Marine Biology - Intertidal Zones
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Producer
An organism that makes its own food
Primary Consumer
An organism that eats producers
Secondary Consumer
An organism that eats primary consumers
Decomposer
An organism that breaks down wastes and dead organisms
Sessile
Describes an organism that remains attached to a surface for its entire life and does not move
Benthic
Bottom dwelling
Plankton
Tiny organisms that float in the water
Phytoplankton
Plant plankton, such as diatoms and dinoflagellates
Zooplankton
Animal plankton, such as copepods and krill
Bivalve
Any two-shelled mollusk, such as clams, oysters and mussels
Biotic vs. Abiotic
Living vs Nonliving
Desiccation
Dehydration
How do intertidal organisms avoid desiccation?
Running and hiding, clamming up, or tolerating it
Which organisms run and hide?
Crabs, snails, and sea stars
Which organisms clam up?
Barnacles, mussels, limpets, clams and oysters
Why does temperature affect intertidal organisms?
Air temperature can lead to overheating and dehydration
What adaptations have some snails developed to withstand heat?
Lighter colored shells, ridges on shells
How much energy is absorbed from one trophic level to the next?
10%
What is the role of phytoplankton in the marine food chain?
Primary producers
How do phytoplankton affect the oxygen supply in the atmosphere?
Using photosynthesis, they release oxygen into the air.
Why are phytoplankton so important to the marine food web?
They are a food source for a lot of marine life.
What is the glassy shell of a plankton called?
Frustule
What kind of feeder are sea stars?
Carnivores and scavengers
What is the job of decomposers?
Breaking down waste and dead organisms into nutrients
How do pollutants move up the food chain?
By getting absorbed by or adhering to producers
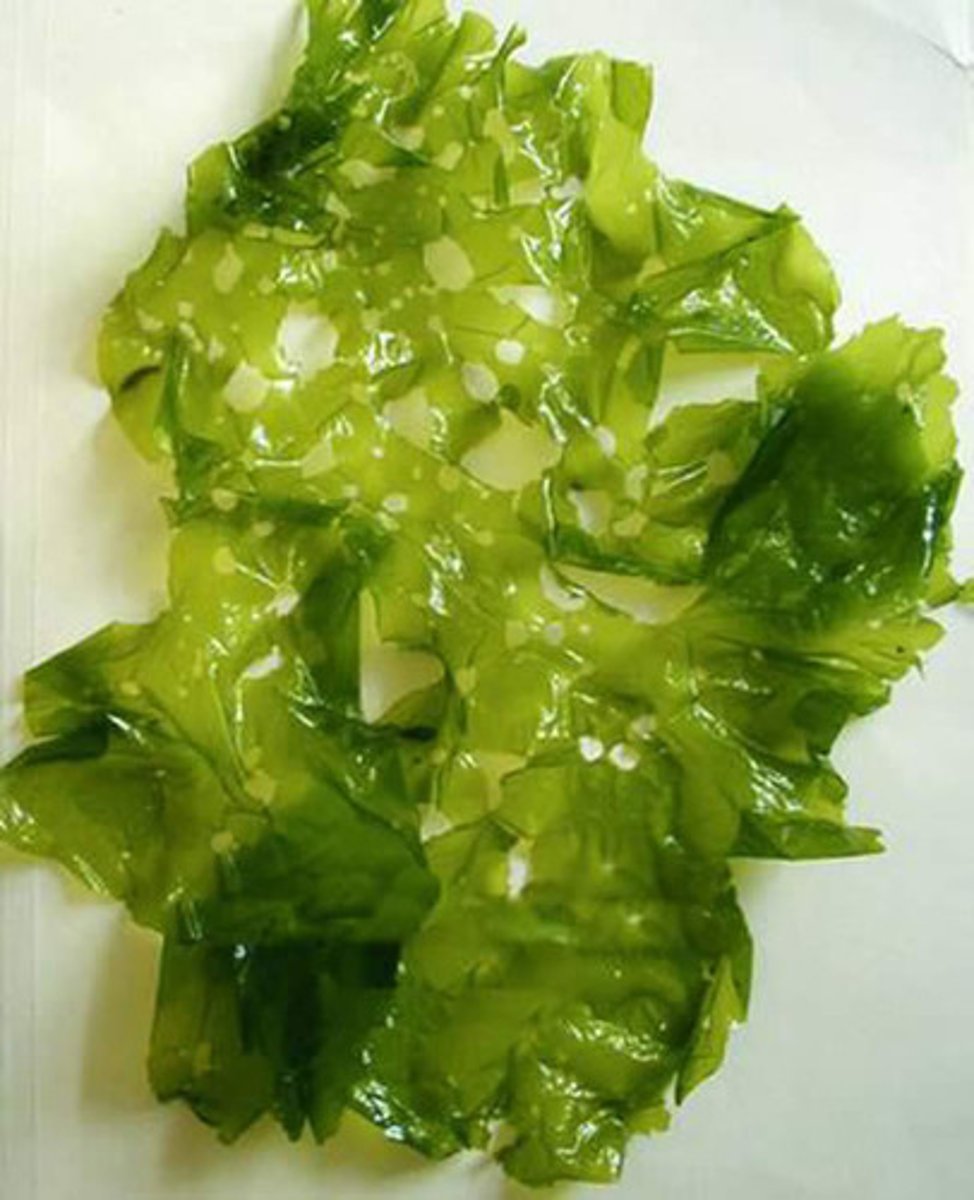
What color is sea lettuce?
Green
What zone is sea lettuce found in?
Zone 2
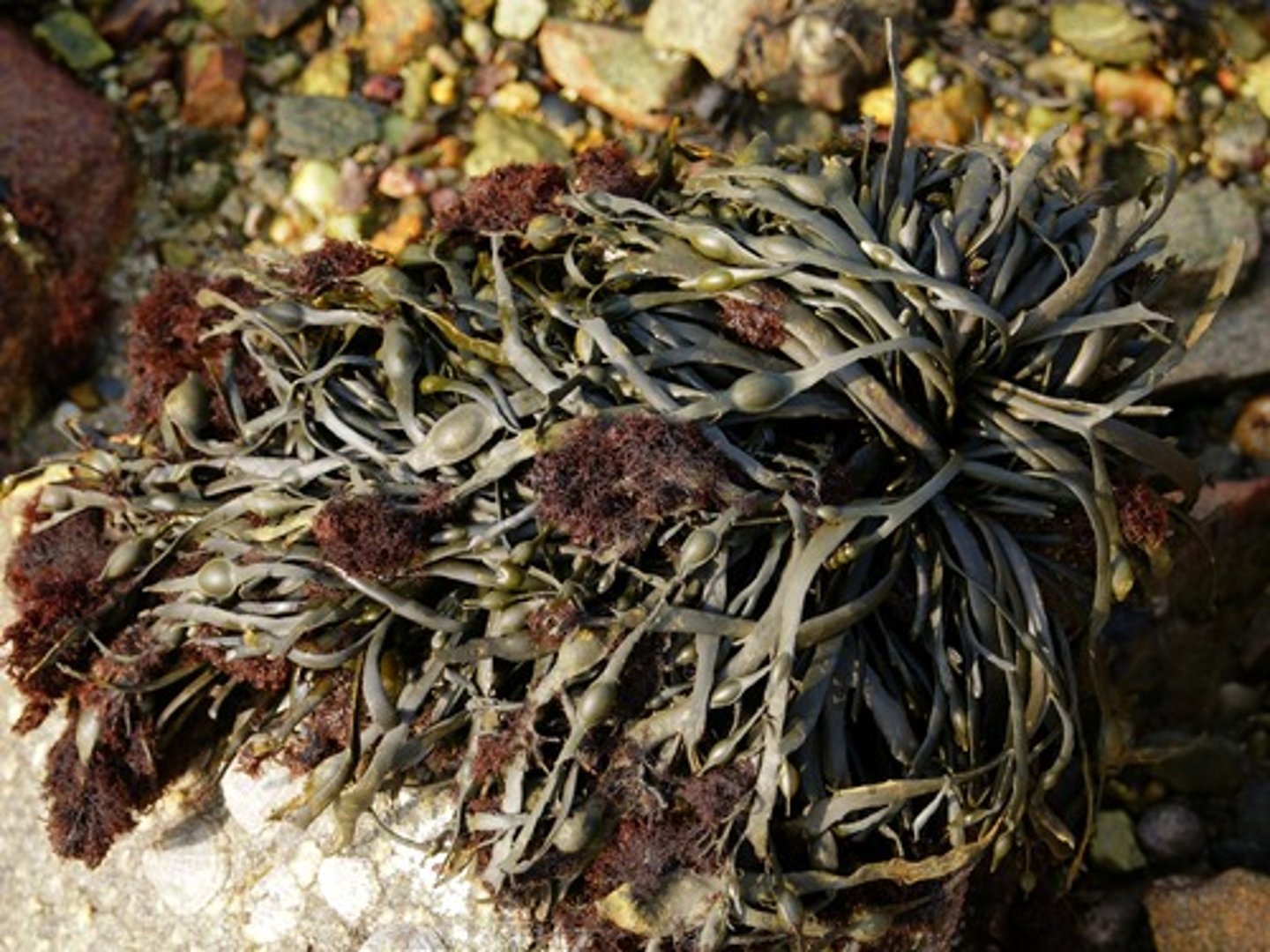
What color is rockweed?
