NEUR 362: Neurobiology of Learning
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
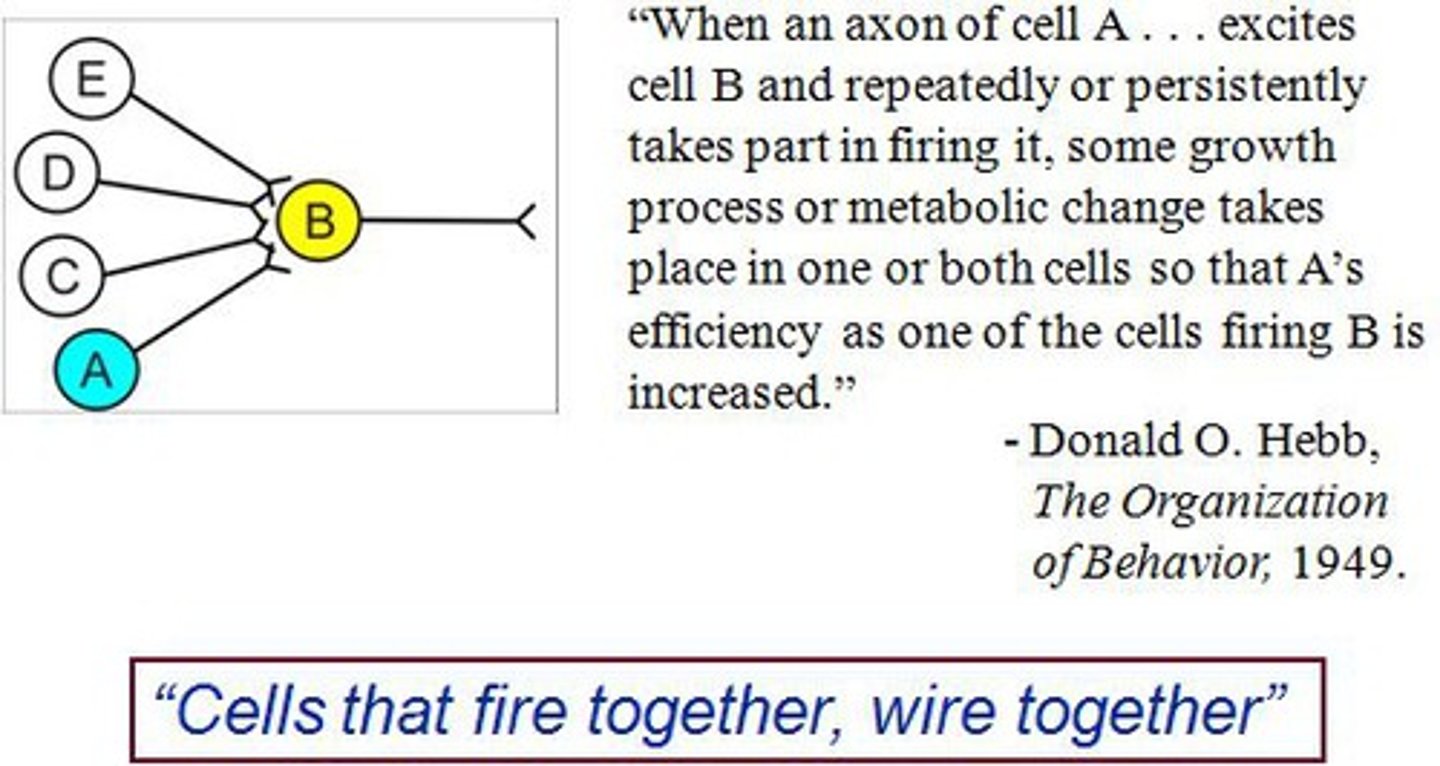
Hebbian synapse
a synapse that becomes more effective because of the simultaneous activity in the pre-synaptic and post-synaptic molecules
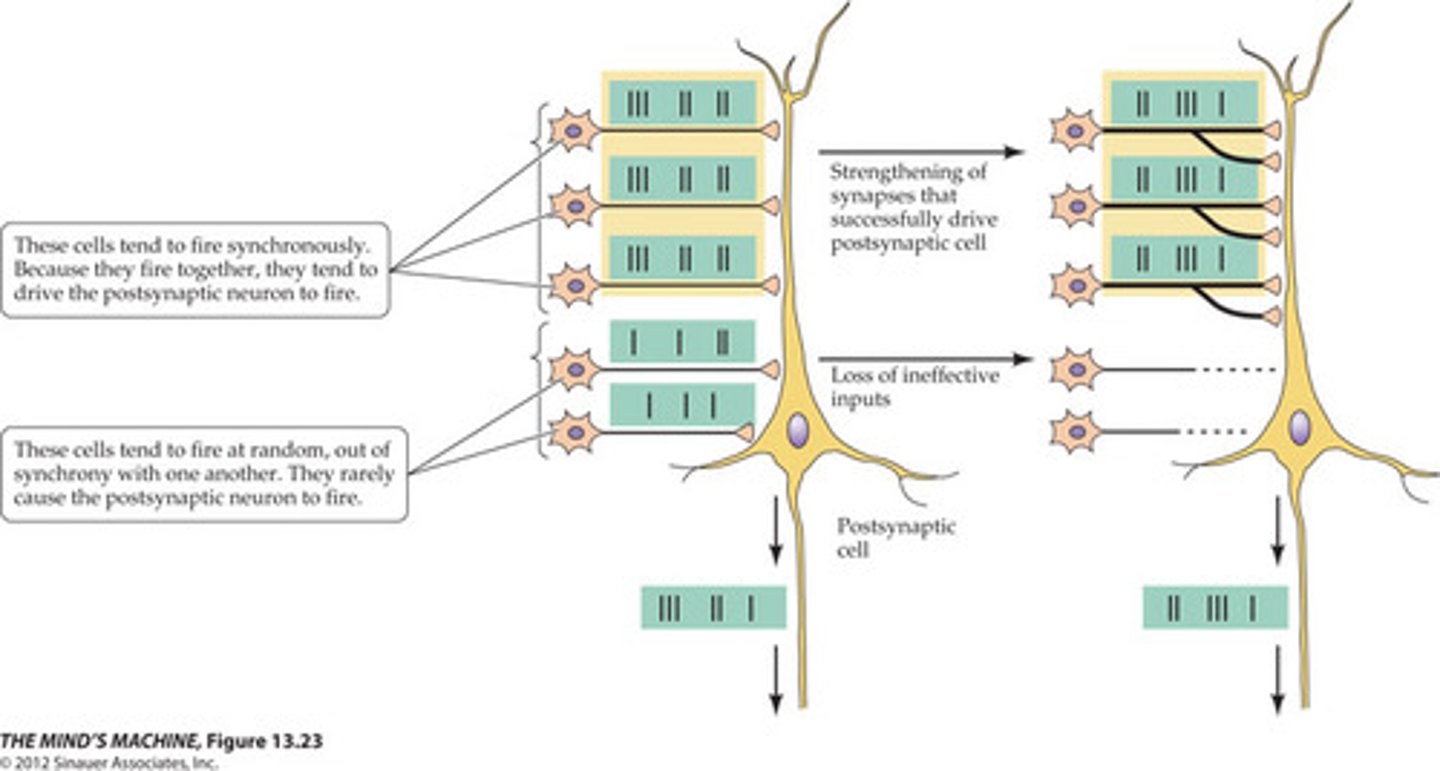
Hebb's rule
"Neurons that fire together wire together" (many synapses in the brain!)
Aplysia californica
Sea slug model for studying learning, memory, and synaptic plasticity

List the 3 main characteristics of the Aplysia that made it ideal for studying the mechanisms of learning.
