Year 11 SACE Chemistry exam semester 1
1/156
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
What are non bonding pairs called?
Lone pairs
Electrons have a mutual force of
repulsion between electron pairs.
Why is electron repulsion important?
Because it can shape the molecule
VSPER THEORY
forms arrangements of molecules to minimize repulsion, it is at the minimum repulson when there is more distance between pairs.
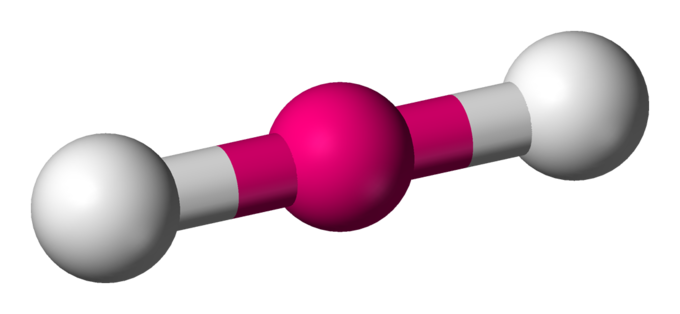
This is:
Linear
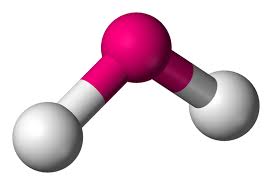
This is:
bent
This is:
Trigonal planar
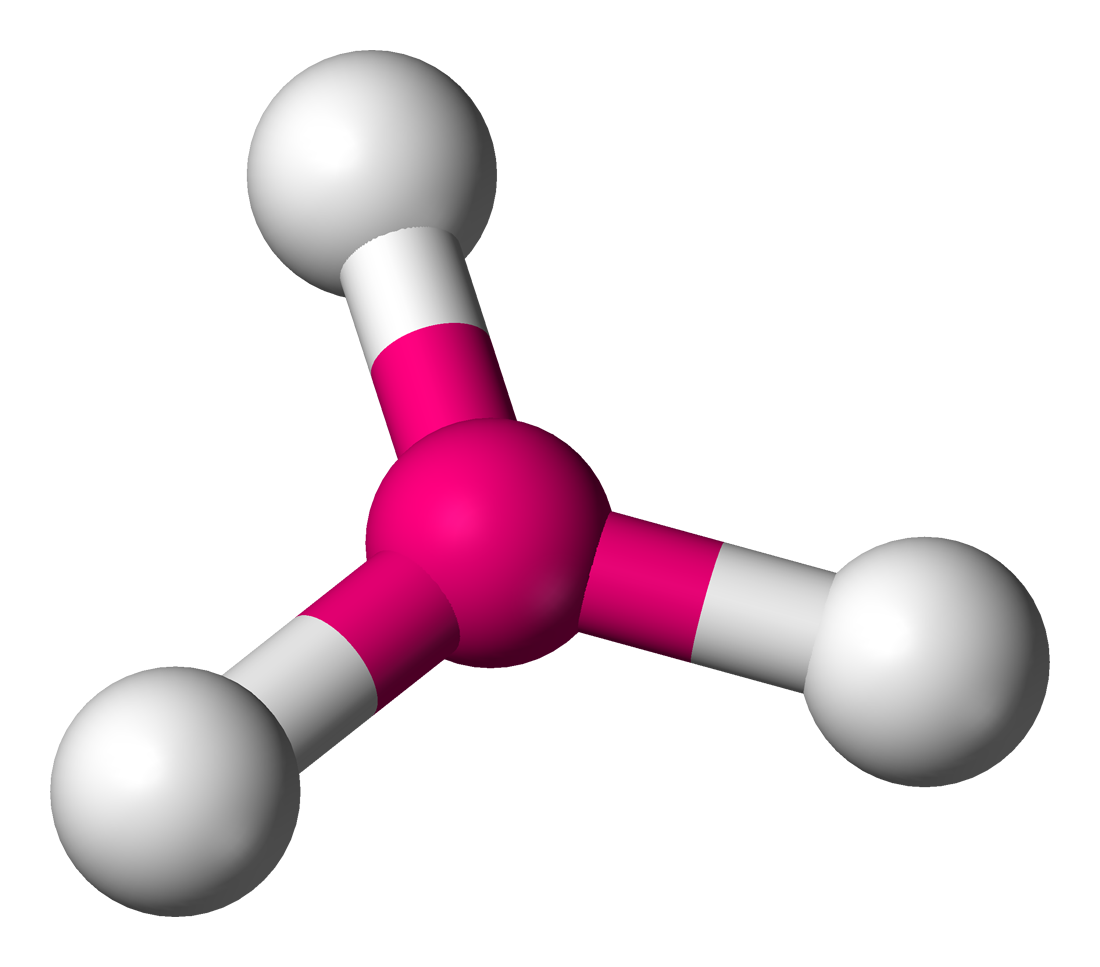
This is:
Trigonal pryamidal
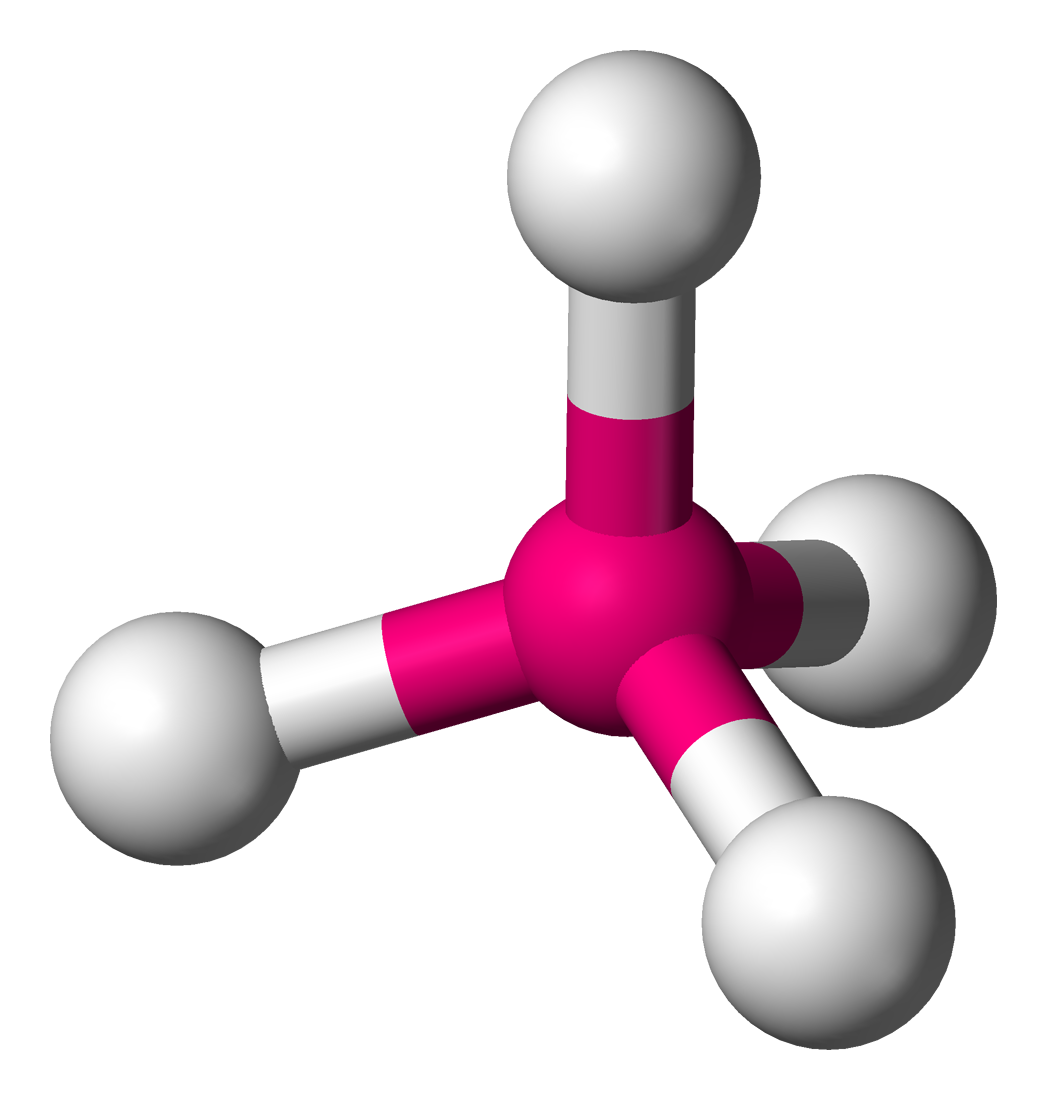
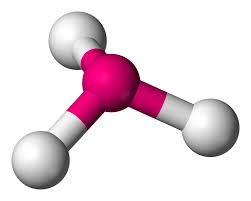
This is:
Tetrahedral
Molecular polarity is
permanent separation of electric charge, and the formation of delta positives and negatives
When does polarization happen?
in a covalent bond
how does polarization happen?
if there is uneven sharing of electrons.