Brown
What zone is rockweed found in?
Zone 3
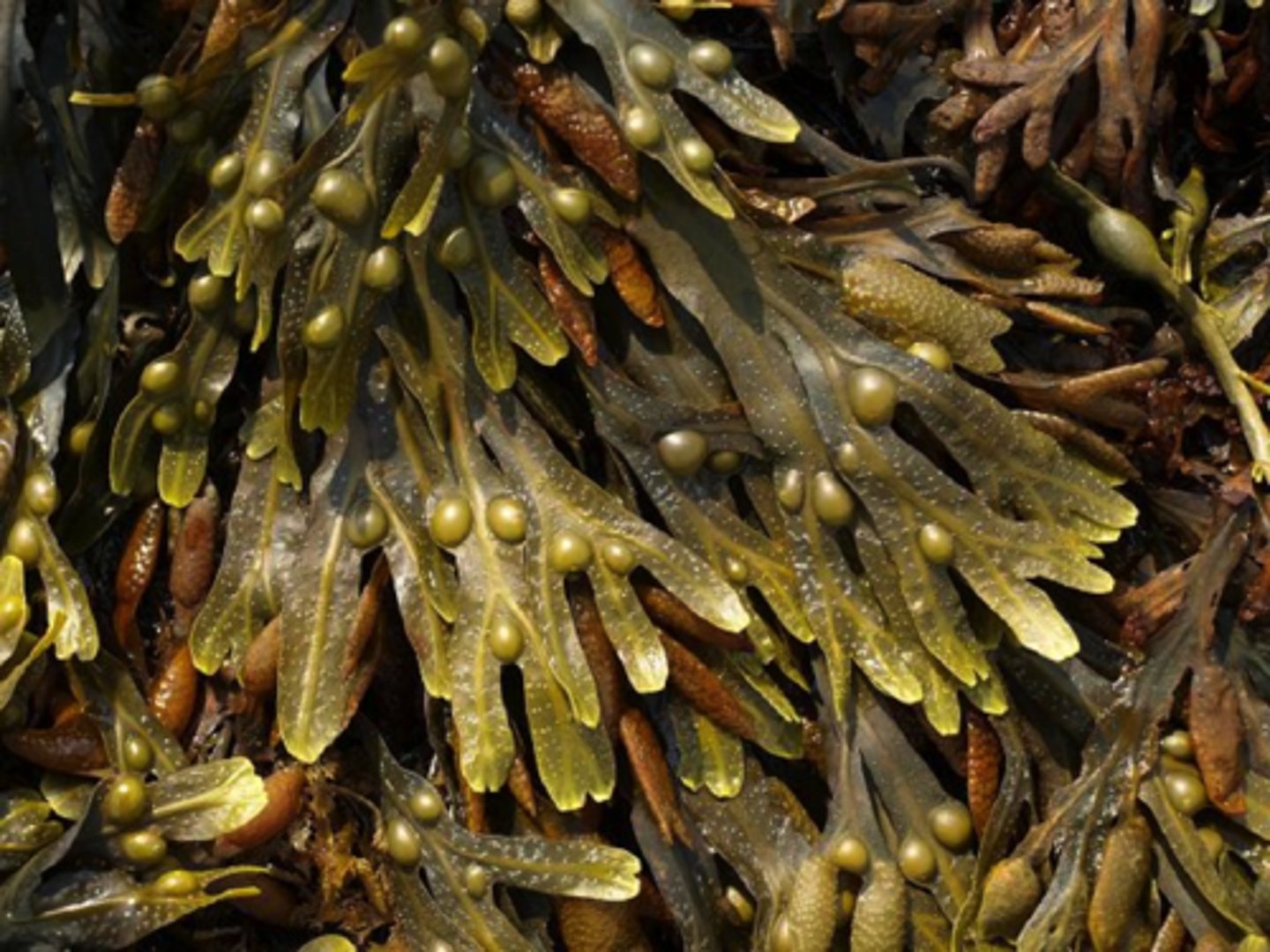
What color is knotted wrack?
Brownish Yellow
What zone is knotted wrack found in?