1) Large, identifiable neurons
2) Simple neuronal circuit
3) Evolutionarily conserved
Gill withdrawal response
Behavioral response in Aplysia to stimuli
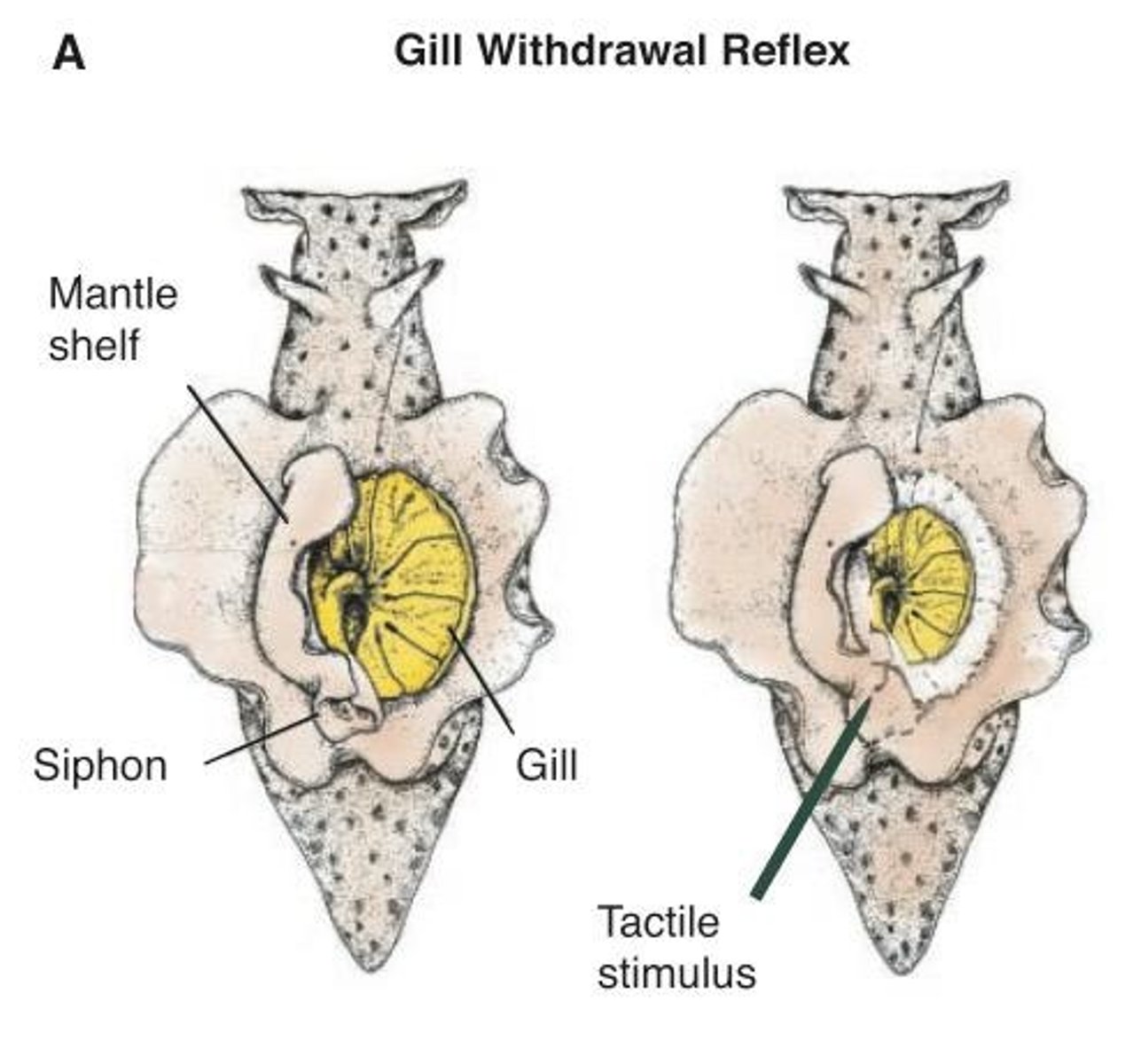
Gill withdrawal response process
1) Touch siphon, gill withdraws (reflex??)
2) Sensory neuron, motor neuron, interneuron (L29) -> 3-neuron circuit?
