S3.2.6 Classification
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Carbon bonded to -OH is attached to one alkyl group.
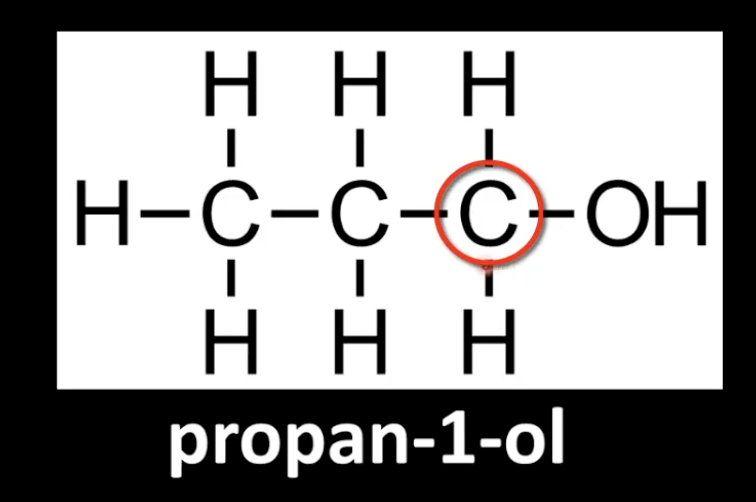
Example: Propan-1-ol.
Classified by counting carbon neighbors of the -OH carbon.
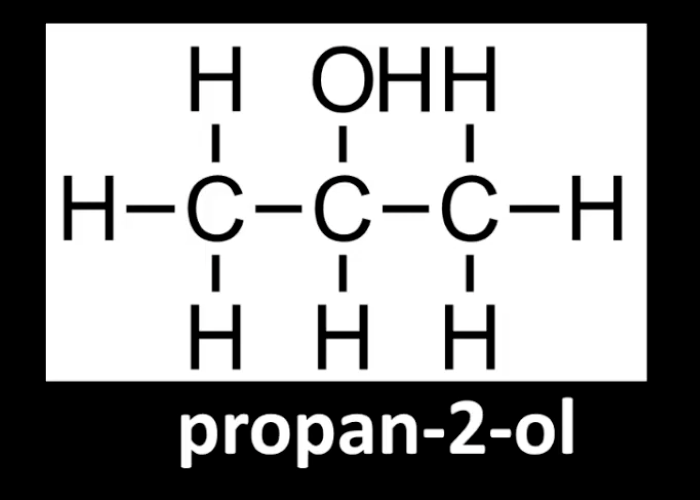
Carbon bonded to -OH is attached to two alkyl groups.
Example: Propan-2-ol.
Identify by checking carbon's neighbors.
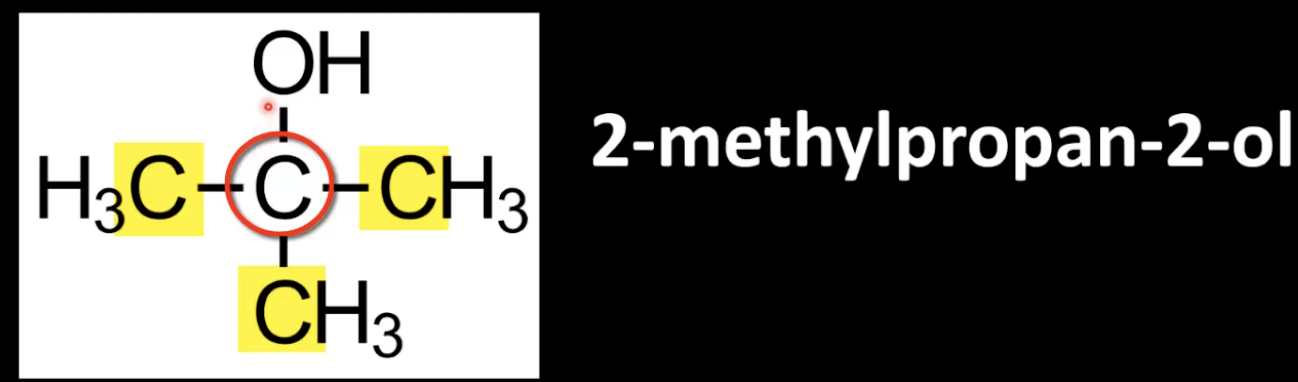
Carbon bonded to -OH is attached to three alkyl groups.