Zone 3
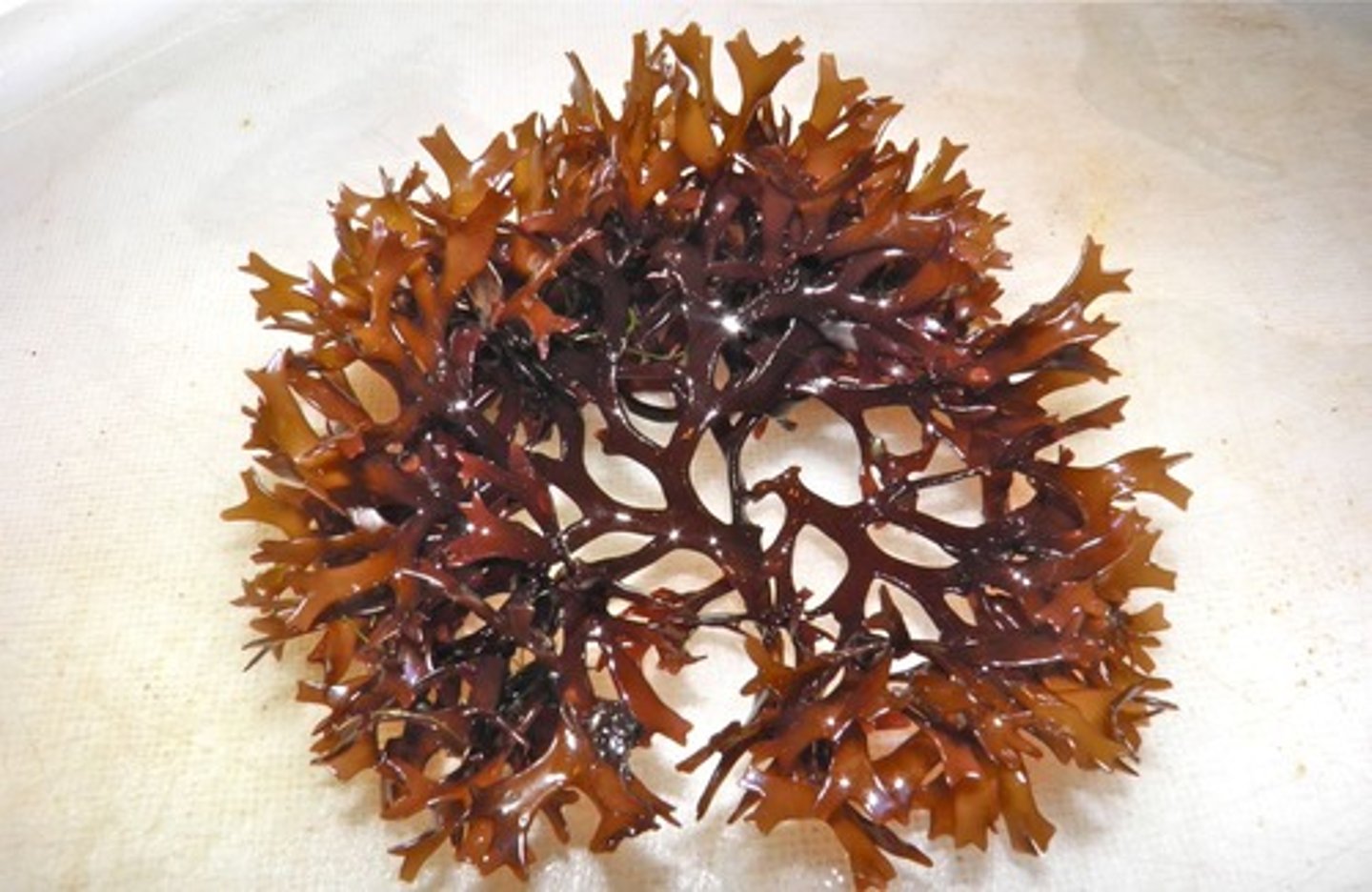
What color is Irish moss?
Red/Purple/Green
What zone is Irish moss found in?
Zone 4
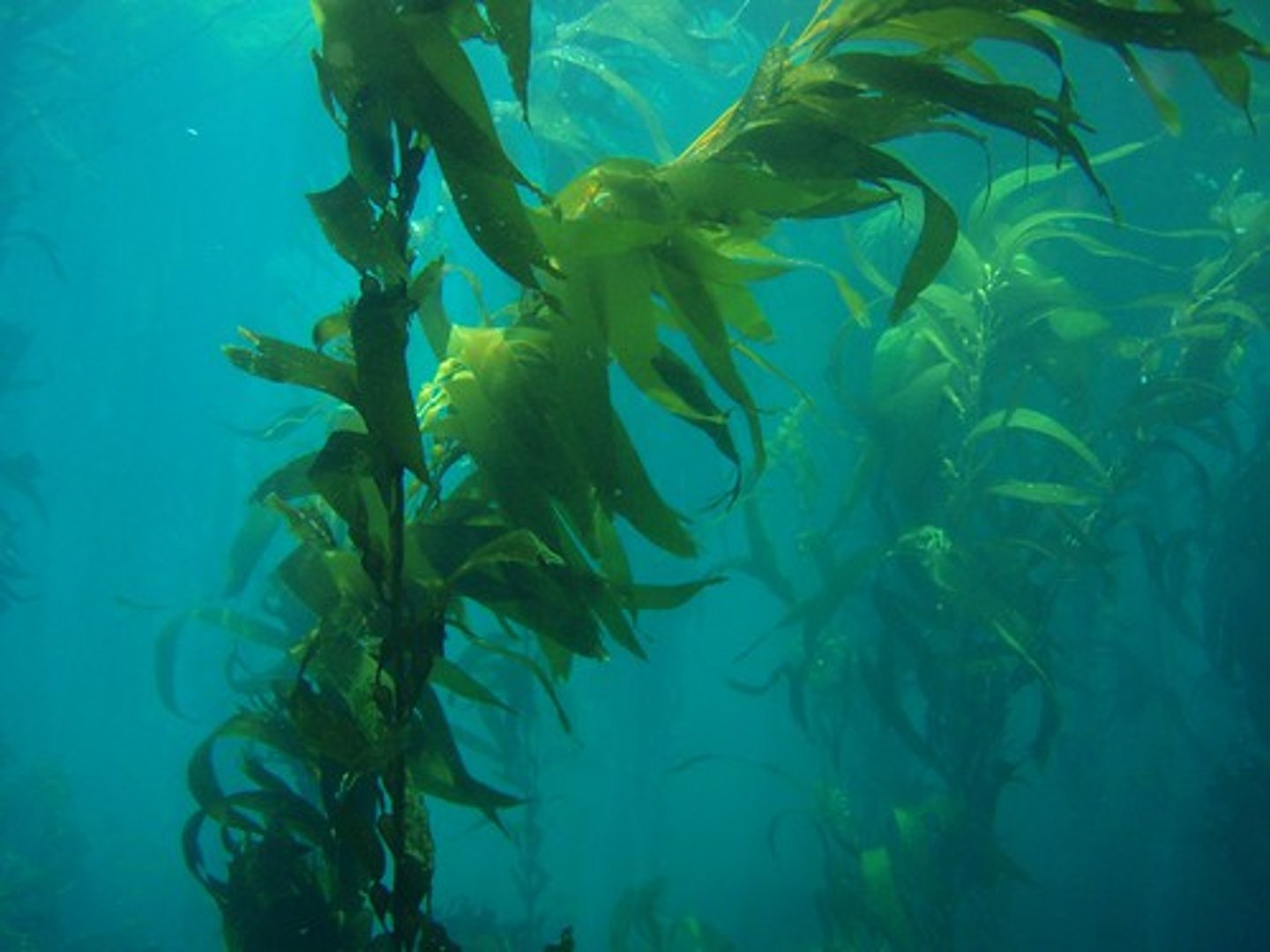
What color is kelp?
Brownish Yellow
What zone is kelp found in?
