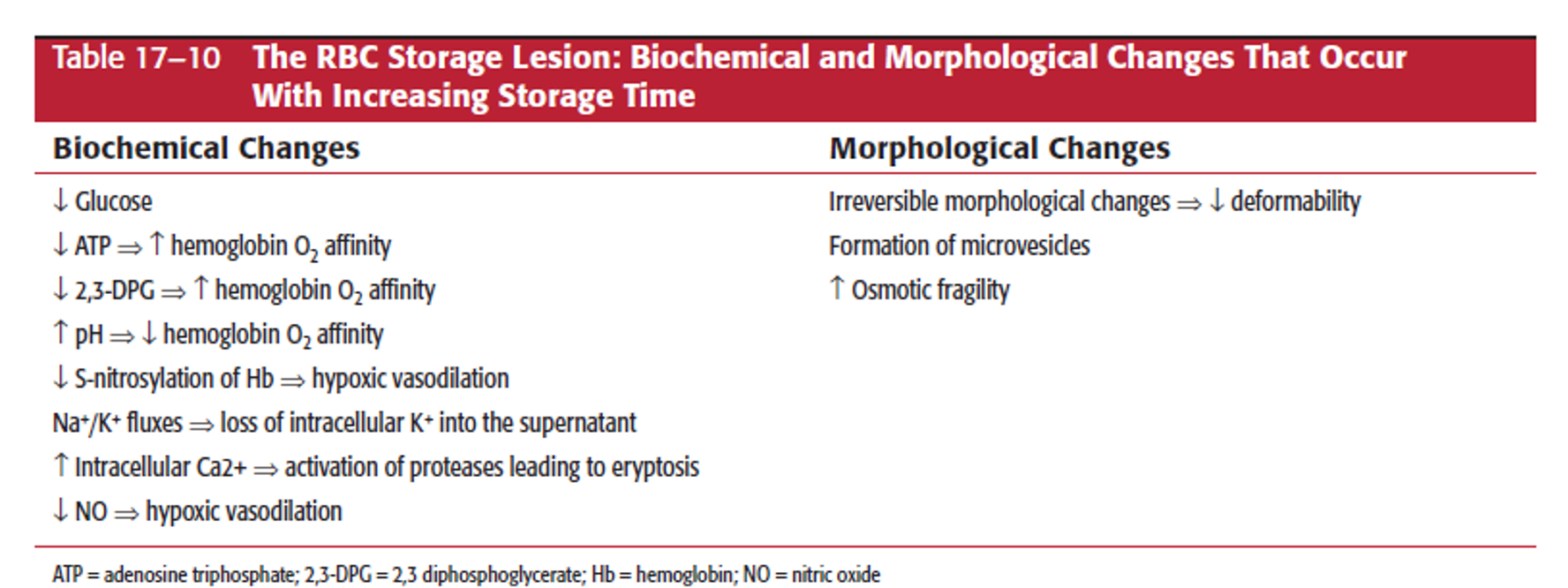
During RBC storage what types of storage lesion is there?
(What increases or decreases and what changes occur as it gets older?)

What are all the types of blood preservation solutions and how long do they make product good for?
•CPD and CP2D: 21 days
•CPDA-1: 35 days
. What are all the types of blood additive solutions and how long do they make product good for? which is preffered for neonates?
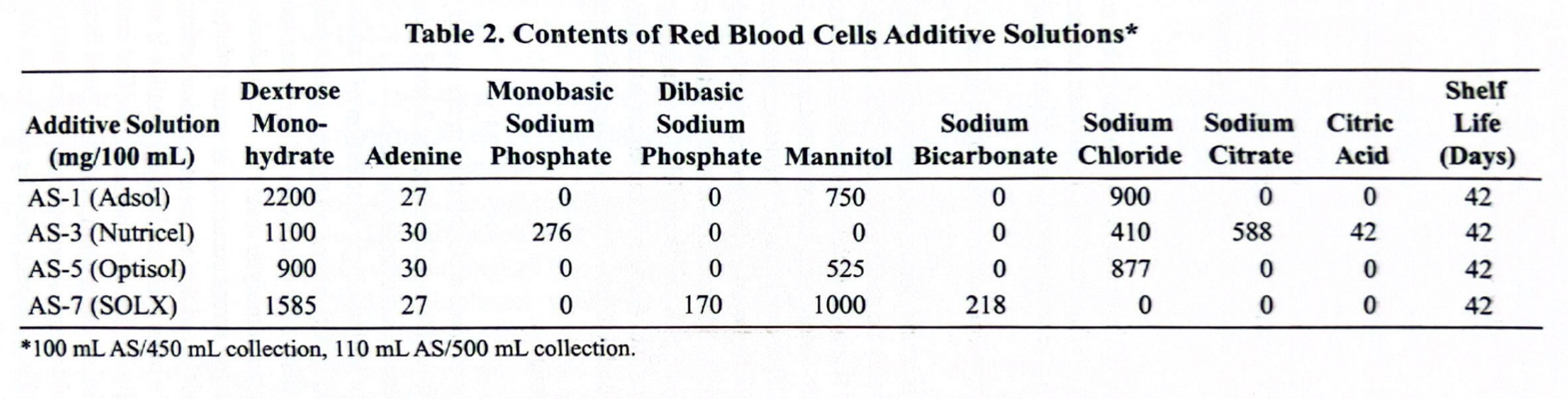
AS-3 b/c its lower in mannitol

How frequent can a person donate each of the following?