Aplysia 3-neuron circuit
1) Sensory neuron
2) Motor neuron
3) Interneuron (L29)
Habituation
idea that with repeated presentation of stimulus, the response will dwindle over time
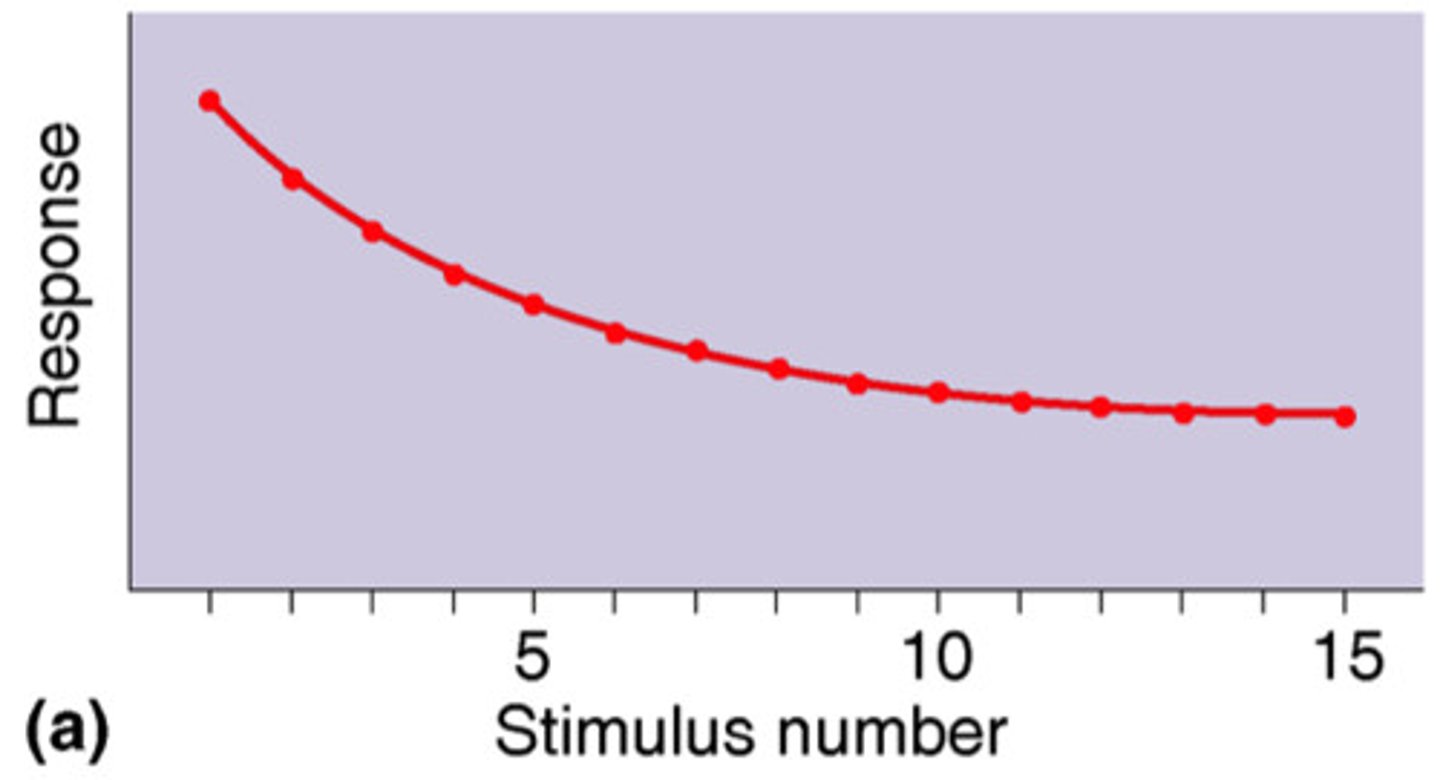
With habituation, change occurs at the synapse, and a ___________________ in glutamate release occurs.
decrease
Sensitization
An increase in response to a stimulus that occurs after repeated exposure
With sensitization, change occurs at the synapse, and an __________________ in glutamate release occurs.
increase
Decrease in behavior associated with less glutamate release at synapse is _______________________
habituation
Increase in behavior associated with more glutamate release at synapse is _____________________________
sensitization
Long-term potentiation (LTP)
an increase in a synapse's firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation. Believed to be a neural basis for learning and memory.