Zone 5
Rockweed

Knotted Wrack

Sea Lettuce

Irish Moss

Kelp

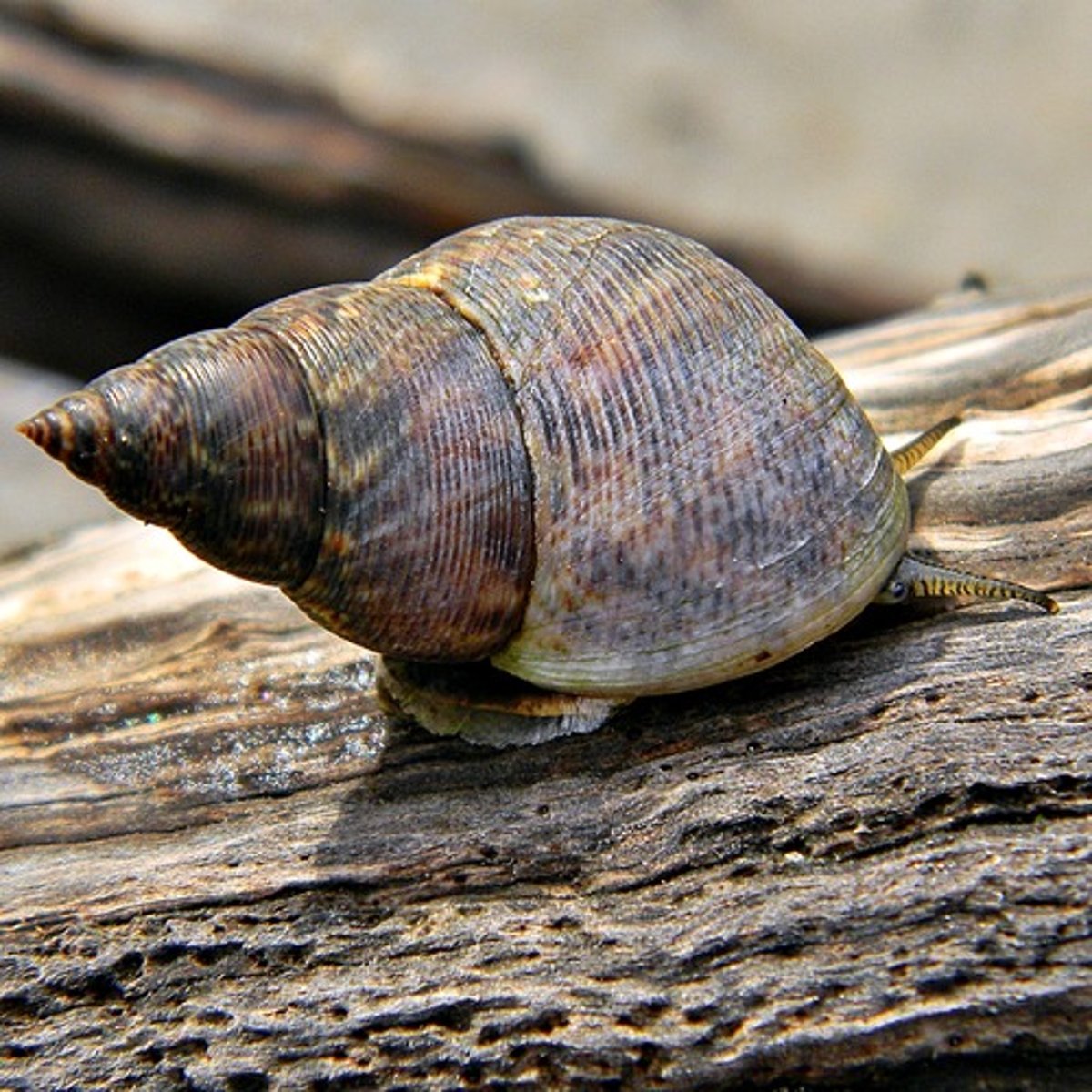
Periwinkle