a.2 PRBCs
a.16 weeks
How frequent can a person donate each of the following?
a.Apheresis FFP (plasma)
a.Infrequent donations no more than once every 4 weeks
b.Frequent donations more than 2 times a week at least 2 days apart
c.Weighed at each donation (must be 50kg (110lb) or higher)
How frequent can a person donate each of the following?
a.Whole blood
a.8 weeks
How frequent can a person donate each of the following? a.Apheresis platelets
a.2 day donation interval, 2 or more donations a week for single donation.
b.Once every 7 days for double or triple donations.
c.Cannot exceed 24 donations in a rolling 12 month period.
d.Platelet count 150,000/uL or greater
Can a person that has lived in UK between 1980 and 1996 donate blood?
•Technically due to recent changes yes, for test purposes no. (BOC lags behind)
Can an individual who has had syphilis donate?
•Current infection, no. Treated and 3 months have past, yes.
•Donor test for syphilis is still used because it is a good indicator of lifestyle choices.
Which diseases require a look back?
•HBV, HCV and HIV
How long is the deferral for body piercings?
•3 months
If someone had gonorrhea and was treated 16 months ago, would they be eligible to donate?
•Yes, eligible 3 months after treatment.
If someone was incarcerated, would they be eligible to donate?
•If less than 72 hours, yes
•If or more than 72 hours, not for a year
How long do you need to be of blood thinning medication to donate platelets? (aspirin, effient, Brilinta, plavix, zontivity)
•Aspirin and Feldene: 2 days after last dose
•Effient: 3 days after last dose
•Brilinta: 7 days after last dose
•Plavix and Ticlid: 14 days after last dose
•Zontivity: 1 month after last dose
Vaccine |
Hepatitis B and Influenza |
Measles, mumps, polio, typhoid and yellow fever |
German measles, chicken pox/shingles (varicella zoster) |
Hepatitis B Immune Globulin, unlicensed vaccines |
what is the deferral period for each?
Deferral period |
None |
2 weeks |
4 weeks |
12 months |
What therapeutic elements are contained in cryoprecipitate?
•Fibrinogen, fibronectin, FVIII, VWF, FXIII
How much fibrinogen and Factor VIII is in a unit of pooled cryo? (5 singles are in a pool)
•Minimum of 400IU FVIII and 750mg fibrinogen
What products do we use pathogen reduction on?
•Yellow products: Plasma, Platelets and Cryoprecipitate
What is the difference between 24 hour thawed plasma and 5 day thawed plasma?
•The information on the product label
If a donor tested Rh negative at immediate spin, would we label the unit as Rh negative?
•No, we would need to confirm donor is Rh negative with Weak D test.
Whole Blood Indication for transfusion:
•Symptomatic anemia with large volume deficit.
•Volume replacement – massive transfusion/trauma
PRBCs Indication for transfusion:
Symptomatic anemia (difficulty breathing, increased pulse)
Washed PRBCs Indication for transfusion
Reduce exposure to plasma proteins and some parts of preservatives like mannitol in AS-1, IgA deficient patient with anti-IgA, reduction of K+ when used right away.
*Remember washing shortens RBC lifespan to 24 hours and a platelet 4 hours.
Platelets Indication for transfusion
•Bleeding due to thrombocytopenia or platelet function abnormality (including anti-platelet drugs);
•Prevention of bleeding from BM hypoplasia; significant bleeding with <50k platelet count
FFP Indication for transfusion:
•Plasma protein deficiencies when clotting factor concentrates are available.
•Lack of multiple clotting factors.
•TTP
•MTP/trauma – can cause volume expansion
RhIg Indication for transfusion
For Rh negative pregnant women down regulates immune system to help prevent sensitization of mom to the D antigen
If a person is transfused, what is the increase in hemoglobin and hematocrit that should be seen on a CBC?