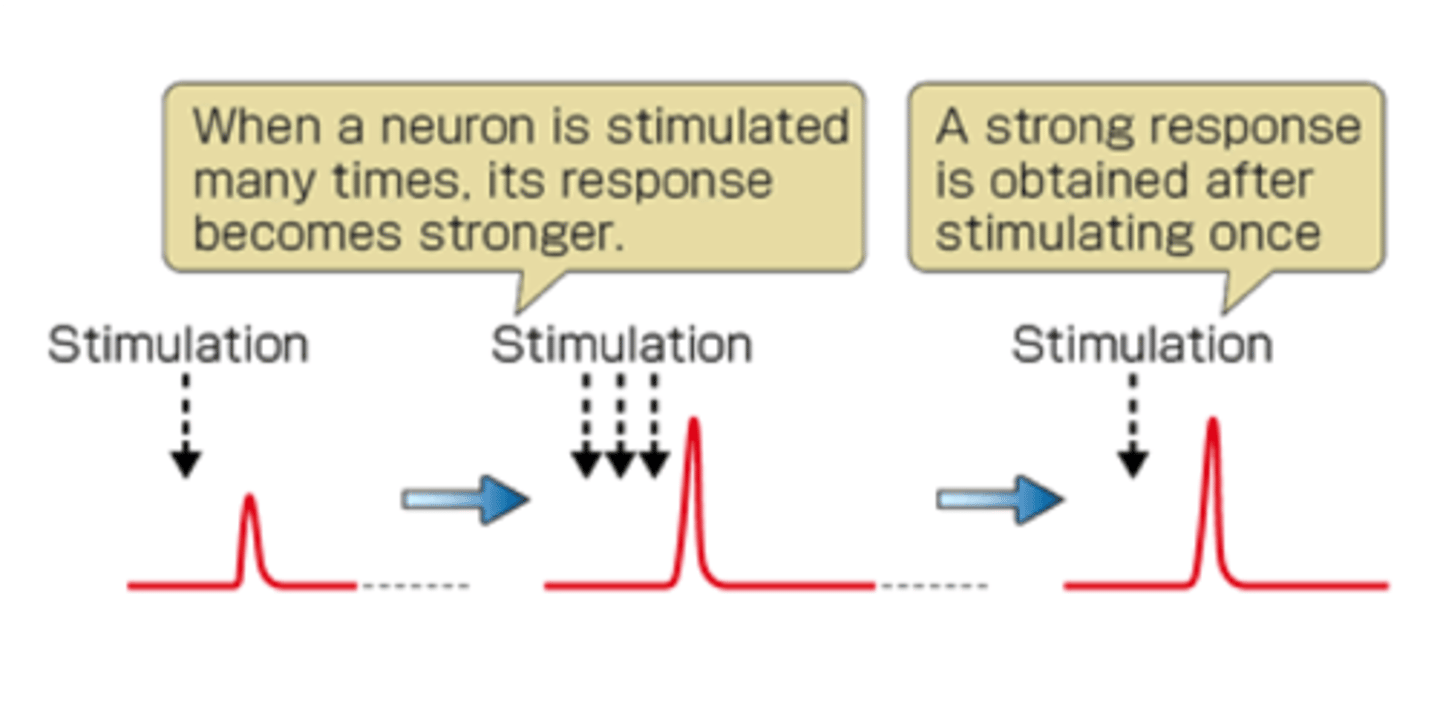
LTP Process
1) Bombard dendrite with brief, rapid series of excitations from several axons
2) Some of that dendrite's synapses become more responsive to excitation (potentiated)
3) Potentiation last minutes to weeks
4) With rapid exciting stimulation, the synapse will become stronger than before
Associative long-term potentiation
If a synapse is weakly stimulated while another synapse on the same dendrite is being strongly stimulated, the weak may be potentiated as well as the strong
Which type of LTP is most likely the basis for classical conditioning?
Associative LTP
Long-term depression (LTD)
An existing synapse can be weakened by decreasing the frequency of stimulation
An "eraser?"
Which glutamate receptors serve to the biochemical mechanisms of LTP?
1) AMPA receptor
2) NMDA receptor
Describe the role that glutamate, glutamate receptors, ions, and protein kinases play in learning.