Example: 2-methylpropan-2-ol.
More substituted center carbon.
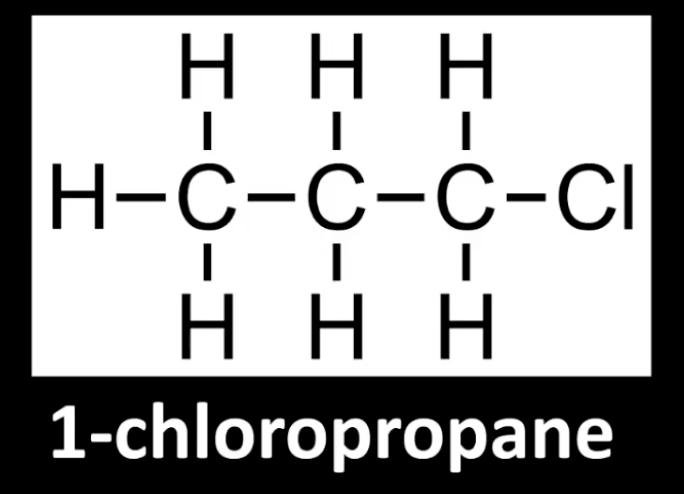
Carbon bonded to halogen is attached to one other carbon.
Example: 1-chloropropane.
Look at the halogen-bearing carbon's neighbors.
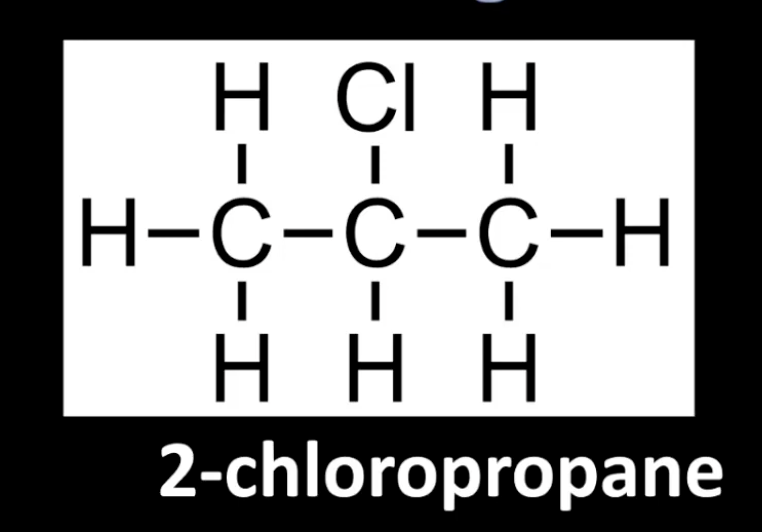
Carbon bonded to halogen is attached to two other carbons.
Example: 2-chloropropane.
Classification based on bonded carbon count.
Carbon bonded to halogen is attached to three other carbons.
Example: 2-chloro-2-methylpropane.
Most substituted center.

