LEGL 2700 - Unit 4
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What classifies broadly as a “security” for the purposes of federal regulation?
Any note, stock, treasury stock, bond, debenture, evidence of indebtedness, certificate of interest or participation in any profit-sharing, agreement...(security = “owning an interest in a business managed by others”)
Why is there security regulation?
Coming out of Great Depression – designed to give potential investors sufficient information to make intelligent investment decisions based on factual information
Who at Federal Level?
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (main federal regulatory agency in charge of securities and their markets):
Responsible for administering the federal securities laws
Are there state level security laws?
"Blue Sky Laws"
Securities Act of 1933
Applies to the initial sale of the security
Requires the disclosure of information to the SEC and potential investors
Information must be true and not misleading
Sanctions for violations:
Criminal punishment
Civil liability
Equitable remedy of an injunction
Issuer
The business organization offering a security for sale to the public
Underwriter
Anyone who participates in the original of securities
Sells securities for issuer or guarantees the sale (generally the larger investment banks)
Helps issuer through process
Seller
Anyone who contracts with a purchaser causing the purchase to occur
What documents are required for an initial sale of securities?
Registration Statement and Prospectus
Who are the players involved in the sale of securities?
Issuer, Underwriter and Seller
Registration statement
Detailed disclosure of financial information about the issuer and controlling individuals (comprehensive document filed with the SEC that discloses detailed information about a company and its securities offering)
Prospectus
Contains financial information related to issuer and controlling person (specific part of that registration statement, serving as the offering document delivered to potential investors):
Provided to interested investor
Just conform to the statutory requirements
Does not mean it is a good investment! Could actually be a worthless investment!
Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (ongoing reporting obigations)
Regulates transfers of securities after the initial sale
Created the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): deals with regulation of securities exchanges, brokers, and dealers in securities
Rule 10b-5
CANNOT TRADE ON MATERIAL NON-PUBLIC INFORMATION!
Rule 10b-5
Principal anti-fraud rule on secondary market fraud issues
Civil action for people who are misled and injured
Criminal sanctions as well
Applies even if not a registered security
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) of 2002
Applies to all public companies in the U.S. and international companies registered with the SEC
Revitalization of SEC
Greater Regulation of Accounting Firms
Decline in restatements of financial reports may indicate the positive impact of Sarbanes-Oxley Act
The law enacted to correct inadequacies in the law that existed and allowed numerous examples of corporate fraud. In essence, through increased criminal sanctions and specific requirements, this law attempts to make corporate CEOs more responsible. It aims to protect investors by improving the accuracy and reliability of corporate financial reporting and disclosures. It was enacted in response to major accounting scandals
Revitalization of SEC
Increased SEC Budget
Increased power over governance issues
Congress empowered the SEC to increase corporate accountability
Greater Regulation of Accounting Firms
Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB)
Monitors accounting firms that audit public companies
Requires auditing firms to refrain from conducting non-auditing services
Changes to reporting structure for external auditors
Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010
Addresses many issues of financial reform
Congress authorized the creation of new administrative agencies to achieve the goals of Dodd-Frank Act
Solve the "too big to fail" issue (i.e., bailouts)
A U.S. federal law aimed at reforming financial regulation after the 2008 financial crisis. It sought to improve accountability, transparency, and stability in the financial system, protect consumers from abusive practices, and prevent future bailouts.
Jumpstart Our Business Startups (JOBS) Act of 2012
Goals
Ease burdensome federal regulations
Allow individuals to invest in start-ups through relaxed rules
Title II
Title III
Title II
Allows companies to advertise that they are seeking investments
Must be accredited investor
Title III
Allows a company to raise up to ~$1 million by selling securities
Crowdfunding
Raising small amounts of money from a large number of people
Who are we protecting with criminal law?
Wrongs against society
Where are the laws published?
Authority in federal and state codes (criminal sections or sometimes referred to as penal codes)
Section 16 for Georgia
Who brings case?
Government is the party prosecuting
What is the standard of proof?
Beyond a reasonable doubt
White-collar crime
Any illegal offense that occurs in a business or professional setting
Committed to harm the business, personal gains, or even competing business gain

Civil v Criminal Law
Focused on types of penalties
Civil: damages or equitable relief
Criminal: fines, prison sentences, probation, community service, restitution, etc.
