W1L2: Glutamate and GABA - Alcohol, Ketamine, Psychosis and Epilepsy
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
GABA and glutamate: evolution
believed to be first to evolve and found in simple organisms
GABA and glutamate: common neurotransmitters
most common neurotransmitters in CNS
glutamate: function
main excitatory neurotransmitter in brain (neurotransmitter released by all excitatory neurons), estimated over half of all brain synapses release glutamate
glutamate: percentage of cerebral cortex
80% cerebral cortex consists of pyramidal cells (glutamatergic)
glutamate: synthesis: glutamic acid
amino acid that acts as neurotransmitter in its original form but doesn’t pass blood brain barrier so needs to be synthesised in brain
glutamate: synthesis: glutamine
released from cells neighbouring neurons and causes synthesisation
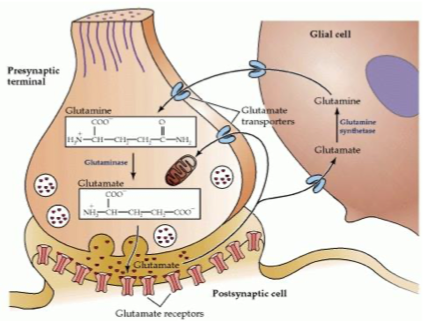
excitatory neurons: location
found in most of long projection neurons throughout cortex - convey info from sensory organs to brain and vice versa
glutamate: receptors
inotropic (ion channels) and metabotropic (g-protein coupled)
glutamate: receptors: ion channels
NMDA receptor
AMPA receptor
Kainate receptor
glutamate: receptors: g-protein coupled
metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR’s)
glutamate: NMDA receptors
has at least 6 different binding sites (lots of complex functions)
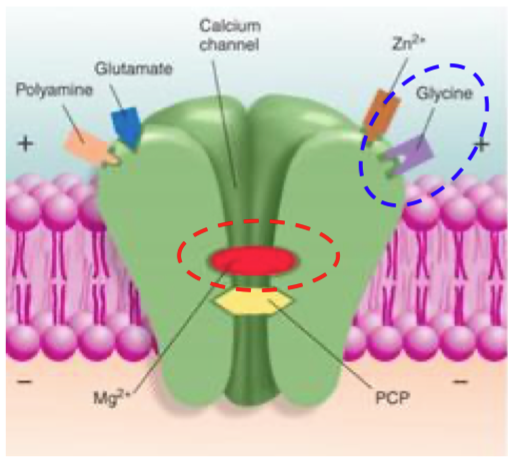
glutamate: NMDA receptors: only work if
also glycine molecule (another amino acid) attached
if magnesium ion is NOT bound inside
glutamate: NMDA receptors: magnesium ion to pop out
if amber receptor depolarises close to it, changes polarisation and magnesium pops out due to depolarisation
glutamate: NDMA receptors: 6 binding sites
polyamide, glutamate, Zn2+ (zinc), glycine, Mg2+ (magnesium), PCP
glutamate: NMDA: alcohol
NMDA antagonist (blocks glutamatergic functioning which blocks info processing and excitatory functioning) - reduction in glutamate by alcohol contributes to sedative effects and memory effects of alcohol
GABA: NMDA: alcohol
also GABA agonist - increasing inhibition, decreasing excitatory functioning
NDMA receptors: PCP
phencyclidine - angel dust
NDMA receptors: ketamine and PCP
NDMA antagonist that cause dissociative hallucinations, disconnect self from reality, diffuse cortical function, synch with auditory stimulation, sensory anaesthetic
glutamate: ketamine: NDMA binding
Ketamin binds to same place PCP and blocks channel from depolarising
ketamine: depression
effective treatment for individuals resistant to depression drugs (works quickly lasts for a while but people snap back)
glutamate and psychosis
regardless of exact neurotransmitter involvement, symptoms of psychosis suggest widespread disruption and lack of coherent integration of sensor information - no major structural differences in psychosis so illustrates importance of chemical balance in healthy perception and cognition
NDMA: activity critical for
learning, memory, perception and synaptic plasticity
GABA (gamma-amino butyric-acid)
primary inhibitory neurotransmitter (decrease likelihood of post-synaptic neuron firing)
without inhibitory synapses
brain would be unstable with neurone firing uncontrollably (causing seizures)
GABA: neuron size
short local inhibitory neurons - form dense web around and between excitatory neuron
GABA: synthesis
produced from glutamic acid (glutamate is same amino acid) - glutamate is converted into GABA and GABA can be converted to glutamate by enzymes
GABA: receptors
A - ion channels, B- G protein-coupled
GABA agonist (+)
can perform natural inhibitory roles
GABA antagonist (-)
can’t exert natural inhibitory roles
GABA agonists
benzodiazepines, muscimol (psychoactive compounds in mushrooms), barbiturates (anticonvulsants + anaesthetics), alcohols
GABA antagonists
picrotoxin (epileptogenic seizure causing drugs)
seizure disorders
relatively common with 400,000 in Australia
generalised seizures
widespread and involve most of brain
partial seizures
definite focus and restricted to small part of brain (often scarred region caused by injury or developmental abnormality)
seizures and heat
heat can kill neutrons - fevers can cause seizures therefore not vaccines which cause seizure but fevers associated with vaccines