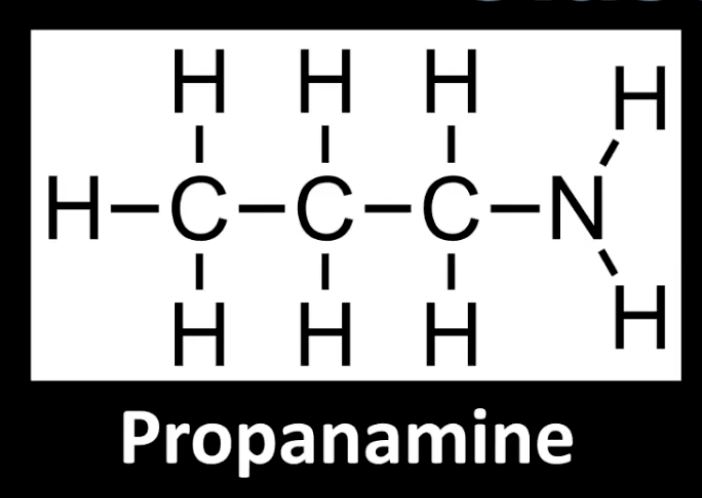
Nitrogen bonded to one carbon group.
Example: Propanamine.
Count the carbon groups directly attached to nitrogen.
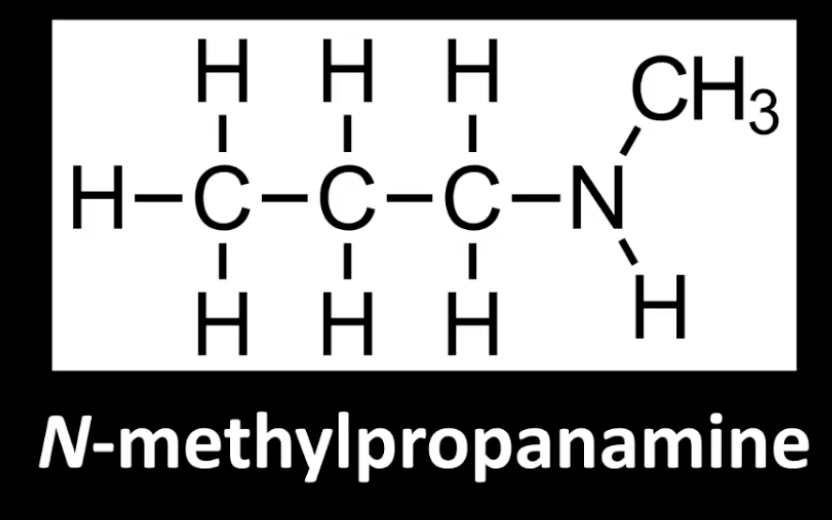
Nitrogen bonded to two carbon groups.
Example: N-methylpropanamine.
Identified by two carbon substituents on N.
Nitrogen bonded to three carbon groups.
Example: N,N-dimethylpropanamine.
Fully substituted nitrogen center.

Same molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms.
Different structural formulas.
Types: chain, position, functional group.
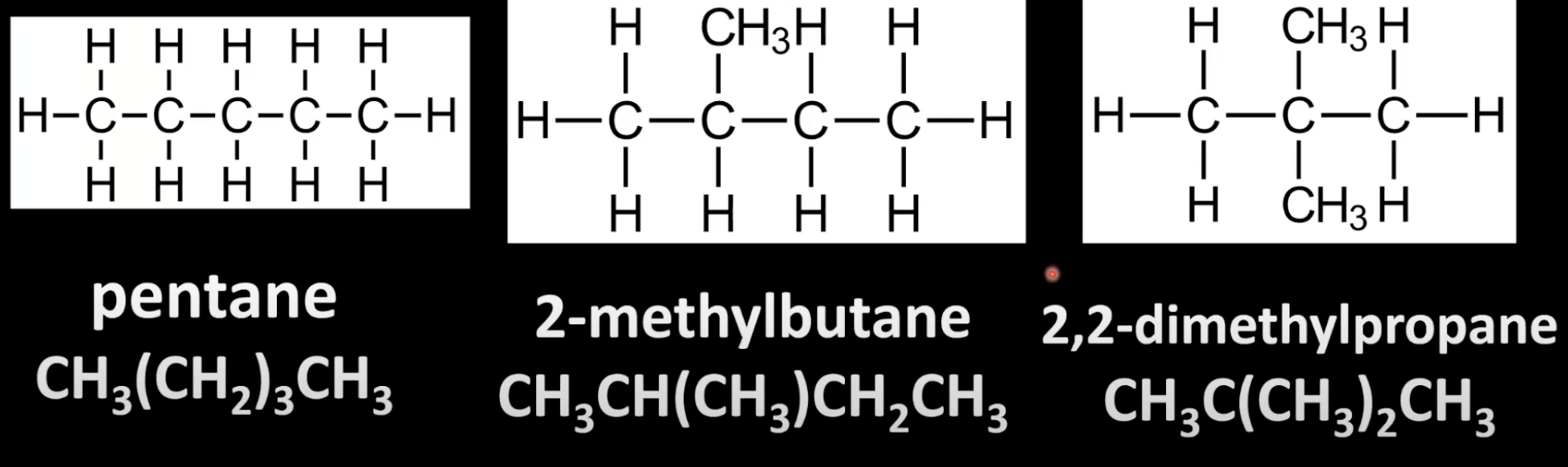
Isomers differ in carbon chain structure.