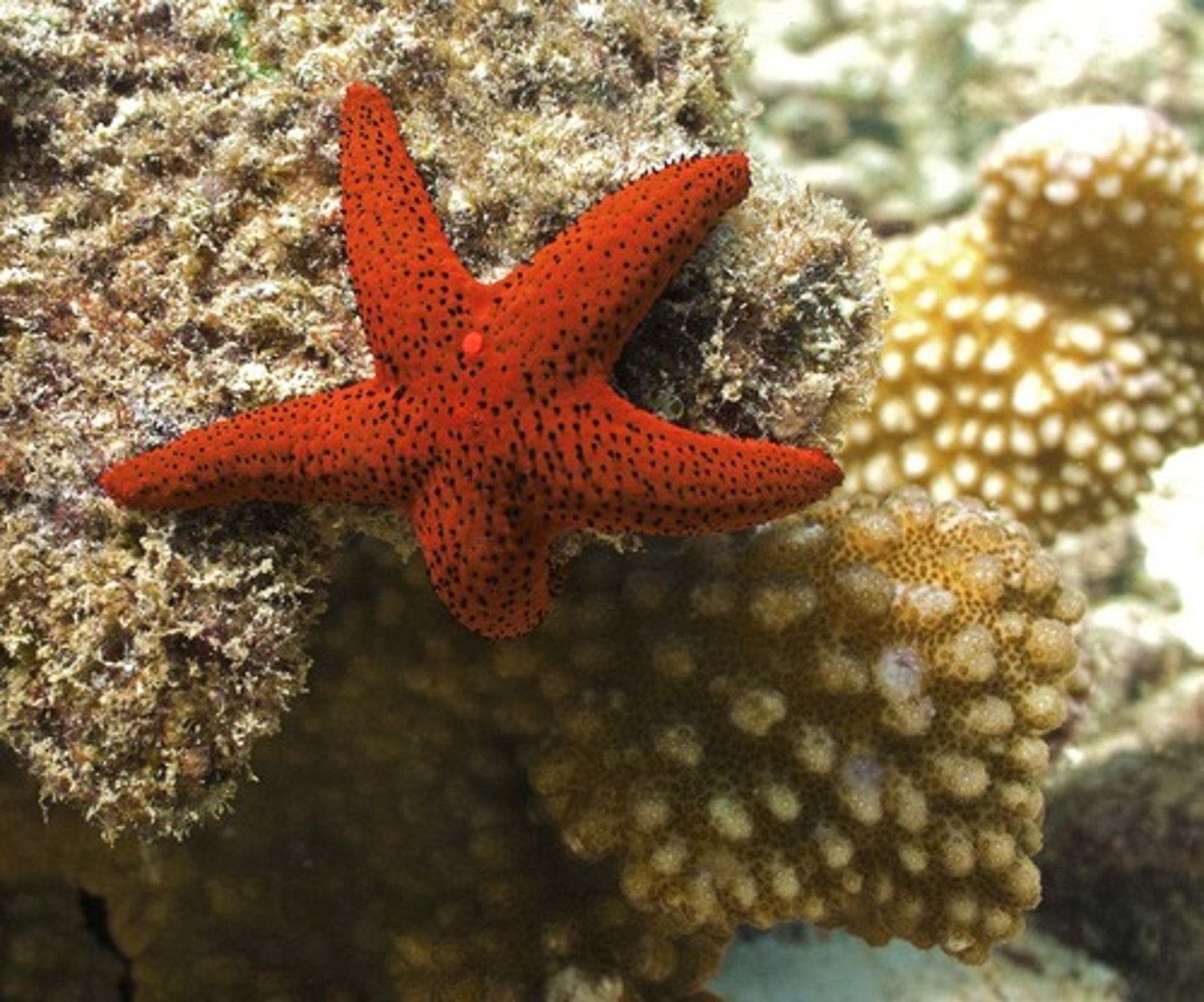
Sea Star

Slipper Shell
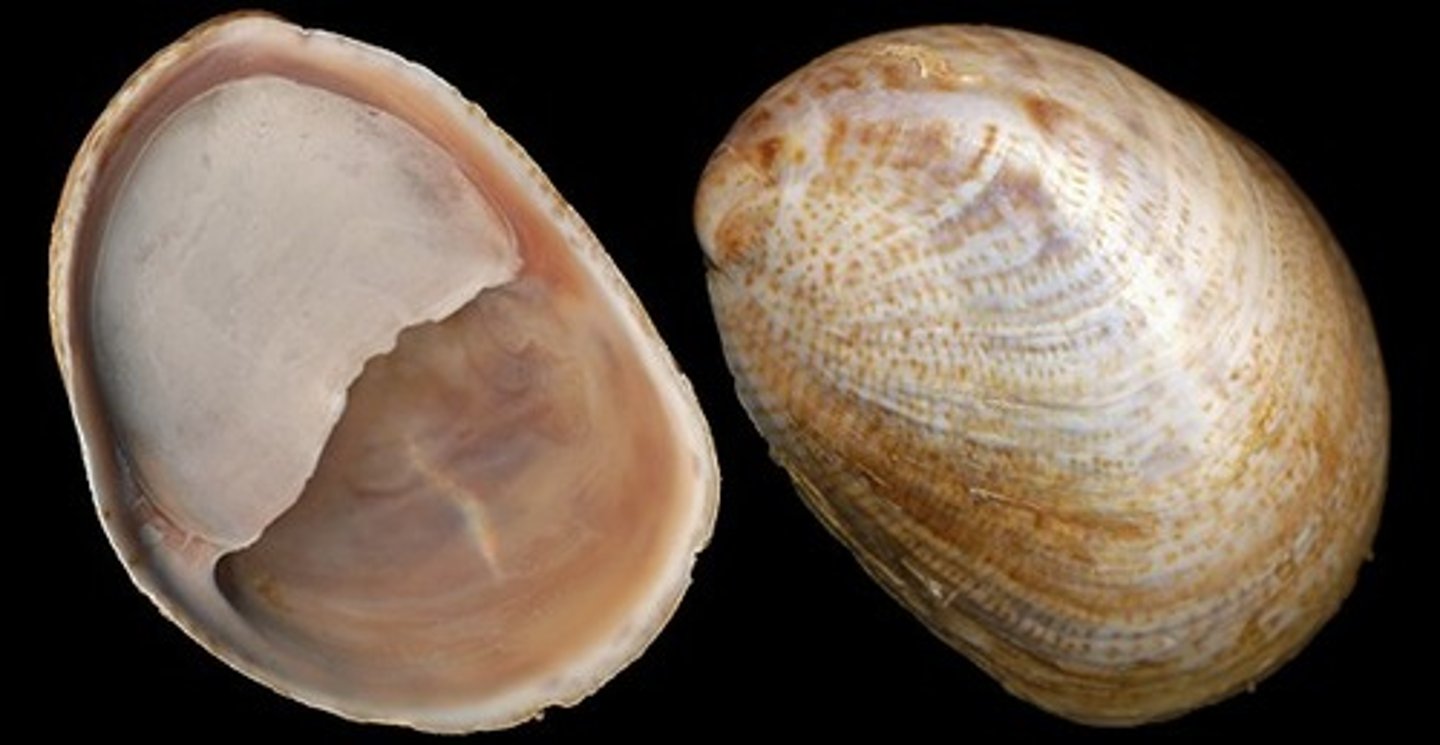

Dog Whelk