•~1 g/dL Hgb or 3% Hct increase per unit in a typical, non-bleeding, non-hemolyzing, 70kg adult
An OB patient has been followed closely throughout her pregnancy by a team of specialists and the local transfusion service and IRL. The patient has a rare antibody anti-Fy3, in addition to an anti-little e. The titers that have been increasing since the 2nd trimester and the baby's current vitals are indicating hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. The rare donor program doesn't have any frozen or liquid RBCs available for either mom or baby. What are the most likely sources to find compatible blood?
•Directed donation by a sibling of the patient or autologous donation by patient with MD approval
ou identify an anti-M in the serum during a workup on a patient which has caused an ABO discrepancy. This identifies the antibody / problem but it does not give you a front type and back type that are complementary. So: How will you perform the reverse type, to confirm/resolve this ABO?
use A1 and/or B cells which are negative for the M antigen
You ran an antibody ID panel and identified anti-Fya; everything else was ruled out. RBCs have been requested. Your next steps include ____? Select all that apply.
- Phenotype units and perform AHG crossmatches on the Fya- units
- Do an enzyme panel to prove that it is really -Fya
- Phenotype the patient for Fya: He should be Fya-
- Do a prewarm technique to abolish the reactions you saw
Phenotype the patient for Fya: He should be Fya-Phenotype units
perform AHG crossmatches on the Fya- units
We like to do "ruling out" using homozygous cells where possible because:
Antigens can show dosage
Why do immediate spin compatibility testing? Why not just type your patient for the ABO, and give identical units?
It will detect ABO-incompatible units, if you make an error in selection
A type and screen is performed on a 49-year-old woman who is scheduled for a hysterectomy in 1 week. Her blood type is A-positive, and her antibody screen was positive. There are 3 PRBCs preoperatively ordered. What must be done before her surgery date?
Identify antibody and phenotype units
Reviewing antibodies: After you've done a panel, performed your ruling out process, and identified what antibody most likely present in a patient sample, what test should you generally do on the patient's RBC?
Antigen/Phenotype
A 17 year old male presents at his high school's blood drive with the following vitals. Can he donate whole blood?
Blood Pressure: 110/70
Pulse: 67 BPM
Temperature: 37C
Hgb: 14.5 g/dL
and when can he donate again?
Yes, he can donate again after 8 weeks
What is the only process that can prevent transfusion associated graft verses host disease?
irradiation
What is the maximum transfusion time for any blood product?
4 hours
Jamie was born in the 1960's and lived through the era of the first discovery of HIV/AIDS and lost many friends. She is skeptical of the safety of blood transfusions and wants to donate for herself in preparation for her hip surgery the following week. Select the best answer for the autologous donation.
Temperature must not be >99.5F
Must donate at least 72 hours prior to surgery
Must have a Hgb >11.0 g/dL
All options are correct
all options are correct
To manufacture whole blood derived platelets, whole blood must be cooled towards 20-24C and then centrifuged in what order?
soft spin, hard spin
To be considered leukocytes reduced, a product must have less than what number of leukocytes?
< 5.0 x10^6
How many IU's of FVIII must be present in a pool of 5 single cryo?
a minimum of 400 IU FVIII
80 IU FVIII/ 1 --> 80 *5 = 400
True or False: Type O whole blood can be used interchangeably with type O packed RBCs.
False
True/ False Apheresis platelets must contain a minimum of 3.0x10^11 platelets per bag.
True
Adding additive solution to a unit of packed RBCs will lengthen the expiration date of the unit to ___________?
42 days
Pre-transfusion testing flow
Type, Screen, Identify, Phenotype, Crossmatch
What are the most commonly used additive solutions?
As-1 and As-3
Which additive solution does not contain mannitol?
AS-3
What is storage lesion?
degradation of cell viability and function over time
What products are whole blood derived?
- Whole blood
- packed RBCs
- Platelets
- FFP/Fp24
- cryoprecipitate
What products are apheresis derived?
- Packed RBCs
- platelets
- FFP/FP24
- liquid plasma
- granulocytes
Required radiation dose at the center of the field
25- 50 gray(gy)
Minimum radiation dose to any portion of the product
15 gy
Contents of cryoprecipitate
250 mg fibrinogen
FVIII (80IU)
FXIII
150 mg fibronectin
vWB factor
max volume to be collected from donors
10.5 mL/kg
What are crystalloids?
Saline, Electrolyte solutions, 5% dextrose in H2O
- volume expansion
What are colloids?
Albumin, Dextrans, hetastarch
What diseases are screened for only by question
Malaria and cjd
What diseases are screened for by both question and test
HBV, HCV, HIV 1,2