organic chemistry: crude oil
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Each fraction consists of groups of hydrocarbons of _______ chain lengths. They have similar _____and ________, which (depends on the number of carbon atoms in the chain)
similar chain lengths
similar properties and boiling points, which depend on the number of carbon atoms in the chain
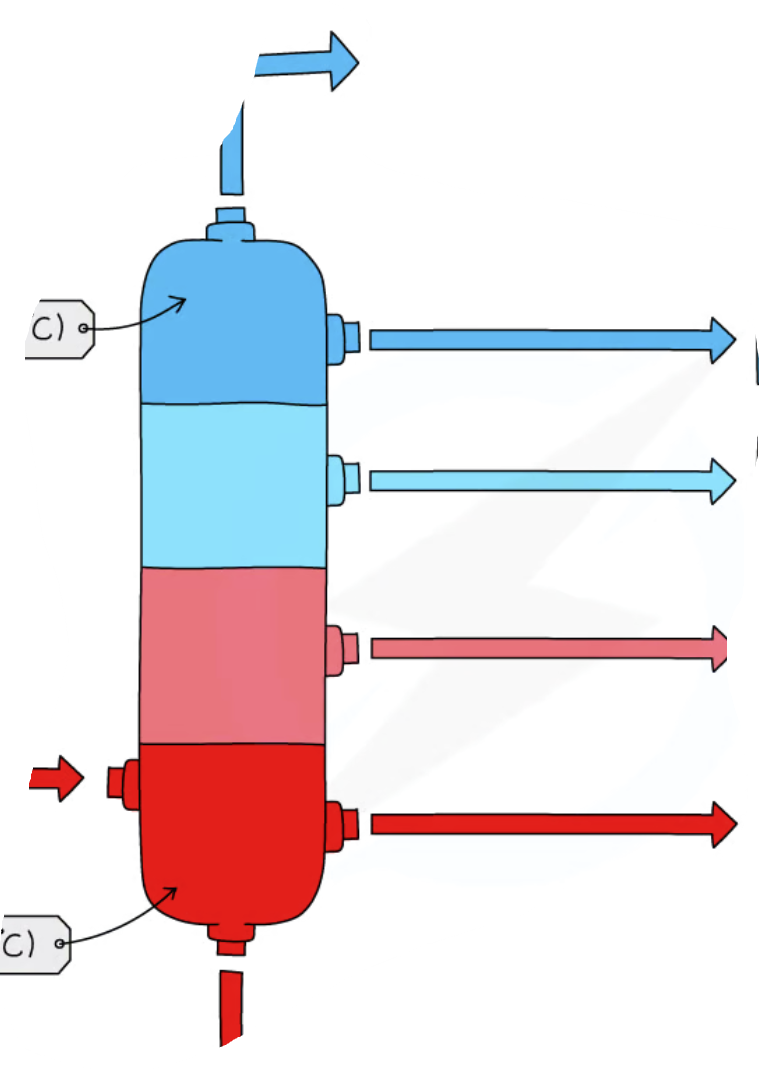
label diagram
each section, name of fraction that comes out
at least one use
top one is methane, so for stoves
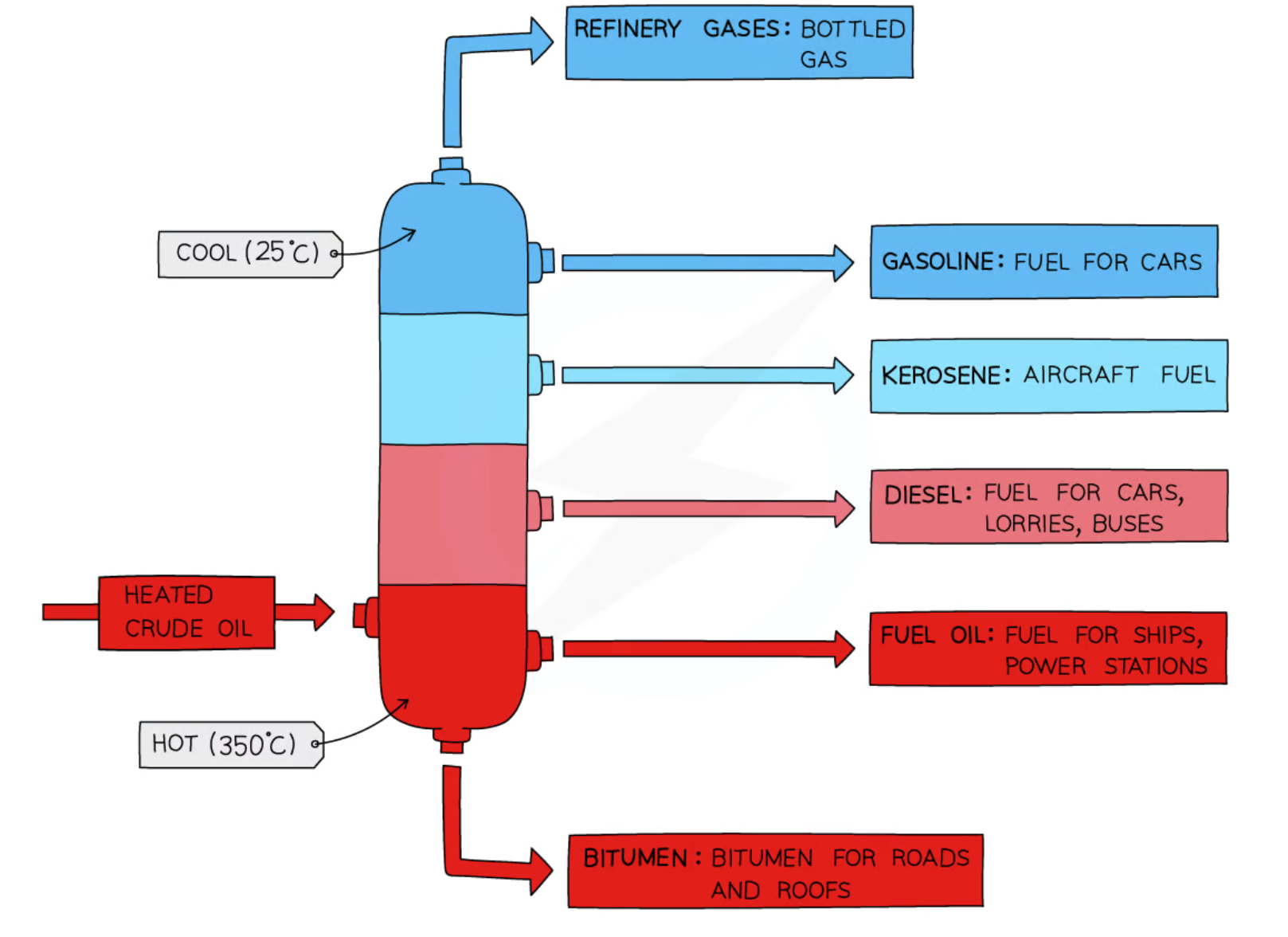
define crude oil
mixture of hydrocarbons with different chain lengths
describe how fractional distillation separates crude oil into fractions [5]
crude oil boiled/vaporised (in furnace);
column is hot at the bottom and cool at the top;
hydrocarbon vapours rise up the column
they condense back into a liquid when their boiling point is reached
smaller / lighter molecules move higher up the column
fractions with lower boiling points move further up column
smaller / lighter molecules have lower boiling points
liquid fractions are removed
crude oil is heated to a high temperature, causing it to vaporize. The vapor is then passed through a series of trays or columns, with each tray or column being at a slightly lower temperature than the previous one. As the vapor cools, different hydrocarbons condense into liquids at different temperatures, allowing them to be separated into fractions.