Glutamate binds to the NMDA receptor -> Na+ and Ca2+ enter -> Activates CaMKII
Glutamate binds to the _____1________ receptor -> __2_____ and ____3_____ enter -> Activates _______4___________
1) NMDA
2) Na+
3) Ca2+
4) CaMKII
CaMKII
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
Enzyme involved in learning and memory by converting short-term synaptic changes into long-term ones
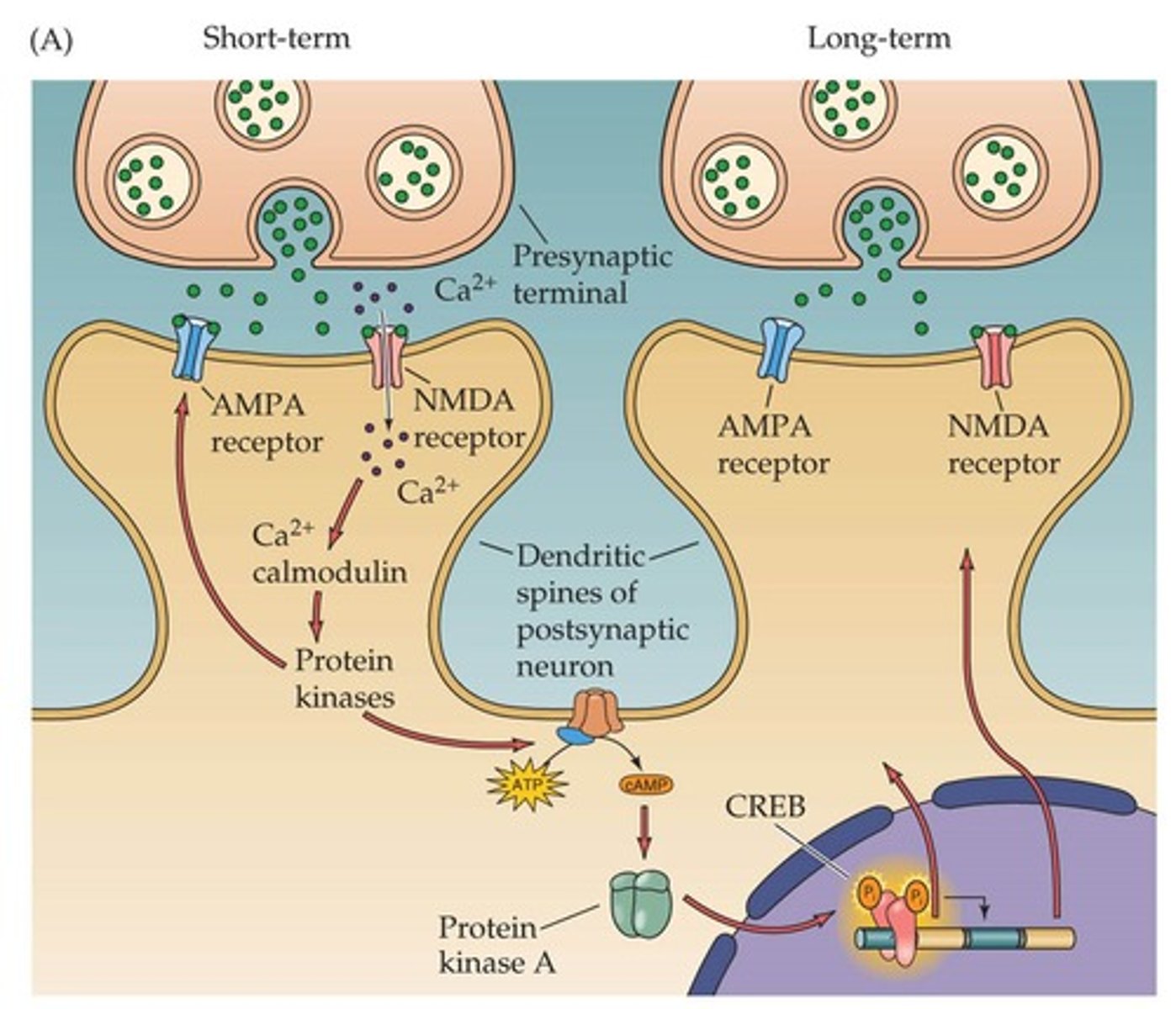
Changes in the dendrite that happen because CaMKII is activated: More ___________________________________ on dendrite
AMPA receptors