-Electrons are attracted to the element with the highest electronegativity.
molecular polarity is determined by
the symmetry of the molecule
and the polarity of electronegativity between the atoms
intramolecular bonds
occur in the molecule (primary bonds) (eg, ionic)
intermolecular bonds
occur with the molecule and other molecules (secondary bonds
What properties are dependent on the strength of intermolecular bonds?
Melting and boiling point
What are (London) dispersion forces
dispersion forces occur when electrons that are constantly moving are unsymmetrically distributed, creating a temporary dipole
what makes stronger dispersion forces?
a bigger molecule, bigger the molecule, more interaction therefore more bonds and bigger melting points
What are dipole dipole interactions?
Occurs between a polar covalent bond,
Dipole dipole interactions are the mutual force Mutual force of attraction between the delta + of one molecule and the delta – of a second molecule.
Dipole Dipole interactions are dependant on
•Distance between molecules
•Magnitude of electric charge on both molecules
What are hydrogen bonds?
A stronger dipole dipole reaction that occurs between a delta positive of hydrogen and a delta negative of fluorine, oxygen, nitrogen
Electrical conductivity
Materials with free electrons
Heat conductivity
Materials with charged electrons for efficient heat transfer.
Homogenous mixture
Evenly distributed mix like solubles; opposite of heterogeneous.
Heterogeneous mixture
Mix with visibly different layers like oil and water.
Filtration
Separation method for solid
Evaporation
Separation method for soluble in a solvent.
Distillation
Separation method for liquids with different boiling points.
Nanomaterial
Material a billionth of a meter with unique properties.
Atomic number
Number of protons in an atom.
Atomic mass number
Sum of protons and neutrons in an atom.
Emission spectra
Light absorbed then reemitted when the electrons jump back down the levels
Absorption spectra
Light absorbed by atoms so the electrons jump energy levels.
Isotope
Atoms with same protons but different neutrons.
Average atomic mass
Weighted average of isotopes' masses.
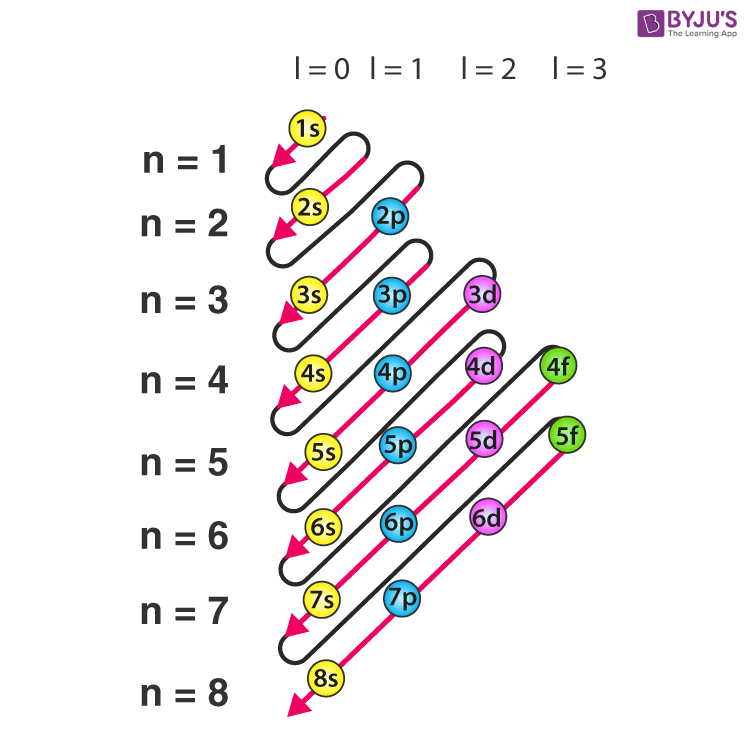
Subshell electron configuration
Arrangement of electrons in subshells of an element.
Moles calculation
Moles = Mass of sample / Molar mass.
Avogadro's number
1 mole = 6.02 x 10^23 particles.
Molar mass calculation
Sum of (Molar mass x number of atoms) in a compound.
Periodic table period
Horizontal rows indicating number of electron shells.
Periodic table group
Vertical columns showing valence electrons.
