[9] Alkali metal and Halogens
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
How do the reactions of lithium, sodium, and potassium with water provide evidence for their recognition as a family of elements?
What is the rule with reactivity in the alkali metals
Lithium, sodium, and potassium react with water by producing hydrogen gas and metal hydroxides and fizzing. The increasing reactivity with water as you go down the group
How do the differences between the reactions of alkali metals (lithium, sodium, and potassium) with air and water provide evidence for the trend in reactivity in Group 1?
The alkali metals react more vigorously with water and air as you go down the group
What explains the trend in reactivity in Group 1 alkali metals in terms of electronic configurations?
The reactivity of alkali metals increases down the group because the outer electron is farther from the nucleus and more easily lost.
What are the colours, physical states at room temperature, and trends in physical properties of the halogens from flourine to astatine
Fluorine yellow gas
Chlorine green gas
Bromine red-brown liquid
Iodine: grey solid, purple vapour
Astatine: black solid
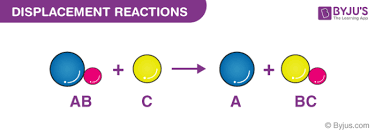
what happens in displacement reactions
In displacement reactions, a more reactive halogen will displace a less reactive halogen.
What explains the trend in reactivity in Group 7 halogens in terms of electronic configurations?
The reactivity of halogens decreases down the group because the outer electrons are farther from the nucleus, making it harder for the atoms to gain an electron.
what is the general equation word for alkali metals and water
alkali metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen
what are the properties of group 1 metals
low melting point
low boiling point
low density
soft
shiny silvery appearance when freshly cut
good conductor of heat and electricity
what are the chemical properties of group 1 metals
very reactive with oxygen and water
what would you observe with lithium reacting with water
floats, fizzes around and disappears
what would you observe with sodium reacting with water
turns into a sphere, fizzes
what would you observe with sodium reacting with water on filter paper
orange flame
what would you observe with potassium reacting with water
fireworks and purple flame
important point about the structure of the halogens?
they are diatomic