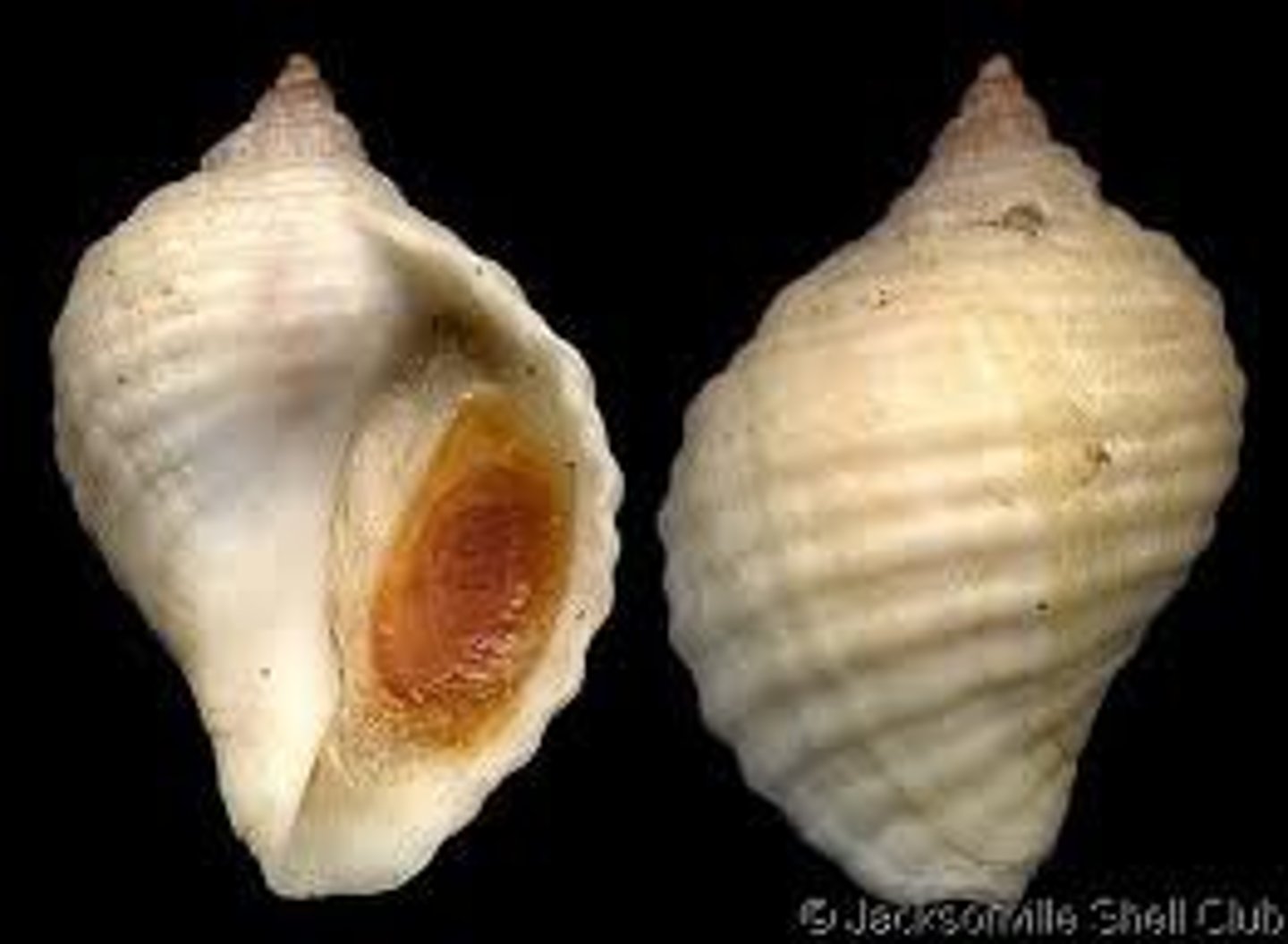

Moon Snail
Rock Crab
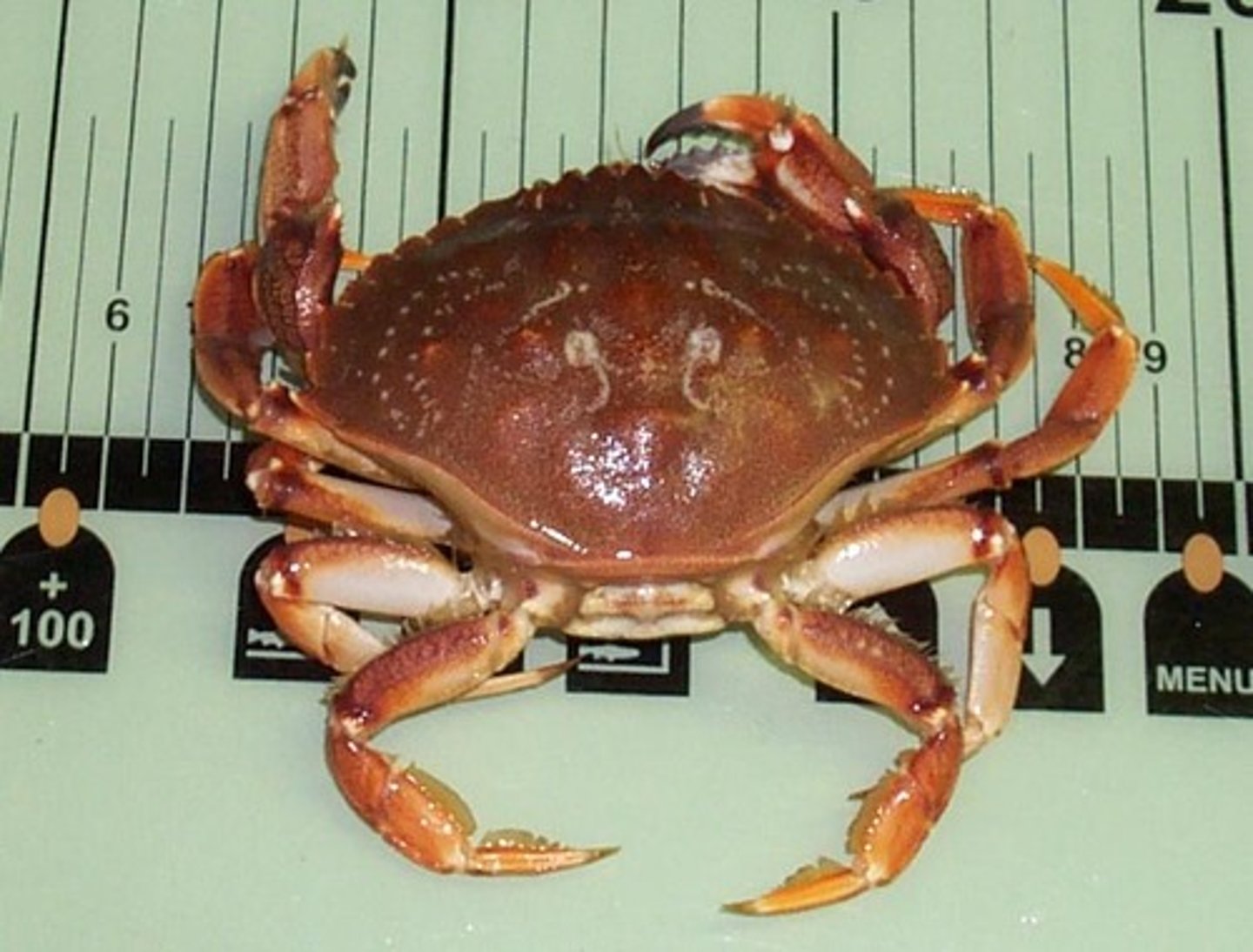