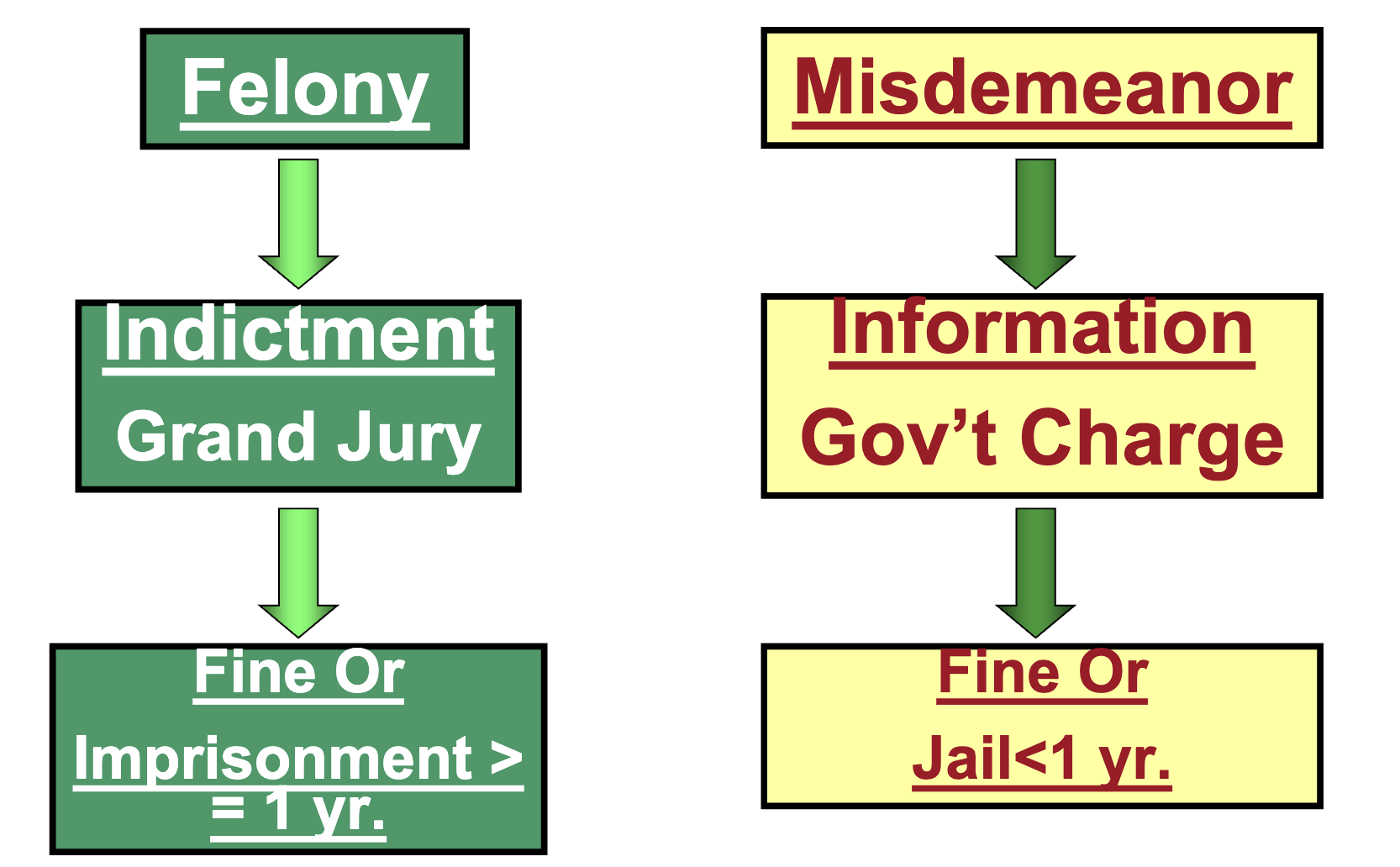
Felony v Misdemeanors
Felony —> Indictment (Grand Jury) —> Fine or Imprisonment >= 1 year
Misdemeanor —> Information (Government Charge) —> Fine or Jail < 1 year
Intent - some level
Willfully, knowingly, recklessly, negligently, strict liability...
Ignorantia juris non excusat
Ignorance of the law is no excuse
A lot of laws to know about
Mistake of fact: misunderstanding or misbelief about a factual matter that leads a person to act in a way that would otherwise be criminal
Mistake of law: someone incorrectly understands or misinterprets the law, leading to a misunderstanding of the legal consequences of their actions
Pleas in Criminal Cases
Guilty
Not Guilty
Nolo Contendere ("no contest")
Criminal conviction may be basis for civil damages suit
Trends in White Collar Crime
Increase in prosecution of white-collar criminals and legislative efforts to protect the public from fraud
E.g., Sarbanes-Oxley Act
Investigation of illegal activities by top management
Plea bargaining with mid-level employees in exchange for testimony against top-level employees
Prosecutors capitalize on high-profile prosecutions
4th Amendment
Protect individuals and businesses from unreasonable searches and seizures by the government
Usually (but not always) requires the police to obtain a search warrant
Expectation of privacy
Warrantless inspection of:
Commercial premises is reasonable in certain circumstances
Higher likelihood a search of a private residence is unconstitutional
Part of the 5th Amendment
Grand Jury
Double Jeopardy
Right Against Self-Incrimination
Grand Jury
Fifth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution
Before a trial for a capital, or otherwise infamous crime, there must be presentment or an indictment by a grand jury
Comprised of 16 to 23 citizens; unanimity is not required
Determine whether probably cause a crime has occurred and accused committed the crime
Still have presumption of innocence: Presuming that an indicted person is innocent until found guilty by a petit (trial) jury
Serve as an investigative body
Functioning depends upon the secrecy of the proceedings
Double Jeopardy
Individuals cannot be tried twice by the same governmental entity for the same offense
Does not prevent two prosecutions – federal and state
On civil side, you can think of doctrine of res judicata
Prohibits subsequent civil actions involving the same parties, claims and causes of action
Protects the accused from being compelled to testify against self
Does not protect:
Against being required to produce physical evidence
A person who is required to produce business records
6th Amendment
Provides multiple protections that offer the right to:
Speedy and public trial
Trial by jury
Be informed of the charge against oneself
Confront the accuser
Subpoena witnesses in one's favor
Have the assistance of an attorney
Key takeaway: 6th Amendment gives more rights to defendants
8th Amendment
Prohibits government from imposing excessive bail, excessive fines, and cruel and unusual punishment
Supreme Court determined test if punishment is cruel and unusual (Furman v Georgia (408 U.S. 238, 1972)); Gregg v Georgia (1976) reinstated death penalty
Specific crimes
Fraud, Conspiracy, Cyber Crimes
Fraud
Creates criminal liability
Fines and/or imprisonment are exerted on individuals who knowingly and willfully defraud another
Scheme to defraud: Plan designed to take from a person the tangible right of honest services – usually multiple victims
Theft by deception - taking another's property under false pretenses (words or conduct that create a false impression)
Conspiracy
Willful agreement or a partnership for criminal purposes (two or more people)
Each member becomes the agent or partner of every other member
An offense occurs when one makes a conspiracy agreement and commits an overt act
Overt act: Any event knowingly committed by a conspirator to accomplish some object of conspiracy
Cyber Crimes