Straight-chain vs branched-chain.
Example: pentane vs 2-methylbutane.
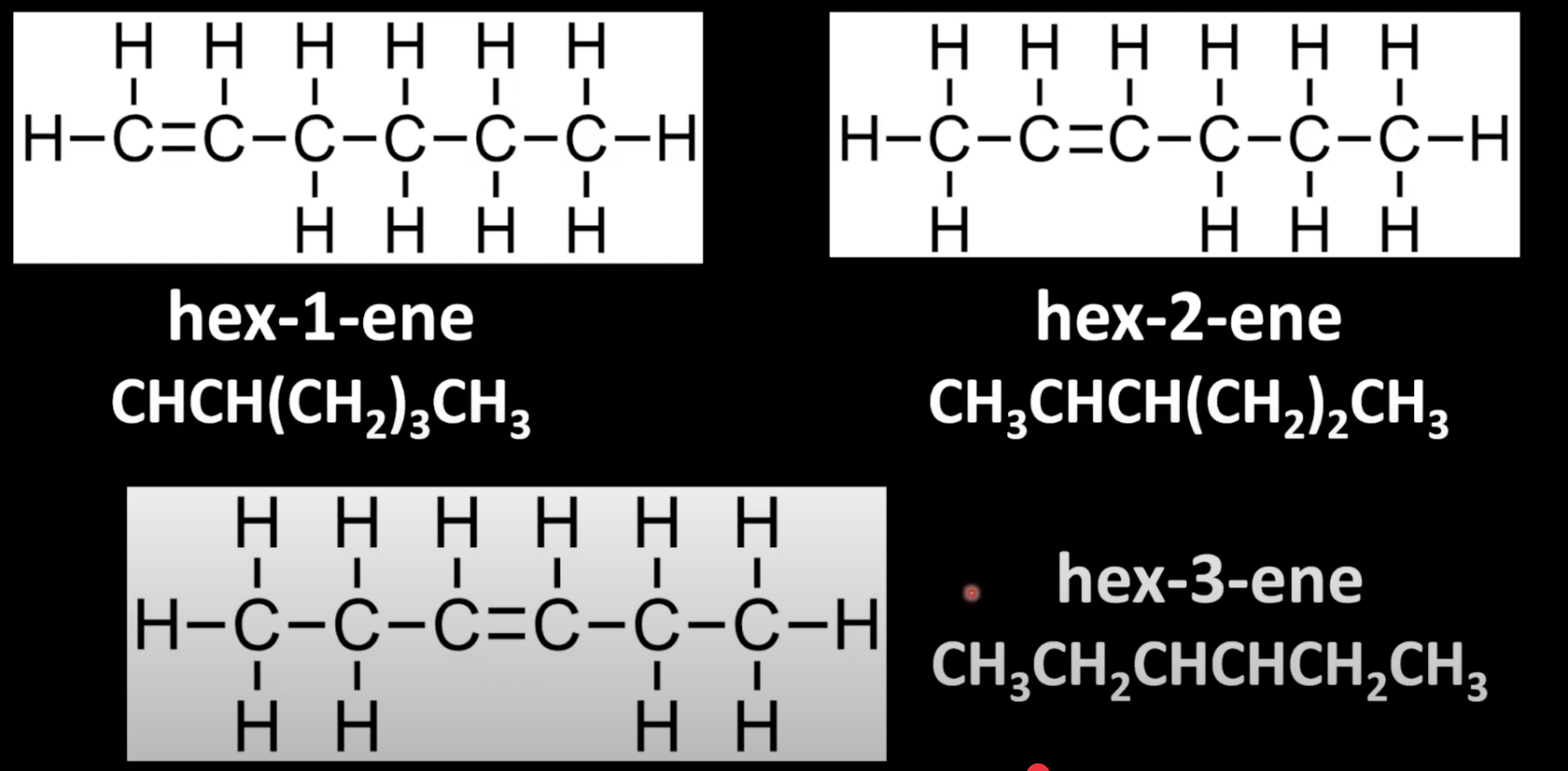
Same functional group, different positions on chain.