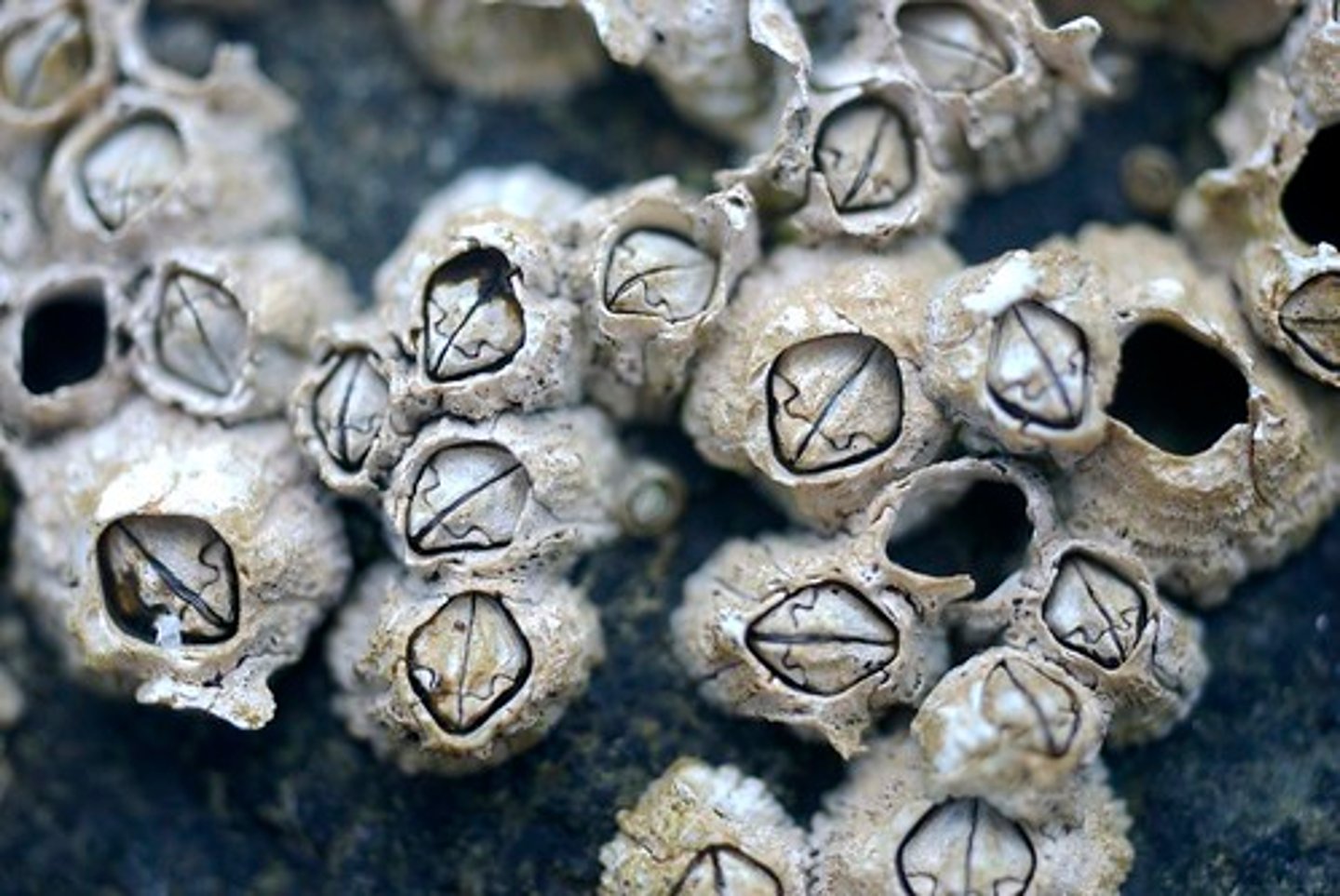
Barnacle

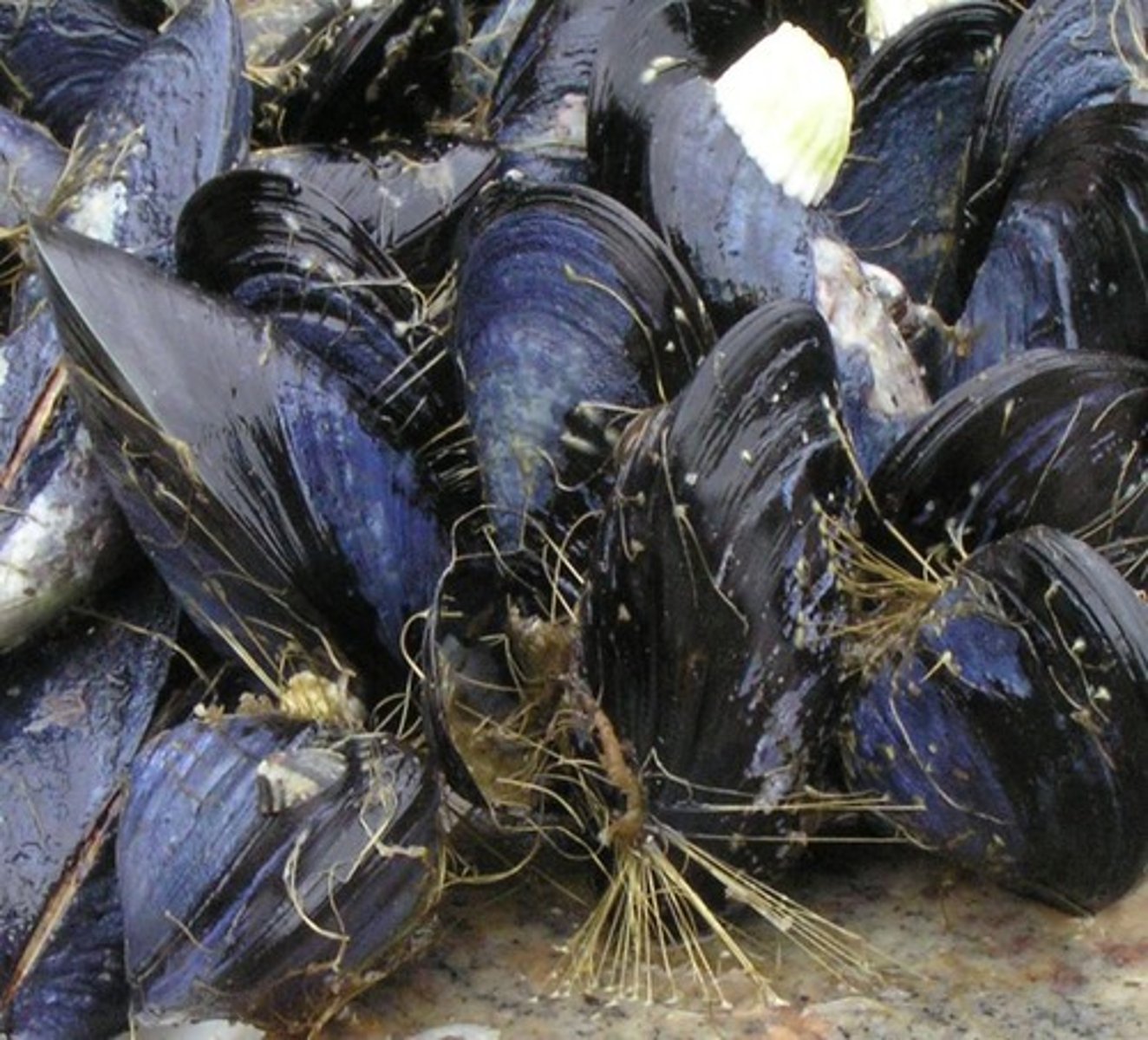
Mussel

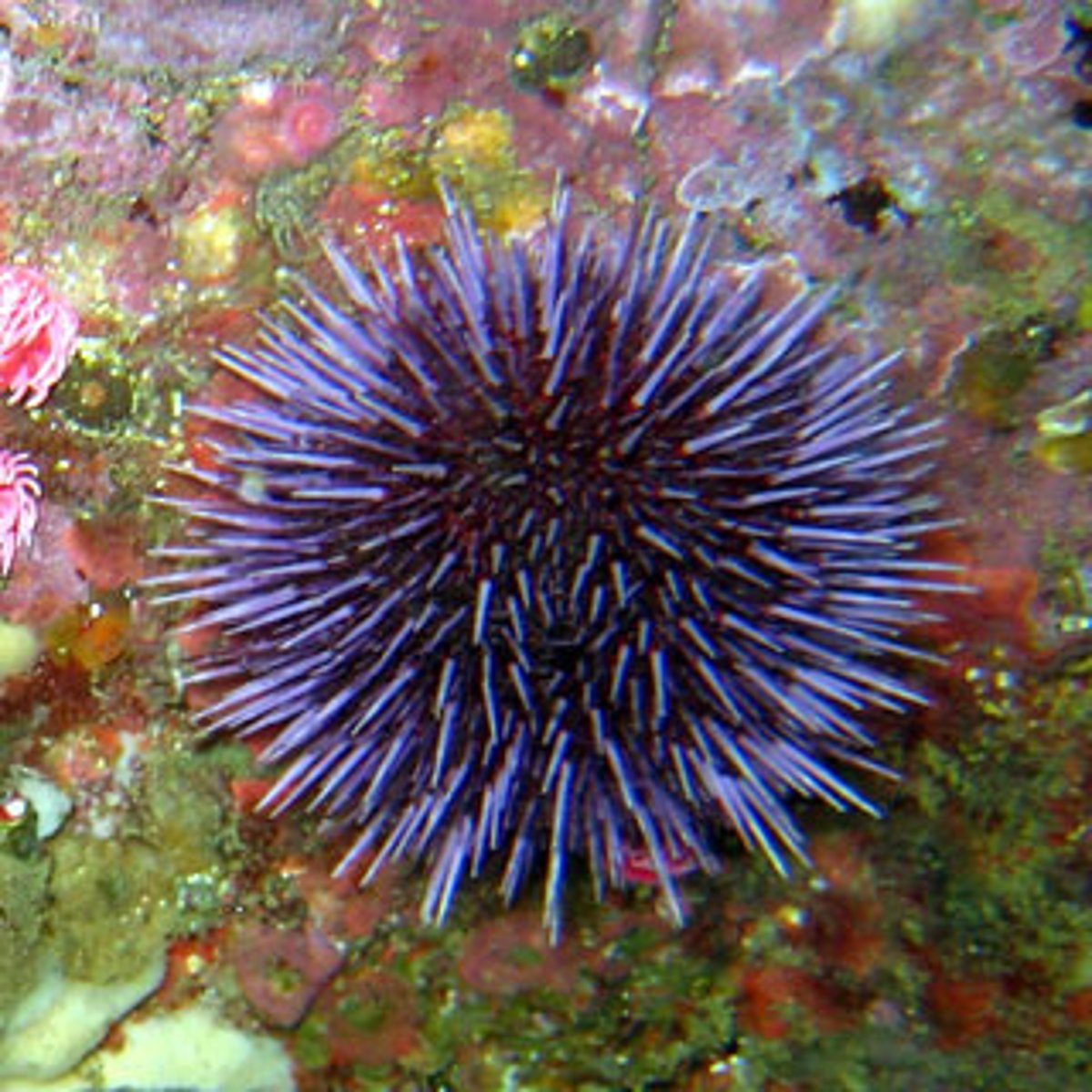