Electronegativity trend
Increases across periods, decreases down groups.
Ionization energy trend
Increases across periods, decreases down groups.
Atomic radius trend
Decreases across periods, increases down groups.
What determines chemical properties?
valence electrons
What determines physical properties?
Protons and neutrons
What does high electronegativity mean?
the atom really want to GAIN electrons to become stable
What group has low ionisation energy?
Alkali metals
What is ionisation energy?
the minimum amount of energy required to remove 1 electron form an atom
What is atomic radius?
the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron
How does atomic radius increase?
It increases by the size of the nucleus, and the amount of shells it has
Number of moles equals
mass/molar mass
number of atoms equals
No. Of mol x Avogadro's number.
Mass equals
Molar mass divided by moles
Electrostatic force of attraction
Attraction between two different charges in a molecule, eg : delocalized electrons and metal cations in metallic materials.
Malleable
Ability to be hammered or rolled into thin sheets.
Ductile
Ability to be drawn into wires.
Thermal Conductors
Materials that allow the flow of heat.
Electrical Conductors
Materials that allow the flow of electricity.
Melting Point (Metallic Bonds)
Increases with higher charge and larger atomic radius of metal cation.
Ionic Bonds are formed by
The transfer of electrons, resulting in cations and anions attracting each other.
Hard (Ionic Bonds)
Physical property due to strong inter-ionic forces.
Brittle (Ionic Bonds)
Easily broken or shattered.
Conductivity (Ionic Bonds)
Poor in solid state, good when dissolved or molten.
Strongest Ionic Bonds
When ions have high charges, leading to higher melting points.
Covalent Bonds
Formed by sharing electron pairs between atoms.
Electron Dot Diagrams
Illustrate electron distribution in atoms and covalent compounds.
Valence Structure
Shows all bonds and non bonded valence electrons
Polar Covalent Bonds
Result from unequal sharing of electrons, creating partial charges.
Non Polar covalent bonds
the covalent atoms have no difference in electron negativity
Electronegativity
Measure of atom's attraction for electrons.
Diatomic Molecules
Molecules composed of two atoms of the same element.
Continuous Covalent Compounds
Diamond, Graphite, Silica; have unique structures and properties.
Empirical Formula
Simplest whole number ratio of elements in a compound.
What make up metallic bonds?
Two metals
The structure of Metallic bonds
Attractive force between free moving delocalised electrons and a metal cation within a metallic material.
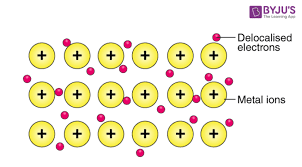
What are the properties of metallic bonds?
Malleable/ductile/thermal and electrical conductors due to sea of electrons within metallic bonds. .Conductive (of heat and electricity) malleable and ductile
In metallic bonds, the bigger the atomic radius
the higher the melting point
What makes up an Ionic compound
A non metal and a metal
How ionic bonds form
both the non metals and metals would like to have a full shell, so one atom gives the other its electron, and one becomes a cation and one becomes a anion
How are ionic bonds held together?
electrostatic force of attraction
what is the structure of ionic bonds
A regular lattice
Why are ionic compounds brittle?
they are brittle due to if they are pushed their lattice will move and negatives and positives will be next to eachother, and they will repell eachother
ionic compound properties
brittle(break easily when lattice move and charges overlap, high melting points (held together by eletrostatic forces)
What happens when ionic compounds are dissolved or are liquid?
they can conduct electricity
When are ionic bonds the strongest?
Ionic bonds are the strongest when each elements ionic charge are high, this makes a high melting point
What are covalent bonds made up of?
two non metals
What ionic charge does group 1 make?
1+
What ionic charge does group 2 make?
2+
What ionic charge does group 13 make?
3+
What ionic charge does group 14 make?
4+-
What ionic charge does group 15 make
-3
What ionic charge does group 16 make?
-2
what ionic charge does group 17 make?
-1
balancing is when
the total positive charge = the total negative charge
What are the 3 types of covalent bonds?
single (share one), double( shares two ), triple( shares 3)
What is a polar covalent bond?
if there is a difference in electronegativity in a covalent bond, a polar bonds.forms
what cant form polar bonds?
diatomic molecules and hydrogen+carbon (and to atoms with every low different in electronegativity
electronegativity
attractive power of electrons
What is a covalent molecular compound?
two or more nonmetal atoms sharing electrons to become more stable (covalently bonding)