Example: hex-1-ene vs hex-2-ene vs hex-3-ene.
Isomers have different functional groups.
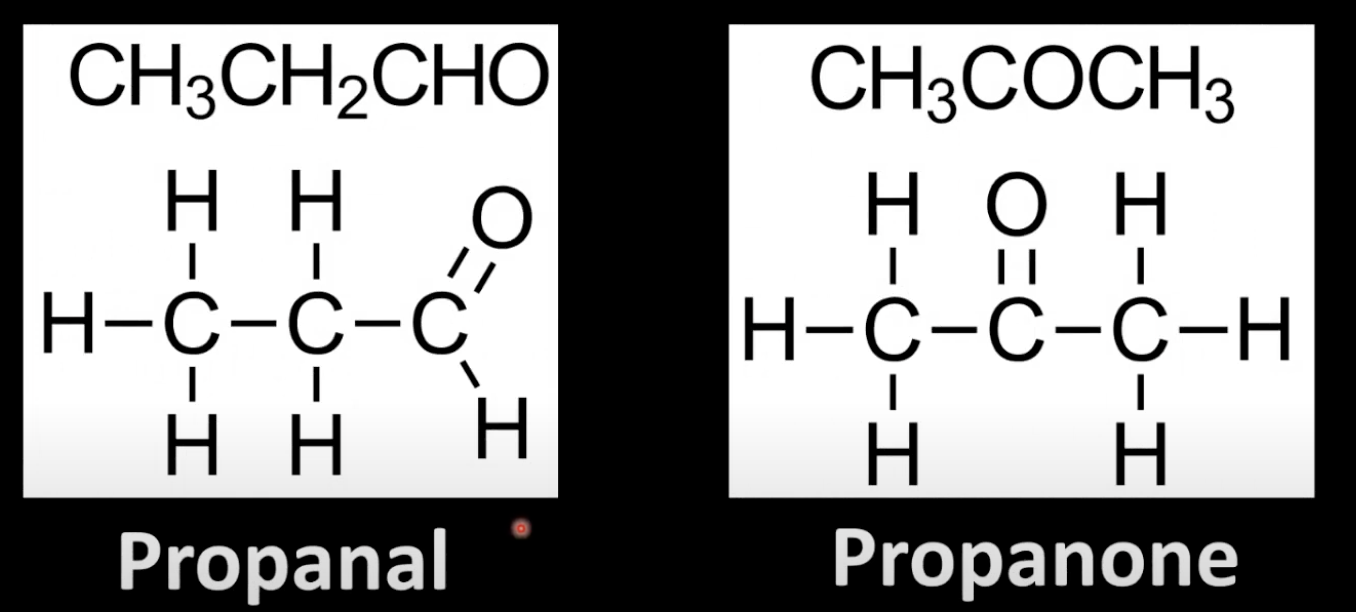
Example: propanol (aldehyde) vs propanone (ketone).