Person who intentionally accesses a computer without authorization or exceeds authorized access to obtain classified, restricted, or protected data, is subject to criminal prosecution
Electronic heft – Hackers steal money, trade secrets, personnel records, and customer lists
Identity theft
Individual Job
As a candidate/employee
Knowing your rights
Interviewer
How you make decisions, what you ask, etc.
Business Community
Value of diversity
Customers
Community
Firm level
Returns
Society
Importance of employment
Fairness
Ideals
Title VII of Civil Rights Act of 1964
Purpose
To eliminate job discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin
Note: only applies to employers with 15 or more employees
What does Discrimination Look Like?
Discrimination (Disparate Treatment, Disparate Impact, and Retaliation) in:
Discharge
Refusal to hire
Compensation
Promotion
Terms, conditions, or privileges of employment
Disparate Treatment
Employer intentionally discriminates (JE directly/obviously)
Disparate Impact
Discriminatory effect (JE: indirectly/subtly)
Examples:
Biased personnel tests
Denying employment to unwed mothers
Poor credit rating
Priority to relatives of present employees
Retaliation
Adverse employment actions against employee
What is a BFOQ and what is a “business necessity"?”
Discrimination allowed on the basis of bona fide occupational qualifications ("BFOQ" for disparate treatment) or "business necessity" (for disparate impact) (BFOQ permits discriminatory practices in employment if a person’s religion, sex, or national origin is reasonably related to the normal operation of a particular business. Business necessity: It’s raised to disparate impact claims and asserts that a facially neutral but discriminatory policy is job-related)
Categories
Race
Color
National Origin (foreign language)
Religion (religious org exception; accommodations)
Sex (male/female)
Sexual Orientation
Age Discrimination in Employment Act
Protects employees or applicants against discrimination based on age
Prohibits employment discrimination against employees aged 40 and above
Prohibits mandatory retirement – exception is high level employees (e.g., CEOs and sometimes when safety may be a concern (e.g., pilots, police officers, etc._
Applies to private employers with 20 or more employees.
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
Disability: Any physical or mental impairment that substantially limits an individual's major life activities
Helps people with disabilities get work
Prohibits employers from:
Requiring a pre-employment medical examination
Asking questions about the job applicant's medical history
Need to make reasonable accommodations
Applies to employers with 15 or more employees
Sexual Harrassment
Quid pro quo: this for that; a situation where someone in a position of authority, like a boss or supervisor, demands or implies that sexual favors or compliance with unwanted sexual conduct is a condition for maintaining a job, getting a promotion, or receiving other workplace benefits
Hostile work environment
Inside Information
Non-public, material information about a company that could influence an investor's decision to buy, sell, or hold securities. It is obtained by someone within the company (an "insider") and is not available to the general public. Trading on inside information is illegal and considered insider trading.
At-will Employment
Some people have employment contracts, but most do not...so the default rule is "employment at will"
Employer can fire at will
Employee can quit at will
(An employer can generally terminate an employee for any reason, with or without cause, as long as the reason is not illegal)
What are the restrictions on at-will employment?
Not absolute
Does not apply if federal, state, and/or local law prohibits (e.g., Title VII of Civil Rights Act of 1964, Age Discrimination in Employment Act, Clean Water Act, Labor-Management Relations Act, etc.), contract (I.e., not employee at will) or public policy