how properties of the hydrocarbons change as you go up the column
going up the column
carbon chain lengths get smaller
more volatile
lower boiling points
lighter
less viscous (flow easier)
why is crude oil considered a finite resource
because it takes so long to form (millions of years)
define fuel
a substance that, when burned, releases energy
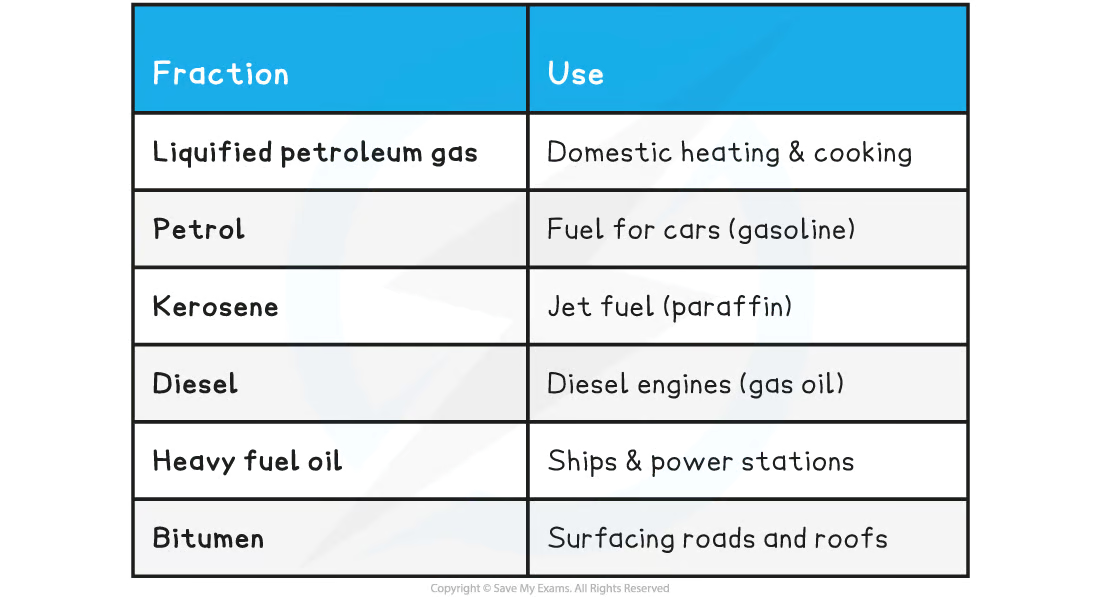
name | use |
|---|---|
liquified petroleum gas | |
petrol | |
kerosene | |
diesel | |
heavy fuel oil | |
bitumen |
how is sulfur dioxide made from burning hydrocarbons
what is the harm caused
produced by combustion of hydrocarbons containing sulfur impurities
dissolves in rain water to form sulfuric acid, and falls as acid rain
this damages rivers and lakes and corrodes limestone
how is nitrogen oxide made from car engines/exhausts
what is the harm caused
when oxygen and nitrogen react at high temperatures
will enter atmosphere, dissolve in rain water to form acid rain
can cause photochemical smog, can cause respiratory problems
sulfur dioxide to acid rain eq
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) + 2H2O (l) → 2H2SO4 (aq)
nitrogen dioxide to acid rain eq
2NO2 (g) + H2O (l) → HNO2 (aq) + HNO3 (aq)
nitrous and nitric acids contribute to acid rain