Sea Urchin

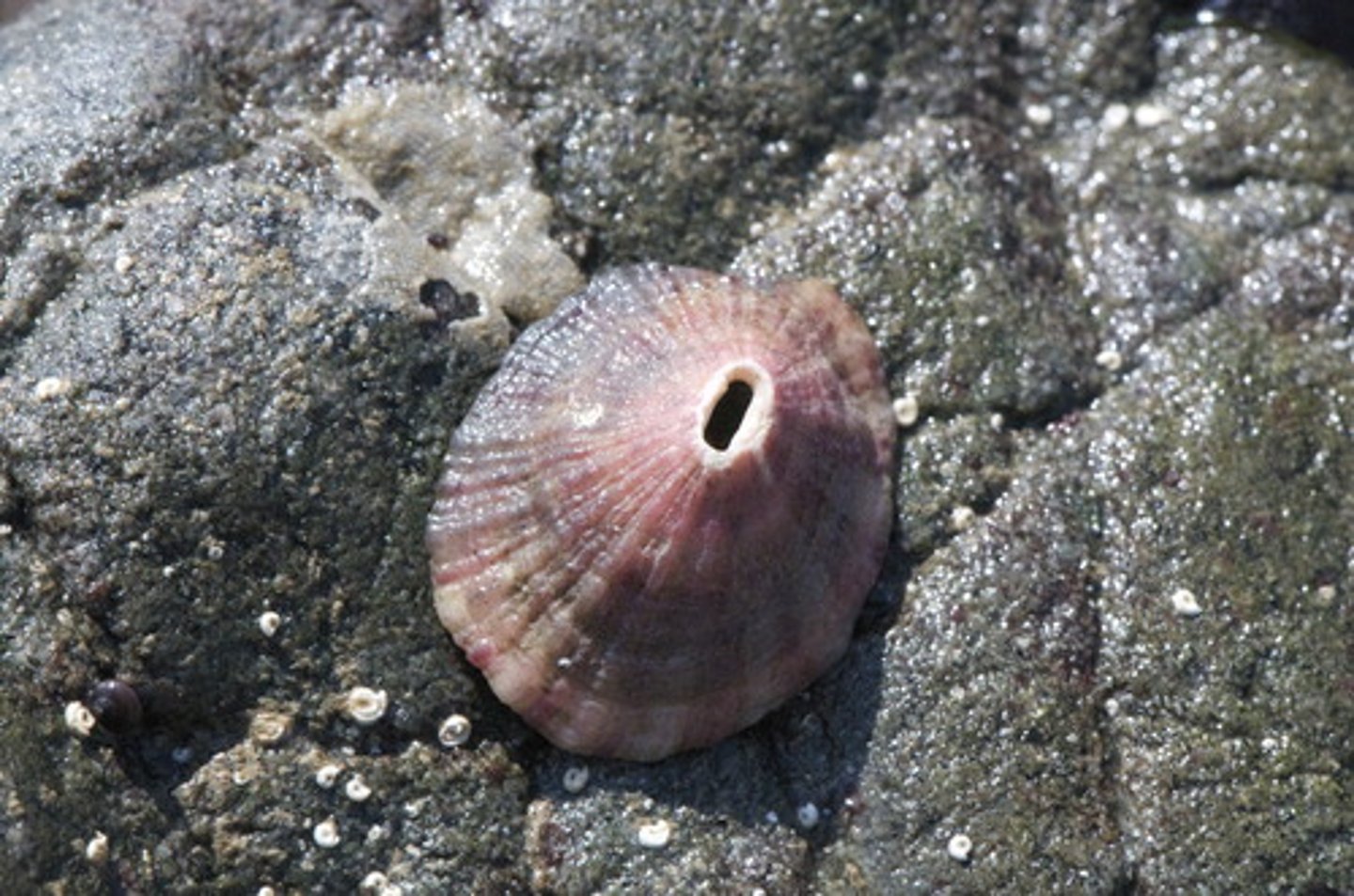
Limpet

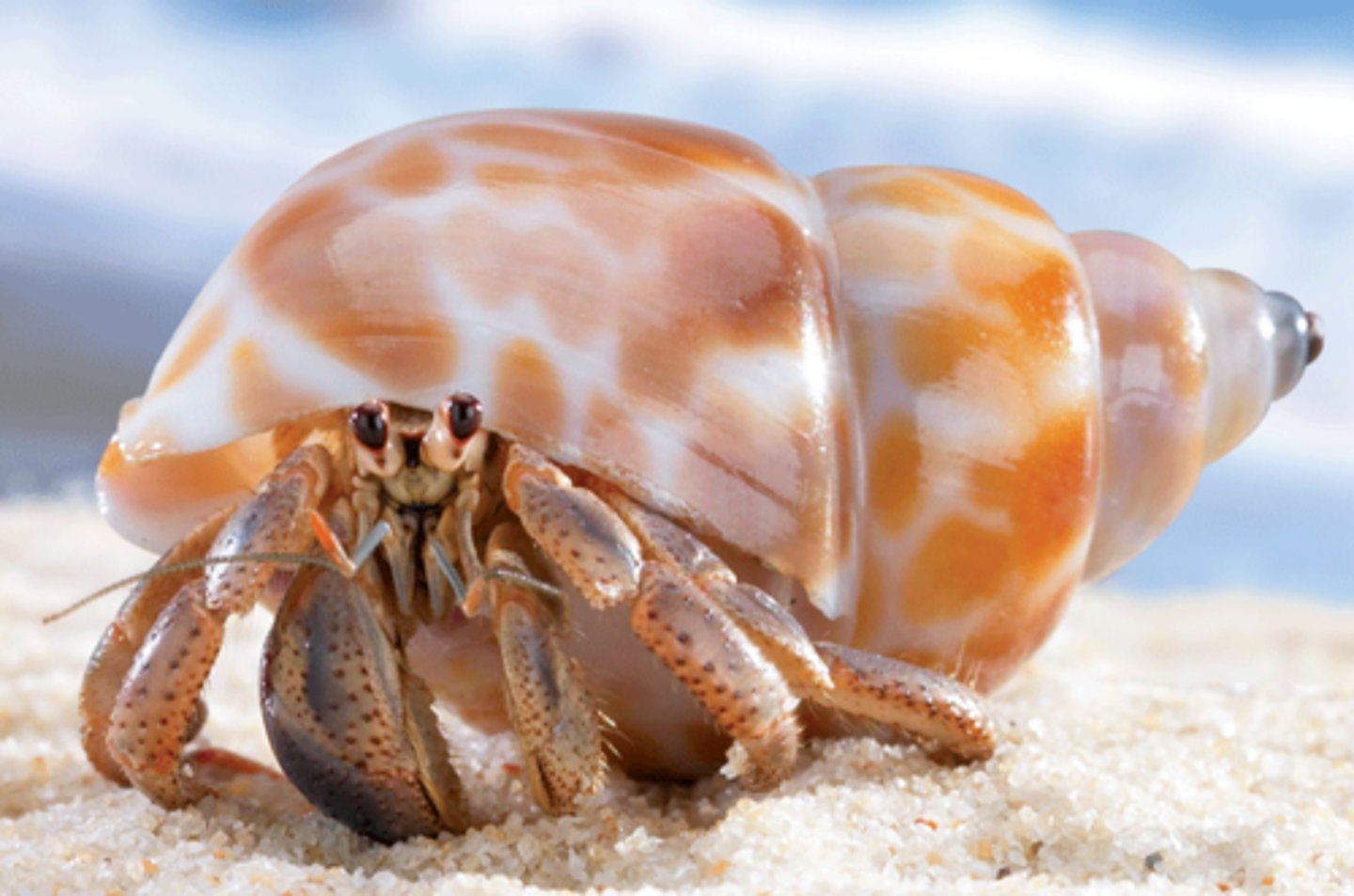
Hermit Crab