Changes in the dendrite that happen because CaMKII is activated: ___________________________________________ become more responsive
AMPA receptors
Changes in the dendrite that happen because CaMKII is activated: More _______________________________
NMDA receptors
Changes in the dendrite that happen because CaMKII is activated: ___________________________ may branch
Dendrite
Changes in the pre-synaptic neuron because of LTP
Decreased threshold for action potential
AMPA KO (Knockout) mice
Poor memory
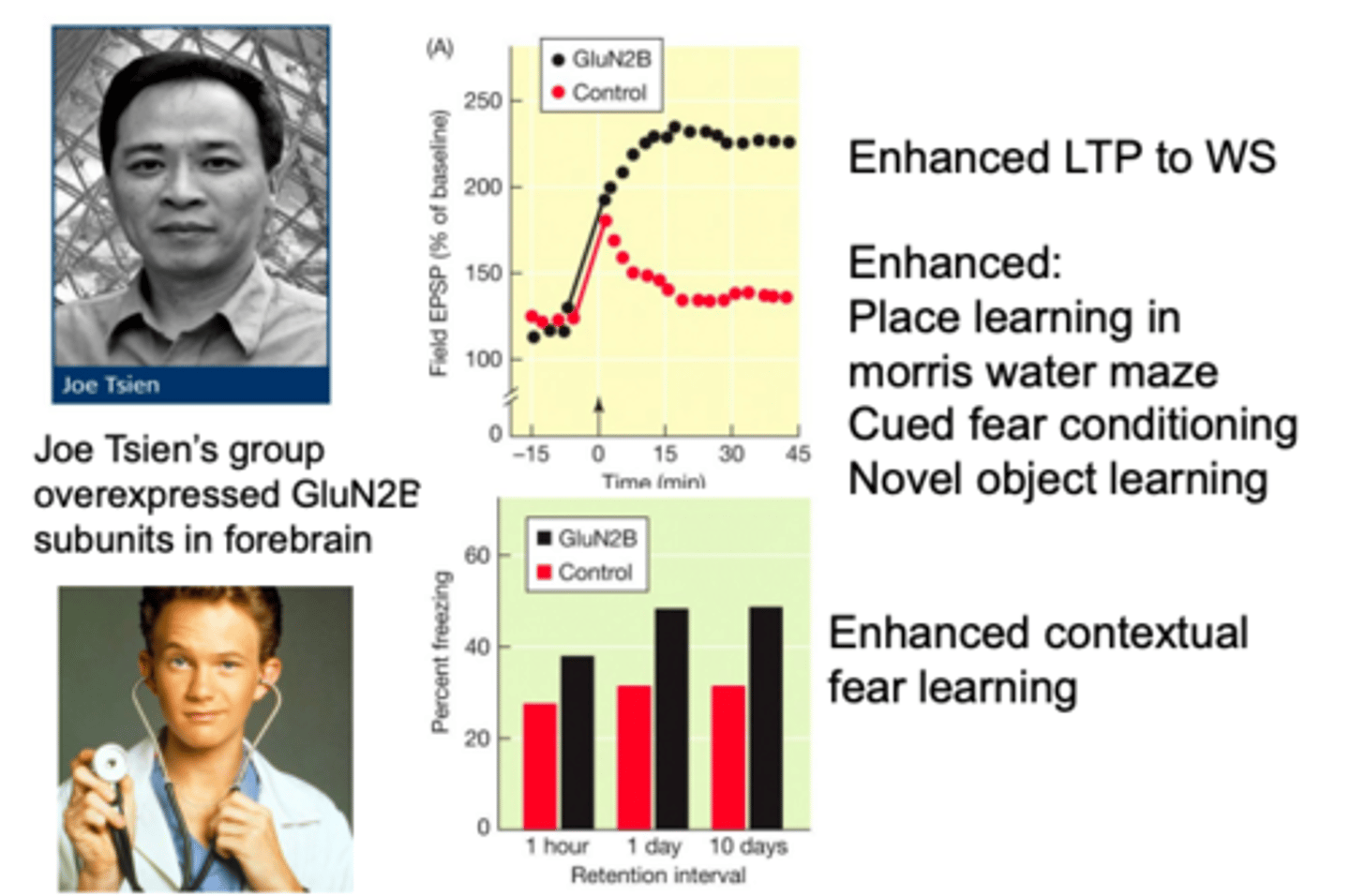
Mice with extra NMDA receptors
Are smart
Doogie mouse
genetically modified mice (NR2B gene) engineered to have enhanced learning and memory